Read in this article:
- Why does blood pressure change in pregnant women?
- Change in pressure by trimester
- Normal blood pressure in pregnant women
- Increased blood pressure in pregnant women
- Reducing blood pressure in pregnant women
- How to measure blood pressure during pregnancy
- Blood pressure control is the key to the health of mother and child
Blood pressure is one of the key indicators of the functioning of the human circulatory system. During pregnancy, the load on the body increases, the heart and blood vessels also react to these changes. Regularly measuring blood pressure in pregnant women allows you to monitor the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and sometimes prevent the development of dangerous complications.
Why does blood pressure change in pregnant women?
The body has to adapt to a special condition - pregnancy. A woman’s body weight gradually increases, and additional blood circulation is activated between the uterus and placenta. The functioning of the heart and blood vessels at this time is affected by:
- Changes in hormonal levels;
- An increasing volume of blood circulating in the body;
- Increased tone of the central nervous system;
- Changing the location of the diaphragm, which rises upward;
- Increased pressure inside the abdominal cavity;
- Displacement of the heart in the chest;
- Increased heart rate.
The body directs all its efforts to improve blood flow in the placenta and in the uterus, because this is necessary to provide the developing fetus with oxygen and nutrients. Under these circumstances, blood pressure changes.
Blood pressure and pregnancy
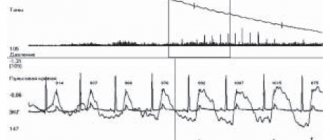
The tonometer reflects to us the force of pressure of blood circulating in the body on the walls of blood vessels. Two indicators - systole and diastole - are the pressure force at the moments of maximum contraction of the heart and its relaxation, respectively. A variety of factors can affect blood pressure - physical activity, stress, food, coffee or sweets, medications, even time of day, so pressure is an extremely variable value.
In the first half of pregnancy, under the influence of the hormone progesterone, which relaxes the blood vessels, the blood load on their walls drops, and the expectant mother’s blood pressure becomes lower than usual by about 5-15 mmHg. Along with the tummy, the force of blood pressure on the vessels increases, the load on the heart increases, the volume of blood in the body increases, and blood pressure rises.
But taking into account the fact that for several months the values have been reduced, blood pressure returns to approximately the same numbers that the woman had before pregnancy.
By measuring blood pressure hundreds of times over the entire nine months, doctors monitor the risks of preeclampsia, a serious complication of pregnancy. Indicators are one of the few signs by which gestosis can be calculated as soon as it begins to develop.
High blood pressure during pregnancy, swelling of the arms and legs, as well as protein in the urine signal that something has gone wrong in the body. It turns out that blood pressure, like a litmus test, reflects many changes inside the body of a pregnant woman. The worst thing is when it is elevated - blood pressure wears out the blood vessels, and this already affects the blood supply to the blood vessels of the placenta, the supply of oxygen to the fetus and the rate of development of the baby.
Change in pressure by trimester
Pressure indicators and its changes are determined by the duration of pregnancy. The entire period of pregnancy is divided into three trimesters, and in each trimester certain changes in blood pressure occur:
- In the early stages, the heart and blood vessels work as usual. But already from the first weeks of pregnancy, the female body actively produces the hormones estrogen and progesterone, which contribute to the dilation of blood vessels. Because of this, the pressure decreases slightly;
- In the second trimester, blood pressure levels decrease even more. This is due to the formation of a new blood circulation between the placenta and the uterus. A decrease in indicators also provokes a decrease in vascular resistance;
- In the third trimester, the volume of blood circulating in the body becomes maximum. Blood pressure gradually increases. Closer to childbirth, blood volume stops increasing, the fundus of the uterus and the diaphragm descend. As a result, the pressure in pregnant women in the later stages returns to the normal level familiar to the woman.
The periods from 4 to 12 weeks are considered especially dangerous, when a drop in pressure combined with toxicosis can significantly worsen the well-being of the expectant mother, as well as from 28 to 32 weeks, when the load on the blood vessels and heart becomes maximum. But regular blood pressure measurements should not be neglected during any period of pregnancy, especially if a woman has pathologies of the cardiovascular system or is predisposed to them.
What is considered normal
Doctors do not always perceive normal blood pressure in pregnant women as the usual 120/80, since changes in hormonal levels directly affect a woman’s well-being and physiological indicators. Until about the twentieth week of gestation, the pressure level is often reduced. This is due to the active production of the hormone progesterone.
This substance controls the tone of the uterus and relaxes muscle tissue to prevent premature birth. For this reason, even a pressure of 100 over 60 is considered normal if the expectant mother feels well. Measuring blood pressure is a standard procedure that is performed on pregnant women at every appointment with a gynecologist, starting from the 12th week.
The tonometer readings that the doctor receives indicate the general condition of the body, in particular, the functioning of the cardiovascular system. If blood pressure is within the normal range, and the woman does not complain about her health, the gynecologist has no reason to perceive even the numbers 130/90 as a pathology.
Below is a visual table showing the permissible pressure limits for women carrying a child. It is advisable to take measurements daily, especially if before conception the expectant mother had problems with the heart and blood vessels.
| Systolic reading (mmHg) | Diastolic reading (mmHg) | |
| Optimal pressure level | Up to 120 | Up to 70 |
| Normal pressure | Below 130 | Below 80 |
| Blood pressure is higher than normal | 130–139 | 80–90 |
| Not expressed arterial hypertension | 140–159 | 90–100 |
| Moderate arterial hypertension | 160–179 | 100–110 |
| Severe arterial hypertension | More than 180 | More than 110 |
Normal blood pressure is different for each person, with which he feels comfortable, works and performs household duties. As for pregnant women, their normal range varies quite widely and this is not considered a pathology. Features of tonometer indicators in expectant mothers:
Psychosomatics of high blood pressure
- pressure may increase in the third trimester, since after 13–14 weeks of gestation the load on the circulatory system doubles;
- An increase in tonometer readings can be observed under stress, fear of future childbirth, lack of awareness about the upcoming process, etc. In this case, the adrenal cortex produces an excessive amount of stress hormones;
- in the early stages of pregnancy, the pressure drops 5–10 units below normal due to the activity of the hormone progesterone, and in the second or third trimester it increases.
It is difficult to single out specific numbers that a tonometer should show in a pregnant woman - they are individual for each expectant mother. If the indicators go beyond the acceptable limits in one direction or another, the number of measurements needs to be increased. And if dangerous symptoms occur, immediately consult your doctor.
Normal blood pressure in pregnant women
Blood pressure levels in pregnant women also depend on the trimester. In general, the optimal indicator is 120-130/80-85. The upper permissible limit is 130-139 mmHg. for systolic and 85-89 mm Hg. for diastolic pressure. Blood pressure exceeding 140/90 is considered elevated.
By trimester, the table of normal values looks like this:
| Pressure norm | Index |
| First trimester | 110-120/70-80 |
| Second trimester | Not higher than 130/85 |
| Third trimester | From 140/90 to 100/60 |
It is important to consider that each body is individual, and each woman has her own normal blood pressure. That is why blood pressure readings should be compared not only with norms, but also with the usual pressure at which a woman feels good.
Frequently asked questions about blood pressure control during pregnancy
- What is preeclampsia?
- What are the symptoms of preeclampsia?
- At what stage of pregnancy does preeclampsia usually occur?
- Who is most at risk for preeclampsia?
- If my blood pressure is high, does it mean I have preeclampsia?
- Why is blood pressure control so important during pregnancy?
- What level of blood pressure during pregnancy is considered normal and what is considered high?
- What blood pressure levels before and after pregnancy are considered normal?
- How dangerous is preeclampsia for my baby and for me?
- How is preeclampsia treated?
- Can preeclampsia be prevented?
- Are there long-term effects of preeclampsia?
- Useful links on preeclampsia..
What is preeclampsia? Preeclampsia is a problem that some women face during pregnancy.
It occurs in the second half of pregnancy. The signs of this disease are as follows: high blood pressure, persistent swelling of the lower extremities and the presence of protein in the urine. What are the symptoms of preeclampsia? A woman with mild preeclampsia may feel very well. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo prenatal checkup for early detection of this condition. Symptoms of severe preeclampsia, which develops in the last weeks of pregnancy, include high blood pressure, headaches, blurred vision, intolerance to bright light, nausea, vomiting and excessive swelling of the feet and hands.
At what stage of pregnancy does preeclampsia usually occur? Preeclampsia can occur at any time during pregnancy, during labor, and during the six weeks postpartum period, but it most often occurs in the last trimester and resolves within 48 hours of delivery. Preeclampsia can develop gradually or appear suddenly, although signs and symptoms may already be present but go undetected for several months.
Who is most at risk for preeclampsia? Preeclampsia is much more likely to develop during the first pregnancy and in women whose mothers or sisters also suffered from preeclampsia. The risk of preeclampsia is higher in multiple pregnancies, during teenage pregnancies, and in women over 40 years of age. Other risk categories include women who had high blood pressure or kidney disease before pregnancy and women with a body mass index above 35. The cause of preeclampsia is unknown.
If my blood pressure is high, does it mean I have preeclampsia? Not necessary. If you have high blood pressure, you should see a doctor because this condition may indicate preeclampsia. In addition to high blood pressure, women with preeclampsia experience increased swelling and protein in the urine. Many women have high blood pressure during pregnancy, however, in the absence of swelling and protein in the urine, we are not talking about preeclampsia. If you have high blood pressure, then it is very important for you to monitor your blood pressure levels on a daily basis.
Why is blood pressure control so important during pregnancy? Preeclampsia manifests itself as high blood pressure. Therefore, it is necessary to measure blood pressure at least 2 times a day - morning and evening. It is necessary to measure in a sitting position, after rest and in a calm environment.
What level of blood pressure during pregnancy is considered normal and what is considered high? To answer this question, use the following table, which shows data on blood pressure values during pregnancy (in mmHg):
| Range | Systolic | Diastolic | What is recommended to do |
| Normal blood pressure | less than 140 | less than 90 | Self-control |
| Hypertension | higher than 140 | higher than 90 | Consult a doctor |
| Severe hypertension | higher than 180 | higher than 100 | Urgent medical attention required! |
Reference: Prof. A.H. Shennan, St. Thomas Hospital, London
What blood pressure levels before and after pregnancy are considered normal? Table of classification of blood pressure levels (in mmHg). Data from the World Health Organization (WHO).
| Range | Systolic | Diastolic | What is recommended to do |
| Pressure is low | < 100 | < 60 | Consult your doctor |
| Optimal pressure | 100 — 120 | 60 — 80 | Self-control |
| Normal blood pressure | 120 — 130 | 80 — 85 | Self-control |
| Slightly elevated blood pressure | 130 — 140 | 85 — 90 | Consult your doctor |
| High pressure | 140 — 160 | 90 — 100 | Consult a doctor |
| Pressure is excessively high | 160 — 180 | 100 — 110 | Consult a doctor |
| The pressure is dangerously high | > 180 | > 110 | Urgent medical attention required! |
How dangerous is preeclampsia for my baby and for me? Preeclampsia prevents the placenta from receiving the amount of blood it needs. If the placenta does not receive enough blood, the fetus suffers from air and nutritional deficiencies, which results in low birth weight and other problems for the baby. Most women with preeclampsia give birth to healthy babies. A small number develop a condition called eclampsia, which is very dangerous for mother and baby. Thanks to well-established antenatal care services, preeclampsia is detected at an early stage, when most problems can be eliminated.
How is preeclampsia treated? The only treatment is the birth of a child. If preeclampsia is diagnosed, mother and baby are closely monitored. It is mandatory to monitor the pressure level, at which measurements are taken 2 times a day. It is necessary to analyze the level of protein in the urine and monitor weight changes. There are now medications and various treatments available that prolong pregnancy and increase the baby's chances of survival.
Can preeclampsia be prevented? Preeclampsia is not a disease that can be prevented by lifestyle changes, such as diet, quitting smoking, quitting alcohol, exercise, getting enough rest, not worrying, etc. There is evidence that calcium supplements reduce the risk of preeclampsia, especially in women living in areas where calcium is deficient in foods. Calcium helps blood vessels relax and thus prevent hypertension.
Are there long-term effects of preeclampsia? For most women, childbirth reverses the effects of preeclampsia. Women who have preeclampsia during pregnancy may later develop high blood pressure. But this may also be a consequence of genetic predisposition, and not preeclampsia itself. In infants, the effects occur if they experienced severe lack of nutrition and oxygen in the womb or had problems as a result of prematurity. There are no health problems associated with preeclampsia in children born to mothers with preeclampsia.
Useful links on preeclampsia
| Organization | Link |
| Preeclampisia foundation | www.preeclampsia.org |
| American Academy of Family Physicians | https://familydoctor.org |
| DrKoop.com | www.drkoop.com/encyclopedia/93/16.html |
| Emedicine (for professionals) | www.emedicine.com/emerg/topic480.htm |
| Preeclampsia Society UK | www.dawnjames.clara.net |
| Action on Preeclampsia (UK based charity) | www.apec.org.uk |
| Australian Action on Preeclampsia | www.aapec.com/index.php |
| Pre-eclampsia experiences and discussion / support group | www.pre-eclampsia.co.uk |
| International Society for the study of Hypertension in Pregnancy | https://www.ncl.ac.uk |
| Mayo Clinic | www.mayoclinic.org |
Increased blood pressure in pregnant women
High blood pressure during pregnancy is dangerous for both mother and baby. In such a situation, the blood vessels narrow and the flow of blood to vital organs, including the placenta, is disrupted. A deficiency of oxygen and essential nutrients creates a risk of complications, slower fetal growth, and placental abruption.
An increase in blood pressure is called arterial hypertension, but such a diagnosis is made only with a constant or regular increase in the indicator. A one-time increase in pressure is a reason to monitor indicators more carefully, but not a reason for such a diagnosis.
The reasons for increased blood pressure during pregnancy are:
- More active blood circulation while maintaining its previous volume - in the later stages, this condition indicates the body is preparing for childbirth;
- Hypertension – women with chronic hypertension have a particularly high risk of blood pressure problems during pregnancy;
- Preeclampsia is a disruption of the functioning of capillaries and internal organs, which manifests itself in the appearance of severe swelling and protein in the urine;
- Concomitant diseases, for example, diabetes or pathologies of the kidneys, thyroid gland, adrenal tumor;
- Hormonal imbalance.
Increased pressure is usually accompanied by dizziness, headache and tinnitus, palpitations, and nosebleeds may occur. This condition is very dangerous; you must immediately consult a doctor, and if your health deteriorates significantly, call an ambulance.
What are the consequences of jumps in the indicator in position?
Increased blood pressure during pregnancy can sometimes be tolerated absolutely calmly, but sometimes leads to disruption of the condition of the fetus and mother.
Spiral arteries are located in the uterus; they nourish the placenta. They need tortuosity so that during menstruation and postpartum hemorrhage, the myometrial fibers can shrink and reliably compress the torn vessels. During pregnancy, the body must first of all ensure normal blood supply to the fetus. Therefore, the spiral arteries lose their ability to contract: the muscular layer of their wall is replaced by rough connective tissue. It forms a stable lumen of blood vessels, and the fetus receives enough blood in almost any condition of the body.
In some women, the degeneration of the spiral arteries does not occur completely or is completely absent. Attacks of arterial hypertension are especially dangerous for the life and health of their future children.
The influence of high blood pressure on individual components of the mother-fetus system
| Suffering organ | Its functions | Mechanism of damage | Possible consequences |
| Placenta | Providing the fetus with oxygen and nutrients from the mother's body | Reduced blood flow from the spiral arteries of the uterus due to their spasm with increased blood pressure | Fetal distress (heart rate in the womb less than 110 or more than 170 per minute), which can lead to developmental pathologies and even intrauterine death |
| Blood vessels | Blood supply to all tissues of the body, transport of nutrients and waste products | Spasm of the vascular wall due to disruptions in regulation (hormonal and nervous mechanisms) | Stagnation of toxic metabolic products in the periphery, lack of oxygen and nutrients, which leads to ischemia and inability to function adequately |
| Blood | The main transport medium of the body | Thickening, increased activity of enzymes of the blood coagulation system | Development of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome - blockage of blood vessels by spontaneously formed blood clots |
| Kidneys | Cleansing the body of toxins, controlling the volume of circulating blood | Vasospasm in the functional parts of the kidney interferes with the normal course of urination processes | Protein from the circulatory system enters the urine. The blood thickens and swelling appears. Acute renal failure may develop |
If you have high blood pressure and find protein in your urine, it is called preeclampsia. Hypertension due to pathology of the spiral arteries is dangerous in itself (the fetus will not receive enough nutrition and oxygen, its development will begin to slow down, and fetal distress is possible during childbirth). And when kidney dysfunction occurs, there is a threat of eclampsia - a convulsive seizure (chaotic contractions of all the muscles in a woman’s body will not bring good to the fetus). In this case, doctors have to fight for the life of the child and even the mother.
To identify a risk group and prevent the development of eclampsia, the norm of blood pressure in pregnant women was determined. This is why blood pressure control is so important, especially in the third trimester.
Reducing blood pressure in pregnant women
A slight decrease in blood pressure during early pregnancy is normal. However, if the levels decrease significantly, it can be dangerous for both mother and child.
Low blood pressure can be a symptom of the development of serious diseases, from stomach ulcers to adrenal insufficiency. Hypotension is especially dangerous due to impaired blood circulation in the placenta. This impedes the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus, hypoxia, non-developing pregnancy and the risk of premature termination of pregnancy.
Blood pressure during pregnancy may decrease due to:
- Constant stress;
- Dehydration of the body;
- Infectious diseases;
- Hormonal changes;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Serious blood loss;
- Malfunctions of blood vessels and heart.
In this case, the woman feels weak and drowsy, gets tired quickly, dizziness, darkening of the eyes and fainting are possible. Self-medication in such cases is unacceptable; you must definitely visit a doctor.
conclusions
To give birth to a healthy baby, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the expectant mother throughout the entire pregnancy. One of the important indicators (screening markers that precede serious disorders) is the level of blood pressure.
By the end of pregnancy, blood pressure may increase slightly, but even in the third trimester they should not exceed 14090 mmHg. Art.
High blood pressure is dangerous due to a chronic decrease in blood supply to the fetus in the uterus (this can lead to developmental delays and even intrauterine death) and eclampsia (a convulsive seizure in which it is very difficult to maintain a pregnancy).
How to measure blood pressure during pregnancy
The blood pressure measurement procedure takes only a few minutes, but can help prevent very serious health problems. Modern automatic blood pressure monitors do almost everything themselves; you need to use them regularly and follow some rules:
- Take measurements at the same time of day so that the indicators do not change under the influence of hormonal fluctuations and biological rhythms of the body;
- Do not measure blood pressure immediately after exercise, including walking - in this state the pressure may temporarily increase, there is nothing to worry about;
- Do not take measurements less than an hour after eating - due to the active activity of the digestive system, the blood volume is redistributed, so the result will be biased;
- Measure the pressure in a sitting position, the hand lies on the table top, the muscles are relaxed;
- Do not move or talk during the measurement.
You should not measure your blood pressure in a state of strong excitement. First you need to calm down, lie down for a few minutes. Repeated measurement is carried out no earlier than after 10 minutes, if necessary.
Rules for measuring pressure
Putting on a tonometer cuff and pressing a button on the device is not enough to accurately measure blood pressure. Doctors adhere to a number of rules that should be used when taking home measurements using an electronic device:
- The pressure should be measured at complete rest, in a sitting position, preferably on both the right and left arms.
- The blood pressure cuff should be approximately at the level of the woman's heart.
- It is advisable to avoid physical activity about an hour before measurements and spend at least five minutes in a calm state.
- While the device is operating, you need to relax, straighten your legs and arms, and lean back in a chair or armchair.
- The first measurements may be too high, so to be sure, measure your blood pressure again.
Regarding blood pressure, doctors advise preventing its elevated levels. For pregnant women, this means proper sleep, rest after lunch, psychological calm, walks outside and exercises feasible for the expectant mother, as well as a moderate diet and control of weight gain.
Deviations from normal blood pressure levels in pregnant women are a reason for the close attention of doctors. A pregnant patient can be hospitalized at any stage. And women who were diagnosed with hypertension before pregnancy are placed “for preservation” at least three times: in the first trimester to analyze the ability to carry a pregnancy to term, at a period of 28-32 weeks, since at this time the maximum increase in blood in the body occurs , and after 38 weeks to determine how the patient will give birth.
Expectant mothers with blood pressure problems often give birth in the department of pathology of pregnant women or specialized maternity hospitals, where they can be assisted by experienced cardiologists.
Blood pressure control is the key to the health of mother and child
Often problems with pressure do not manifest themselves until the situation becomes truly threatening. Sometimes pregnant women attribute the deterioration in their health to their “interesting situation” and hormonal changes and fatigue. But pressure surges during such a period can have quite serious causes and dangerous consequences.
The sooner such prerequisites are identified, the easier it will be to normalize the state of health. This is why pregnant women are advised to regularly monitor their blood pressure, especially since it is very easy to do this with modern home blood pressure monitors.
Too low
For some women expecting a baby, their blood pressure, on the contrary, decreases. The reason for this may be hormonal changes in the first trimester and early toxicosis. Signs of hypotension are lethargy, noise or ringing in the ears, headache or dizziness, a feeling of shortness of breath, and some women experience fainting.
Since low blood pressure cannot provide adequate blood supply to organs, hypotension can lead to serious consequences, for example, the unborn baby will lack nutrients and oxygen. Therefore, you need to try to adjust the pressure in accessible ways and make sure that it does not drop too low.
“Read forums less.” Advice from a gynecologist on preparing for pregnancy
More details