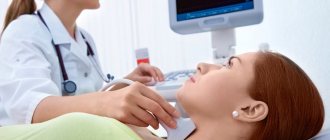
Ultrasound of cerebral vessels
Dopplerography of cerebral vessels is prescribed for suspected neurological diseases. The following symptoms may indicate this:
- Panic attacks.
- Difficulty speaking.
- Difficulties in perceiving information.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Decreased visual, auditory, kinesthetic sensations.
Based on the results of the ultrasound, the doctor can determine what changes in the structure of the blood vessels could cause these symptoms and prescribe treatment, if necessary.
The procedure is simple and safe and has no age restrictions. It can be carried out at home using a portable scanner.
The essence of Doppler ultrasound
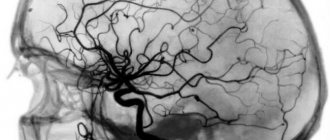
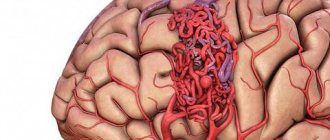
Based on the name of the procedure, it is performed using ultrasonic waves. Their work is based on the Doppler effect. The procedure differs from a standard ultrasound: a vessel with blood passing through it is displayed on the monitor screen. Looking at the resulting image, the specialist assesses the state of blood flow and vascular patency, which affects the quality of blood supply to the brain.
Dopplerography of cerebral vessels makes it possible to study the work of the veins, which “supply” blood to the brain, and the arteries, which are responsible for the outflow of waste products from it. The vessels being examined are located in the cervical and cranial regions. The type of ultrasound will depend on their location:
- Dopplerography of extracranial vessels located on the surface of the neck (jugular veins, carotid, vertebral and subclavian arteries). Any disturbances in their structure affect the state of the brain, which is why these vessels are called “maternal” vessels.
- Dopplerography of transcranial, or “daughter” vessels. The doctor installs an ultrasound sensor in the thinnest parts of the skull and evaluates the functioning of the veins and arteries that supply the brain.
Prices for services
- Diagnostics
Note! Prices are for adult patients. Please see the “Pediatrics” section for the cost of children’s appointments.
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen) | 1700 |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen) + kidneys | 2500 |
| Ultrasound of the gallbladder with functional tests | 1940 |
| Ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder | 1500 |
| Kidney ultrasound | 1500 |
| Ultrasound of the adrenal glands | 800 |
| Ultrasound of the bladder | 970 |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum | 1600 |
| Ultrasound of the bladder and prostate | 1340 |
| Ultrasound of the bladder and prostate with determination of residual urine | 1820 |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland transrectally | 2100 |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs with an abdominal sensor (gynecology, urology) | 1600 |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs with a vaginal sensor (gynecology) | 2000 |
| Folliculometry (ultrasound of follicles) | 1100 |
| Ultrasound of the thyroid gland with determination of blood flow | 1600 |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands with determination of blood flow | 2000 |
| Ultrasound of soft tissues | 1400 |
| Ultrasound of lymph nodes (1 area) | 1500 |
| Ultrasound of the heart in color Doppler mode (echocardiography) | 3500 |
| Ultrasound (duplex) of veins of the extremities | 2600 |
| Ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography in children) | 1700 |
| Ultrasound of cerebral vessels (duplex scanning) | 2700 |
| Ultrasound of neck vessels (extracranial) | 2700 |
| Ultrasound of the knee joints (2 joints) | 2490 |
| Ultrasound of the hip joints (2 joints) | 2700 |
| Ultrasound of small (elbow, wrist, ankle) joints (1 joint) | 1460 |
| Fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNA) of a thyroid cyst/nodule under ultrasound control (1 cyst), without the cost of histology | 3340 |
| Ultrasound of the sinuses (maximum) | 1200 |
| Ultrasound of the eyeball and orbital structures (1 eye) | 1460 |
| Ultrasound measurement of the anteroposterior segment of one eyeball | 1000 |
| Ultrasound of the parathyroid glands | 1200 |
| Ultrasound of the spleen | 1200 |
| Duplex scanning of the renal arteries* | 2700 |
| Duplex scanning of neck and brain vessels* | 4400 |
| Hysterosalpingography (HSG)* (without the cost of manipulation) | 2790 |
| Doppler ultrasound of the abdominal aorta* | 2200 |
| Doppler ultrasound of the renal arteries* | 2700 |
| Ultrasound of the stomach* | 2010 |
| Ultrasound of one organ* | 1200 |
| Ultrasound of pleural sinuses* | 1100 |
| Abdominal ultrasound + study of blood flow of the liver and abdominal aorta* | 2500 |
| Ultrasound of the lungs, bronchi and pleural cavities | 2500 |
In what cases is ultrasound ultrasound prescribed?
The main symptoms signaling a cerebrovascular accident are:
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Deterioration of hearing and memory.
- Frequent attacks of headache.
- Impairment or partial loss of taste.
- Insomnia, difficulty falling asleep.
- Noise, whistling and ringing in the ears.
- Deterioration of visual function, manifested in loss of visual fields.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Decreased sensitivity and motor activity of the arms and legs.
A doctor may prescribe a procedure in the following cases:
- The patient has diabetes mellitus.
- For arrhythmia, as this increases the risk of cardiac clot rupture and artery blockage.
- The patient has suffered a heart attack or stroke.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Before planned heart surgery.
- If the patient is a smoker with many years of experience.
- An area with strong pulsation is visible on the neck (in this case, an ultrasound of the neck is prescribed).
Based on the above symptoms, the doctor can determine the location and name of the vessel in which the patency is impaired. Several pronounced symptoms indicate poor blood flow in a large vessel. In this case, extracranial Doppler ultrasound is prescribed. Violation of only one function will be the reason for conducting transcranial Doppler ultrasound.
Indications
The main indications are the following conditions:
- general lethargy, accompanied by headache, memory and thinking disorders, ringing or noise in the ears, dark circles before the eyes;
- disturbances in facial sensitivity that are predominantly transient in nature;
- pathological changes in heart rhythm (arrhythmias).
Patients with a history of myocardial infarction or stroke are also subject to routine examination using ultrasound. Ultrasound is also used in the event of upcoming cardiac surgery. In addition, such screening is often part of a comprehensive examination and makes it possible to recognize abnormalities in the brain substance visible from the results of computer and magnetic resonance imaging.
Rules for preparing for research
On the day of the procedure, you must refrain from:
- Taking antispasmodics such as “Riabal”, “No-shpa”, “Drotaverine”, “Papaverine”, “Baralgin”, “Cinnarizine”.
- Smoking.
- Drinking black tea and drinks containing caffeine.
- Staying in unventilated, stuffy rooms with large crowds of people, which can have a detrimental effect on vascular tone.
If the patient is undergoing treatment with cardiovascular medications, then the advisability of discontinuing them before the procedure must be agreed with a neurologist. In any case, the sonologist must be informed about the treatment being performed before the ultrasound.
Stages of extracranial Dopplerography:
1. In the office, remove all jewelry from your neck and head.
2. Remove clothing from those parts of the body through which the sensor will be passed: neck, collarbones, shoulder blades.
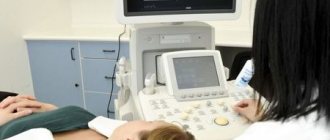
3. Lie on the couch with your head facing the monitor. The doctor will apply acoustic gel to open areas of the body and begin to move the device over them, placing it in areas where medium and large arteries and veins are located. To obtain more accurate data on the state of vascular tone, the patient will need to hold his breath at the doctor’s request, take special medications and change body position.
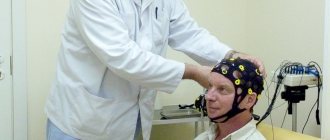
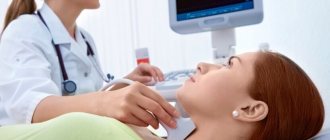
Doppler ultrasound of vessels located in the cranial area has a different specificity. Acoustic gel is applied to the temples, the back of the head and the area above the eyes. The device is installed there because in these places the bones of the skull are the thinnest and are able to transmit ultrasonic waves.
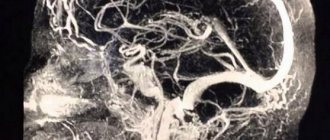
What does duplex scanning show?
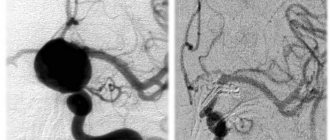
When performing duplex scanning, the structure of the main vessel is studied, the diameter of its lumen is determined, possible obstacles are identified (atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, foci of inflammation, solid, liquid or gaseous intravascular substrates, etc.). Also during the procedure, signs of arterial aneurysm, vascular spasm, impaired venous outflow and other pathological conditions may be detected. This technique allows us to assess the reserve capabilities of blood circulation and regulation of vascular tone.
By what principle is the received data decrypted?
Each vessel has its own parameters, on the basis of which calculations are made and the degree of their discrepancy with the norm is assessed.
Transcranial and extracranial Dopplerography of arteries compares digital data in each vessel segment:
- Artery wall thickness.
- Vessel diameter.
- Phases of blood flow, its features.
- The degree of symmetry of blood flow through identical arteries located on different sides.
- Diastolic blood velocity.
- Maximum systolic blood flow velocity.
- Pulsation and resistive indices, systole and diastole ratio.
- The degree of pathological narrowing of blood vessels (stenosis), the condition of the artery beyond its limits.
Dopplerography of veins evaluates the following parameters:
- Condition of the venous wall of the vessel.
- The nature of blood movement through the studied vessels.
- Vein diameter
Data obtained at rest and after functional tests are compared with normal values. Any deviations are marked with a special abbreviation of letters and numbers. Based on them, the neurologist prescribes further studies or forms a course of treatment.
Procedure
During the ultrasound, the patient is in a supine position. The sensor is placed on the temple area, above the eye socket and in the back of the head. In some cases, it is necessary to examine the vessels of the neck that carry blood to the brain. A cushion is usually placed under the head. To complete the obtained picture, functional tests are also performed. The position changes to vertical, breathing becomes deeper and more frequent, and it may be delayed for certain periods of time.
Diagnosis of the state of the cerebral vascular network is carried out in segments, each of which is marked with an alphanumeric code. The starting points are the bones of the skull, vertebrae and other elements of the skeletal system. Based on the obtained values, the doctor interprets the results, paying attention to the resistive index (RI), wall thickness, artery diameter, etc. All data is entered into an ultrasound diagnostic protocol.
Where can I get Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels?
The study is carried out in municipal clinics and public hospitals, specialized clinics, and general medical centers. Depending on the location of the ultrasound, the cost of each type of Doppler ultrasound will be in the range of 500-6000 rubles. The procedure has many advantages, including painlessness and the absence of side effects. Within 20 minutes, a sonologist will be able to determine the presence of anomalies in venous or arterial inflow and assess the degree of development of danger to blood vessels.
However, the procedure will not help determine the cause of compression of the thin arteries, since the capabilities of the device do not allow them to be seen from the outside.
Where to do ultrasound duplex scanning of blood vessels
If you need to do an ultrasound scan and duplex scanning of the vessels of the head and neck in St. Petersburg, contact the medical office. Our specialists have at their disposal the latest Italian expert-class ultrasound equipment, which allows them to make a diagnosis as quickly and accurately as possible.
You can find out the price of a diagnostic test, make an appointment and find out other questions by telephone or by filling out an electronic form.
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price, rub.) | In installments* |
| Transcranial duplex scanning (TCDS) of cerebral vessels | 3 600 | — |
| Ultrasound scanning of brachiocephalic vessels and vertebral arteries | 3 200 | — |
| Transcranial ultrasound scanning (TCDS) of arteries and veins, brachiocephalic vessels and vertebral arteries | 6 700 | — |
* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments.