Basic functions of platelets
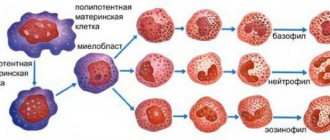
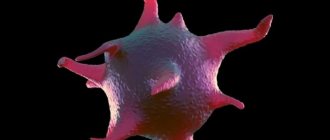
In appearance, platelets are round or oval red plates with a smooth surface. They are formed in the bone marrow. They mature in approximately 8 days. These components constantly circulate in the bloodstream.
The main function of platelets is to ensure blood clotting. In addition, the ability of these blood components to stop bleeding is important. This is ensured by the fact that individual platelets can stick together and stick to sites of vascular damage. The process is automatically started by the human body when there is a risk of bleeding.
An important question is how long platelets live. Their viability time lasts approximately 10 days. Depending on the age of the red plates, their size changes: from 2 to 5 microns in diameter.
The process of platelet renewal in the blood occurs constantly. Therefore, an important factor to ensure the maintenance of blood condition is the balance between the formation of red plates and their death. Otherwise, there may be a tendency to blood clots or increased bleeding.
Normal platelet count
The normal platelet level is two hundred to four hundred thousand units/μl. Depending on the age of the person, their number may vary. Thus, for example, in newborns the norm is two hundred eight to four hundred ten thousand units/μl. In the future, as the child grows and develops, their normal number may differ. Therefore, in order to adequately interpret a child’s blood test, you should use special tables of blood indicators according to the baby’s age. What is the norm of platelets - it was said above. A change in the number of blood platelets increases the risk of blood clots or bleeding. If there are abnormalities in the blood test, the test should be taken several times a year as directed by a doctor.
In laboratories, several methods are used to count platelet counts:
- in a special counting chamber with a phase contrast device,
- in painted smears,
- using special hematology analyzers.
Then the obtained indicators are entered into a special form.
Blood test for platelets
A complete blood test can determine the platelet count. The main indications for its implementation are the following:
- Increased bleeding of gums.
- Heavy menstruation.
- The appearance of bruises from minor impacts.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- Difficulty stopping bleeding from minor injuries.
The number of platelets in the blood is measured in thousands per 1 microliter of blood. Counting is carried out in specialized laboratories in various ways that guarantee high accuracy.
The normal platelet count in the blood depends on gender and age and is:
- For men, 200–400 thousand.
- In women, 180–320 thousand, during menstruation the amount can decrease to 75–220 thousand, and during pregnancy to 100–310 thousand.
- In children, indicators depend on age, and the corresponding values are given in special tables.
To conduct a general blood test, blood is taken from a finger. No special preliminary preparation is required before this. To ensure accurate results, it is better to donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach. At the same time, 12 hours before the procedure it is not recommended to consume fatty spicy foods, carbonated drinks, and alcohol.
Additionally, to determine blood clotting indicators, Sukharev and Lee-White tests are performed. They are informative and allow you to obtain the necessary additional data about the pathological condition. This will allow you to carry out correct treatment measures and avoid dangerous consequences.
Platelet count (according to Fonio)
Platelets are involved in the entire process of blood coagulation, starting from the formation of a primary thrombus in the area of damage to blood vessels and ending with participation in the processes of regulating vascular permeability and tone.
The calculation of the most accurate number of platelets is carried out using the Goryaev camera and the Fonio method. The Fonio platelet count is quite accurate. The Fonio method is most convenient for automatic counting.
Units
In a stained smear, 1000 red blood cells and all platelets found are counted. The result is a number expressed in ppm. To obtain the absolute number of platelets, a clinical laboratory diagnostics physician multiplies this value by the number of red blood cells present in 1 μl, and then divides by 1000.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous, capillary blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate alcohol and medications from your diet (in consultation with your doctor) the day before donating blood.
- Do not eat for 8 hours before the test; you can drink clean still water.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress and do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
An important condition for the correct functioning of the coagulation system is the presence of a certain number of mature platelets in the bloodstream. Deviations in any direction can have adverse consequences. The normal platelet count in the blood differs depending on age and gender. If their level is reduced, there is a tendency to bleeding, blood clotting worsens, and is difficult to stop. If the platelet count exceeds the norm, the blood becomes thick, and there is a risk of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels.
Platelets are formed in the bone marrow from giant cells called megakaryocytes. In fact, they are fragments of these cells and are small, nuclear-free, colorless oval or round shaped plates surrounded by a membrane, including granules. The diameter of platelets ranges from 2 to 4 microns. They are usually called blood cells, like leukocytes and red blood cells, although they are not. These are postcellular structures, or Bizzazero plaques (named after the Italian scientist who made a great contribution to their study). About 2/3 of all platelets are found in the blood, the rest are found in the spleen.
Functions of blood platelets
When the vascular wall is damaged, blood platelets are immediately activated. They take on a spherical shape and outgrowths appear on them, making them look like a star. Platelets in their active form are capable of sticking to each other (aggregation) and sticking to the vessel wall (adhesion). They secrete an enzyme into the blood plasma, under the influence of which soluble fibrinogen is converted into insoluble fibrin, which entangles the formed elements of the blood with its threads, like nets. The resulting thrombus closes the defect in the damaged vessel. Platelets take part in the dissolution of the fibrin clot and maintain spasm of damaged vessels. Another important function is to provide nutrients to the cells that line the inner surface of blood vessels.
What do the results mean?
Platelets
| Age | Reference values |
| Less than 10 days | 99 - 421 *10^9/l |
| 10 days – 1 month | 150 – 400 *10^9/l |
| 1-6 months | 180 – 400 *10^9/l |
| 6 months – 1 year | 160 - 390 *10^9/l |
| 1-5 years | 150 – 400 *10^9/l |
| 5-10 years | 180 - 450 *10^9/l |
| 10-15 years | 150 – 450 *10^9/l |
| More than 15 years | 180 - 320 *10^9/l |
Thrombocytopenia
Causes:
- thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic-uremic syndrome;
- DIC syndrome (disseminated intravascular coagulation);
- drug thrombocytopenia (co-trimoxazole, procainamide, thiazide diuretics, heparin);
- hypersplenism;
- idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
It should be remembered that in pregnant women, platelets can normally decrease to 75-150×109/l.
Thrombocytosis
Causes:
- Primary thrombocytosis (malignant disease of the myeloid lineage of the bone marrow, including essential thrombocytosis and chronic myeloid leukemia);
- Secondary thrombocytosis after removal of the spleen, during an infectious process, iron deficiency anemia, hemolysis, trauma and malignant diseases (reactive thrombocytosis).
- An increase in Hb, MCV, or total leukocyte count suggests primary thrombocytosis.
Increased platelet levels
Elevated platelets are a pathological condition. It is called thrombocytosis. The main danger of the pathology is the increased risk of blood clots.
The cause of an increase in the level of platelets in the blood can be various diseases. Most often thrombocytosis occurs against the background of:
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Infectious diseases.
- Helminthic infestations.
- Surgical operations.
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Kidney failure.
High levels of platelets in the blood are observed in older people. Temporarily, indicators may increase after heavy physical exertion, for example, after playing sports.
The symptoms of thrombocytosis are characteristic, but mild. It is imperative to conduct a general blood test if the following symptoms are noted:
- Pain in the fingers and toes.
- Itching of skin surfaces.
- Unreasonable weakness, which leads to decreased performance.
- Lack of appetite.
Decreased platelet levels
Low platelet levels, the norm of which differs between men and women, provoke the development of a condition known as thrombocytopenia. Very often it occurs against the background of uncontrolled use of medications: antidepressants and antibiotics.
The reasons for a decrease in the level of platelets in the blood can be various infectious diseases: ARVI, hepatitis, herpes, etc. Thrombocytopenia can be observed when a large number of blood thinning products are included in the diet. These are ginger, cherries, garlic, onions, etc.
Non-infectious factors that reduce the level of platelets in the blood include pregnancy, vitamin deficiency, alcohol or heavy metal poisoning.
Thrombocytopenia can be suspected based on the following signs:
- Heavy menstruation.
- Frequent nosebleeds.
- The appearance of hematomas.
With a constant pathological decrease in the level of platelets in the blood, the risks of developing severe bleeding and stroke conditions, which are life-threatening, increase.
Decreased platelet count
This condition is called thrombocytopenia ( platelet count 100 ) and often develops after uncontrolled medication use. Leukocytopenia can accompany pathologies such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, bone marrow damage, thyroid diseases, hematological diseases, alcoholism and other pathologies. As a result of these diseases, the fragility of blood vessels increases. Long periods of menstruation, cuts, tooth extraction, bleeding gums, and frequent nosebleeds can also contribute to low platelet counts.
Thrombocytosis rate table
First of all, medications are used to treat a low platelet count. If necessary, doctors prescribe platelet transfusions.
Restoring platelet levels in the blood
You can normalize the level of platelets in the blood with a balanced diet. It is important to saturate your diet with foods high in materials and microelements. You need to give up spicy food, alcohol, fast food and sweet carbonated drinks, lead a healthy lifestyle and maintain a drinking regime.
If it is not possible to normalize the indicators using natural methods, then you need to undergo a full examination by a hematologist. If platelet levels are elevated, special medications may be prescribed - anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents. They thin the blood and minimize the risk of blood clots. But at the same time, they should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. It should be understood that stabilization of the condition is possible only after eliminating the underlying causes that provoke deviations from the norm.
Causes of increased platelet count
This condition is called thrombocytosis. A large number of platelets occurs with the appearance of diseases such as leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, oncological diseases of the blood, kidneys and liver, as well as lung diseases (COPD). It can also be accompanied by erythrocytosis, arthritis, enteritis, acute infectious diseases, hemolysis and myeloid leukemia. The number of plates increases under stress, poisoning, and as a result of bleeding. Their number may also increase if the hematopoietic system in the bone marrow is disrupted. Now you know what platelets are in a blood test.
Important! An interesting and important fact is that during bleeding, the number of platelets increases. This is influenced by the body’s compensatory ability. Our body tries to compensate for blood loss as quickly as possible. At the beginning of bleeding, their amount decreases, and after a day it increases noticeably.
causes of thrombocytosis
There is such a condition as secondary thrombocytosis, it develops with obesity, after injuries and surgical interventions, and alcoholism. In this case, the body increases the production of thrombopoietin, which promotes the maturation of bone marrow cells.
In any case, a deviation from the norm requires consulting a doctor and prescribing appropriate treatment. Only after additional research can the doctor identify the cause of the increase in platelet count.