Rheumatoid factor (RF) is a group of autoantibodies that react to particles entering the bloodstream from affected joints. Bacteria, viruses and other internal factors influence the properties of the protein. The body's immune system perceives them as foreign particles, as a result of which antibodies begin to be actively produced, which are detected in the laboratory.
The representative of rheumatoid factor is predominantly immunoglobulin M. At the beginning of the development of the disease, it is produced only in the joints in which pathological changes occur, but then it is also produced in the red bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes, and subcutaneous rheumatoid formations.
Little is known about the nature of rheumatoid factor, but we can say for sure that RF (rheumatoid factor) in a biochemical blood test indicates the presence of autoimmune and inflammatory processes.
This analysis is prescribed in the following cases:
- If rheumatoid arthritis is suspected (symptoms include pain, swelling, impaired mobility in the joints, as well as the formation of characteristic thickenings in the form of nodules under the skin);
- Sjögren's syndrome (patients complain of xerophthalmia (dry and burning eyes) and xerostomia (dry mouth));
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of unknown etiology;
- As an additional diagnostic method for autoimmune diseases;
- Included in the complex of rheumatoid tests.
Rheumatoid factor in the blood indicates many diseases, but one of the main ones is rheumatoid arthritis, which affects every 3 residents of Russia.
At the Yusupov Hospital, qualified rheumatologists are always ready to offer you any medical services. The department's specialists provide medical and advisory assistance to all rheumatology patients. The Yusupov Hospital uses modern instrumental and laboratory research methods to identify diseases at the earliest stages. There is a laboratory on the territory of the hospital complex, so you will not need to go to other medical institutions to get tested. The Yusupov Hospital was created to make it as comfortable as possible for patients to stay in the hospital.
Detailed description of the study
Rheumatoid factor (RF) is a group of antibodies to human tissues that are formed as a result of disorders in the immune system. The name of these antibodies explains their frequent detection in rheumatoid arthritis. However, RF may be elevated in other rheumatic and inflammatory diseases. Detection of RF is an important part of the diagnostic search when determining the causes of joint inflammation and confirming the presence of rheumatoid arthritis. This disease of an autoimmune nature develops mainly in women over 40-50 years of age. The reasons for it have not yet been sufficiently studied. The role of genetic and hormonal factors in combination with the adverse effects of the external environment is assumed. The formation of various antibodies to joint tissues leads to inflammation in them. Mostly small joints of the hands and feet are affected, inflammation is accompanied by redness and pain, and impaired motor activity. An important diagnostic sign of rheumatoid arthritis is stiffness in the limbs after waking up, which goes away within an hour. Chronic inflammation of the joints ultimately leads to their destruction and deformation of the hands and feet. RF is detected in more than 75% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Its titer weakly correlates with disease activity, but patients with high titers tend to have more severe rheumatoid arthritis. Sjögren's syndrome is a disease in which there is also an increase in RF levels. It is based on progressive damage to the salivary and lacrimal glands due to their erroneous destruction by the human immune system. Violation of salivary secretion is manifested by dry mouth, destruction of the lacrimal glands - dry eyes. There is insufficient hydration of the skin and mucous membranes. In addition, high RF titers can be found in a number of other diseases, which include: systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, tuberculosis, syphilis, viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, subacute septic endocarditis, autoimmune hepatitis and other autoimmune liver lesions. An increase in RF titer is sometimes observed among healthy people over 60 years of age, as well as during pregnancy and after blood transfusions (especially in the case of frequent blood transfusions). For a more accurate diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis, it is recommended to determine not only the RF, but also the antibody titer to the cyclic citrulline-containing peptide. The use of both tests increases diagnostic sensitivity.
Preparing for the study
No special preparations are required. It is recommended to donate blood on an empty stomach in the morning. You must stop drinking alcohol 24 hours before the test. It is advisable to refrain from smoking an hour before the study. The test results can be affected by taking a number of medications. In such cases, their use may be temporarily suspended in consultation with the doctor. If discontinuation of drugs is not possible, you must inform the laboratory staff about this. Children are given small amounts of water for several hours before donating blood. If additional preparatory measures are necessary, detailed recommendations will be provided by the attending physician.
References
1. Chaltsev, B. D., Vasiliev, V. I., Palshina S. G. [etc.]. Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of Schörgen's disease with anticentromere antibodies. Scientific and practical rheumatology, 2019. 2. Rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical recommendations. approved Ministry of Health of Russia, 2021. - URL: https://legalacts.ru/doc/klinicheskie-rekomendatsii-revmatoidnyi-artrit-utv-minzdravom-rossii/ (access date: 02/11/2021). 3. Croia, C, Bursi, R, Sutera, D, One year in review 2021: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Experience in Rheumatology, 2021.
Interpretation of results
To obtain a competent interpretation of the results of a blood test for rheumatoid factor
you need to see a doctor. When assessing them, it is necessary to take into account a large number of different factors that only a specialist can determine. The test results cannot be used for self-diagnosis. It is important to remember that self-medication can cause irreparable harm to health.
In the absence of pathologies, RF activity is low. Normally it is up to 14 IU/ml. An increase in indicators may indicate pathologies such as arthritis, biliary cirrhosis, cryoglobulinemia, malignant neoplasms, etc. A slight excess of the norm is possible in old age.
Sometimes patients present with characteristic symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, but RF levels remain within normal limits. In such cases, a comprehensive examination is carried out to establish an accurate diagnosis and choose treatment tactics. Test results are required to diagnose Sjögren's syndrome and to confirm rheumatoid arthritis. The results obtained are considered in conjunction with the clinical picture and medical history. It is impossible to confirm or refute the diagnosis based on test results alone.
Results of rheumatic factor analysis
Based on the results of the analysis, we can conclude that the rheumatic factor increases:
- slightly increased – from 15 to 50 IU/ml;
- elevated – 50-100 IU/ml;
- significantly increased – above 100 IU/ml.
By the amount of rheumatic factor, the severity of the autoimmune process can be determined.
The analysis is very important, since its result will show the presence and intensity of autoimmune processes and will allow you to quickly select the most effective treatment.
Indications for testing
Rheumatoid tests or rheumatic tests are prescribed by a doctor to confirm autoimmune pathologies:
- arthritis;
- thyroiditis;
- polymyositis and autoimmune prostatitis (in men);
- multiple sclerosis;
- scleroderma.
Often, a rheumatoid test is prescribed to determine pathological changes in connective tissue (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, gout).
Indications for such a study are the following symptoms of disorders in soft tissues:
- swelling and pain in the joints;
- changes in body asymmetry;
- impaired mobility of joints and ligaments;
- pain in the lower back, and with weather changes - aches throughout the body;
- frequent headaches that do not respond to analgesics (a symptom of vasculitis);
- prolonged increase in body temperature without a clear reason.
Rheumatological examination for such symptoms allows one to assess the activity of the pathological process and predict the further course of the disease.
How to prepare and take tests
Blood is drawn from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach, 8-12 hours after the last meal. In emergency cases and in infants - without prior preparation.
Seven days before the test, do not introduce complementary foods to your baby, but feed as usual the day before. The day before the test, in an older child, avoid eating fatty foods and physical exercise.
Are norms constant indicators?
Yes. However, numbers and units of measurement in different laboratories may differ, depending on the equipment, reagents and methods used.
Types of rheumatic tests
To confirm autoimmune diseases, a rheumatic complex of several types of markers is used:
- Antistreptolysin-O (ASLO) – identification of the body’s protective cells to streptococcal antigens. This is a kind of test for rheumatism, since ASLO in the blood helps to distinguish a similar disease from rheumatoid arthritis (the concentration of this marker in such pathologies is different).
- Rheumatoid factor (rheumofaktor). With rheumatoid disease, a protein appears in the blood, which the immune system accepts as a foreign body and begins to develop protection against it. The test for rheumatic factor consists of detecting such antibodies to self-antigens. The results allow the identification of connective tissue disease.
- C-reactive protein (CRP) is a type of rheumatic test that indicates an acute inflammatory process in soft tissues. The analysis helps to identify pathology in a timely manner and prescribe antibacterial therapy.
- Total protein. The marker makes it possible to determine the level of protein and its components - albumin and globulin.
- Circulating immune complexes (CICs). Identification of cells that are damaged by the body's protective compounds.
- General blood test (with leukocyte formula) - study of biological material for changes in the number of lymphocytes or neurophils. The test helps identify inflammation caused by infections.
Rheumatological analysis makes it possible to accurately determine the type and location of negative changes in soft tissues. Studying rheumatic tests in a biochemical blood test allows you to prevent the further development of a dangerous disease and select effective treatment.
Norms of blood parameters
There are generally accepted standards for rheumatic complex indicators that help confirm or refute the presence of pathology in the body.
Table “Acceptable values of rheumatic tests”
| Indicators and age group | Meaning |
| ASLO | |
| In adults | From 0 to 203 U/ml |
| In children (up to adolescence) | Up to 151 U/ml |
| Rheumatic factor | |
| In adults | Up to 15 IU/ml |
| In children (up to 12 years old) | Up to 13 IU/ml |
| C-reactive protein (regardless of age) | 0 (an indicator when the rheumatic test is positive, but not more than 5 IU/ml can also be considered a negative value) |
| Albumen | |
| In adults under 60 years of age After 60 years of age | 35–50 g/l 33–49 g/l |
| In children (up to 14 years old) | 37–54 g/l |
| Total protein | |
| In adults from 15 to 60 years | 65–85 g/l |
| In older people (after 60 years) | 63–84 g/l |
| The child is under one year of age | From 46 to 74 g/l |
| From one to 4 years | 60–76 g/l |
| 5-15 years | 58–77 g/l |
Values may vary slightly depending on laboratory, equipment and starting materials for analysis. Therefore, many research institutions indicate their limit norms for rheumatic test indicators on a special form.
Where can I get it and the price of the procedure?
Rheumatic tests can be done in any medical laboratory.
How much it costs, the analysis depends on the study itself:
- The price of a standard three-component rheumatic complex is on average 1230 rubles. ASLO – 300 rubles, C-reactive protein – 360 rubles, rheumatic factor – 300 rubles. The cost of collecting material is 270 rubles.
- The price of a comprehensive rheumatological examination is 2950 rubles. To the cost of a regular rheumatic test, a general blood test is added - 400 rubles, a study of erythrocyte sedimentation rate, albumin level - 500 rubles, detection of antinuclear antibodies - 550 rubles. Blood sampling for analysis – 270 rub.
Usually the doctor prescribes a standard rheumatic test. If its results do not coincide with the symptoms or the specialist has certain doubts, there is a need for a comprehensive rheumatological examination.
Analysis of rheumatic tests allows you to identify inflammatory processes in soft tissues in the early stages. Thanks to the study, it is possible to detect the cause of pathological changes, determine the dynamics of the disease and select adequate therapy. The main thing is that the results are reliable, and this largely depends on the correct preparation of the patient for the test.
Methods for determining RF in blood
There are three ways to detect rheumatoid factor.
- Nephelometry. Classic laboratory test. It is based on an approximate calculation of the quantitative index of autoantibodies.
To perform the test, a small amount of blood is taken. Then an intense light flux is passed through the biomaterial (it is specially prepared in advance).
The presence and actual amount of rheumatoid factor are determined by the degree of turbidity and the quality of the “solution”. This is one of the simplest and therefore popular diagnostic methods.
- Qualitative methods are sometimes used for screening. For example, latex test. For this analysis, a special reagent based on class G immunoglobulins is used. Rheumatoid factor is “tailored” to attack this substance, so it quickly reacts to a foreign compound.
Autoantibody particles settle on the latex. Next, doctors study the material and check whether there is rheumatoid factor.
This technique is not so popular because it does not answer the question of how much of the substance is in the blood. This is a purely screening method. Aimed at prevention and early detection of pathological processes.
- The most effective method is ELISA, also known as enzyme immunoassay. Allows you to check your blood for both the presence of rheumatoid factor and its quantity. Considered the gold standard for diagnosis. However, this is still not enough.
It is not enough to detect the presence of RF in the blood and the degree of excess of the norm. We need to find the cause of the changes. Because without correcting the basis, it is impossible to reduce the indicators.
When a child needs a biochemical blood test:
* Yellowness of the skin and/or mucous membranes is a suspicion of hepatitis or stagnation of bile in the gallbladder.
* Colorless stools - possible hepatitis (sometimes occurs without jaundice) or a disease of the gastrointestinal tract (for example, pancreatitis).
* Vomiting and diarrhea - often associated with pancreatitis or viral hepatitis A.
* Strong thirst and hunger, rapid weight loss and fatigue, frequent urination - indicates diabetes.
* Poor appetite and weight gain . It is not necessary that the child is sick, but he needs a comprehensive examination.
* Nausea, abdominal pain, repeated indomitable vomiting and a pronounced odor of acetone from the mouth are signs of diabetic ketoacidosis (complications of diabetes mellitus - a life-threatening condition) or an acetonemic crisis in neuro-arthritic diathesis.
Read more about neuro-arthritic diathesis here
Biochemical blood test - an assistant in assessing the functioning of the body
Allows you to judge the condition of many organs (liver, kidneys, heart, pancreas), the metabolism of proteins and some important substances.
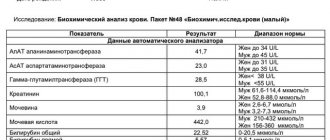
Norms
| Indicator and units of measurement | Age | ||
| 1 month | Up to 1 year | From 1 year to 14-15 years | |
| Total protein, g/l | 49-69 | 57-73 | 62-82 |
| Albumin, g/l | 34-44 | 36-49 | 37-55 |
| Total bilirubin, mmol/l | 17-68 | 3,4-20,7 | |
| Direct/bound bilirubin | 4,3-12,8 | 0,83-3,4 | |
| Bilirubin indirect/unbound | 12,8-55,2 | 2,56-17,3 | |
| ALT, U/l | 50-55 | Up to 40 | |
| AST, U/l | 73 gradually decreasing to 60 | 38-40 | |
| Alkaline phosphatase, U/l | 130-700 | 100 -600 | |
| LDH, U/l | 150-785 | From 1 to 6 months – 160-437, from 7 months to a year – 145-365 | 100-290 |
| Cholesterol, mmol/l | 1,6-3,0 | 1,8-4,9 | 3,7-6,5 |
| Triglycerides/mmol/l | 0,2-0,86 | 0,39-0,93 | 0,4-1,86 |
| B-lipoproteins, g/l | 1,5-3,5 | 1,4-4,5 | 3,55-5,5 |
| Glucose, mmol/l | 1,7-4,7 | 3,3-6,1 | |
| Uric acid, mmol/l | 0,14-0,29 | 0,14-0,21 | 0,17-0,41 |
| Creatinine, mmol/l | 35-110 | ||
| Urea, mmol/l | 2,5-4,5 | 3,3-5,8 | 4,3-7,3 |
| Amylase, U/l | up to 120 | ||
Decoding
| Index | Meaning | Increased | Downgraded | |
| Squirrels | They reflect metabolism and participate in the transfer of hormones, fats, and bilirubin. | Dehydration, inflammatory processes (autoimmune, infectious), chronic hepatitis. | Prolonged fever, poisoning, diabetes, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys. | |
| Glucose | Nourishes our cells. | Diabetes mellitus, diseases of the pancreas, liver and kidneys. | Insulin overdose, poisoning, fasting. | |
| Creatinine and urea | They are formed during the breakdown of proteins and are excreted from the body by the kidneys. | Renal dysfunction, intestinal obstruction, endocrine diseases, protein-rich diet, dehydration (diarrhea/vomiting). | Infections, malnutrition, liver disease. | |
| Bilirubin | The pigment is formed during the breakdown of red blood cells and turns the skin yellow. | Hepatitis, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, vitamin B12 deficiency, malignant tumors. | Does not have much diagnostic value. | |
| Amylase | Pancreatic enzyme | When the pancreas is damaged (for example, pancreatitis), the enzyme enters the blood. | — | |
| Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) | Enzymes produced in the cells of the liver, kidneys, muscles and heart. | Problems with the liver, kidneys or heart. | — | |
| Triglycerides and cholesterol | Reflects the metabolism of fats in the body. | They rarely deviate from the norm in children. | ||
| Uric acid | The end product of the breakdown of purines (found in meat, fish, smoked meats, canned food). | With food comes a lot of purines, neuro-arthritic diathesis. | Kidney damage, hepatitis, hereditary disorder of uric acid metabolism (xanthinuria). | |
| Alkaline phosphatase | Takes part in the exchange of calcium and phosphorus. | Hepatitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, rickets. | Excess vitamin D, decreased thyroid function. | |
Note: the tables show the most commonly used indicators. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe an extended study.