How does serum differ from blood plasma?
Blood is a red liquid that moves through blood vessels, arteries and capillaries.
It carries nutrients to cells, organs and tissues. It is also responsible for cleansing cells of decay products to prevent self-poisoning of the body. Blood performs the following important functions:
- Transports nutrients to cells.
- Transports breakdown products to places of excretion.
- Saturates tissues with oxygen.
- Protects the body from the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Regulates body temperature.
- Provides stability when external conditions change.
In various types of studies, it is the remaining 10% that is of interest, which includes protein components:
- Albumin.
- Globulins.
- Fibrinogen.
During research, only the level of albumin and globulin is important. Fibrinogen is responsible for blood clotting, so its indicators are often not taken into account.
Serum cannot be obtained directly from blood collection, so plasma must first be isolated. Only after this can serum be prepared in laboratory conditions.
Blood composition
How is blood serum obtained?
To study the state of the body, it is necessary to obtain plasma, for which blood is taken from a vein. Before the procedure, the patient is recommended to follow a special low-fat diet. It is also necessary to avoid the use of alcohol, nicotine and medications that can affect the results.
Thanks to this, the serum has the possibility of long-term storage, which allows it to be actively studied and used for treatment.
The serum contains the following elements:
- Creatinine, responsible for kidney function.
- Enzymes.
- Good and bad cholesterol.
- Nutrients.
- Vitamins.
- Hormones.
They allow you to study your general health and identify various pathologies at the initial level. If the laboratory technician was careless when taking the analysis, red blood cells may be destroyed. They will turn the serum pink, making it unsuitable for study.
If the blood is drawn correctly, the specialist determines how to obtain the serum:
- Through the use of calcium ions.
- Through natural blood clotting.
Serum contains the most antibodies, which allows it to be used for various purposes:
- Carrying out biochemical analysis.
- To determine the type of pathogen in infectious diseases.
- To obtain an individual treatment serum.
- Checking the effectiveness of the vaccination.
It is stored longer, which makes it different from plasma. Thanks to this feature, the serum is subjected to long-term preservation in order to test for the presence of pathogens. Such measures make it possible to prevent the infusion of contaminated material into patients.
How to get serum
How is blood plasma different from serum?
Plasma is a yellowish, cloudy substance that is part of the blood. It contains basic information about the individual's health status. It helps to identify hormonal imbalances and problems in the functioning of individual organs and systems.
Serum is plasma without fibrinogen, which increases its lifespan. The serum can be used to obtain various drugs that have medicinal properties.
It helps conduct large-scale studies of the capabilities of the human body, testing the reaction of blood cells to various types of pathogenic microorganisms.
The difference between plasma and serum is as follows:
- Plasma is the entire component of blood, while serum is only a part.
- Plasma contains fibrinogen, a protein responsible for blood clotting.
- Plasma is always yellowish, and serum may have a reddish tint due to damaged red blood cells.
- Plasma coagulates under the influence of the enzyme coagulase, and serum is resistant to this process.
Blood in a test tube
Serum study
Laboratory tests of serum can determine the amount of proteins, carbohydrates and minerals in the blood. The results are used to draw conclusions about the coherence of the internal organs.
If a decrease in total serum protein is detected, prolonged fasting or a low-protein diet may be suspected.
When a person has not limited his diet, and the indicators are significantly below the norm, they speak of the following violations:
- Serious pathologies of the liver, kidneys, endocrine system.
- Burns or major blood loss.
- Presence of neoplasms.
- Problems with protein production under the influence of medications.
Exceeding the norm leads to:
- Dehydration.
- Vaccination.
- Tumor.
In such cases, additional diagnostics are often required. If the problems are caused by dehydration, the patient is recommended to adjust the drinking regime. In other situations, special treatment is necessary, which is prescribed by an appropriate specialist.
Serum is the most informative reagent when performing blood biochemistry, which allows you to diagnose pathologies:
- Pancreas.
- Liver.
- Kidney.
- Prostate gland.
- Bone tissue.
- Muscle fibers.
If its levels are reduced, problems begin with the level of iron in the blood. Neopterin reflects the speed of the immune response to adverse conditions.
Each protein is responsible for its own area, so the likelihood of error when making a diagnosis is minimal.
Blood serum
Treatment with immune serums
Sometimes people wonder why serums are used for medicinal purposes. This possibility is explained by the large number of antibodies in the serum and the absence of rejection of one’s own biomaterial. The product is used to treat and prevent various diseases.
There are two types of antiserum:
- Homologous.
- Heterogeneous.
Homologous is obtained from the blood of a person who has been vaccinated and has developed antibodies to a certain type of microorganism.
Immune serums are used for the prevention and treatment of infectious pathologies. They also allow you to accurately determine the type of pathogen, which facilitates diagnosis and makes therapy effective. Serums help fight the venoms of snakes and scorpions, and reduce the effect of botulism toxins.
In case of animal bites, anti-rabies serum must be administered, which is the only way to prevent the development of a dangerous disease.
Source: //znk-mos.ru/otlichaetsya-syvorotka-plazmy-krovi/
Difference between plasma and serum
Many people know that plasma and serum are related to blood. But not everyone has deeper knowledge on this issue. Let's consider what the declared substances are and how they fundamentally differ.
So, one of the fluids that performs its important functions in the body is blood. Obedient to the beats of the heart, it constantly moves, transporting various substances to their designated places. In addition to transportation, blood is responsible for many other aspects. Solving a large number of problems, this substance is quite complex.
A significant part of the blood consists of the so-called formed elements. They are represented by a certain number of leukocytes, platelets and bodies called erythrocytes. All mentioned components exist in a liquid medium, which is plasma. This substance can be observed at the top of the settled blood in the form of a light layer, while heavier particles settle down.
Plasma itself is also a combination of many components, each of which has a clear purpose. The basis here is water. Some types of proteins, vitamins, and nutrients are dissolved in it. In addition, mineral compounds, excreted metabolic products and other various elements are found in the plasma.
As we can see, we are talking about a rich substance that is naturally found in the blood, which always functions in the body. At the same time, serum can only be obtained outside the body. It is produced on the basis of plasma. The latter contains fibrinogen, a protein component responsible for blood clotting.
Serum remains after fibrinogen is removed using certain techniques. The resulting fraction is usually yellowish, but may also have a reddish tint due to the presence of certain particles. The value of such a liquid lies in its stability. Whey that is not subject to coagulation is stored for a long time. At the same time, its composition remains uniform, without unnecessary clots.
At the same time, the practical significance of the serum lies in the fact that it is rich in antibodies, which pathogens are afraid of. This blood processing product is indispensable in the manufacture of drugs that perform not only a therapeutic, but also a preventive function. A similar composition is used in the process of diagnosing diseases, for conducting various studies, as well as for some other purposes.
Difference Between Serum and Plasma
Serum and plasma are two derivatives of blood that lack blood cells such as red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Both contain proteins, drugs, hormones, toxins and electrolytes.
Both serum and plasma have therapeutic and diagnostic uses. They can be separated from the blood by centrifugation, which removes the cellular portion of the blood. Anticoagulants are added to the blood after a transfusion to prevent blood clotting.
The serum is amber in color and the plasma is straw in color.
The main difference between serum and plasma is that serum is a protein-rich liquid that is released when blood coagulates while plasma is the liquid component of blood that keeps the blood cells in whole blood in suspension.
This article looks at,
1. What is serum - definition, composition, properties 2. What is plasma - definition, composition, properties 3. What is the difference between serum and plasma
What is serum
Serum is a watery, amber-colored portion of animal blood that remains after the blood has clotted. Consequently, the serum lacks blood cells such as red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. It also lacks blood clotting factors such as fibrinogen.
But serum contains all the proteins such as albumin and globulin, which are not involved in the blood clotting process. It also contains antibodies, antigens, electrolytes, hormones, drugs and microorganisms. Serology is the study of serum. Serum is separated from the blood by centrifugation, which removes the cellular component of the blood, followed by coagulation.
Coagulation removes clotting factors such as fibrinogen, prothrombin, and tissue thromboplastin from the blood. Whey is a good source of electrolytes. It is used for various diagnostic tests for hormones and enzymes. It is also used to determine blood groups.
Animal serums are used as antidotes, anti-toxins and inoculations. The serum can be stored at 2-6 ºC for several days.
Figure 1: Serum separated from blood
What is plasma
Plasma is a liquid portion of blood. It is a straw-colored protein-saline solution that traps blood cells and platelets. Therefore, plasma serves as an extracellular fluid. This takes up 55% of the total blood volume. water in plasma is about 92%.
Plasma contains dissolved proteins such as albumin, globulin and fibrinogen, glucose, clotting factors, hormones, electrolytes, carbon dioxide and oxygen.
It maintains satisfactory blood pressure and volume, balances the body's pH and serves as a medium for the exchange of minerals such as sodium and potassium.
Plasma is separated from its cellular part by centrifugation. Four units of plasma are diluted with one part of the anticoagulant, citrate-phosphate-dextrose (CPD), to a total volume of 300 ml. When a plasma sample is frozen within 8 hours of collection, it is called fresh frozen plasma (FFP).
When it is frozen for more than 8 hours but less than 24 hours, the plasma sample is called frozen plasma (FP). Once preserved by adding anticoagulants, frozen plasma can be stored for up to one year at -18ºC.
Plasma transfusion is performed in trauma patients, patients with severe liver disease and multiple clotting factor deficiency. Plasma derivatives, such as special plasma proteins, can be obtained by fractionation.
Viruses that cause HIV, hepatitis B and C are destroyed by treatment with heat or solvents. A diagram of a blood sample after centrifugation is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Diagram of a blood sample after centrifugation
Definition
Serum: Serum is an amber-colored protein-rich liquid that is released when the blood coagulates.
Plasma: Plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are suspended.
correspondence
Serum: Serum is that part of the blood that does not contain blood cells or clotting factors.
Plasma: Plasma contains serum and clotting factors.
Purchased from
Whey: Whey is obtained from the spinning after coagulation.
Plasma: Plasma is acquired by spinning before folding.
separation
Serum: Anticoagulants are not required to separate serum from blood.
Plasma: Anticoagulants are necessary to separate plasma from the blood.
Separation process
Whey: Whey is difficult to separate and time consuming.
Plasma: Separating plasma is comparatively easier and requires less time as compared to serum.
volume
Serum: Serum has a smaller volume than plasma.
Plasma: Plasma occupies 55% of the total blood volume.
Clotting factors
Serum: Serum lacks clotting factors.
Plasma: Plasma consists of clotting factors.
density
Serum: The density of serum is 1.024 g/ml.
Plasma: The density of plasma is 1.025 g/ml.
water
Whey: Whey contains 90% water.
Plasma: Plasma contains 92-95% water.
Medical use
Serum: Serum is used for enzyme tests and hormonal tests.
Plasma: Plasma transfusion is done for trauma patients, patients with severe liver disease, etc.
Storage
Whey: Whey can be stored at 2-6 ºC for several days.
Plasma: Once preserved by adding anticoagulants, frozen plasma can be stored for up to one year at -18ºC.
Conclusion
Serum and plasma are two derivatives of blood. Plasma is the liquid part of the blood in which the blood cells are suspended. It is a protein-rich liquid. Serum is the liquid part that remains after blood clotting.
Consequently, the serum lacks proteins that are involved in coagulation, such as fibrinogen. Both serum and plasma have medical uses.
However, the main difference between serum and plasma lies in the differential processes of release of both derivatives.
Reference: 1. “Blood serum.” Merriam-Webster. Merriam-Webster, n.d. Web. May 27, 2017
Source: //ru.strephonsays.com/difference-between-serum-and-plasma
Blood composition. Plasma. Serum
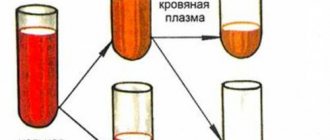
Blood belongs to the supporting trophic tissues. It consists of cells - formed elements and intercellular substance - plasma. The formed elements of blood include erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets. Blood plasma is a liquid. It is important to note that blood is the only tissue of the body where the intercellular substance is a liquid. To separate the formed elements from the plasma, the blood must be protected from clotting and centrifuged. The formed elements, being heavier, will settle, and above them there will be a layer of transparent, slightly opalescent yellow liquid - blood plasma.
Figure 1 - Blood smear: 1 - red blood cells; 2 - segmented neutrophil; 3 - band neutrophil; 4 - eosinophil; 5 - basophil; 6 - lymphocyte; 7 - monocyte. Staining according to Romanovsky - Giemsa
Figure 2 - Blood cells (electron scanning microscopy)
Figure 3 - Whole blood. When centrifuged, red blood cells are at the bottom, and cell-free plasma is at the top.
Blood plasma consists of water and dry matter (9:1), which includes organic and inorganic compounds. Organic substances in blood plasma are proteins (albumin, globulins, fibrinogen, prothrombin, etc.) - 60-90 g/l, amino acids - 5-14 mg/100 ml, urea - 3.33-8.32 mmol/l, glucose - 0.6-1.2 g/l, neutral fats - 1.5-3.0 g/l, minerals - 9 g/l (mainly sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, chlorine ions), enzymes, hormones and other substances. The specific gravity of plasma is 1.025 - 1.029; The pH varies slightly between 7.37 and 7.43. Plasma that does not contain fibrinogen and some other substances involved in coagulation is called serum. Just like blood, plasma can clot. It is involved in many vital processes of the body, transports blood cells, nutrients and metabolic products and serves as a link between all extravascular (that is, located outside the blood vessels) fluids. The latter include, in particular, the intercellular fluid through which communication with cells and their contents occurs. Thus, plasma comes into contact with the kidneys, liver and other organs and thereby maintains the constancy of the internal environment of the body, i.e. homeostasis. The blood reaction can range up to a maximum of pH 7.8 and a minimum of pH 7.0. Impaired blood reaction, its decrease (acidosis) and increase (alkalosis) can lead to the death of the animal. The blood plasma reaction is ensured by four buffer systems: carbonate, phosphate, hemoglobin and blood plasma proteins. The concentration of substances dissolved in plasma can be expressed by osmotic pressure, which is provided to a greater extent by sodium chloride. A solution of sodium chloride at a concentration of 0.85% has the same osmotic pressure as the pressure of blood plasma. If the blood volume is taken as 100%, then the formed elements will be about 40-45%, and plasma - 50-60%. The volume of formed elements in the blood, mainly red blood cells, is called the hematocrit value or hematocrit. Hematocrit can be expressed as a percentage (40-45%) or in liters of red blood cells contained in one liter of blood (0.40-0.45 l/l). When an animal has not been given water for a long time or it has lost a lot of fluid (with severe sweating, diarrhea, profuse vomiting), the hematocrit value increases. In this case, they talk about “thickening” of the blood. This condition is unfavorable for the body, since the resistance of the blood during its movement significantly increases, which causes the heart to contract more strongly. As compensation, part of the water passes from the tissue fluid into the blood, its excretion by the kidneys decreases and, as a result, thirst arises. A decrease in hematocrit often occurs during illness - with a decrease in the formation of red blood cells, increased destruction, or after blood loss.
Related:
- The amount of blood in animals, blood depot
- Red blood cells (structure, functions, quantity)
How does BLOOD SERUM differ from PLASMA?
The cells of our body are washed by a certain amount of bodily fluids, or humors.
Due to the fact that these fluids occupy an intermediate position between human cells and the external environment, they ensure the survival of cells and play the role of a so-called shock absorber during sudden external changes, in addition, they are an effective means of transporting nutrients and waste products in the body.
An important role in the human metabolic process is played by blood, which consists of the liquid part of blood plasma and formed elements suspended in it:
- leukocytes - white blood cells that perform protective functions;
- erythrocytes - red blood cells containing hemoglobin (red respiratory pigment);
- platelets - blood platelets necessary for blood clotting.
Formed elements make up 40–45%, plasma – 55–60% of the total blood volume. This ratio is called the hematocrit ratio, or hematocrit number. In some cases, the hematocrit number includes only the volume of blood that accounts for the formed elements.
Blood plasma is a solution that consists of:
- water (90-92%) and dry residue (10-8%);
- organic and inorganic substances;
- formed elements (blood cells and plates);
- dissolved substances: proteins (albumin, globulins and fibrinogen); inorganic salts that are dissolved in the form of anions (sulfate, chlorine ions, phosphate, bicarbonate) and cations (potassium, magnesium, sodium and calcium); transport substances derived from digestion (amino acids, glucose) or respiration (oxygen and nitrogen), metabolic products (urea, carbon dioxide, uric acid) or substances absorbed by the lungs, skin and mucous membranes.
Plasma constantly contains all microelements, vitamins and intermediate metabolic products (pyruvic and lactic acids).
Lymph, blood, tissue, pleural, spinal, joint and other fluids form the internal environment of the human body. They originate from blood plasma and are formed through the process of plasma filtration by passing through the capillary vessels of the human circulatory system.
Plasma protein contains fibrinogen, which appears due to changes in the physicochemical state during blood clotting. Fibrinogen has the ability to pass from a soluble to an insoluble form, converting into fibrin and forming a clot.
Blood serum is a clear, yellowish (or light yellow) liquid separated from a blood clot after blood has coagulated outside a living body. From the blood serum of animals and people immunized with certain antigens, it is possible to obtain immune sera used in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of various diseases.
The serum can be either red due to hemolysis - this is the process of destruction of red blood cells with the release of hemoglobin into the environment surrounding the red blood cells, or icteric - due to increased values of bilirubin (a pigment that is contained in the blood and excreted with bile, due to which it is called bile pigment).
Blood serum is used for preventive, diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
To obtain it, it is necessary to place sterilely collected blood in a thermostat for 30–60 minutes, remove the clot from the wall of the test tube with a Pasteur pipette and place it in the refrigerator for several hours (preferably for a day). The settled blood serum is aspirated or drained using a sterile Pasteur pipette into a sterile test tube.
Conclusions:
- Blood plasma is the liquid part of the blood that remains after the removal of formed elements. In a suspended state, it contains formed elements - blood cells and platelets (or blood cells).
- Blood plasma in its composition is a very complex liquid biological medium, which includes vitamins, carbohydrates, proteins, various salts, lipids, hormones, dissolved gases and intermediate metabolic products.
- Blood serum (or blood serum) is the liquid fraction of clotted blood.
- Blood plasma is obtained by precipitation of formed elements, and serum is obtained by introducing coagulants (substances that promote blood clotting) into the blood plasma.
- Blood serum differs from plasma in the absence of a number of proteins of the coagulation system, such as fibrinogen and antihemophilic globulin, therefore it does not coagulate in the presence of coagulase, incl. microbial
Source: //thedb.ru/items/Chem_KROVYANAYA_SYVOROTKA_otlichaetsya_ot_PLAZMY/
How is blood plasma different from serum? Definition, composition, preparation
Blood plays an extremely important role in the metabolic processes of the human body. It contains plasma and formed elements suspended in it:
- erythrocytes are red blood cells that contain hemoglobin;
- leukocytes – white blood cells whose main function is protective;
- platelets are platelets of blood used for blood clotting.
Formed elements occupy 40–45%, and plasma – 55–60% of the total blood volume. This ratio is called hematocrit (hematocrit number).
Blood plasma is a liquid with a homogeneous viscous consistency of light yellow color. If it is presented in the form of a suspension, blood cells are found there. Plasma is most often clear, but may become cloudy after eating fatty foods. In this article we will understand how blood plasma differs from serum.
Plasma composition
A significant part of the plasma composition is occupied by water (about 92%). In addition, it contains the following substances:
- glucose;
- proteins;
- amino acids;
- fat and similar substances;
- enzymes;
- hormones;
- minerals.
Albumin is the main protein in plasma, having a small molecular weight. Makes up more than 50% of the total volume of proteins. Formed in the liver.
Functions of the main protein
Albumin performs the following functions:
- transport – transfer of hormones, fatty acids, ions, drugs, bilirubin;
- participates in metabolism;
- carries out protein synthesis;
- controls oncotic pressure of plasma and serum;
- preserves amino acids.
If the plasma albumin level changes, this becomes an additional diagnostic sign. Protein concentration helps determine the condition of the liver, since its decrease is a characteristic sign of chronic diseases of this organ.
Other proteins
Other blood plasma proteins are large molecular globulins produced in the immune system and liver. The following types are distinguished: alpha, beta and gamma globulins.
Alpha globulins connect thyroxine and bilirubin, stimulate the production of proteins, transport hormones, vitamins, lipids and trace elements.
Beta globulins provide the connection between iron, vitamins and cholesterol, and are responsible for the transport of phospholipids, hormones, sterols, etc.
Gamma globulins bind histamine and take part in immunological reactions, therefore they are called antibodies (immunoglobulins). They are represented by five classes: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, IgM. The chemical composition of plasma and serum is unique.
They are produced in the liver, spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes and have different biological properties and structure, different ways of connecting antigens, stimulating the work of immune proteins, differentiated by the ability to pass through the placenta and avidity, that is, the speed of connection with the antigen and strength. IgG makes up 80% of immunoglobulins. Only they can penetrate the placenta and have high avidity. IgM is initially synthesized in the fetus and appears first in the blood serum after most vaccinations.
Fibrinogen is a soluble protein produced in the liver. When exposed to thrombin, it becomes insoluble fibrin, which causes a blood clot to form in the damaged area of the vessel. The difference between blood plasma and serum is of interest to many. More on this later.
In addition, blood plasma also includes proteins such as transferrin, complement, haptoglobin, prothrombin, C-reactive protein and thyroxine-binding globulin.
Non-protein components
Non-protein components include:
- organic nitrogen-free (lipids, carbohydrates, ketones, lactate, glucose, pyruvic acid, cholesterol, minerals);
- organic containing nitrogen (urea nitrogen, amino acid nitrogen, creatine, indican, creatinine, bilirubin, low molecular weight peptides);
- inorganic: magnesium, sodium, calcium, potassium cations, iodine and chlorine anions.
Functions of proteins and plasma
Proteins perform the following functions:
- ensure stable functioning of the immune system;
- support self-regulation of the body and the aggregate state of the blood;
- transport nutrients;
- take part in blood clotting.
Plasma itself performs many functions, including:
- transports blood cells and metabolic products;
- binds liquid media outside the circulatory system;
- provides contact with body tissues through extravascular fluids, thereby carrying out self-regulation.
Obtaining plasma and serum
Most often, transfusion now requires not so much whole blood as its components and plasma.
It is extracted from whole blood using centrifugation, that is, separation of the liquid part from the formed elements by hardware. The blood cells are then returned to the donor. The duration of this procedure is forty minutes.
In this case, blood loss is much less, and after two weeks you can donate plasma again, but no more than twelve times a year.
Venous blood is taken in the morning on an empty stomach. In this case, it is worth taking into account factors that can affect the result of the analysis: emotional arousal, excessive physical activity, eating or drinking alcohol before the study, smoking, etc. To exclude their influence, the following conditions for preparing the donor must be met:
- blood is taken after fifteen minutes of rest;
- the patient must sit (lying blood is taken from seriously ill people);
- Smoking, drinking alcohol and eating before the study are excluded.
Blood serum
Let us give the definition of blood serum. This is a clear liquid with a yellowish tint, which is separated from the blood clot after it has coagulated.
If the serum of a person or animal is immunized with certain antigens, it is possible to obtain its immune variety, which is used in the diagnosis, prevention and therapy of various diseases.
The color of the serum may also be red due to hemolysis, a process in which red blood cells are destroyed and hemoglobin is released. The icteric color indicates an increase in the value of bilirubin.
Serum, unlike plasma, does not contain fibrinogen, but it contains all the antibodies that can fight pathogens.
In order to obtain it, you need to put sterile blood taken in a thermostat for 30-60 minutes, peel off the clot from the wall of the tube using a Pasteur pipette and put it in the refrigerator for several hours (preferably for a day).
After it has settled, the serum is drained or pipetted into a sterile test tube. We have looked at the definition of blood serum, but what is the difference between it and plasma?