01 Aug 2021 at 10:37 MRI of the heart in Tushino 6147
“Aneurysm of the aorta of the heart - what is it?” Many patients in whom a specialist has just discovered this disease ask a similar question. An aortic aneurysm is a widespread or limited dilation of the largest vessel in the human body. With this disease, the diameter of the aortic lumen exceeds the norm by two or more times. Aortic aneurysm is one of the most dangerous heart diseases.
Reasons for the development of pathology
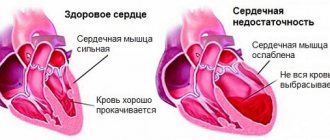
An enlarged heart in an adult is also called myocardial hypertrophy syndrome. Occurring against the background of an underlying cardiac disease, this condition can aggravate the overall clinical picture and worsen the prognosis of the underlying pathology. Enlargement of the right ventricle of the heart is less common than the left; in rare cases, there are changes in the size of both ventricles. According to statistics, against the background of concomitant cardiac pathologies, myocardial hypertrophy leads to mortality in 75-80% of cases. Therefore, timely detection and treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system will be the key to a stable state of health.
The average heart weight in adult men is about 330 grams, in women - about 250 grams; to determine the external size of your own heart, just look at your clenched fist - the volume of the heart is about the same.
This pathology can be detected both in childhood and in adulthood. Athletes are susceptible to myocardial hypertrophy, since during active training the heart is subjected to an inappropriately increasing load, actively pumping blood. The heart muscles become overstrained, an enlargement of the ventricle or even two occurs, and a state of myocardial hypertrophy occurs.
With coronary heart disease, reduced blood flow to the organ occurs. The cells of the main muscle do not receive sufficient nutrition, as a result of which they begin to actively contract, and the process of their degeneration into connective tissue begins. It no longer has the ability to stretch or contract, so only the cavities of the heart can be enlarged.
This phenomenon is most pronounced during myocardial infarction - a certain part of the muscle tissue of the wall becomes inactive, which leads to the formation of a scar in this place.
The most common factors leading to an increase in myocardial size are excessive stress on the heart during heavy physical work, too much activity during sports, bad habits, as well as concomitant pathologies of the cardiovascular system. To summarize, the main reasons can be identified:
- heart defects (both congenital, hereditary, and acquired during life);
- physical labor and various strenuous sports that place excessive stress on the heart;
- ischemia;
- arterial hypertension;
- abuse of tobacco products and alcoholic beverages;
- excess body weight;
- sudden, unexpected stress on the heart muscle, against the background of an inactive, sedentary lifestyle.
This condition may have a hereditary etiology, that is, transmitted through generations from relatives suffering from cardiovascular diseases. In the presence of such an acquired “inherited” disease as aortic stenosis, arterial hypertension, mitral valve stenosis, a large heart is not such a rare occurrence. Enlargement of the ventricle, or both, occurs under excessive loads, when the organ triggers a compensation mechanism in order to protect itself. As a result, the size of the myocardium is increased.
Carditis, rheumatic carditis are diseases of the heart, which can also lead to the fact that it becomes enlarged against the background of flabbiness of the myocardial muscles, while the ventricles grow in size, and the heart dilates transversely. There have been cases when such a hypertrophied organ occupied both sides of the chest.
Myocarditis is a heart pathology that occurs as a consequence of a severe viral infection. When the disease worsens, the patient feels shortness of breath, becomes lethargic, a picture of general malaise appears, and the heart beats at an accelerated pace. There is an enlargement of the right ventricle of the heart against the background of acute heart failure. This condition also causes myocardial hypertrophy.
Septic endocarditis is considered a dangerous disease because it occurs against the background of infection of the inner surface of the heart by the microbial environment. As a result of infection, the valves, muscles, and left and right ventricles undergo significant changes. The patient suffers from fever, aching joints, increased body temperature (which is often confused with cold symptoms), and the myocardium increases in size.
Right ventricular hypertrophy
The right ventricle allows blood to pass through and pushes it deep into the vessels connecting to the lungs. It is enriched with oxygen. Due to the fact that the right side of the heart and lungs are connected, various difficulties with the respiratory system lead to cardiomegaly.
The right ventricle is 3 times smaller in volume than the left, therefore the electrical activity of the latter is higher. The increase can be pronounced when the mass of the right one exceeds the left one. With moderate expansion, the sizes of the ventricles do not vary. Insignificant excitement is noted. At the initial stage of the disease, symptoms are mixed or absent at all. If there is a tendency towards stable expansion, symptoms are expressed in difficulty breathing, a feeling of heaviness in the chest, and the appearance of painful discomfort.
In addition to these signs, the patient experiences fluttering or freezing and delayed heartbeat. Possible dizziness and unconsciousness.
Symptoms
Any manifestations of pathology may be absent for a long time, which is why this syndrome is considered very dangerous. The patient may not be aware that he has a large heart, as well as the reasons that caused this condition. Pathology can be detected on an X-ray, during a routine preventive examination, or in worst cases, during an autopsy after sudden death. Myocardial hypertrophy can be manifested by the following symptoms:
- Shortness of breath of unknown etiology, occurring both during physical exertion and at rest.
- Pain in the chest, similar to the symptoms of angina pectoris.
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
- Swelling of tissues, deterioration in the removal of fluid and salts from the body.
- Dizziness, fainting.
The listed symptoms should be the reason for a mandatory visit to a therapist, who, after a thorough examination and examination of the patient’s complaints, will send him to a cardiologist for examination.
Myocardial hypertrophy is diagnosed using ultrasound; it shows itself to be the most informative in terms of identifying cardiac pathologies.
If they are detected, it is recommended to conduct an ECG (recording of an electrocardiogram), and to clarify concomitant diseases, magnetic resonance imaging is recommended.
When does the heart axis “go to the left”?
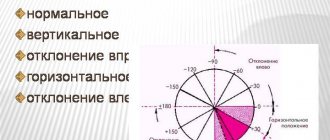
Sharp deviation of the electrical axis of the heart to the left
The conclusions of a functional diagnostics doctor about the deviation of the cardiac axis to the left are not an independent diagnosis. But they always give reason to wonder why the heart axis “went to the left.” A slight shift of the EOS to -190, as well as its semi-vertical position, in some cases is not considered a pathology. This position of the axis can be observed in healthy, tall, thin people, in athletes with a trained heart, in children with an asthenic physique, and with a high position of the diaphragm dome.
If the cardiac axis is significantly deviated to the left, then this pathological condition indicates problems with the heart; the cause of such a displacement must be established. After all, this symptom can sometimes be the first “bell” in case of pathology of the heart and blood vessels. According to some data, a deviation of the electrical axis of the heart to the left up to -29-300 is sometimes called a slight deviation, and if the angle is from -450 to -900 they speak of a sharp deviation.
Consequences of the disease
In case of increased myocardial activity and its subsequent increase, it is necessary to be observed by an experienced cardiologist and undergo regular examination courses. An important part of drug therapy will be a review of your lifestyle. In particular, you need:
- Give up bad habits - alcohol and cigarette abuse.
- Get rid of obesity and extra pounds to reduce the load on the heart muscle.
- Reduce the amount of salted, smoked, cholesterol-rich foods you consume.
- Balance the diet, enrich it with microelements and substances to normalize heart function.
- Reduce inadequate stress on the heart.
If measures are not taken to maintain the myocardium in a healthy state, this can lead to the development of stroke, heart attack, heart failure and even death.
People with alcohol addiction are at particular risk. Against the background of constant intoxication, the heart of a drinker sometimes reaches very large sizes. Restoration of myocardial size can only occur if alcohol is completely abstained.
Medicine offers modern drugs and treatment methods that, if used in a timely manner, will help reduce blood pressure, normalize blood flow to the myocardial muscle and return the heart to its original size. The main thing for successful treatment is to detect the pathology in time.
General recommendations
In addition to treatment recommendations, it is imperative to follow preventive measures. For heart problems, it is very useful to follow these tips:
- You should avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, which have a toxic effect on the myocardium (heart muscle).
- In order to prevent the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels, foods high in cholesterol should be excluded from the daily diet. It is advisable to consume fish, olive, flaxseed, corn and soybean oil at least 2 times a week.
- To strengthen and maintain the heart muscle in normal working condition, it is useful to include viburnum, cranberries, cabbage, eggplants, peaches, dried apricots, apples, pomegranates, walnuts, melons, etc. in the daily diet.
- It is necessary to reduce salt intake to at least 2 grams. per day, especially for patients with increased swelling.
- If obesity is recorded, it is necessary to create a proper balanced diet aimed at eliminating extra pounds.
- Sleep at least 8 hours, do not become physically and emotionally overtired.
- Walk outdoors more often.
Enlargement of the heart is not a diagnosis, but only a temporary condition of the heart muscle. With correct and timely actions, you can get rid of this disorder and significantly alleviate your condition.
Clinical manifestations
To understand what an enlarged heart means, it is necessary to identify its manifestations. The most common symptom indicating changes inside the left ventricle is angina. It develops against the background of compression of blood vessels that provide nutrition to the myocardium. As a result, its expansion in size and its consumption of a significant amount of oxygen in parallel with nutrients are noted. In addition to these symptoms, atrial fibrillation appears, signs of atrial flutter and starvation of the heart muscle are observed. Often a pathology occurs during which the organ freezes for 3-5 seconds and the beat is not visible, which leads to an unconscious state. In certain situations, shortness of breath may indicate the presence of cardiomegaly. The following symptoms are considered additional:
- high blood pressure;
- unstable blood pressure;
- headache;
- disturbances in heart rhythm;
- disturbed sleep;
- poor condition and general malaise;
- painful discomfort in the heart area;
- painful discomfort in the chest.
Dilatation of the right ventricle is not accompanied by any complaints. Only its causes and adverse effects can be demonstrated in the laboratory:
- dilatation of the right ventricle;
- disturbances in heart rhythm;
Left ventricular hypertrophy
This pathology is a typical heart lesion for those suffering from hypertension. Dilatation of the left ventricle is considered a rather unsafe phenomenon, which is characterized by high mortality. This process involves structural adaptation of the organ regarding metabolism and changes that occur in hemodynamic data.
Cardiomegaly causes significant thickening of the walls. Often it leads to a significant change in the septum, which is located between the 2 ventricles. Due to the expansion that occurs, the elasticity of the walls is lost. Thickening can be either uniform or in certain areas of localization. This specificity directly affects the course of the disease.
Diagnostic methods
Before making a diagnosis, your doctor will take your medical history and perform a thorough physical examination, including taking your blood pressure and testing your heart function. If preliminary studies indicate that the ventricle may indeed be enlarged, a number of additional screening tests are performed.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrical signals will not confirm ventricular enlargement. But cardiologists can identify some difficulties in the passage of the impulse, which will indicate a violation of the density of the muscle tissue of the heart.
MRI
Images of the heart taken with a special tomograph will directly indicate ventricular hypertrophy.