Types of arrhythmias
There are many different types and forms of arrhythmias, but those that affect the ventricles are usually more serious than atrial problems. Arrhythmias can be caused by either a slow heartbeat (bradycardia) or a fast heartbeat (tachycardia) . A low heart rate can occur due to sick sinus syndrome. This occurs when the heart's natural pacemaker fails, causing the electrical signals that contract the heart to be transmitted more slowly. The condition is more common in older people and may be worsened by certain medications (such as beta blockers) that also slow the heart rate.
Heart block occurs when the electrical signal sent from the upper chambers of the heart (atria) to the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) is interrupted. Without this signal transmission, the heart cannot contract effectively to pump blood to the body.
An increased heart rate may be the result of atrial fibrillation (AF). The arrhythmia clinic involves random signals that are fired in rapid succession. They cause fibrillation, which is an uncoordinated shaking of the muscular wall of the atria. It is often described as "heart cramps". The atria stop pumping blood effectively, but the ventricles receive enough blood for the heart to function. However, AFib is potentially dangerous because blood can pool in the atrium and lead to the formation of a clot. If one of these clots enters the brain, it causes a stroke. AF is the most common form of dangerous arrhythmia, affecting almost 1% of the population. It is more common in older people, affecting about 5% of the population over 69 years of age. One study showed that one in four people over 40 years of age develops FIP. Source: On the issue of classification of cardiac arrhythmias. Batyanov I.S., Batyanova E.I. Cardiovascular therapy and prevention, 2005.
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is the most dangerous form of arrhythmia. The ventricles twitch but do not pump blood. If the twitching does not stop on its own or as a result of a defibrillator discharge, this complication of arrhythmia can be fatal.
Causes of cardiac arrhythmia in men or women
There are two common ways in which arrhythmias develop, which can be determined in a particular patient. There may be problems with the initiation of the electrical signal: either the sinus node is firing abnormally, or there is a competing impulse elsewhere in the heart. The second option is problems with the conduction of electrical impulses: connections from the atria to the ventricles are difficult (this is often called heart block).
People with heart disease are especially likely to develop arrhythmias, because heart disease, damage can prevent signals from the atria from reaching the ventricles, or certain areas of the heart may not fire normally.
High blood pressure and an overactive thyroid gland also increase the likelihood of arrhythmias. Alcohol can also cause atrial and ventricular arrhythmias. Some medications, such as decongestants and many prescription drugs, can make the heart susceptible to arrhythmias and should be used with caution in people with heart disease.
There are also hereditary and congenital (present from birth) types of arrhythmia, often resulting in a weak or delayed signal reaching the ventricles. The ventricles can emit their own signal, but it is often less than 40 beats per minute instead of the usual 60-90 beats characteristic of the sinus node. Source: "New Arrhythmia Theory" Clarifies Causes of Arrhythmia. Ermoshkin V.I. Educational bulletin “Consciousness”, 2015. p. 22-30.
Symptoms
When the heart beats faster than normal, it is called tachycardia . Symptoms and signs of arrhythmia include:
- chest discomfort
- cardiopalmus,
- dizziness,
- sometimes fainting.
When the heart beats slower than normal, it is called bradycardia . It can cause fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness and fainting as it usually causes low blood pressure.
Almost everyone's heart will flutter from time to time, and it usually doesn't mean anything. More often, symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia occur in men and treatment is not always necessary. But if a person has chest pain, feels weak, or notices that the pulse is irregular, either very fast or very slow for a long period, it is time to see a doctor. Source: Insider's View Focus on the Arrhythmia Patient. Boqueria O.L. Annals of Arrhythmology, 2014. p. 196-199.
Symptoms of this disease may not appear. Arrhythmia can be detected by a specialist during a routine clinical examination: before any of its signs appear. But predominantly, heart rhythm disturbances are characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain in the chest;
- increased feeling of heartbeat;
- accelerated heartbeat;
- slow heartbeat;
- dyspnea;
- loss of consciousness or fainting.
In most cases, in a person who has a certain type of arrhythmia, such arrhythmia occurs repeatedly.
Some types of arrhythmias are initially asymptomatic or with few symptoms. Other types of arrhythmias, on the contrary, manifest themselves in pronounced symptoms, but do not have serious consequences. Typically, the nature and severity of the underlying heart disease that causes the arrhythmia are more important than the arrhythmia itself.
Factors in the development of ischemic heart disease
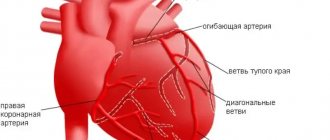
The heart muscle, which is essentially the “motor” of the body, itself needs oxygen and unhindered blood flow. Blood flows to the heart through 2 coronary vessels. In the heart, both of these arteries are divided into small vessels that supply one of the sections of the myocardium.
There are simply no other vessels involved in feeding the heart with blood. Consequently, narrowing of the arteries or blockage of any of them leads to a lack of oxygen in the tissues of the heart and coronary disease develops.
One of the risk factors for the development of coronary artery disease is atherosclerosis of the great vessels and, as a consequence, the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of these arteries. As a result, plaques block blood flow, and the heart does not receive the required amount of blood.
In the early stages of the disease, the lack of oxygen in the heart is expressed only when the load increases, for example, during fast running. Pain that occurs in the chest is called angina pectoris. Over time, the lumen of the main vessels decreases, metabolic processes in the myocardium deteriorate, as a result of which the frequency of pain becomes more frequent; During the course of the disease, pain can occur during low-intensity exercise, as well as at rest.
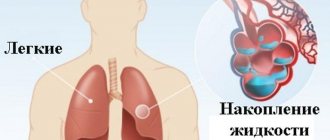
Angina pectoris may be accompanied by the development of heart failure with the appearance of shortness of breath and fluid retention (due to the presence of edema).
When plaque detaches from the walls of the artery, blockage of the vessel can occur, thereby provoking the development of a heart attack and cardiac arrest. The severity of symptoms when heart tissue is damaged depends on the location of the blockage. Blockage of the main arteries can be fatal.
For the development of a heart attack, the vascular lumen must be reduced to 80% of the original. Rapid and sudden blockage of blood vessels prevents the heart from adapting to changes in blood flow and often leads to early death.
Symptoms of IHD are:
- Rhythm disorders
- Muscle weakness
- Feeling of heaviness behind the sternum
- Nausea
- Shortness of breath during moderate exercise
- Increased sweating
Symptoms of coronary heart disease are characterized by the occurrence of paroxysmal pain that lasts a short time. The feeling of tightness in the chest is popularly called “angina pectoris.” Ischemia and angina are distinguished by the presence of chest pain. As a rule, pain occurs in one part of the body and radiates to the arms, legs, shoulder blades, neck and jaw. Often, the symptoms of IHD can be confused with symptoms of gastrointestinal dysfunction. In such cases, heartburn and dyspeptic disorders may occur against the background of coronary artery disease. Therefore, a person may not suspect the presence of ischemia for a long time.
Ischemic disease is accompanied by:
- Mental stress
- Panic
- Bad mood
- Apathy
Also a symptom of the disease is pain in the chest that does not go away after using nitroglycerin. Often, coronary heart disease and angina are accompanied by constant pain that occurs suddenly, for example, this can happen while taking a shower, with a sudden change in temperature, while smoking, and also with sudden movements.
Most people often do not take the signs of IHD seriously and therefore do not consult a doctor for a long time. At the same time, the symptoms of IHD should not be left to chance, since complications of the disease can lead to dire consequences.
IHD is one of the causes of mortality from cardiovascular diseases in many countries, regardless of the level of development of medicine. If the patient has significant complications of this disease, for example, a significant decrease in the lumen of blood vessels, then for the treatment of IHD it is necessary to use surgical methods of therapy: coronary bypass surgery (replacing the affected vessel with an implant), angioplasty (insertion of a stent or balloon into the affected vessel) and other surgical procedures .
Treatment of ischemic disease consists of several stages:
- Pain relief and rest. In severe cases of coronary artery disease, epidural anesthesia should be used.
- Anticoagulation of blood and improvement of its rheological properties. It is necessary to conduct a laboratory examination of the blood, determine the level of platelets, measure the concentration of cholesterol in the blood and other parameters.
- Use of antiplatelet drugs. Treatment of coronary heart disease involves the mandatory use of such drugs, as they will help minimize the risk of developing blockage of blood vessels with blood clots.
- Prevention of atherosclerosis – one of the main causes of impaired blood flow.
- Diagnosis and appropriate therapy of other diseases. This includes other diseases of the heart and blood vessels, as well as disorders of the central nervous system.
- The use of prostaglandins.
- The use of medications that affect the transport of oxygen molecules. Such drugs include antihypoxants, calcium channel blockers and beta blockers. (They reduce the oxygen demand of heart tissue).
- Ultrasound diagnostics of the arteries of the heart, determination of gas exchange indicators and other examinations prescribed by a surgeon.
To relieve symptoms of ischemia, drugs containing potassium and magnesium are often used. They reduce the likelihood of thrombosis, normalize the elasticity of vascular walls, suppress the growth of cholesterol plaques, accelerate metabolic processes in the myocardium and energy exchange in it.
Diagnostics
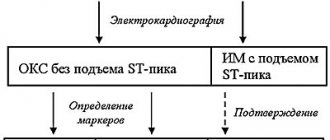
The stethoscope is still a valuable tool for identifying arrhythmias, but there are modern tests that can pinpoint the problem and signs of cardiac arrhythmias in women or men. An electrocardiogram (ECG) displays a graph of the heart's electrical activity using small electrodes attached to the chest. The curve on these graphs shows the type of arrhythmia. Since the arrhythmia may not occur in the hospital, there are portable ECGs that the patient wears at home. Some are turned on continuously over a period of time (called a Holter monitor), while others turn on when a person senses an arrhythmia (called an event monitor or loop recorder).
Certain arrhythmias may be associated with exercise, so patients may be asked to walk on a treadmill or ride an exercise bike while connected to an ECG machine.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) is a more complex test. Thin tubes are inserted into a blood vessel in the leg and directed toward the heart. They hold electrodes that can find muscle tissue that may be causing abnormal electrical activity.
Modern methods of treatment
In some cases, arrhythmias occur due to bad habits, such as drinking too much alcohol. Giving up the habit will be a real help for arrhythmia. Reducing stress, avoiding caffeine, improving diet, and increasing the amount of exercise the patient does during the week can also reduce the incidence of arrhythmias. Before you begin making these changes, you should first talk to your doctor. For others, arrhythmias are a symptom of heart disease and will not go away unless the underlying problem is addressed. Fortunately, many people can benefit from invasive treatment of cardiac arrhythmias using modern medical interventions, especially surgery and special electrical devices.
Drug treatment for cardiac arrhythmia is also possible. There are several medications that can slow a fast heartbeat (known as "antiarrhythmic drugs"). Beta blockers are medications that are very useful in controlling heart rate in people with various heart conditions. Calcium channel blockers may also be used to control heart rate. Often these drugs can be used for more than one purpose (eg, to control heart rate, high blood pressure, protect the heart after a heart attack). The drug Digoxin is derived from a substance called Digitalis, which has been used for arrhythmias for over 200 years.
Other medications called antiarrhythmics can convert the abnormal rhythm to a normal one and prevent seizures from recurring (known as "rhythm control"). Patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) are usually prescribed the anticoagulant Warfarin, which thins the blood and prevents blood clots and strokes. Recent studies have shown that heart rate control and adequate anticoagulation are very important (perhaps even more important than rhythm control) for people with certain types of arrhythmias (eg, AF).
In some cases, AF returns to a normal rhythm with a treatment called cardioversion. The patient is given a small electrical shock that resets the heart's natural pacemakerSource: Innovations in the Treatment of Cardiac Arrhythmia. Zh.A. Arzykulov, A.A. Omarov, B.B. Kituev, F.A. Tursunova, A.A. Yeshtay, N.G. Pavlova. Bulletin of Surgery of Kazakhstan, 2012. p. 4-5.
Many arrhythmias can be completely treated with radiofrequency ablation. Thin catheters are passed into the heart to send radio waves directly to electrical pathways carrying inappropriate signals. These waves destroy abnormal tissue, preventing it from causing abnormal heart rhythms. Artificial pacemakers can take over the job of generating electrical signals. They are not limited to treating low heart rates, newer pacemakers can also control high heart rates. They can operate for up to 15 years on a single battery to prevent heart arrhythmia. Some save energy by turning off when the heartbeat is normal. Most units are placed under the skin, requiring only minor surgery.
Unexpected situation
Many people are interested in whether a heart attack can develop in young people, as they say, out of the blue. “Yes, indeed, at a young age, myocardial infarction most often develops without previous heart pain. But, as we said above, if you pay attention in time to developing changes that at first glance are not related to the heart, you can begin to implement preventive measures in time and prevent the development of an attack,” says Galina Lazarenko.
Prevention of flaming motor. How to influence the age of the heart Read more
First aid for an arrhythmia attack
Defibrillators are devices that restart blocked heart muscles by delivering electricity to the chest. Defibrillators are effective in stopping the heart from ventricular fibrillation, but because ventricular fibrillation can be fatal in less than 4 minutes, they should be used as soon as possible. Most defibrillators are external devices, but there are now automated implantable cardioverter/defibrillators (AICDs). These devices can be as large as pacemakers. They can detect dangerous fibrillation and return the heart to normal before any damage is done.
Article sources:
- "New Theory of Arrhythmia" clarifies the causes of arrhythmia. Ermoshkin V.I. Educational bulletin “Consciousness”, 2015. p. 22-30
- Innovations in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmia. Zh.A. Arzykulov, A.A. Omarov, B.B. Kituev, F.A. Tursunova, A.A. Yeshtay, N.G. Pavlova. Bulletin of Surgery of Kazakhstan, 2012. p. 4-5
- On the issue of classification of cardiac arrhythmias. Batyanov I.S., Batyanova E.I. Cardiovascular therapy and prevention, 2005
- A look from the inside focuses on a patient with arrhythmia. Boqueria O.L. Annals of Arrhythmology, 2014. p. 196-199
- Cardiac arrhythmias from the point of view of their dimension. Ubiennykh A.G. Measurement. Monitoring. Control. Control, 2021. p. 70-76
- Epidemiology of arrhythmias (review of literature data). Zatonskaya E.V., Matyushin G.V., Gogolashvili N.G., Novgorodtseva N.N. Siberian Medical Review, 2021. p. 5-16
Preventive actions
“First, it is necessary to assess the risk factors when identifying the first signs of metabolic syndrome: increased abdominal circumference, increased blood pressure, increased cholesterol, C-reactive protein, blood sugar. You should immediately contact a cardiologist or endocrinologist. This will allow us to develop an individual plan of preventive measures as early as possible,” says Galina Lazarenko.
It is also worth quitting smoking as early as possible and optimizing physical activity. “All healthy people need moderate-intensity aerobic exercise for 30 minutes a day, 5 times a week, or vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise for at least 20 minutes a day, 3 times a week. Walking 10,000 steps a day every day is required.
Question answer
How can climbing stairs help check your heart health? You can determine the desired intensity of the load by your pulse during training. The maximum heart rate will be equal to the difference between 220 and the patient's age. 60-70% of the obtained value will be the optimal heart rate for moderate-intensity exercise, 75-85% for intense training,” notes the cardiologist.
And, of course, the doctor emphasizes, it is extremely important to normalize nutrition: exclude fast carbohydrates, alcohol, saturated fats (meat with visible fat, for example) from the diet, increase the proportion of foods containing polyunsaturated fats (omega-3 acids - they are contained in sea fish, olive, flaxseed oil), whole grains, vegetables and fruits (at least 5-6 servings per day), reduce salt intake (up to 2-3 grams per day).