What is extrasystole?
Listen, can you feel the rhythm of your heart?
Normally, you should not hear or feel its beating. If this does happen, then this is a reason to think about it and go to the doctor. Moreover, if you feel a slight blow to the chest, and then a pause, and this brings discomfort, then you are faced with an extrasystole. In scientific terms, extrasystole is a process during which a sudden additional contraction of the heart occurs due to an electrical impulse in one of its sections. Extrasystole is the most common type of arrhythmia.
According to statistics, extrasystole is recorded in 70% of healthy people. In more than 65% of cases, ventricular extrasystoles develop, 25% occur in the atrial ones and the rest - in
combined variants of extrasystole.
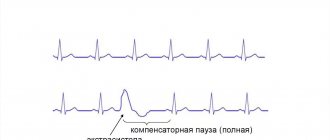
In its normal state, the heart contracts rhythmically, impulses are generated regularly, the sinus node and the electrical signal move according to the direction, down to the ventricles. But when the work of the heart is disrupted, a premature electrical jump occurs - an extrasystole. After it there is a pause, and then the heart begins to beat rhythmically again.
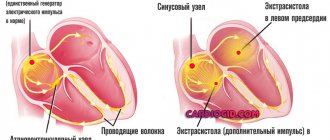
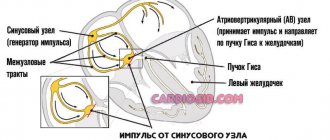
How does the heart's electrical system work? The sinus node is the main conductor of rhythm; its electrical signal is distributed throughout the atria, lingers slightly in the articular node and spreads throughout the ventricle.
During extrasystole, the sinus node temporarily stops functioning, because of this, the heart seems to turn off for a moment, literally freezing. Then an electrical surge appears in the ventricle and a contraction occurs, the heart begins to beat again, and the rhythm is restored.
What is premature contraction? This is a heart condition in which the heart beats earlier than it should. When the heart functions normally, the organ fills with blood. And when an extrasystole occurs, its work is suspended for a split second.
Atrial flutter
There are typical (classical) and atypical variants of atrial flutter. In the classic version of atrial flutter, the circulation of the excitation wave occurs in the right atrium in a typical circle; in this case, a flutter frequency of 240-340 per minute develops. Typical atrial flutter is isthmus-dependent, i.e., it can be stopped and restored to sinus rhythm using cryoablation, radiofrequency ablation, transesophageal pacing in the area of the cavo-tricuspid isthmus (isthmus) as the most vulnerable link of the macro-re-entry loop.
Depending on the direction of circulation of the excitation wave, two types of classic atrial flutter are distinguished: counterclockwise - the excitation wave circulates around the tricuspid valve counterclockwise (90% of cases) and clockwise - the excitation wave circulates in the macro-re-entry loop clockwise (10% of cases ).
Atypical (isthmus-independent) atrial flutter is characterized by the circulation of an excitation wave in the left or right atrium, but not in a typical circle, which is accompanied by the appearance of waves with a flutter frequency of 340–440 per minute. Taking into account the place of formation of the macro-re-entry circle, right atrial (multicycle and upper loop) and left atrial isthmus-independent atrial flutter are distinguished. Atypical atrial flutter cannot be treated with TEE due to the absence of a slow conduction zone.
From the point of view of the clinical course, a distinction is made between newly developed atrial flutter, paroxysmal, persistent and permanent forms. The paroxysmal form lasts less than 7 days and resolves on its own. The persistent form of atrial flutter lasts more than 7 days, and independent restoration of sinus rhythm is impossible. A permanent form of atrial flutter is said to occur if drug or electrical therapy does not bring the desired effect or is not carried out.
The pathogenetic significance of atrial flutter is determined by heart rate, on which the severity of clinical symptoms depends. Tachysystole leads to diastolic and then systolic contractile dysfunction of the left ventricular myocardium and the development of chronic heart failure. With atrial flutter, there is a decrease in coronary blood flow, which can reach 60%.
Symptoms
Like most diseases of the cardiovascular system, extrasystole does not have obvious signs and symptoms. Patients simply do not realize that they are experiencing heart rhythm disturbances. And if they do notice, then unscheduled contractions of the heart do not bother them.
Extrasystole feels comparable to a strong push to the chest and a sharp attenuation afterwards. For a second, the patient may feel as if his heart is turning over. Then everything abruptly returns to its place. Some people have such sensations, while others do not. It all depends on the height of the pain threshold, the tolerance of this kind of symptoms, the number and frequency of extrasystoles. As well as the presence of a patient with a cardiovascular disease. For many people, the presence of extrasystole does not bother them at all and they can live with it.
During frequent or prolonged attacks, oxygen starvation occurs, and feelings of panic and anxiety may occur. Such sensations are explained by the production of the hormone adrenaline, which provokes an even greater disruption of the heart rhythm.
Let's consider the common symptoms of extrasystole in patients with heart pathologies:
- Patients with cerebral atherosclerosis experience dizziness and sometimes fainting;
- Angina attacks occur in patients with coronary heart disease.
Other symptoms of extrasystole may be: fever, weakness, sweating, lack of air and pain in the heart area.
To summarize, we can say that during extrasystole, blood does not enter the brain. Because of this, the patient may feel:
- dizziness;
- fainting (if there are many extrasystoles, the person may lose consciousness);
- heat;
- sweating;
- oxygen starvation;
- weakness;
- heartache;
- anxiety.
What is cardiac arrhythmia?
Arrhythmia is the name of a group of all pathologies that are characterized by disturbances in heart rhythm. Arrhythmias themselves can differ radically from each other in terms of their occurrence, complications, effects on the body, and manifestations. Let's figure out what arrhythmia is, what causes it, what symptoms it manifests, what types of arrhythmia there are, and how to treat the “motor” of your body.
Causes
Extrasystole of the heart can be caused by a number of reasons, which can be divided into two sources.
The first and most basic is diseases of the cardiovascular system. Extrasystole can occur against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the heart, which are accompanied by organic damage to the myocardium. The second block is external:
- pathology of the thyroid gland;
- electrolyte disturbances;
- external influences. For example, being in a stuffy room where there is a lack of oxygen;
- excessive caffeine consumption. This factor causes tachycardia.
Causes of cardiac arrhythmia in women and men
It is worth noting that the causes of arrhythmia are not divided by gender and are practically the same in women and men. The only thing is that women may experience pathology due to premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and menopause. Undoubtedly, there are many reasons for the occurrence of arrhythmia. Let's list the main ones.
Symptoms of a panic attack
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating);
- muscle tremors, chills;
- tachycardia;
- dystonic or physiological tremor;
- hot flashes (instant sensations of heat);
- asphyxia (suffocation);
- dyspnea (difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air);
- irradiation of pain to the left side of the chest;
- nausea, urge to vomit;
- abdominal pain syndrome (stomach pain);
- sensation of a foreign body, coma in the throat;
- paresthesia (tingling in the limbs, feeling of numbness);
- lightheadedness, dizziness;
- stool disorders (constipation, diarrhea);
- dysbasia (gait disturbance);
- high blood pressure;
- impairment of vision and/or hearing;
- frequent urination.
- derealization (feeling of unreality, alienation, indistinctness of the surrounding reality);
- fear of schizophrenia, obsessive fear of going crazy, losing control over one’s actions;
- disorientation, confusion;
- depersonalization (the patient perceives his actions as if from the outside and feels that he cannot control them);
- interrupted sleep, insomnia (insomnia), nightmares;
- Thanatophobia (fear of death).
- more frequent repetition of attacks with the appearance of new symptoms;
- isolated attacks;
- the addition of depressive symptoms (sleep disturbances, loss of appetite, persistently depressed mood);
- constant fear for your health;
- refusal to perform habitual life rituals (patients stop traveling in public transport, going outside, and their performance sharply decreases).
What does a person experience during a panic attack?
- feeling of fear of varying strength;
- feeling of impending danger;
- fear of death;
- stiffness reaching the point of stupor (in some people);
- motor activity (in others);
- fear of committing an uncontrollable act;
- fear of going crazy;
- confusion of thoughts;
- unreality of what is happening;
- loss of orientation in personality, space and time.
Physical symptoms of a panic attack
The main reason for their appearance is the release of biologically active substances (norepinephrine and adrenaline) into the blood in large quantities. Mediators have a stimulating effect on the nervous, respiratory systems, heart and blood vessels.
- Rapid breathing and heart rate.
- Shortness of breath, lack of air.
- Chills.
- Dry mouth.
- Increased sweating.
- Weakness, body numbness, dizziness.
- Diarrhea.
- Involuntary urination.
- Vomit.
The most pronounced physical symptoms are in anxiety, which develops due to pathology of organs and systems.
Reasons for appearance
The pain may occur intermittently. Sometimes it is a regular spasm, and in some cases it is attacks of pain. Also, unpleasant feelings can begin during inhalation and exhalation, sudden body movements, such as coughing or sneezing. Doctors distinguish between primary and secondary causes of intercostal neuralgia.
Primary:
- problems with the spine. This may be loss of elasticity of the intervertebral discs, infection or inflammation in the roots and joints of the vertebra;
- incorrect posture. Also one of the primary reasons, it occurs in most people who lead an inactive lifestyle, constantly sit in one position, and slouch;
- rib fractures. This includes deformation of the thoracic region, its pathology or tumor.
Secondary causes include:
- hypothermia of the human body;
- long periods of sitting in drafts;
- infectious diseases associated with the lungs: pneumonia, tracheobronchitis;
- heart disease: myocardial infarction, ischemia, dissecting aortic aneurysm;
- problems with the mammary glands in women, such as swelling or inflammation;
- improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. For example, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis.
But the main and most common cause of intercostal neurosis is stress. People who are constantly stressed experience stiffness in their movements and muscle spasms. That is why any sudden movement causes pain and can provoke intercostal neuralgia.
Sinus arrhythmia. Diagnosis and treatment
Characterized by uneven pauses between heartbeats. That is, there is a feeling that at first the heart is about to jump out, and then it seems to freeze for a while. Sinus arrhythmia is present in people after suffering stress, eating food, physical activity, etc.
Symptoms of sinus arrhythmia
This type is characterized by the possible presence of all the symptoms of arrhythmia. When the heart rate accelerates, there is a feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath, and chest pain. When the heart rate slows down, weakness, dizziness and headaches appear. Severe sinus arrhythmia may manifest as loss of consciousness. In this case, you must urgently call an ambulance.
Symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia
Many people believe that it is impossible not to pay attention to heart rhythm disturbances. But most often, cardiac arrhythmia is asymptomatic. All signs are attributed to stress, overload or fatigue. But nevertheless, it is very important to diagnose heart pathology in a timely manner. Contact a specialist immediately if you notice at least one of the symptoms of arrhythmia:
- cardiopalmus;
- chest pain, a feeling that someone is pressing on the chest;
- daily dizziness and headaches;
- sensations of interruptions in the rhythm of the heart or simply the feeling of your own heartbeat;
- shortness of breath even during everyday simple activities;
- loss of consciousness or lightheadedness.
Please note that these symptoms are common to many other diseases. Often this is the reason why people do not contact a specialist on time. For example, fainting is attributed to overwork or hunger, and headaches are attributed to frequent stress. Therefore, we would like to draw your attention once again to the fact that if any of the symptoms are present, consult a doctor immediately! To which? We'll tell you a little later.
Atrial fibrillation. Diagnosis and treatment
This arrhythmia is one of the most common types. Atrial fibrillation is manifested by a feeling of uneven heart contractions: the ventricles contract unevenly, and the atria seem to flutter. Up to 60 years of age, this type of arrhythmia occurs only in 1% of cases, but after 75 years of age it is detected in 30% of patients.
Symptoms of atrial fibrillation
First of all, it is characterized by a rapid heart rate (130-150 beats per minute), in some cases even a heart rate of up to 180 beats per minute occurs.
Cardiac health and arrhythmia treatment
To prevent heart disease, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Remember that as soon as you notice the presence of symptoms of any type of arrhythmia, contact your physician or cardiologist. If you feel a sharp deterioration in your health, call an ambulance.
Tachycardia. Diagnosis and treatment
With this type of arrhythmia, the number of heartbeats per minute exceeds 90 beats. Tachycardia is of two types: pathological or physiological.
Pathological tachycardia
Characterized by disorders of the cardiovascular and other systems. This type of tachycardia can cause myocardial infarction, acute heart failure and sudden cardiac arrest.
Physiological tachycardia
It differs from pathological in that it is caused by exposure outside the body. Often physiological tachycardia is a normal reaction of the body to any changes. For example, during physical exertion, during excitement or anger and similar situations, physiological tachycardia is the norm.