Among diagnostic cardiac procedures that are informative, it is worth highlighting echocardiography or ultrasound examination of the heart. This is a hardware procedure performed using high-frequency sound waves. It is indispensable for accurately identifying problems that are directly related to the work of the myocardium and the entire cardiovascular system.
The effectiveness of echocardiography is directly related to the evaluation of its results. Competent interpretation of cardiac ultrasound is a direct path to a speedy diagnosis and drawing up an effective treatment plan. Entrust the solution to the problem to an experienced specialist, contact us for qualified medical support!
Minute blood volume
To determine the IOC, the amount of blood passing through one of the atria in 1 minute is calculated. The characteristic is measured in liters or milliliters. Taking into account the individuality of the human body, as well as the difference in physical data, experts introduced the concept of cardiac index (CI). This value is calculated by the ratio of the IOC to the total surface area of the body, which is measured in square meters. The SI unit is l/min. m².
When transporting oxygen through a closed system, blood circulation plays the role of a kind of limiter. The highest indicator of minute volume of blood circulation obtained during maximum muscle tension, when compared with the indicator recorded under normal conditions, allows us to determine the functional reserve of the cardiovascular system and specifically the heart in terms of hemodynamics.
If a person is healthy, the hemodynamic reserve varies from 300 to 400%. The figures inform that without any danger to the body’s condition, a three- to four-fold increase in IOC, which is observed at rest, is possible. In people who regularly engage in sports and are physically well developed, this figure can exceed 700%.
When the body is in a horizontal position and any physical activity is excluded, the IOC is in the range from 4 to 5.5 (6) l/min. Normal SI under the same conditions does not leave the range of 2–4 l/min. m².
Relationship between the IOC and organs at rest
The amount of blood filling the circulatory system of a normal person is 5–6 liters. One minute is enough to complete a full circuit. With heavy physical work and increased sports loads, the IOC of an ordinary person increases to 30 l/min, and for professional athletes even more - up to 40.
In addition to physical condition, IOC indicators largely depend on:
- systolic blood volume;
- heart rate;
- the functionality and condition of the venous system, through which blood returns to the heart.
Systolic blood volume
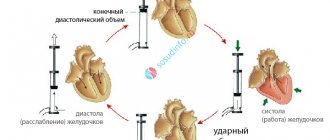
Systolic blood volume refers to the amount of blood pushed by the ventricles into the great vessels during one heartbeat. Based on this indicator, a conclusion is made about the strength and efficiency of the heart muscle. In addition to systolic, this characteristic is often called stroke volume or VT.
Systolic volume of blood circulation is calculated by the amount of blood pushed by the heart into the vessels during one contraction
At rest and in the absence of physical activity, during one contraction of the heart, 0.3–0.5 volumes of blood are pushed out to diastole, filling its chamber. The remaining blood is a reserve, which can be used in case of a sharp increase in physical, emotional or other activity.
The blood remaining in the chamber becomes the main determinant that determines the functional reserve of the heart. The larger the reserve volume, the more blood can be supplied to the circulatory system as needed.
When the circulatory system begins to adapt to certain conditions, the systolic volume undergoes a change. Extracardiac nervous mechanisms take an active part in the process of self-regulation. In this case, the main effect is on the myocardium, or more precisely, on the force of its contraction. A decrease in the power of myocardial contractions leads to a decrease in systolic volume.
For the average person, whose body is in a horizontal position and does not experience physical stress, it is normal if the OC varies between 70–100 ml.
How to do an ultrasound of the heart at the MedicCity clinic?
It is advisable for every person to have an echocardiogram at least once in their life. The fairly low cost of cardiac ultrasound is another reason to prefer this particular diagnostic method.
At MedicCity you can undergo all types of cardiac diagnostics - ECG, EchoCG, bicycle ergometry, HOLTER, ABPM, etc.
Just type in a search engine: “Ultrasound of the heart, Savelovskaya metro station, Dynamo metro station.” Or call us at: +7 (495) 604-12-12.
The doctors of our multidisciplinary clinic will do everything possible to relieve your heart pain!
Factors influencing IOC
Cardiac output is a variable value, and there are quite a few factors that change it. One of them is pulse, expressed as heart rate. At rest and in a horizontal position of the body, its average is 60–80 beats per minute. Changes in pulse occur under the influence of chronotropic influences, and inotropic influences affect strength.
An increase in heart rate leads to an increase in minute blood volume. These changes play an important role in the process of accelerating the adaptation of the IOC to the relevant situation. When the body is exposed to extreme stress, there is an increase in heart rate by 3 or more times compared to normal. Heart rhythm changes under the chronotropic influence exerted by the sympathetic and vagus nerves on the sinoatrial node of the heart. In parallel with chronotropic changes in cardiac activity, inotropic effects may be exerted on the myocardium.
Systemic hemodynamics is also determined by the work of the heart. To calculate this indicator, it is necessary to multiply the data on the average pressure and the mass of blood that is pumped into the aorta over a certain time interval. The result informs how the left ventricle is functioning. To establish the work of the right ventricle, it is enough to reduce the resulting value by 4 times.
If cardiac output indicators do not correspond to the norm and there are no external influences observed, then this fact indicates abnormal functioning of the heart, therefore, the presence of pathology.
Interpretation of EchoCG results in adults
The diagnostic conclusion is made only by the attending physician. The document in written (sometimes electronic) form is transferred to the patient in the diagnostic room, after which it is recorded in the hospital record. The individual indicators of the person undergoing the examination are entered into a special table, which already contains the normal figures for a specific age and gender.
Trying to decipher an ultrasound of the heart on your own is stupid and unsafe. The combination of several deviations may indicate different pathologies. You can’t do without experience and knowledge here.
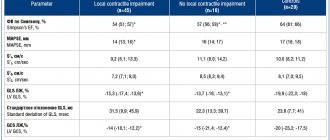
| Cardiac parameter | Men's answers | Women's answers |
| LVMM—left ventricular myocardial mass | 135-180 g | 95-142 g |
| LVMI—left ventricular mass index | 71-92 g/m2 | 71-88 g/m2 |
| ESD – LV end-systolic size | 31-42 mm | 31-42 mm |
| ESD – LV end-systolic size | 31-42 mm | 31-42 mm |
| EDV - end diastolic size | 46-58 mm | 45-58 mm |
| Volume of fluid in the pericardial cavity | 10-30 ml | 10-30 ml |
| LV wall thickness in diastole | up to 11 mm | up to 10 mm |
| Blood ejection volume during LV systole | 60-100 ml | 60-100 ml |
| Wall thickness of the RV - right ventricle | 5 mm | 4.8-5 mm |
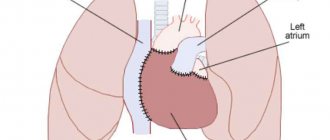
| LA size - left atrium | 18.5-33 mm | 17.5-33 mm |
| LA end-diastolic volume | 50-82 ml | 38-57 ml |
| End-diastolic volume of the RA – right atrium | 20-100 ml | 20-100 ml |
| Thickness of the IVS - interventricular septum in systole | 5-9.5 mm | 5-9.0 mm |
| IVS thickness in diastole | 7.5-11 mm | 7.5-11 mm |
| Aortic opening area | 20-35 mm2 | 20-35 mm2 |
| Thickness of the outer membrane of the pericardium | 1.2-1.7 mm | 1.2-1.7 mm |
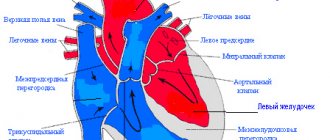
Only a cardiologist can evaluate an ultrasound of the heart; the results are interpreted according to standard values, taking into account the general health of the patient, the medications he is taking and other factors. The size, weight, volume and location of the organ, the condition of the valves and tissues are studied. Parameters for contractions, blood vessels and blood flow, wall thickness and other important nuances are recorded. The speed of blood distribution through the chambers of the heart helps to determine Doppler measurements. It is often performed in conjunction with traditional ultrasound examination.
Decreased cardiac output
The most common causes of low cardiac output are disturbances in basic cardiac functions. These include:
- damaged myocardium;
- blocked coronary vessels;
- abnormally functioning heart valves;
- cardiac tamponade;
- disrupted metabolic processes occurring in the heart muscle.
When cardiac output decreases and tissues are no longer supplied with nutrients, cardiogenic shock can occur.
The main reason leading to a decrease in cardiac output lies in the insufficient supply of venous blood to the heart. This factor has a negative impact on the IOC. The process is determined by:
- a decrease in the amount of blood involved in circulation;
- decrease in tissue mass;
- blockage of large veins and expansion of ordinary ones.
A decrease in the amount of circulating blood helps to reduce the IOC to a critical threshold. A shortage of blood begins to be felt in the vascular system, which affects the amount of blood returned to the heart.
When fainting occurs due to disorders in the nervous system, small arteries become dilated and veins become enlarged. The result is a decrease in blood pressure and, as a consequence, insufficient blood volume entering the heart.
If the vessels supplying blood to the heart undergo changes, they may partially block. This immediately affects peripheral vessels that are not involved in the supply of blood to the heart. The resulting reduced amount of blood sent to the heart causes low cardiac output syndrome. Its main symptoms are expressed:
- drop in blood pressure;
- low heart rate;
- tachycardia.
This process is accompanied by external factors: cold sweat, low volume of urination and changes in skin color (pallor, blueness).
The final diagnosis is made by an experienced cardiologist after carefully studying the test results.
Increased cardiac output
The level of cardiac output depends not only on physical activity, but also on the psycho-emotional state of a person. The functioning of the nervous system can reduce and increase the IOC index.
Sports activities are accompanied by an increase in blood pressure. Accelerating metabolism contracts skeletal muscles and dilates arterioles. This factor allows oxygen to be supplied to the muscles to the required extent. Loads lead to a narrowing of large veins, an increase in heart rate and an increase in the strength of contractions of the heart muscle. High blood pressure causes increased blood flow to the skeletal muscles.
Increased cardiac output is most often observed in the following cases:
- arteriovenous fistula;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- anemia;
- vitamin B deficiency.
In an arteriovenous fistula, the artery is directly connected to the vein. This phenomenon is called a fistula and comes in two types. A congenital arteriovenous fistula is accompanied by benign formations on the skin and can be located on any organ. In this variant, it is expressed by embryonic fistulas that have not reached the stages of veins or arteries.
Arteriovenous fistula
An acquired arteriovenous fistula is formed under the influence of external influence. It is created if there is a need for hemodialysis. Often a fistula becomes the result of catheterization, as well as a consequence of surgical intervention. Such a fistula sometimes accompanies penetrating wounds.
A large fistula provokes increased cardiac output. When it takes a chronic form, heart failure is possible, in which the IOC reaches critically high levels.
Thyrotoxicosis is characterized by a rapid pulse and high blood pressure. In parallel with this, not only quantitative changes in the blood occur, but also qualitative ones. An increase in the level of thyraxine is promoted by an abnormal level of erythropatine and, as a consequence, a decreased erythrocyte mass. The result is increased cardiac output.
With anemia, blood viscosity decreases and the heart is able to pump more of it. This leads to increased blood flow and increased heart rate. Tissues receive more oxygen, and accordingly, cardiac output and IOC increase.
Vitamin B1 deficiency is the cause of many pathologies
Vitamin B1 is involved in blood formation and has a beneficial effect on blood microcirculation. Its action significantly affects the functioning of the heart muscles. A lack of this vitamin contributes to the development of beriberi disease, one of the symptoms of which is impaired blood flow. With active metabolism, tissues stop absorbing the nutrients they need. The body compensates for this process by dilating peripheral vessels. Under such conditions, cardiac output and venous return can exceed the norm by two or more times.
Cardiac output fraction and diagnosis
The concept of ejection fraction was introduced into medicine to determine the performance of the heart muscles at the time of contraction. It allows you to determine how much blood was pushed from the heart into the vessels. The unit of measurement is set to percentage.
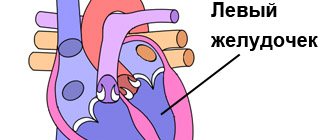
The left ventricle is selected as the object of observation. Its direct connection with the systemic circulation makes it possible to accurately determine heart failure and identify pathology.
Ejection fraction is prescribed in the following cases:
- with constant complaints about heart function;
- chest pain;
- shortness of breath;
- frequent dizziness and fainting;
- low performance, rapid fatigue;
- swelling of the legs.
The initial analysis is carried out using ECG and ultrasound equipment.
When is a cardiac ultrasound performed?
Indications for cardiac ultrasound are:
- alarming changes in health (increased or interrupted heartbeat, shortness of breath, swelling, weakness, prolonged fever, chest pain, cases of loss of consciousness);
- changes detected in the last ECG;
- increased blood pressure;
- heart murmurs;
- cardiomyopathy;
- manifestations of coronary heart disease;
- heart defects (congenital, acquired);
- pericardial diseases;
- lung diseases.
Fraction norm
During each systolic state, the heart of a person who is not experiencing increased physical and psycho-emotional stress throws up to 50% of the blood into the vessels. If this indicator begins to noticeably decrease, insufficiency is observed, which indicates the development of ischemia, heart disease, myocardial pathologies, etc.
A – normal fraction, B – 45% fraction
The ejection fraction norm is 55–70%. Its drop to 45% and below becomes critical. To prevent the negative consequences of such a decline, especially after 40 years, an annual visit to a cardiologist is necessary.
If the patient already has pathologies of the cardiovascular system, then in this case there is a need to determine an individual minimum threshold.
After conducting the study and comparing the data obtained with the norm, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes appropriate therapy.
Ultrasound does not reveal the full picture of the pathology and, since the doctor is more interested in identifying the cause of this disease, most often it is necessary to resort to additional studies.
Cardiac ejection fraction on ultrasound
Is cardiac echocardiography safe?
During this study, there is no radiation or other load on the organ. Therefore, if necessary, it can be prescribed even several times a week.
This study is characterized by the absence of complications and side effects.
EchoCG does not harm either the expectant mother or the fetus during pregnancy.
Limitations for the procedure may include inflammatory diseases of the skin of the chest, chest deformities and some other reasons.
Treatment of low fraction level
Low cardiac output is usually accompanied by general malaise. To normalize health, the patient is prescribed outpatient treatment. During this period, constant monitoring of the functioning of the cardiovascular system is carried out, and the therapy itself involves taking medications.
In particularly critical cases, surgery may be performed. This procedure is preceded by the identification of a severe defect or serious disorders of the valve apparatus in the patient.
Surgery becomes inevitable when low cardiac output becomes life-threatening for the patient. In general, conventional therapy is sufficient.
Self-treatment and prevention of low ejection fraction
To normalize the ejection fraction, you must:
- Introduce control over the liquids taken, reduce their volume to 1.5–2 liters per day.
- Avoid salty and spicy foods.
- Switch to dietary foods.
- Reduce physical activity.
Preventive measures to avoid deviations from the normal cardiac ejection fraction include:
- rejection of bad habits;
- maintaining a daily routine;
- eating iron-containing foods;
- exercises and light gymnastics.
If there is the slightest malfunction of the heart or even suspicion of these manifestations, you must immediately see a cardiologist. Timely detection of pathology greatly simplifies and speeds up its elimination.