Indications for use
It is necessary to have a child have an REG of the head if he/she has:
- regular headaches of unknown origin;
- hearing or vision impairment;
- hypertension or hypotension;
- tinnitus;
- fainting conditions;
- swelling of the face;
- coordination problems.
The procedure is also prescribed to control blood circulation after operations, neck and head injuries. In some cases, the examination is part of an analysis of the effectiveness of drug therapy and non-drug treatment.
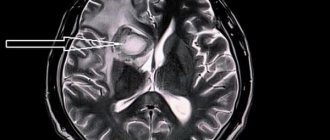
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Electroencephalography (EEG) is an accessible and safe method of studying the brain by recording brain biocurrents.
Neurons - the main elements of the central nervous system (and the brain, including) - are capable of generating and conducting electrical impulses that are recorded by an electroencephalograph. This method is of great importance for the early detection of injuries, tumors, vascular and inflammatory diseases of the brain, and epilepsy. In addition, this is the only neurological outpatient study that is performed during attacks of loss of consciousness.
In our clinic, electroencephalography is performed by highly qualified neurologists-neurophysiologists with extensive practical experience in working with patients of various age groups.
1 Electroencephalography (EEG)
2 Electroencephalography (EEG)
3 Electroencephalography (EEG)
EEG is absolutely harmless, has no contraindications, and therefore is used for patients of any age, both children and the elderly.
Electroencephalography is a highly informative study that reflects the functional state of the cortex, subcortical structures of the brain, as well as complex cortical-subcortical interactions, including the hidden pathology of diseases that have not yet manifested against the background of the complete clinical health of the subject.
EEG allows you to monitor the course of the disease over time, adjust treatment if necessary, and evaluate the effect of drug therapy (overdose or withdrawal of antipsychotics, tranquilizers, barbiturates, antidepressants) on brain activity. Unlike CT and MRI studies, EEG reveals structural and functional (reversible) changes that persist for a long time in the brain, for example, after a mild traumatic brain injury.
The role of EEG in the diagnosis of epilepsy
EEG is the most important diagnostic method for epilepsy. Every year, from 20 to 120,000 new cases of epilepsy are registered per year (on average - 70 - 100,000). In the CIS countries alone, about 2.5 million people suffer from this disease. Epilepsy is often combined with other diseases, such as cerebral palsy, chromosomal syndromes, and hereditary metabolic diseases. The incidence of epilepsy, for example, in patients with cerebral palsy is up to 33%.
An experienced neurologist/neurophysiologist can confirm the diagnosis of epilepsy based on the results of an EEG. In addition, diseases that occur without clinical manifestations have recently become widespread, but are characterized by pathological activity in the brain that significantly impairs its functioning (for example, epileptic encephalopathies). In such cases, EEG is the leading research method.
Electroencephalography technique
EEG is completely harmless and painless. During the examination, the patient sits comfortably in a chair. Using a special helmet, small electrodes are attached to his head, connected by wires to an electroencephalograph. The device amplifies the biopotentials received from the sensors hundreds of thousands of times and records them in the computer memory.
1 Electroencephalography (EEG) in MedicCity
2 Electroencephalography (EEG) in MedicCity
3 Electroencephalography (EEG) in MedicCity
No special preparation is required to conduct an EEG, but there are several recommendations. It is important that the patient is not hungry during the examination, as this may cause changes in the EEG. And you should wash your hair the day before the test - this will allow for better contact of the electrodes with the scalp and, accordingly, the results will be more reliable. You should not give up your usual medication intake, as this can provoke seizures and even epistatus. The interpretation of EEG results may depend on the patient’s age, medications he is taking, the presence of tremor of the head and limbs, visual impairment, skull defects, etc.
1 Electroencephalography (EEG) in MedicCity
2 Electroencephalography (EEG) in MedicCity
3 Electroencephalography (EEG) in MedicCity
Diagnostic capabilities of EEG
With EEG you can:
- distinguish epileptic seizures from non-epileptic ones and classify them;
- identify areas of the brain responsible for triggering seizures;
- track the dynamics of the action of drugs;
- assess the functional state of the brain (even in the absence of changes on a CT scan of the brain);
- resolve the issue of professional suitability (the detection of epileptiform phenomena serves as the basis for the selection of professions related to driving, requiring constant attention and quick response to sudden situations and stimuli in conditions of increased risk).
Indications for EEG:
- epilepsy and other types of paroxysms;
- brain tumors;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- vascular diseases;
- inflammatory diseases;
- degenerative brain lesions;
- headache;
- dysontogenetic diseases;
- hereditary diseases of the central nervous system;
- functional disorders of nervous activity (neuroses, neurasthenia, obsessive movement neurosis, somnambulism, etc.)
- psychiatric pathology;
- encephalopathy of various origins (vascular, post-traumatic, toxic);
- post-resuscitation conditions due to somatic pathology.
Our clinic uses the latest biofeedback-EEG training technique, which includes taking an electroencephalogram, which records the main rhythms of the brain (alpha, beta, delta, tetarhythms). An EEG (electroencephalogram) assessment is carried out by an experienced neurologist-neurophysiologist, and a conclusion is given about the characteristics of brain rhythms and the distribution of biopotentials in various areas of the cerebral cortex. Depending on the indications, the necessary course of biofeedback-EEG training is selected (relaxing, activating, etc.).
Preparation for the event
Before the examination, the patient must eat 1.5 hours before the appointment. Light, familiar food is recommended. Breastfed children are examined immediately after feeding. On the day of the test, you do not need to give your child drinks with caffeine and taurine: coffee, tea, cola, kvass.
You need to tell your child that a completely painless procedure awaits him. He must understand that during the doctor’s manipulations he needs to relax and not worry. The more calmly he behaves during the analysis, the more accurate data the diagnosticians will be able to obtain.
What is the technique?
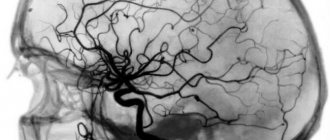
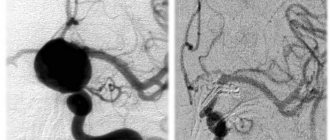
REG of the brain is one of the methods for diagnosing the condition of blood vessels, which can be used to assess the functioning of the veins and arteries of the head and cervical region.
This study is carried out by recording changes in the electrical resistance of tissues after a weak electric current is passed through them. Since blood is an electrolyte (a substance that conducts electric current), when the vessels are filled with blood, the electrical resistance in them decreases, and this is detected using REG. Taking into account the speed and time of change in resistance, the doctor draws conclusions regarding the patient’s health.
Rheoencephalography is a painless method for studying the condition of cerebral vessels
Using this method, you can evaluate the pulsation of blood flow in the head arteries, determine the degree of venous outflow from the skull, and study the tone and elasticity of the walls of blood vessels. REG is a non-invasive study.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), unlike rheoencephalography, is more informative and can indicate the exact location of a damaged vessel, blood clot or any other abnormality in the vascular system.
How the research is carried out
Before the examination begins, the child lies on his back or sits on a chair in a comfortable position. If the child is worried, parents are allowed to be present.
After this, the specialist attaches electrodes to the areas of the head being examined. For diagnostics, a rheographic attachment and a recording device are used. The equipment records the indicators on a special tape. During the examination, the specialist may ask the child to follow simple commands: turn or tilt his head. A functional test allows you to obtain the most complete information. The procedure lasts no more than 10-20 minutes. A transcript of the results is provided 30 minutes after completion of the manipulations.
Decoding the results
To correctly assess the data obtained, the doctor takes into account the patient’s age, since the indicators will be very different for young and elderly people.
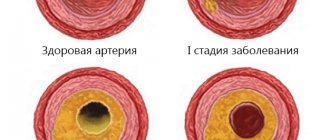
- Treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis
The resulting rheoencephalogram is studied, which has a wave-like appearance and consists of an anacrota (growing part), catacrota (falling part), incisura (bend between them) and a dicrotic tooth that appears immediately behind it.
Based on the waves of the resulting graph, the doctor evaluates the work of blood vessels
The doctor evaluates the regularity of the waves, the nature of the construction of their peaks, the appearance of anacrota and catacrota, the location of the incisura and the depth of the dicrotic tooth. The presence of additional waves is also being studied.
After evaluating the data obtained, we can talk about the following results based on the appearance of the rheogram:
- dystonic type of REG indicates possible hypotonic deviations, decreased pulse filling and problems with blood outflow through the veins;
- angiodystonic type indicates a decrease in the tone of the vascular walls and a decrease in blood flow speed;
- The hypertensive type indicates increased pressure and tone of the vessels through which blood flows to the head and their obstructed outflow.
The amplitude indicator of the rheogram (APR) indicates volumetric pulse filling:
- APR less than normal by no more than 40% indicates a moderate decrease in pulse blood supply;
- at 40–60% - a significant decrease;
- at 60–90% - pronounced;
- at 90–100% - critical.
The coefficient of asymmetry (CA), which indicates differences in blood supply to different parts of the brain, is very important for studying. Depending on the severity of CA, several degrees of asymmetry are distinguished:
- less than 7% - no pronounced asymmetry;
- 8–14% - weak asymmetry;
- 15–25% - moderate asymmetry;
- more than 26% - severe asymmetry.
What deviations do the external characteristics of waves show - table
| Possible diagnosis | Type of rheoencephalography |
| Cerebral atherosclerosis | |
| The waves take on a strongly pronounced dome shape. | |
| Arterial hypotonicity | Increased amplitude, sharp rise with a sharp apex, shortened anacrosis. |
| Arterial hypertonicity | Reduced amplitude, extended anacrotic with additional waves, displaced apex. |
| Vascular dystonia | Floating prongs, extra waves on catacrota. |
| Obstruction of blood outflow | Catacrota increased, many small waves before the next cycle. |
| Spasm of vascular walls | Rounding the top of the wave. |
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a neurologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS) of cerebral vessels | 3600 rub. |