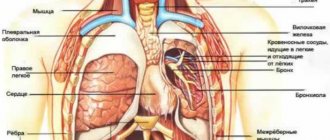
A burning sensation in the chest is a clinical manifestation of a number of pathological conditions. The rib cage (or, as it is also called, the chest) is a part of the body that contains the entire chest cavity and the upper component of the peritoneum. They are a “receptacle” for vital human organs. Discomfort in them often signals the presence of pathologies of the heart, liver, gastrointestinal tract or lungs.
You can get rid of this symptom forever only by identifying its initiating factor. To do this, you need to seek professional advice. The specialist with whom you make an appointment will conduct an examination and prescribe appropriate diagnostic tests, thanks to which it will be possible to accurately diagnose, determine a treatment strategy and begin to implement it.
Where to go if you have a burning sensation in your chest?
Are you a resident or guest of the capital and are you faced with a similar problem? Contact CELT. Our clinic is multidisciplinary and has departments of various specializations. You can make an appointment with a cardiologist, therapist, neurologist or gastroenterologist and get the help you need.
Our diagnostic department offers ample opportunities for correct diagnosis and identification of pathological conditions in the initial stages of development. Our staff is staffed with highly qualified specialists: doctors of the highest category, candidates and doctors of science with decades of medical practice behind them.
You can find out our prices by going to the “Services and Prices” tab in this section. To avoid misunderstandings, we recommend that you check the numbers with our operators by calling the number.
Physiological causes of burning in the chest
Experts identify a number of initiating factors for such a phenomenon as a burning sensation in the chest. The most common of these is poor diet, including fatty, spicy, salty foods, carbonated water and fast food, along with frequent overeating or eating food before bed.
The above leads to the contents of the stomach entering the esophagus, where it irritates the mucous membrane, which causes discomfort. They are accompanied by nausea, heartburn and belching, as well as bloating. In order to exclude this, it is enough to change your diet by minimizing the above-mentioned foods, optimizing portion sizes and eliminating the consumption of food before bedtime.
The same can be said about excessive consumption of coffee and alcoholic beverages, as well as smoking. All of them can cause a burning sensation in the chest, which will stop as soon as their consumption is reduced to a reasonable limit. It is important to understand that it is not the norm and its appearance is a reason to visit a doctor.
A number of reasons are associated with diseases of the cardiovascular system, characterized by the inability of blood vessels to provide the heart with a sufficient volume of oxygen. This occurs with ischemia, which is manifested by a local decrease in blood supply due to narrowing or blockage of the arteries, due to which the most important organ of the human body suffers.
Do not forget about neurological factors, when a burning sensation occurs due to compression or damage to the nerve ending or in stressful situations, with neuropsychiatric disorders. In addition, it can be caused by pathological conditions characterized by damage to the bronchial mucosa or trachea.
conclusions
There are many reasons why the heart burns. Most of them are associated with chronic pathologies that require complex and long-term treatment.
However, other sources of intense pain include pathologies that directly threaten human life. Therefore, at the first symptoms, which are accompanied by disorders of the nervous system (arms or legs begin to go numb), expressed by respiratory failure (shortness of breath, debilitating cough), consult a doctor for qualified help.
Diseases that cause burning in the chest
Only a doctor who has everything necessary for diagnosis can identify the cause of a burning sensation in the chest in the middle, right or left. You should not engage in self-diagnosis, as it is fraught with the risk of complications.
| Diseases | Triggering factors |
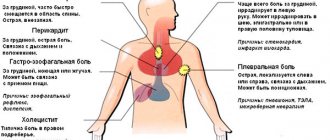
| Hearts | Sharp pain and burning in the chest near the heart may be a sign of a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. This occurs with the following diseases:
|
| Liver | Experts identify a number of diseases of the liver and biliary tract, the symptoms of which are manifested by a burning sensation in the sternum. These include:
Other clinical manifestations of the above diseases are as follows:
|
| Gastrointestinal tract | A phenomenon such as heartburn always leads to a burning sensation and pain symptoms due to irritation of the walls of the esophagus by gastric juice. As for diseases, one of the symptoms of which is a burning sensation in the chest, they are as follows:
|
| Intercostal neuralgia | It is a pain syndrome that develops as a result of damage to the intercostal nerves due to various reasons, ranging from compression to infection or intoxication. This syndrome is a sign that the patient has diseases of the organs of the chest wall, mediastinum, and spinal cord. Clinical manifestations are as follows:
|
| Pneumonia | Acute inflammatory infectious lesion of the lungs, which can be lobar or focal. Symptoms of the first include a cough, a sharp increase in temperature, burning and pain in the sternum, and weakness. As for the second, its onset is hardly noticeable; it appears after acute respiratory diseases. Clinical manifestations in addition to pain on inspiration, shortness of breath, cyanosis, wet cough. |
| Scoliosis | Persistent sideways curvature of the spinal column relative to its axis. A burning sensation in the chest occurs due to the fact that with this disease, abrasion of the intervertebral discs and compression of the nerve endings occurs, which provokes serious discomfort. |
| Intercostal myositis | Inflammatory processes of skeletal muscles located between the ribs. On palpation, pain symptoms appear along the entire intercostal space. Experts identify three pain points: the spinal column, the sternum and its lateral surface. In addition, there is swelling of the affected part, redness or, conversely, paleness of the skin, sore throat, cough and headache. |
Esophageal carcinoma
In very serious cases, untreated gastroesophageal reflux disease (and subsequent Barrett's esophagus) can lead to esophageal cancer. The main risk factors are alcohol consumption, smoking, poor nutrition, and chronic esophageal diseases with reflux.
Symptoms include weight loss, trouble swallowing, or gastrointestinal bleeding. This is something that happens over decades of untreated reflux (30-40 years), so those who are 30 and otherwise healthy have no reason to suspect cancer. But if you're over 50 and have had heartburn for years and suddenly lose weight, for example, this is definitely what your doctor will suspect first.
Which doctor should I contact if I have a burning sensation in my chest?
Regular repetitions of this symptom are a reason to contact a therapist. He will conduct an examination, collect anamnesis, ask questions that interest him - and either prescribe treatment or refer him to:
- gastroenterologist - if gastrointestinal diseases are suspected;
- orthopedist - if osteochondrosis is suspected;
- neurologist - if osteochondrosis is suspected;
- cardiologist - if you suspect diseases of the cardiovascular system.
They, in turn, will prescribe diagnostic tests to make an accurate diagnosis.
How is the diagnosis done?
In order to diagnose a symptom, the doctor only needs to conduct a survey and hear the patient’s complaints. The disease causing it can be diagnosed by conducting comprehensive studies. First of all, the patient is examined and a medical history is collected, after which laboratory tests of blood and urine, a detailed blood test, and determination of hormonal levels are prescribed. In addition, hardware tests are prescribed, the selection of which is based on preliminary studies. It could be:
- X-ray of the sternum;
- Ultrasound scanning of the internal organs of the chest cavity;
- Electrocardiography;
- Gastroenterological studies.
Methods for treating pneumonia
If pneumonia is bacterial in nature, antibiotics are prescribed. Their effectiveness can be assessed after 48-72 hours. If the temperature subsides, the cough becomes less frequent, and the patient begins to feel better, the treatment continues. You cannot interrupt the course of medications, and it is important to take them correctly as prescribed by your doctor. If antibiotics do not help, another treatment is prescribed or changed to a drug from another group.
For viral pneumonia, antibiotics are not effective, so antiviral drugs are prescribed. Vitamins and immunomodulators can be prescribed as auxiliary substances.
Once the patient's body temperature has returned to normal, physical therapy can be prescribed. It allows you to remove phlegm from the lungs. For this purpose, herbal medicines are often taken, for example, licorice root or complex breast mixtures.
Along with drug treatment, patients need bed rest, meals containing protein and vitamins, and plenty of warm drinks. For the best effect, therapeutic methods are recommended - electrophoresis, inhalation, massage, magnetic therapy, etc.
Preventive actions
In order to prevent the development of this unpleasant symptom, you need to take a number of measures:
- Treat inflammatory processes in a timely and correct manner;
- Eat right, minimize the consumption of salty, spicy, excessively fatty foods;
- To live an active lifestyle;
- Avoid stressful situations;
- Follow a daily routine, set aside enough time for sleep;
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations.
Don't forget: a burning sensation in the sternum can be a sign of serious illness. Its occurrence is a reason to seek professional medical help!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Barrett's esophagus
If left untreated for many years, persistent acid reflux can form changes in cells known as Barrett's esophagus, which is considered a precancerous condition. This condition does not cause many symptoms other than those of reflux. A doctor can diagnose it by performing an endoscopy.
If you have heartburn more than twice a week for a long time, or if you have symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease that are getting worse or you have discovered new ones that you didn't have before, these are all reasons to get checked and have an endoscopy.