The most common cause of death in our time is diseases of the cardiovascular system. More than a million people die from them every year in our country! And it’s not bad medicine that’s to blame for this - modern cardiology has a wide range of opportunities to help sick people. But the problem is that many of us go to the doctor too late, often arriving at the hospital already in an ambulance, with a heart attack or stroke.
Along with atherosclerosis, the development of which is difficult to prevent, one of the causes of life-threatening conditions (such as impaired blood supply to the heart or brain) is the “trifling”... hypertension. Not everyone knows that this disease can develop over many years, starting at a young age, asymptomatically and gradually. In their 30s, few people pay attention to an increase in upper or lower blood pressure by several units, and not everyone has a tonometer at home. And those who accidentally find out about their hypertension often brush it off: just take pills when nothing bothers you!
Another problem associated with the diagnosis of hypertension is the “white coat syndrome.” Some of us have retained an unconscious fear of doctors and medical institutions since childhood. Therefore, at an appointment with a cardiologist, a tonometer may show unreasonably high blood pressure numbers, while there is no illness. And for some in the hospital, the pressure, on the contrary, drops, while during work or at night its values can be high... How to catch insidious hypertension?
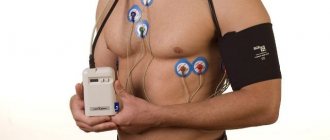
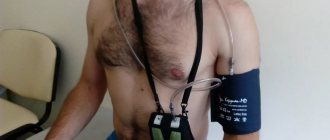
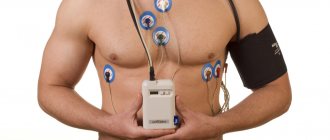
A good way to see an objective picture is to conduct 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM). During this procedure, the patient wears a special device on his body for 1-2 days that records blood pressure readings in conditions as close as possible to natural ones. Based on the results of the study, the doctor receives all the necessary information in order to confirm or refute the presence of hypertension or symptomatic arterial hypertension (increased blood pressure caused by a particular disease).
Another useful use of ABPM may be to monitor the treatment of patients with already diagnosed hypertension. In this case, they continue to take medications during the procedure.
Sometimes ABPM is carried out simultaneously with Holter monitoring (24-hour ECG monitoring). This combined study significantly expands the possibilities for diagnosing cardiovascular diseases.
Cause of white coat syndrome
Although the exact causes of high blood pressure are unknown, there are many factors that can increase the risk of hypertension, such as:
- white coat syndrome during pregnancy;
- obesity;
- lack of physical activity;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- stress;
- high salt intake;
- a family history of high blood pressure;
- elderly age;
- thyroid diseases;
- sleep apnea;
- kidney disease;
- genetics.
Managing these factors can help people keep their blood pressure in a healthy range. However, white coat hypertension is a condition in which blood pressure usually only rises in the doctor's office and may be related to nervousness and anxiety.
Target blood pressure level
All patients with hypertension receiving therapy, regardless of age and risk level, are recommended to reduce blood pressure to less than 140/90 mm as the first target level. rt. Art., and with good tolerance - up to the level of 130/80 mm. rt. Art. or even lower. It is with these figures that a reduction in the risk of cardiovascular complications mentioned above has been proven. However, it must be remembered that an excessive decrease in blood pressure can be dangerous.
Your attending physician will definitely tell you about your target blood pressure level, since these numbers are individual for each patient with hypertension. During treatment, achieving the target blood pressure level allows reducing the risk of death and complications of hypertension.
Diagnostics
The study notes that 15 to 30% of people with high blood pressure in the doctor's office may have white coat syndrome. Doctors speculate that white coat hypertension may be a precursor to hypertension.
Although white coat syndrome can cause a spike in blood pressure, doctors are not convinced that it is the only cause of high blood pressure. Stress and anxiety can play a role in high blood pressure, so people with white coat hypertension may be at risk for problems caused by blood pressure. Cardiologists believe that white coat hypertension is common in people with cardiovascular disease. Therefore, it is imperative that doctors find a way to accurately diagnose blood pressure and begin the necessary treatment on time.?
How is 24-hour blood pressure monitoring performed?
To undergo ABPM, you must make an appointment with a cardiologist. The study is carried out on an outpatient basis: the tonometer cuff is fixed on the patient’s shoulder, as in a normal blood pressure measurement, and the device itself (its weight is no more than 300 g) is attached to the belt, under clothing. After consulting a doctor, you can go home or work. The device will automatically, at certain intervals, measure your blood pressure and record the data obtained. ABPM does not interfere with leading a normal lifestyle: eating, sleeping and even playing sports. Your doctor will likely ask you to keep a diary to record episodes of physical activity (climbing stairs, lifting heavy objects), periods of rest, sleep, waking up at night, and symptoms of discomfort, such as heart pain or dizziness, if you experience them. After 24 or 48 hours (depending on the recommended duration of the study), you will need to turn off the device and return to the cardiologist for a consultation. He will decipher the data received, comparing it with the information in your diary, and make a conclusion about the state of your health.
There are simple recommendations for patients undergoing daily blood pressure monitoring:
Watch the position of the cuff on your shoulder. Its lower edge should be fixed 1-2 fingers above the elbow. If you feel that the cuff has slipped off your arm, be sure to adjust it.
Before each measurement, the ABPM device beeps. If you have the opportunity, do not move while measuring pressure, so the results will be more accurate. While the device pumps air into the cuff, relax your hand. At the end of the measurement, a repeat beep will sound.
Make sure that the tube connecting the monitor to the cuff is not pinched by clothing or when you are sitting or lying down.
Do not allow water to come into contact with the device (do not take a shower during the study), and also try to avoid prolonged stay near sources of electromagnetic radiation (power lines, microwave ovens, television and radio transmitters) during ABPM.
If you think that the ABPM device is out of order, do not try to fix it yourself and do not disassemble it. Report the incident to your healthcare provider.
Prevention of white coat syndrome
Relaxation techniques such as breathing exercises and meditation can help calm people down. If you feel nervous when it's your turn to see the doctor, you can take a few deep breaths to calm yourself.
White coat syndrome can put you at risk for cardiovascular disease, and not all doctors believe the condition is harmless. Anyone who thinks they have white coat hypertension should see a doctor to get a proper diagnosis.
Risk group
Most often, white coat hypertension is observed in impressionable individuals. What makes them nervous is that they take going to the doctor to heart. Also at risk are individuals who are weak in spirit. People with mental disorders also fall into this group; their fear of medical workers is more obvious and can lead to a panic attack.
In addition, people who lead an unhealthy lifestyle and have bad habits are at risk.
It is important to note that the syndrome can manifest itself in children one year old and older (children under one year old quickly forget everything) - this is most often associated with a child’s bad experience: without warning, blood was taken from a finger, and a painful injection was given.
These negative emotions are a source of anxiety.
How not to be afraid of medical workers
You can cope with white coat syndrome on your own by following simple rules.
Choosing a doctor
Healthcare should be trusted to professionals with whom the patient has a long-term, trusting relationship. You can freely discuss any problems with them. They know the person’s health status and diagnose the problem more accurately.
This applies not only to the therapist or cardiologist, but also to other medical professionals.
Before measuring your blood pressure, you should tell your doctor about this syndrome.
Good mood
It is advisable to raise your emotional state before taking measurements. It is worth listening to music, watching your favorite movie, taking a walk in the fresh air or doing meditation.
Help from friends
A loved one will help you cope with your anxiety and accompany you to the clinic. If mental stress interferes with communication with the doctor, a friend can provide important details.
Sedatives
Anxiety or fear can be reduced by taking sedatives or antidepressants. You can also use traditional remedies such as mint tea. Help from a psychologist is possible.
How to get rid of the disease
Coping with this syndrome is not easy - doctors do not recommend using conventional antihypertensive drugs.
Antihypertensive drugs may cause additional complications. An integrated approach is usually prescribed - a combination of using traditional medicine and taking sedatives.
Among the folk remedies for this syndrome, it is recommended to take valerian infusion, soothing infusions of knotweed herb, and lemon balm. The use of home remedies is allowed only with the permission of a doctor; self-medication is prohibited. Before visiting a doctor, it is not advisable to use sedatives - they may interfere with making an accurate diagnosis.
If the manifestation is observed at every visit to the doctor, it is recommended to visit a psychotherapist and take a self-study course. To increase effectiveness, the doctor prescribes psychotropic drugs and antidepressants. Pregnant women often experience anxiety symptoms; hormonal imbalance also contributes to the development of the syndrome. Fear of the white coat usually disappears immediately after childbirth, and there is no need to take medications or consult a psychologist.
If, after the birth of the child, blood pressure problems do not disappear when visiting medical institutions, the doctor will prescribe medications and additional therapy.
Forecast. Prevention
The prognosis depends on the level of blood pressure and the presence of complications. Timely initiation of adequate treatment for hypertension contributes to a favorable prognosis.
The best prevention of hypertension is a healthy lifestyle and diet, as well as the elimination of existing risk factors (obesity, inactivity, smoking, chronic stress).[6] In case of existing hypertension, in order to prevent complications, the following recommendations are added to these recommendations:
- women with hypertension before pregnancy need to undergo a full examination before planning pregnancy with treatment adjustment if necessary;[1][5]
- women with hypertension during pregnancy need careful monitoring of their condition and strict adherence to medical prescriptions.[1][2][5]
For the addition and verification of the material, we thank Elena Karchenova , a cardiologist, therapist, and scientific editor of the ProBolesni portal.
An invisible disease. Childhood and adolescent hypertension
17 December 2021 09:12
Quantity
My son had an exam yesterday. And a day later another one. Of course, both he and I have stress and insomnia. I measured my blood pressure and his at the same time. One hundred forty to ninety. What is this? Arterial hypertension at 17 years old?! Well, okay with me. And with him!.. The son says that he doesn’t feel anything, everything is fine. Maybe it just happened by chance and will go away tomorrow? And if not?..
We asked a pediatric cardiologist, deputy chief physician for the medical department of the Arkhangelsk Regional Children's Clinical Hospital named after A. P.G. Vyzhletsova Svetlana Nazarenko.
– Svetlana Yuryevna, recently they say that arterial hypertension has become younger and is often found in adolescents and young people.
– Rejuvenated. The number of cases of hypertension is increasing not only in adults, but also in children, especially in adolescents and young men of military age.
– What is this connected with?
– Firstly, more attention has been paid to measuring blood pressure. We used to think: what kind of blood pressure do children have?! Today, the standards of treatment for absolutely all diseases require daily blood pressure measurements in hospitals, regardless of what we are treating or age. The examination standards at the clinic also include measuring the pressure of each child from the first days of life.
- And secondly?
– Blood pressure depends on the activity of the heart, on the tone of the arteries and can change under the influence of physical activity, emotions, and illness. Emotional stress and increased workload can cause increased blood pressure. For example, in physics and mathematics schools, the percentage of children with high blood pressure is 2–3 times higher than in ordinary schools.
At a young age, the cause of arterial hypertension is most often a high level of work of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The desire to do everything, the thirst for competition, a feeling of lack of time, aggressiveness, determination, the need to be a leader, a high degree of control over behavior in situations - qualities characteristic of people with hyperactivity of the sympathetic nervous system. It’s probably great if young people strive to get the most out of life, but there is another side to the coin - these are the mechanisms that trigger an increase in blood pressure.
The development of hypertension is also facilitated by low physical activity in children who lead a sedentary, sedentary lifestyle and are overweight. And if in the family it is still customary to constantly add salt and even over-salt food... then all the risk factors for hypertension are evident.
– And then a lifelong diagnosis?..
– In a teenager, increased blood pressure does not always mean stable hypertension, which will remain with him for life. Although there are studies that say: if an increase in blood pressure is recorded at the age of 13 either once or constantly, then the likelihood of developing arterial hypertension in a person by the age of 35 increases 9 times. That is, its mechanisms start early.
– Are there any features of hypertension in children? What is “juvenile hypertension”?
– If we see an increase in blood pressure per year, at five years (I’m not even talking about newborns), this is not at all the same hypertension as in adults. Until 10–11 years of age, hypertension in children is only symptomatic (secondary), that is, you need to look for the disease that causes it. For example, the cause may be heart defects or renal vessels, kidney disease. The child definitely needs to be examined.
Juvenile hypertension involves the age period after 10–12 years , regardless of gender. At this time, all the causes of secondary hypertension have usually already been identified and children who come to us with high blood pressure have exactly the same primary hypertension that occurs in adults.
– Can a child’s complaints “Mom, I have a headache” foreshadow hypertension?
– Very rarely, arterial hypertension can cause headaches - it is not typical for this disease. Of course, if this is not a hypertensive crisis, when a headache is caused by a sharp rise in pressure. According to its symptoms, hypertension is an invisible disease, which is most often detected by chance, for example, when measuring blood pressure during an examination with a doctor. Increased blood pressure is rarely accompanied by complaints; children usually feel well.
– What about “white coat hypertension”?
– There is a lot of “desktop” hypertension, the so-called “white coat hypertension”, as a specific reaction to stress due to tension in the same sympathetic nervous system. In about 30% of teenagers and young adults, this is a reaction to stress at the moment when blood pressure is measured... Then everything goes away.
– Still, are there any specific complaints with this invisible disease?
– There is nothing special. Arterial hypertension, I repeat, is detected by chance, for example, at a military registration and enlistment office, in a hospital where a child was admitted with an injury. Complaints occur more often if hypertension is accompanied by vegetative-vascular dystonia, with which the teenager comes to the doctor. Then there are many complaints: weakness, lethargy, sweating, motion sickness in transport... Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a dysfunction between the control structures of the brain and as a functional disorder in most cases it goes away. Although it may be delayed if there is a predisposition, especially on the part of the mother. Of all childhood periods, vegetative-vascular dystonia is most typical for adolescents.
– There are diseases that are inherited from parents...
– There is no gene responsible for arterial hypertension. It is not genetically transmitted, but if hypertension began early in the parents, then the child can be classified as a risk group with a family predisposition.
– How is the diagnosis made?
– It is impossible to make a diagnosis at one appointment; the pressure itself is very labile. This is not the hemoglobin level - they took a test, saw anemia, prescribed treatment. When visiting a doctor, your blood pressure is measured three times and the average value is taken. Then it is measured after two weeks. To exclude “white coat hypertension”, daily blood pressure monitoring at home is prescribed. Then the device is installed for a day, and the child leads a normal life. Then the fundus and heart are checked, and an ECG is taken. It is very important to have a tonometer and a properly selected cuff for measuring blood pressure at home. There are three sizes: for infants, preschoolers, schoolchildren and adults. If there is no suitable cuff, then it is better to have your blood pressure measured by a doctor in a clinic.
– How is childhood and adolescent hypertension treated?
– In pediatrics, there are big problems in the treatment of arterial hypertension. There are very few clinical studies in the pediatric population. Recommendations for the treatment of hypertension in children are based on adult recommendations. In the instructions for new drugs, in 95% of cases it is written “safety for use under 18 years of age has not been established,” that is, all responsibility for prescriptions rests with the doctor. It will take time for the drugs to become sufficiently researched and migrate to pediatrics. Therefore, we have a larger percentage of not only outdated, but already tested and long-used medications. The second problem is that there are no children’s forms of the drug. And third, there is no scientific data on how early treatment of arterial hypertension with medications will affect the future health of a young patient. After all, a person grows, blood vessels grow and develop, and the heart grows.
– Where does the prevention of arterial hypertension in children begin? What can replace medications?
- We need to move! Swim, hike, ski. With hypertension, static load is harmful: pumping up muscles, jumping, wrestling. It is important to alternate mental and physical activity during the day: to avoid sitting at the computer or watching TV for many hours. Children over 5 years old should spend at least half an hour daily on moderate dynamic aerobic exercise and 30 minutes 3-4 days a week on intense exercise. What is moderate physical activity? This is dancing at a fast pace, walking at a fast pace, playing volleyball or basketball...
We should not forget about factors that provoke hypertension, such as stress, excess weight, and smoking. N.I. Amosov said: “To be healthy, you need your own efforts, constant and significant. There is nothing to replace them!”
The effectiveness of all these measures has been proven in numerous studies, so in most cases it is necessary to resort to drug therapy if lifestyle adjustments for several months do not have an effect.
Material: Elena Antropova
Source of material : magazine “Your Health Formula” No. 38.
https://zdorovie29.ru/healthy-life-style/bolezn-nevidimka-detskaya-i-yunosheskaya-gipertoniya/
Track. news
Prev. news
What to do during a medical examination
What should people do who must undergo a medical examination at work or study? This condition can be prevented if you take a sedative before going to the clinic in the evening and in the morning.
When measuring blood pressure, you should try to monitor your breathing! The air should be inhaled smoothly and exhaled very slowly.
Features and associated symptoms
A peculiarity of the team caused by a visit to a medical institution is that only the upper pressure rises, the lower one usually remains in place. Statistics show that more than 10% of people suffer from this globally recognized symptom.
These values will return to normal as soon as you return home.
This syndrome can develop against the background of accompanying symptoms and health problems:
- Age (the problem is more common in older people);
- Weight problems (obesity, anorexia)
- diabetes;
- Increased cholesterol in the blood;
- Unhealthy eating habits (excessive consumption of foods rich in salt and fat, alcohol, regular smoking);
- heart or vascular disease.
High blood pressure is often accompanied by abdominal pain, defecation disorders and nervous irritability.