Human health is largely determined by the state of the vascular system. Modern diagnostic technologies are informative, painless and have no contraindications. They provide an opportunity to obtain vital information about the functioning of the circulatory system.
Each technique identifies certain parameters:
- traditional ultrasound shows the vessels in a two-dimensional image;
- Doppler ultrasound of veins and arteries allows you to assess the speed of blood movement;
- duplex scanning combines the two methods mentioned above;
- triplex diagnostics provides an image of the vascular bed and moving blood in color.
All these studies, carried out together, make it possible to obtain the most complete picture of the condition of the vessels and the presence of pathological processes in them.
Ultrasound examinations performed
- Duplex/triplex angioscanning of the arteries of the lower extremities
- Duplex/triplex angioscanning of the veins of the lower extremities
- Duplex/triplex angioscanning of extracranial brachiocephalic arteries
- Duplex/triplex angioscanning of intracranial brachiocephalic arteries
- Duplex/triplex angioscanning of arteries and veins of the upper extremities
An ultrasound of the neck and head will show changes in the vertebral and carotid arteries. The scan will accurately determine the condition of the vessels from the inside and outside. They are involved in the functioning of the brain, so it is important to objectively assess the ability of the cervical vessels to supply blood and the ability to bypass blood flow in conditions of obstruction. Also, such a procedure makes it possible to identify the consequences of birth injuries and developmental pathologies in a newborn.
Ultrasound of the vessels of the uterus and ovaries with Doppler measurements will allow you to assess its size, shape and identify anomalies. The basis for the study is the inflammatory process.
Ultrasound of the lymphatic vessels reveals various pathologies of the system and the development of tumors.
Diagnosis of diseases of internal organs is impossible without ultrasound examination. The data obtained, together with the results of laboratory tests, are the basis for making a correct diagnosis.
An examination of the thyroid gland will show the presence of nodes, size and structure, and will allow an objective conclusion to be made about the nature of the formations.
No preparation is required for examination of the spleen and liver; the gallbladder is examined on an empty stomach.
Ultrasound of the renal vessels and bladder will reveal changes in structure and size and will become the basis for diagnosing diseases and identifying malformations. The procedure is performed with a full bladder to improve visualization. The kidney examination does not require preliminary preparation, but may take more time.
Check your blood vessels
Atherosclerosis is a disease that develops gradually. How to know in time that the process of atherosclerosis development has started?
High cholesterol levels are not the only factor in the development of atherosclerosis. Laboratory tests can help monitor this and other indicators of cardiovascular disease risk.
everything about cholesterol. Lipid profile, extended.
Total cholesterol will show whether there is an excess of this substance in the blood. The level of total cholesterol in patients who have had a heart attack is a sign of the need to prescribe cholesterol-lowering drugs.
Low- and very-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL and VLDL) is what is colloquially referred to as “bad cholesterol.” Their excess indicates lipid metabolism disorders. If the increase is not very large, then to correct the situation it is enough to reduce weight, move more, and remove excess fats and carbohydrates from the diet. Significant excesses of the norm require the prescription of appropriate medications.
Triglycerides are another type of fat present in the blood. Normally, triglycerides are the source of energy for cells and are present in the blood only “on the way” from the intestines to the cells. Triglyceride levels fluctuate throughout the day: after the first meal, their concentration in the blood increases rapidly and remains at this level for 9-12 hours. Therefore, a blood test for triglycerides (including the lipid profile) should be taken no earlier than 12 hours after eating.
The extended lipid profile also includes the following parameters:
Apolipoprotein A1 is a representative of “good cholesterol” (high-density lipoprotein, HDL). It prevents cholesterol from being deposited in plaques, protecting, among other things, the blood vessels of the heart and brain. This test shows how well the vascular protection system works.
Apolipoprotein B is the main protein of LDL. One of the accurate markers of atherosclerosis. With its help, it is possible to identify the initial stage of this disease even with normal LDL levels.
Lipoprotein (a) shows how high the hereditary risk of atherosclerosis of the heart and brain vessels is.
A set of tests is recommended for all people over 50 years of age, as well as for those who are at risk of developing atherosclerosis due to heredity, lifestyle, and poor nutrition.
Independent and dangerous
The homocysteine test helps assess the risk of thrombosis. Homocysteine is an amino acid that is produced in the body from the essential amino acid methionine. It is necessary for the normal functioning of the entire metabolism and is a donor of the methyl group. However, if the body does not have enough vitamins B6, B9 (folate) and B12 or there is a genetic defect, the level of homocysteine in the blood increases. Then it can damage the walls of blood vessels.
The test can be done as an additional test to the lipid profile. It is important to remember that smokers and heavy coffee drinkers should have their homocysteine levels determined annually, along with a cholesterol test or lipid profile.
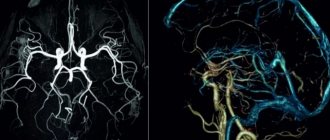
What is duplex scanning (USDS)?
Ultrasound of veins
Duplex scanning
is an ultrasound examination method that allows you to obtain an image of blood vessels (black and white) and a display of blood flow (which is coded in different shades of color depending on the speed of blood flow).
The ultrasound method uses the effect of echolocation. Tissues in the body reflect ultrasound differently, so ultrasound makes it possible to visualize objects inside the human body that have different densities. Ultrasound is a non-invasive method; it does not require disruption of the integrity of the skin. The examination is completely painless and safe.
Ultrasound also uses the Doppler effect, which consists in the fact that an ultrasonic wave, reflected from a moving particle, changes its frequency. This makes it possible to calculate the speed of blood flow.
What diseases does it detect?
Doppler ultrasound is a highly informative method used to diagnose various vascular pathologies:
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- phlebeurysm;
- vascular malformations;
- deep vein thrombosis;
- hypoplasia of the vertebral arteries;
- atherosclerosis;
- temporal arteritis;
- postthrombotic syndrome;
- vasculitis;
- aneurysms and other vascular pathologies.
The examination allows you to identify the presence of formations that impede or change blood flow (sclerotic plaques, blood clots), check the homogeneity and rhythm of blood flow, assess the compensatory capabilities of blood flow, identify defects in the structure and flow of blood vessels - narrowing, kinks, tortuosity, aneurysms, compression by scars, vertebrae or spasmodic muscles.
How to prepare for the procedure?
- To perform an ultrasound, you need to wear comfortable, loose clothing. You may need to remove all clothing or jewelry from the area being examined.
- You may be asked to wear a gown during the procedure.
- If you are indicated for an examination of the veins or arteries of the abdominal cavity, you must do this on an empty stomach. In this case, you should not consume food or liquids other than water 6-8 hours before the procedure.
Otherwise, you will not need any special preparation for a vein ultrasound.
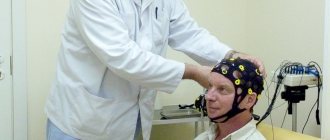
How is Doppler sonography done?
The Doppler ultrasound procedure is done as follows:
- The patient should lie down on the couch and take a comfortable position. The position can be changed at the request of the doctor, it depends on the area being studied.
- The desired area of the body must be left without clothing.
- The doctor applies a special gel to the ultrasound sensor. In paid clinics, the client is offered napkins to wipe it off; in free clinics, most often you are required to bring your own.
- The device is applied to the patient’s skin, and the necessary organs are viewed.
- The ultrasound specialist may require the patient to change the breathing rate and tension of certain muscles. This is necessary for analyzing the blood flow of peripheral vessels and large arteries.
- The readings received through the sensor are recorded by a specialist and deciphered for the patient.
Decoding the results
Indicators for deciphering ultrasonography:
- systole size;
- diastolic blood flow velocity;
- the ratio of the above indicators;
- resistivity index.
Standards for Doppler ultrasound results for pregnant women:
| Pregnancy time (weeks) | Systole-diastolic ratio | Resistance index |
| 12-13 | 2-3,5 | 0,52-0,71 |
| 14-16 | 1,9-3,1 | 0,48-0,68 |
| 17-19 | 1,7-2,6 | 0,44-0,62 |
| 20-24 | 1,6-2,5 | 0,41-0,61 |
| 25-31 | 1,7-2,4 | 0,4-0,58 |
| 32-37 | 1,6-2,3 | 0,35-0,58 |
| 38-40 | 1,4-2,1 | 0,32-0,55 |
Norms of Doppler ultrasound indicators:
| Index | Group | Norm |
| Vessel diameter | vertebral artery | 3.5 mm |
| carotid artery | 5.5 mm | |
| internal carotid artery | 4.6 mm | |
| external carotid artery | 3.7 mm | |
| Blood flow speed | young | 0,663-0,71 |
| elderly | 0,685-0,73 |
Pathologies:
| Index | Stages of development |
| Narrowing of the lumen of the vessel |
|
| Artery deformation |
|
| Aortic change |
|
| Vascular diseases |
|
Only a specialist in this field can accurately decipher the results of an ultrasound scan.
Examination in children
Ultrasound with Doppler is prescribed to babies at the age of 1 month to identify disorders associated with blood supply to the brain. Usually this procedure is carried out in the maternity hospital. There is no need to re-examine if no problems were found during the first examination.
Indications for ultrasound examination for children:
- prolonged headaches;
- poor sleep;
- dizziness;
- causeless tearfulness;
- restlessness and overexcitability;
- delayed speech development;
- memory and school performance disorders;
- fast fatiguability;
- vascular pathology;
- diabetes;
- other diseases associated with impaired blood circulation in the brain.
Children tolerate Doppler sonography well, since it is a painless research method that is performed only on the surface of the skin without penetration.
Doppler ultrasound examination during pregnancy
Doppler ultrasound examination during pregnancy (DPM) is carried out twice:
- at 18-21 weeks;
- at 32-34 weeks.
If necessary, additional research can be carried out if the following abnormalities are suspected:
- gestosis;
- multiple pregnancy;
- deviation in the structure of the umbilical cord;
- kidney diseases;
- maternal autoimmune diseases;
- fetal death;
- Rhesus conflict.
Before diagnosis, doctors do not require special preparation from the patient. But according to reviews from pregnant women and young mothers, it is better to refrain from eating fried and spicy foods before an ultrasound scan and not to overeat the day before.
The following characteristics are studied on Doppler ultrasound:
- blood flow in the umbilical cord and fetal circulatory system;
- the state of the baby's heart;
- picture of the mother's circulatory system.
Ultrasound ultrasound does not affect the health of the mother and child.
Ultrasound specialist Maria Medvedeva on the channel of the Clinic for Reproductive Medicine named after. Academician V.I. Grishchenko talks about Dopplerography during pregnancy.
What is Dopplerography?
Dopplerography is an ultrasound examination of internal organs based on the Doppler effect. The abbreviation for the procedure is UZDG.
The Doppler effect in medicine is used to study the speed of sound in a stationary environment. It is based on the broadening method - the frequency of radiation increases when moving towards the observer and decreases when moving away from him.
This study has several subtypes:
- USDG MAG stands for checking the main arteries of the head;
- Ultrasound Doppler Doppler (BCS) means the study of abnormalities associated with the vessels of the head and neck;
- BCA ultrasound is a scan of large arteries: carotid, vertebral and subclavian.
What is the difference between Doppler and ultrasound?
Ultrasound produces waves at the same time interval, and also receives the signal back. This creates a general picture of the internal organs and their static structure.
Dopplerography differs in that it emits waves at one speed and receives them at another. The difference in such fluctuations shows the movement of blood flow through the vessels and its speed.
When is it prescribed?
Doppler ultrasound is prescribed if a circulatory disorder is suspected, which manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- memory impairment;
- prolonged insomnia;
- nervous and mental disorders.
Other indications for Doppler ultrasound:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebra;
- stroke;
- persistent headache;
- transient ischemic attack;
- visual impairment;
- phlebeurysm;
- arterial hypertension;
- vascular aneurysm;
- vascular malformation;
- encephalopathy;
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- acute cerebrovascular accident.
Are there any contraindications?
Ultrasound ultrasound is a harmless procedure that is prescribed to both pregnant women and infants. It does not have a negative effect on the body and does not disrupt the structure of tissues.
Contraindications occur when the patient cannot remain in a horizontal position due to severe illness, for example:
- bronchial obstruction;
- respiratory failure;
- heart failure.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of Doppler ultrasound examination:
- the procedure does not require special preparation;
- only this diagnostic method will reveal some types of vascular pathology;
- painless for the patient;
- does not emit dangerous rays;
- has no age contraindications;
- the procedure takes from 15 minutes to 1 hour;
- affordable for most residents of the country.
Flaws:
- does not visualize the cause of vascular stenosis;
- does not show the appearance of vascular tissue;
- does not assess the condition of the veins.
Doppler ultrasound cannot replace procedures such as CT and MRI.
What does it reveal?
Dopplerography reveals:
- narrowing of the lumen of the arteries and severity;
- condition of the vertebral arteries;
- blood flow speed in the main arteries;
- causes of headaches, increased blood pressure;
- organ disorder from the consequences of the formation of plaques and blood clots;
- condition of blood vessels and their deformations.