The human brain is the crown of development of human nature, allowing us to develop and transform our own lives in accordance with our goals. We owe most of the body functions responsible for our life to the work of the central nervous system. The human brain is an incredibly complex organ that leads to the coordinated functioning of almost all systems in the body. not to mention the higher nervous activity responsible for cognitive skills and thought processes. Unfortunately, a fast pace and far from the healthiest lifestyle slowly undermine the body, depleting its reserves and compensatory mechanisms. Today, the world faces an acute problem associated not only with high morbidity, but also with disability and even mortality from cardiovascular diseases. Among such diseases, organic brain damage of an ischemic and hemorrhagic nature is in the first place. It is important to note that despite the significant preponderance in the morbidity structure of people in the older age group, namely 45 years and older, organic brain damage can also occur in children.
A brief excursion into the anatomy of the central nervous system
The human brain is a complex organ responsible for the functioning of the entire organism. There is a clear hierarchy in the structure of the brain, which allows the entire body to work effectively. The central nervous system can be divided into several main parts:
- The cerebral cortex is responsible for higher nervous activity, i.e. thought processes, speech, memory, writing, hearing and many other functions.
- Subcortical structures that form the midbrain. The midbrain is responsible for the primary reflex units and the formation of unconditioned reflexes.
- The bridge is a connecting link between all parts of the central nervous system and the cerebral cortex.
- Cerebellum. It is located in the lower occipital part of the head and is responsible for human coordination in space.
- The medulla oblongata connects the brain with the spinal cord and is its continuation. The medulla oblongata contains vital centers: vasomotor and respiratory.
Treatment of organic pathology and mental disorders
First of all, the cause of organic pathology should be established. Treatment tactics will depend on this.
In case of infectious pathology, antibiotics sensitive to the pathogen should be prescribed. For viral infections - antiviral drugs and immunostimulants. For hemorrhagic strokes, surgical removal of the hematoma is indicated, and for ischemic strokes, decongestant, vascular, nootropic, and anticoagulant therapy is indicated. For Parkinson's disease, specific therapy is prescribed - levodopa-containing drugs, amantadine, etc.
Correction of mental disorders can be medicinal and non-medicinal. The best effect is shown by a combination of both methods. Drug therapy includes the prescription of nootropic (piracetam) and cerebroprotective (citicoline) drugs, as well as tranquilizers (lorazepam, tofisopam) and antidepressants (amitriptyline, fluoxetine). To correct sleep disturbances, hypnotics (bromizoval, phenobarbital) are used.
Psychotherapy plays an important role in treatment. Hypnosis, auto-training, Gestalt therapy, psychoanalysis, and art therapy have proven themselves well. This is especially important when treating children due to possible side effects of drug therapy.
What is brain damage?
Organic brain damage is primarily a symptom of a disease, manifested by disruption or loss of a number of functions as a result of the pathogenic effect of some factor on brain tissue. The etiology of brain damage can be very diverse, and this will be discussed in more detail later in the article. Organic damage means that brain cells - neurons - are exposed to a variety of influences, which lead to the formation of dystrophic processes inside neurons and disrupt their functional activity. In the most serious cases, neurons simply undergo first necrobiosis and then necrosis, i.e. are dying. The death of a large number of neurons localized in a single anatomical space leads to the loss of one or another function in the body of the affected person, and the identification of a disturbed function allows specialists to understand in which part of the brain the catastrophe occurred - this is called topical diagnostics. Symptoms of organic brain damage in children manifest themselves differently than in adults, since the full activity of the higher nervous system has not yet been formed. Children may experience delays in mental, mental and physical development, unstable mood and behavioral abnormalities.
Pathogenetic mechanisms of neuronal damage
A number of mechanisms of different nature can lead to organic damage to the brain. This pathological condition can be provoked by both external and internal factors, and this must be taken into account, since therapeutic measures, depending on the pathogenetic type of development of damage to brain neurons, will differ radically.
Violation of energy supply
The most common pathogenetic variant of brain damage is associated with an imbalance between the need of neurons for energy and its entry into the cell. Energy deficiency can develop due to insufficiency:
- Nutrients in the victim's body, for example as a result of hypoglycemia, when there is not enough glucose in the blood;
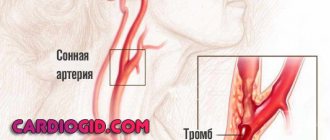
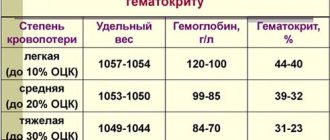
- Oxygen, which causes a condition such as hypoxia. Brain hypoxia causes damage to nervous tissue and often occurs in acute ischemic or hemorrhagic cerebrovascular accidents. In children, brain hypoxia can develop in the antenotal period and during childbirth, which leads to anoxic brain damage in the child.
- When the concentration of potassium, calcium, sodium and chlorine ions increases or, conversely, excessively decreases, transmembrane proteins may malfunction, which also entails energy deficiency inside the cell.
It is worth noting that energy deficiency leads to rapidly progressive damage to brain tissue and within 5-7 minutes, in the absence of sufficient oxygenation, neurons begin to experience acute hypoxia and die. Damage to the blood vessels of the brain has the following symptoms:
- The patient notes memory impairment;
- There is a decrease in vision and hearing;
- The synthetic activity of the brain slows down;
- When performing angiography of cerebral vessels, multiple stenoses of cerebral vessels can be detected;
- MRI of the brain shows dystrophic disorders and a decrease in the volume of the cerebral cortex.
All of the above symptoms are signs of systemic atherosclerosis, which affects most older people. Atherosclerosis leads to the formation of discirculatory encephalopathy.
Traumatic injuries
Injuries are always associated with mechanical damage to the brain and the subsequent development of edema, which leads to an increase in intracranial pressure. Since the brain is located in the cranium and literally floats in the cerebrospinal fluid - intracerebral fluid, the consequences of blows and bruises become serious. Despite. The cerebrospinal fluid plays a protective and shock-absorbing role; with the development of a brain contusion, an increase in intracranial pressure occurs, since the fluid is not physically compressible. Brain cells are exposed to excessive pressure and begin to die. Brain tissues occupy up to 96% of the volume of the cranial cavity, which makes this organ very sensitive to changes in intracranial pressure.
It is very important to note that quite often injuries are accompanied by internal hemorrhage, which can lead to the formation of an extensive hematoma and displacement of the brain. Dislocation of the brain leads to wedging of its subcortical structures into the foramen magnum, which inevitably leads to the death of neurons located in the nuclei of the vasomotor and respiratory centers, without which the life of the victim is impossible.
Infectious
Brain damage can be caused not only by physical factors. But also biological. Conditions such as meningitis, encephalitis, and ventriculitis can significantly impair the functional activity of the brain.
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining of the brain. Etiological factors can be very diverse, so the brain can be affected by many bacterial and viral diseases. Inflammation of the membranes of the brain can occur primarily through direct infection through the wound gate. And secondarily – as a result of an immunodeficiency state.
- Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain tissue itself. Encephalitis is an even more severe infectious disease than meningitis. As a result of encephalitis, purulent melting and liquefaction of areas of the brain can occur, which leads to the formation of persistent disturbances in the functioning of various organs of the victim. With encephalitis, brain damage very often leads to disability or even death.
- Ventriculitis is an inflammation of the integumentary tissues lining the ventricles of the brain. This disease occurs in newborns and infants and leads to increased intracranial pressure and the development of hydrocephalus due to insufficient drainage function of the cerebrospinal fluid.
The brain can be affected by both specific and nonspecific infectious agents; this is important to consider when prescribing treatment, since antibacterial therapy regimens will vary.
Congenital pathology
Anomalies of brain development can form in the very early stages of a child’s development. The first trimester of pregnancy is the most dangerous for the woman and the fetus, since the pregnant woman’s body and the fetus are unprotected from external factors, and at the time of the initiation and formation of organs, the most dangerous anomalies and gross developmental pathologies can form, for example micro or acephaly.
Toxic damage
Not the most common type of brain damage, but nevertheless it does occur. Brain damage occurs if the chemical has neurotoxic properties and is able to cross the blood-brain barrier. Neurotoxic agents lead to organic damage in various parts of the nerve cell; most often, neurons suffer from disruption of the transmembrane transfer of nutrients and disturbances in the synthesis of neurotransmitters. Toxic injuries of varying severity can lead to both persistent encephalopathy and complete loss of some functions of the person affected by intoxication. Most often, gross organic damage to the brain is caused by substances such as arsenic and nitrogen metabolism products, with excessive accumulation of the latter in the blood plasma.
Oncological diseases
Brain damage in oncology can be primary. When a tumor develops directly from brain tissue or secondary - when atypical tumor cells are metastatically introduced into the brain.
Reasons for the development of residual mental retardation
ZPR of residual organic origin are disorders that can be caused by:
- injury or disease affecting brain tissue;
- chemical or hormonal disorders;
- exposure to toxic materials;
- neurological disorders or abnormal changes associated with aging;
- diseases of the liver, kidneys or thyroid gland;
- vitamin deficiency.
Concussions, blood clots, or bleeding in or around the brain from injury can lead to organic brain syndrome. Low oxygen levels in the blood, high amounts of carbon dioxide in the body, strokes, brain infections and heart infections can also lead to organic mental disorder.
Degenerative disorders such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease and multiple sclerosis may also be contributing factors.
Types of brain lesions
Brain damage can be either focal or disseminated. Let's figure out what focal brain damage is. This is a condition in which there is a clearly demarcated single focus with necrotic tissue, i.e. This is a local brain lesion. This type of damage often occurs during acute cerebrovascular accident.
Disseminated or multifocal brain damage is a type of injury in which multiple scattered foci of damage to brain tissue are detected. The multifocal form occurs in infectious diseases of the brain, for example, when an infectious agent is introduced hematogenously into the medulla or with an oncological lesion.
Outcomes and consequences of CNS PP
The consequences of PP CNS can be determined by 1 year of life. Below are their main manifestations:
- Impaired motor development: delay in acquiring the skills of holding the head, rolling over, sitting, crawling, standing up, and walking independently relative to the physical age of the child.
- The formation of paresis and paralysis of both one and several limbs (monoplegia, diplegia, hemiparesis, tetraparesis), which belong to various forms of cerebral palsy.
- Violation of psycho-speech development: delay in acquiring the skill of humming, babbling, the first words and phrases, the quality of pronounced sounds, the timing of the formation of pincer grip and pointing gestures, understanding of addressed speech, interest in surrounding objects and using them for their intended purpose, the nature of the game, memorizing new information , concentration of attention with the formation of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
- Disorders of behavior and emotions: timing of the formation of the revitalization complex, differentiation of relatives and strangers, emotional resonance, degree of expression of emotions, communication with peers and adults, the possibility of playing together, the formation of neatness skills, possibly leading to autism spectrum disorders.
- Hydrocephalus: excessive increase in head circumference, head deformation, pronounced saphenous veins in the temporal areas, signs of hypertension and hydrocephalic syndromes.
- Paroxysmal conditions of non-epileptic origin: affective-respiratory seizures, benign myoclonus of infancy (Fijerman's syndrome), benign neonatal sleep myoclonus, Sandiffer's syndrome, infantile torticollis, restless sleep, night terrors, rhythmic movements in sleep (rocking, head shaking, thumb sucking, grinding teeth).
- Age-dependent epileptic syndromes: early infantile epileptic encephalopathy (Ohtahara syndrome), early myoclonic encephalopathy, Dravet syndrome, West syndrome, benign neonatal epileptic syndromes, benign myoclonic epilepsy of infancy, benign partial epilepsy of infancy.
Treatment tactics
Treatment of organic brain damage can be very diverse and depends on the pathogenetic mechanism of development of the damage and the immediate cause.
Treatment of organic brain damage can be surgical and conservative. For example, the development of high intracranial pressure, which poses a threat to life, can be treated both surgically and conservatively. Surgical treatment - the application of a burr hole for brain decompression is applicable in the formation of a severe hematoma due to trauma or hemorrhagic stroke, and conservative therapy is possible with a moderate increase in intracranial pressure without brain dislocation. For conservative therapy, diuretics are used that cause forced diuresis, allowing for the rapid elimination of edema.
Treatment of cerebral artery atherosclerosis can also be either surgical or conservative. Surgical – angiography with the installation of stents to widen the lumen of the arteries. Conservative – antithrombotic therapy and correction of dyslepidemia.
Residual ZPR: reviews
| Positive | Negative |
| I was very sick during pregnancy, which caused my daughter to suffer greatly. From birth we were noticeably lagging behind in development. When all the children our age were actively trying to roll over on their stomachs or sit up, we just lay there and did not show the slightest interest even in rattles. Even then we became alarmed and began to look for “our” doctor. Today we are 3, and we just learned to hold a spoon in our hands on our own; we started at 2.5 years old, and we learned to get up from the floor ourselves at 2.7. We have a real struggle for every skill, but we believe that complex therapy will show more effective results. Mommies, endurance and perseverance to you. (Alla) | I also understand different types of therapy, but stuffing me with medications is an absolute no-no! (Rita) |
| Our mental retardation began to manifest itself after our son, at the age of one, fell and hit his head hard, causing a concussion. After that, we lost speech instantly and completely forgot our self-care skills. We all went through it all over again. Today we are 4 and everything is fine with us. By the way, hippotherapy and drug treatment work wonders. (Sonya) | Often children with residual mental retardation are fed nootropics or sedatives, which simply inhibit development and completely kill the ability to concentrate. Just spend more time with your child and don’t stuff him with medications. (Anna) |
| The reason for everything is a genetic predisposition, and yes, we are constantly on medications that change course after course, while we take the medications - we see the result, take a break and there is a stop in development. And every disease rolls back all our achievements significantly. We are waiting for more powerful medications to be released to nourish and stimulate brain function. (Galina) | We had a hematoma in the head after birth, which resolved on its own, but the doctors tried to prescribe something, especially sedatives, but I persistently refused. And now we have noticeable signs of mental retardation, but we are successfully fighting them through ABA therapy. We are used to feeding children pills for any deviation from the norm. (Alice) |
| It is important not to let everything take its course and everything will definitely work out. By the way, in the absence of corrective work, the child’s condition with residual mental retardation will only worsen and be complicated by more serious diseases. (Nina) | Well, they gave us a diagnosis, well, they outlined what kind of therapy we need to attend, and what the price for these classes is - simply unaffordable for the average family. That is why you have to study hard at home, which is not so effective. (Irina) |
| Our son was completely silent until he was 2 years old, we were diagnosed with residual mental retardation, we selected a course of treatment and therapy, there was no change for six months, and then it broke through and began to fill his vocabulary like a sponge. Treatment is very important. (Galina) | In our city, people with a diagnosis of mental retardation are not admitted to kindergartens, regardless of the background of the disease, or to schools. The question arises, how can we socialize and develop our children? As always, no one needs children with special needs. (Yana) |
Conclusion
Although there is no cure for organic mental disorders, many of these conditions can be treated through psychotherapy and prescription medications.
Unfortunately, not all patients will respond to treatment in the same way. In most cases, it will take weeks or even months before treatment starts to work. In some cases, medications may have little effect on symptoms caused by an organic mental disorder.