In this article we will study an important characteristic of the heart - its pulse with a frequency of 80 beats per minute.
The pulse is a mirror reflection of the work of the heart itself. That is, this is the frequency of narrowing of the artery walls in response to heart contractions or beats. Each age and sex group has its own normal indicators. Therefore, a pulse of 80 beats cannot specifically indicate increased or increased indicators, because everyone has their own standards, which largely depend on lifestyle. The number of strokes of 80 is the maximum medical limit. But is it really dangerous and what to do in this case, we will find out in this article.
Heart rate indicators
The first thing every person should know is that a rapid pulse is how many beats there are in one minute, as well as what the normal limits are.
It is known that medicine calls an absolutely normal pulse of 60-80 beats in 60 seconds. And what’s interesting is that the younger a person is, the more often he experiences such a rhythm.
Depending on age, the pulse should show the following numbers:
For reference! In newborn infants, the normal heart rate is 140 beats per minute; in children aged 3 years and older, it is 100 beats per minute.
Accordingly, in adulthood, for example, at 45 years old, the norm will be 70 strokes.
Helpful advice
If you feel a palpitation, you should measure your heart rate yourself in order to record these indicators for your doctor. The easiest way to do this is on your wrist. Optimally - by palpation method. With 2-4 fingers of one hand, feel the pulsation of the radial artery near the thumb of the other hand. Press a little in this place and calculate the number of blows in 1 minute. If the wave is weak, you can measure the pulse in the carotid artery.
Causes of tachycardia
Tachycardia is an increased heart rate that occurs regularly . Moreover, the situation when in a person it is higher than 100-120 beats per minute can be observed from 15 minutes to several days in a row.
And the first thing to begin with the examination and treatment of such patients is to determine the reasons and factors why the pulse and heartbeat increase.
There are different reasons:
Physiological - a more harmless situation, which can be corrected in alternative ways.
It could be:
- excessive smoking of tobacco products;
- taking drugs;
- excessive coffee consumption;
- physical and nervous overstrain;
- intellectual loads;
- insomnia;
- temperature increase;
- taking drugs of a certain group;
- hot weather.
Pathological is a dangerous situation that can only be corrected by a medical specialist and competent treatment. It could be:
- vascular and heart diseases;
- blood diseases;
- presence of oncological tumors;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- endocrine disorders;
- severe infectious diseases.
Important! Diuretics, hormones, hypotensive drugs, nitrates, caffeine-containing or vagolytic agents, as well as sympathomimetics can provoke the development of tachycardia.
Main manifestations
Tachycardia is a symptom in itself, but it is often accompanied by other manifestations:
- feeling of heartbeat;
- increased pulsation of the carotid artery;
- the appearance of shortness of breath;
- dizziness;
- feeling of discomfort behind the sternum;
- feeling of anxiety, fear.
Almost all people with tachycardia feel their heartbeat. This is due to uneven blood flow and abnormal myocardial activity. This symptom has a name - palpitation. If such a feeling occurs during stress or physical activity and goes away over time, this is normal. In other cases, you need to consult a doctor to conduct an examination and find out the cause.
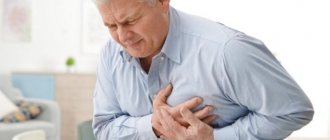
Feeling anxious is also a common symptom. The person seems to be afraid for his life, afraid of sudden death. When the heart rate stabilizes, the sensation goes away on its own. Accompanying tachycardia with pain or discomfort in the heart area is a dangerous symptom. It can occur against the background of damage to the heart muscle, for example, with covid pneumonia.
Consequences of increased heart rate
A pulse of 130 beats or more - is this normal or is it still dangerous?
The doctor will definitely notify him of the consequences of this condition.
Prolonged tachycardia can lead to the development of complex diseases, such as:
- arrhythmic shock;
- stroke;
- cerebral ischemia;
- thromboembolism;
- cardiac asthma;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- decreased immunity;
- acute ventricular failure.
An accelerated heart rate of 130 beats indicates certain risks, such as heart overload.
Which will sooner or later lead to its wear. The condition is accompanied by insufficient blood circulation and oxygen starvation, which will cause other organs and the brain to suffer.
Risks and consequences of tachycardia
A pulse of 130 creates the danger of rapid wear and tear of the heart, which is working under overload. This leads to the development of serious diseases of the cardiac and vascular systems.
Insufficient blood circulation, which occurs over a long period of time, leads to diseases of other organs. This happens because the oxygen in the blood does not reach the body's systems in sufficient quantities.
As a result, the brain and other organs suffer. Cerebral ischemia, various disorders in the endocrine system and other diseases develop that rapidly develop and lead to death.
As a result of impaired blood flow, red blood cells sometimes begin to break down and the ability of blood to clot is impaired. As a result, clots form that clog the blood vessels. Thromboembolism develops. Blood clots are localized in different areas. The cells of the body suffer from hypoxia. The combination of thromboembolism with an increased pulse is an explosive mixture. Trophic ulcers, stroke, and cardiac arrest may develop.
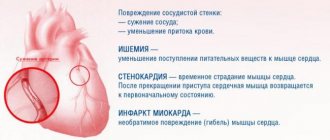
If the pulse rate increases during coronary artery disease, the myocardial muscle consumes oxygen in huge doses. The cardiac output is disrupted and hypoxia develops. Oxygen starvation provokes tissue death in the myocardium, which leads to stroke.
Ischemic stroke
With prolonged tachycardia, insufficiency develops in the ventricles of the heart, resulting in a disturbance in the large blood vessels of the valves. Blood does not enter the general circulation. Blood pressure begins to drop sharply, leading to cardiac shock, which carries a risk of death.
As a result of lack of oxygen, pulmonary edema and fibrillation sometimes develop, which can also cause death. The patient constantly loses consciousness, resulting in injuries.
A constant lack of oxygen in the blood provokes a disruption of metabolic processes in the body and a decline in immunity. The patient easily picks up any infections, which, in turn, aggravate the situation.
Pathological tachycardia is an extremely dangerous sign. It indicates that a person has a serious heart condition.
If attacks occur periodically, this indicates that the disease is developing in the initial stage. Don't delay visiting a cardiologist.
The main consequences of tachycardia are:
- development of heart failure;
- cardiac conduction disturbance;
- ischemic stroke;
- rapid wear and tear of the heart muscles;
- persistent oxygen starvation of the whole body;
- cardiac asthma;
- the onset of death.
Clinical picture of tachycordia
In order to promptly diagnose an attack of tachycardia, it is important to know the first and characteristic signs of this condition.
They are the following manifestations:
- darkness in the eyes;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- prostration;
- lightheadedness or fainting.
Prevention of tachycordia
If tachycardia regularly makes itself felt, you should resort to a number of manipulations to stop the attack. In some cases, it will be necessary to provide primary medical care to the patient to stabilize the heart.
If an increase in heart rate occurs during physiological tachycardia, it is possible, by taking certain preventive measures, to stop the attack and thereby alleviate the patient’s condition.
Doctors recommend lying down for a while and trying to relax. The heart will calm down and the signs of tachycardia will disappear.
If this doesn't help, you should try this exercise:
- Inhale, tense your muscles, hold your breath, exhale and relax.
- Repeat several times until your heart calms down.
The purpose of the exercise is to activate the parasympathetic system. Its main carrier is the vagus nerve. By straining it, we stabilize the pulse.
Massaging the carotid artery helps a patient stop an incipient attack of tachycardia. It is necessary to apply light pressure with your fingertips on the neck area under the lower jaw. If you inadvertently put more pressure on the artery, you may faint.
Cold water will also help prevent an attack of tachycardia. You need to put it in a basin and immerse your face in water for one minute. Cold will help relax the heart and stabilize its functioning.
Diagnostics
To confirm or detect tachycardia, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- heart rate determination;
- general examination of the patient;
- auscultation of the heart;
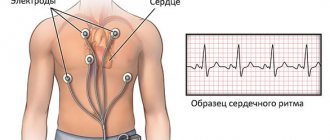
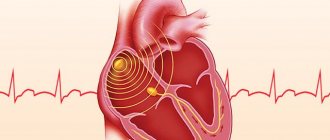
- ECG;
- phonocardiography (rare);
- Holter monitoring.
| Survey | Peculiarities |
| Pulse rate detection | Most often it is checked on the wrist, less often in the area of the carotid artery. If the rhythm is stable, the indicator is calculated over 30 seconds and multiplied by 2. For arrhythmia, it is measured over a minute. The method refers to primary diagnosis |
| General examination of the patient | Assess skin condition, presence of muscle weakness, response to questions |
| Auscultation of the heart | Standard heart sounds and murmurs are heard. With tachycardia, normal heart murmurs may be almost continuous |
| ECG | Allows you to evaluate the regularity of the heartbeat, frequency, location of the heart, whether there are areas of ischemia, impulse conduction |
| Holter monitoring | Continuous recording of heart dynamics on an ECG. Performed for rare periodic attacks of tachycardia |
Treatment for high heart rate
A rapid pulse in men and women above 100 beats per minute can develop at any time of the day. This can happen day or night, during nervous shocks or at rest.
What this means can only be determined by the attending physician. First, you can provide first aid to the victim.
It is as follows:
- providing the patient with bed rest and rest;
- deep breaths for patients, holding their breath, generally measured deep breathing;
- performing simple breathing exercises, which consists of taking deep breaths and quick exhalations for 10 minutes.
For short-term attacks of tachycardia, homeopathic medications are first taken. For example, tincture of valerian or motherwort.
You can also take Valocordin or Corvalol on your own.
If the patient requires complex medical treatment, the following drugs are used:
- beta-blockers (for example, Metoprolol, Atenolol, Timolol, etc.);
- antiarrhythmic drugs (for example, Diltiazem);
- sodium or calcium channel blockers (for example, Verapamil or Novocainamide);
- thyreostatic agents (for example, Mercazolil);
- sedative sedatives (for example, Persen, Valerian, etc.);
- tranquilizers in advanced cases (for example, Phenazepam, Alprazolam, etc.).
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine will tell you what to take when your heart rate is elevated to normalize your readings.
The following plant substances are recognized as the best stabilizers of the heart, blood vessels, and blood pressure:
- Melissa;
- linden blossoms;
- chamomile flowers;
- stinging nettle;
- Birch buds;
- lavender blossoms;
- lemongrass;
- green parts of mistletoe;
- mistletoe.
Advice! Traditional medicine can be used in practice in parallel with basic drug treatment. The main thing is that the chosen means are approved by the attending cardiologist.
According to the standard recipe:
- take a couple of glasses of boiling water
- dissolve 2 tablespoons of any plant material in it
- after which the mixture boils in a water bath for about 10-15 minutes.
It is also important to ensure that the body receives the full amount of magnesium. It helps to reduce tissue permeability, as a result of which potassium cannot enter the blood in unlimited quantities.
It is recommended to eat more of:
- soy;
- nuts;
- legumes;
- bran;
- dark green vegetables;
- crayfish and shrimp;
- chocolate;
- cocoa.
Proper nutrition during tachycardia does not independently reduce the pulse, but creates conditions for the action of drugs and prevents an increase in rhythm.
Necessary:
- give up alcohol, coffee and caffeinated drinks, reduce cocoa and chocolate consumption;
- take food in fractional quantities, avoid overeating;
- drink enough water;
- exclude spicy and hot foods from the diet;
- Foods high in potassium and magnesium are beneficial: legumes, peaches, bananas, melon, nuts.
If the cause of a frequent rhythm is neurocirculatory dystonia, then non-drug methods are successfully used:
- baths: pine, with essential oils (geranium, sage, rose);
- relaxing massage;
- reflexology (acupuncture, acupressure);
- electrosleep.
Good effectiveness in slowing heart rate was noted for dosed physical activity. At a low level of training, walking, therapeutic and breathing exercises, and yoga are used.
Exercises should not cause discomfort.
Is running safe with a heart rate of 120-130?
Running with a heart rate of 120-130 beats per minute is safe for the heart in the absence of diseases and for people under 55 years of age.
This load belongs to the recovery mode and helps:
- adapt the heart to the increased need for oxygen;
- open reserve capillaries;
- improve overall endurance;
- reduce the amount of fat in the body;
- strengthen muscles.
When training, trained athletes have a pulse of up to 150-160 beats. This rhythm leads to a gradual slowdown in resting heart rate if the training plan is correctly constructed.
If you are sick, you cannot rely on such numbers. It is necessary to choose a load that does not cause a deterioration in the nutrition of the heart; most often, a heart rate of 115-120 beats per minute is considered the limit.
Recommendations from experts
To prevent the development of pathological tachycardia, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle:
- spend more time in the fresh air,
- quit smoking,
- drink less alcohol.
It is necessary to sleep enough hours, try not to overload yourself physically, and avoid stress.
You can find out how to lower your heart rate when your heart rate is 130 beats per minute or higher by consulting a doctor.
- In severe cases, you need to call an ambulance and provide first aid to the patient. And then undergo a course of treatment with medications of different groups.
- The folk remedies indicated in the article are suitable for the prevention of tachycardia and further stabilization of the condition after the main treatment.
What to do?
If rapid heartbeat is a result of stress due to fear of coronavirus, the patient is advised to take sedatives. You can use not only pharmaceutical preparations, but also homemade products (tea with lemon balm, mint, motherwort, valerian, hops).
If there is no positive dynamics, the doctor may recommend a drug that directly affects heart contractions. You cannot select and take such medications on your own!
It is recommended to eat well, maintain a drinking regime, regularly ventilate the room, and patients should refrain from significant physical activity. It is recommended to give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol). Specialists also select a treatment regimen for concomitant pathologies in order to reduce the likelihood of complications, including those from the heart.
If tachycardia is caused by the development of pneumonia, antipyretic drugs are prescribed (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen), drugs to reduce intoxication of the body (drips in a hospital setting), antibacterial drugs are selected, and, if necessary, blood thinning medications are prescribed (to prevent blood clots).