What is cholesterol
To understand this issue in more detail, you should understand what cholesterol is and why the human body needs it.
Cholesterol is a substance without which the body cannot function normally. It performs a number of important functions:
- Contained in the membranes of all cells of the human body, which makes them more durable and resistant to external influences.
- Participates in the production of essential hormones, including sex hormones.
- Affects choleretic metabolism and fat absorption.
- Helps normalize the functioning of the nervous system, as it is contained in myelin cells that conduct nerve impulses.
Cholesterol is usually divided into “good” and “bad”. “Good” is produced by the human body itself, or more precisely by the liver, and makes up more than 80% of all cholesterol. It is very important for the functioning of all organs and cells. A person receives “bad” cholesterol from the outside, that is, through food.
There is an opinion that to lower blood cholesterol levels it is necessary to reduce the amount of animal fat consumed.
In other videos on Dr. Shishonin’s blog, you can learn more about this topic and find out why this statement is a myth leading to severe forms of atherosclerosis. Important:
Low cholesterol levels are worse than high cholesterol levels in the blood.
This may indicate a variety of biochemical problems.
What is cholesterol?
Low-density cholesterol (LDL)
– this is “bad” cholesterol. It settles on the walls of blood vessels and forms plaques. They grow over time and narrow the arteries, complicating or completely blocking blood supply to the heart and brain. As a result, the supply of oxygen and nutrients to these organs is disrupted.
High LDL levels are a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, heart attack, heart attack and stroke. LDL also has positive benefits, for example, it neutralizes harmful toxins.
Sources of “bad” cholesterol are animal products: pork, beef, bacon, chicken leg and fried skin, sausage, egg yolks, sour cream, cream, hard cheeses, cottage cheese, chocolate.
High density cholesterol (HDL)
- This is “good” cholesterol. It plays a structural role in cells, takes part in the synthesis of hormones and vitamin D. The liver produces bile acids, which help process fat in the small intestine, from “good” cholesterol.
“Good” cholesterol binds “bad” cholesterol and heavy triglycerides, removes them from cells, and transports them to the liver for processing. It helps prevent cardiovascular diseases.
Sources of “good” cholesterol: wild salmon, mackerel, tuna, halibut, avocado, olive oil, walnuts.
Triglycerides
are part of very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), which are involved in the formation of cholesterol plaques. Increased levels of these fats in the blood can lead to heart disease and diabetes. After eating, the body converts excess calories into triglycerides. They accumulate in fat cells.
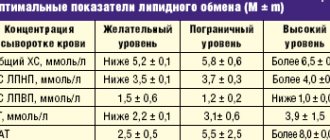
Problems arise if cholesterol levels exceed 5.0 mmol/L.
It is important to know the blood levels of all types of cholesterol. This:
- total cholesterol;
- low-density cholesterol (LDL) or “bad cholesterol”;
- high-density cholesterol (HDL) or “good” cholesterol;
- triglycerides.
Reduced cholesterol levels
A decrease in cholesterol levels not only indicates internal problems of the body, but also increases the risk of developing various diseases several times. Among them are:
- stroke;
- liver cancer;
- emphysema and asthma;
- alcoholism and drug addiction;
- clinical depression.
There can be many reasons for low blood cholesterol, here are some of them:
- Limiting the consumption of foods containing animal fats. Dr. Shishonin in his blog dispels the myth that vegetarianism is a great way to lower cholesterol and become healthier. This diet can lead to metabolic disorders and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Liver diseases. As mentioned above, the liver is involved in the production of cholesterol, which is so necessary for the functioning of all systems and organs. If there are problems with it, the balance is upset.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Poisoning.
- Anemia.
- Overactive thyroid gland and many others.
You can find out more information about this and many other important aspects of health related to blood pressure, osteochondrosis, atherosclerosis by becoming a member of the Club of Former Hypertensive Patients
.
Join our community, download gymnastics, which has already helped hundreds of thousands of people overcome blood pressure surges and hypertension. Get the most up-to-date and correct information, ask your questions to Dr. Shishonin and just communicate.
New cholesterol controversy
When do you really need to lower cholesterol and who can live long with high levels? The material about this, prepared by KP, was among the top most read on the newspaper’s website.
Dossier "KP"
Philip Kopylov is a professor at the Department of Preventive and Emergency Cardiology, Director of the Institute of Personalized Medicine at Sechenov University, Doctor of Medical Sciences, researcher, cardiologist.
THE MAIN CHALLENGE FOR DOCTORS
Recently, an international group of cardiologists from Sweden, Italy, France, Japan and other countries made a revolutionary statement: there is no evidence to conclusively support the connection between high levels of “bad” cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. The researchers came to this conclusion after studying data from 1.3 million patients. Their health status was monitored for a total of about 50 years. Even more surprising, according to cardiologists, was that older people with high levels of low-density lipoproteins (the same “bad” cholesterol) live on average longer than others! How is this possible? Does this mean that scrambled eggs, butter and fatty meats have been finally rehabilitated, and doctors need to reconsider their approaches to treating heart patients with statin drugs?
“There may be two people standing in front of us, both of them have high cholesterol, only one needs to be treated, and the second can be left alone,” says Philip Kopylov. - Essentially, this is a solution-explanation of the results of a study on the role of cholesterol, which surprised many. The secret is that monitoring people from different risk groups gives different results. And medications act in different ways: if you give them to a sick person according to medical indications, his condition will improve. But if you feed someone who is healthy or who is not so sick that they really need serious medications, then there will be no improvement. The main task, I would even say a challenge, for modern doctors is to determine those who really need to lower cholesterol and when such patients really need statins. Because other people can live longer without treatment, including those with relatively high levels of “bad” cholesterol.
CHECK YOURSELF
What is your risk of cardiovascular disease?
A person is at low risk if they:
a) no high blood pressure. That is, the pressure is not higher than 130/80 mm Hg. Art. under the age of 65 and not higher than 140/80 after 65 years;
b) no excess weight. That is, the body mass index is not higher than 29 (we talked about how to calculate it in the first part of the publication);
c) no diabetes;
d) no atherosclerosis.
- Under such conditions, the patient usually does not need to be treated even if the level of “bad” cholesterol is elevated. That is, if the level of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) in the blood is up to 4.9 mmol/l, explains Philip Kopylov.
If a person is at high risk of cardiovascular disease, including a high risk of heart attack and stroke, then the cholesterol level should be no more than 2.6 mmol/l. And at a very high risk - a maximum of 1.8 mmol/l . If the indicators are higher, they need to be reduced, including with the help of medications.
into the high and very high risk group (depending on the number of risk factors and the degree of neglect) if:
1) is obese. The most dangerous thing is abdominal, that is, in the abdomen. Measure your waist width: for men the critical mark is 102 cm and more, for women – 88 cm and more;
2) high blood pressure (see point “a” above);
3) there is a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus (as a general rule, it is made when the blood sugar level is above 6.7 mmol/l on an empty stomach);
4) the patient abuses salt - exceeds the norm of 5 mg per day, including salt in all dishes and products;
5) overindulges in alcohol. Let us remind you that, according to the latest data, up to 14 servings of alcohol per week for men and up to 8 servings for women are considered relatively safe for health (how much this will be in different types of drinks - see the “Health” section on kp.ru);
6) male gender - the risk of cardiovascular diseases in men is a priori higher;
7) age - for women over 50 - 55 years old; for men - from 45 years old, and if the above factors are present - then starting from 35 years old.
CHOLESTEROL PLAQUE DIFFERENCES PLAQUE
- If I am not in a high or even medium risk group, does this mean that I can unlimitedly eat foods with animal fats - butter, fatty meat, etc.?
— The question is not easy. When we begin to lean on foods rich in animal fats, with a modern sedentary lifestyle, this often results in obesity. You receive at least one risk factor and move from a more “favorable” group to a less favorable one, with a higher risk. And in general, we must admit: the regulation of the system of production and metabolism of cholesterol in the body still partially remains a mystery to scientists. We don't know everything about her.
— Is it undeniable that cholesterol plaques in blood vessels are harmful and dangerous? Or do you also have doubts?
— In humans, already from adolescence, damage to the internal lining of blood vessels begins. And atherosclerotic plaques develop with age in the vast majority of people (essentially, such plaques are accumulations of cholesterol deposits in places of vascular damage. - Author) . However, the problem is that plaques are not all the same. They can be of two types: stable and unstable. And the most serious challenge in cardiology now is to learn to identify and calculate unstable plaques.
- What is their danger?
- At least half of myocardial infarctions occur due to plaques that do not narrow the lumen in the blood vessels or narrow it less than 50%. Such plaques have a thin covering film and a liquid core, where inflammation constantly occurs. Eventually the tire simply breaks. A blood clot forms at this site and blocks the lumen of the vessel. And everything downstream of the blood begins to die.
TO EXERCISE OR NOT TO EXERCISE?
- It is often said that aerobic exercise - brisk walking, running, swimming, ice skating - is useful for increasing blood circulation. And if the plaques are unstable, then it turns out that increased blood flow can worsen the situation?
— Purely theoretically, yes. However, if these loads are regular and reasonable (see below for the “golden” formula for calculating heart rate. - Author) , then they will have a positive effect. Weight and blood pressure will decrease. Also, as a rule, there is a decrease in cholesterol. That is, risk factors are eliminated, and due to this, competent physical exercise brings undeniable benefits. And if you exercise from time to time, and even try to set an Olympic record in the rare moments of your appearance at the gym, then the threat of rupture of plaques and a heart attack really increases significantly.
ON A NOTE
How to determine safe exercise intensity
Use the “golden formula” for calculating your optimal heart rate: 220 minus your age. the resulting figure by 65% - this is the pulse at a moderate load; multiply by 80% - heart rate during intense physical activity. If it is higher, there is already an excessive load, unfavorable for the blood vessels and heart.
QUESTION: WHO NEEDS STATINS?
— Philip Yuryevich, what about statins? Recently, there has been heated debate; the authors of an international study claim that the benefits of such drugs are very doubtful. To whom and why should they be prescribed from your point of view - as a researcher and cardiologist?
- Let's remember: cholesterol enters our body not only with food, 60 - 70% of it is produced in the liver, even if you are on a lean diet. The effect of statins is, on the one hand, to inhibit the production of cholesterol in the liver. At the same time, a mechanism is launched that turns existing unstable plaques into stable ones. And this actually cuts the risk of heart attacks in half.
— It turns out that if a person’s plaques are stable and do not block the lumen of blood vessels, then there are no indications for taking statins? After all, these drugs have serious side effects - from muscle and joint pain to increased blood sugar. When the task is to protect against a real threat, a fatal heart attack, then such “costs” are the lesser of the evils. Are there any current developments to determine the type of plaque in a particular patient?
— There is an intravascular method, when we insert a special sensor into the vessel and use ultrasound or optical coherence tomography to determine the structure of the plaque.
- Do you need to check every plaque?
- Yes. And the sensor, unfortunately, is expensive. Another approach is computed tomography. We put the patient in a computer scanner and do an X-ray examination with contrast of the heart vessels. The resolution of computed tomographs today makes it possible to determine what kind of plaque it is - stable or unstable.
The third approach is a blood test. Now it is actively developing. Very interesting research work is being carried out on microRNAs, that is, small molecules that are responsible for inflammation and the development of atherosclerosis. Based on their presence, concentration and combination, they are trying to build diagnostic systems to identify unstable plaques.
— Are any of these methods used in Russia?
- So far - on a minimal scale, only in large cardio centers, and then as research work for the most part. In general, the problem of determining the type of plaques is solved in different ways throughout the world. The latest international recommendations propose the introduction of computed tomography with contrast as a method of primary diagnosis.
CONGRATULATIONS!
“Sechenovka” has an anniversary!
In 2021, Sechenov University, First Honey, the legendary “Sechenovka”, as it is often called among the people, turns 260 years old. Over these centuries, they worked, taught, treated, created breakthrough methods for saving people here, and most Russian medical luminaries continue to do so. Among the stars of the university is the founder of the school of military field medicine, Nikolai Pirogov ; famous surgeon, professor Nikolai Sklifosofsky ; the founder of Russian forensic psychiatry Vladimir Serbsky ; founder of the medical examination system Nikolai Semashko ; founder of neurosurgery Nikolai Burdenko; founder of the school of cardiovascular surgery Alexander Bakulev . Now among the professors at Sechenovka are academician Leo Bockeria , the chief transplantologist of the Russian Ministry of Health, academician Sergei Gauthier , one of the leading Russian oncological surgeons, an expert on head and neck tumors, academician Igor Reshetov , and many others.
«
Komsomolskaya Pravda" congratulates Sechenov University and wishes new scientific and medical breakthroughs!
Link to publication:
Symptoms and consequences
Not every disease actively manifests itself with symptoms. A person can live for a long time with low cholesterol levels in the blood and not even suspect it. Nevertheless, there are a number of signs that may indicate that, against the background of low cholesterol levels in the blood, a person develops pathologies and diseases:
- loss of appetite and its complete absence for no apparent reason;
- constant weakness;
- fatty stools;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- mood swings;
- decreased sexual desire.
Low cholesterol levels can lead to serious diseases, including:
- deterioration of vascular elasticity and, as a result, hemorrhagic stroke;
- the development of obesity, since the metabolism of fat cells is disrupted and incoming fats cannot be absorbed normally;
- problems of the reproductive system, since cholesterol is involved in the synthesis of sex hormones;
- impaired body resistance to insulin and, as a result, diabetes mellitus;
- disorders of the nervous system, because with a lack of cholesterol, serotonin receptors cannot function normally. Because of this, anxiety, depression and even degradation develop.
What is good and bad cholesterol
In tissues and blood, cholesterol forms special complexes with groups of lipoprotein proteins. They ensure its stable suspended state. Some of them have high density, others low. These properties of lipoproteins determine the types of cholesterol:
- “good”: HDL, protects cells from damage, ensures normal blood flow and vascular elasticity;
- “bad”: LDL, prone to precipitation, forming atherosclerotic plaques.
It is low-density cholesterol that is meant when they talk about its harm to health. This is true, since its excess is directly related to cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, poor circulation and the risk of strokes. LDL promotes the accumulation of triglycerides - simple fatty acids, overloads the liver, and contributes to the development of gallstones. High-density cholesterol inhibits these pathological processes and partially neutralizes the effect of the “bad”.
What to do?
Since a person receives only 5-10% of the total cholesterol contained in the body from the outside, we can conclude that a low level indicates serious failures of internal metabolic processes in the body. There are situations when the patient takes certain drugs that reduce his levels. In other cases, the problem should be resolved immediately.
To improve your cholesterol levels, you first need to understand why your cholesterol levels have dropped. This can only be done by a competent specialist, so if the test shows low cholesterol in the blood, you should immediately go to the doctor.
It is impossible to give a general recommendation, since it is completely specific for each person. Low blood cholesterol levels indicate serious problems in the body.
Dr. Shishonin argues that if cholesterol levels drop, it is necessary to contact a competent specialist, otherwise there is a risk of seriously suffering from metabolic disorders.
Symptoms
It is impossible to determine hypocholesterolemia by external manifestations. To determine cholesterol levels, the patient must take a biochemical blood test performed on an empty stomach. In cases where you cannot visit the hospital for some reason, you should pay attention to your own well-being.
Symptoms such as lack of appetite for a long time, decreased sensitivity, systematic weakness, fatigue, and the presence of fatty loose stools can signal low cholesterol.
Enlarged lymph nodes, rapid mood swings, and decreased sexual activity appear. The listed symptoms may indicate hypocholesterolemia, so it is important to urgently consult a doctor and get tested!