Causes of rib pain
Pain on the left or right under the ribs can have a different nature, as well as the reasons that cause it. It can be strong and almost imperceptible, aching or sharp, occurring at certain moments or continuous. In almost every case, the cause of pain may be a disease that develops in the chest area.
At CELT you can get advice from a specialist algologist.
Make an appointment
Chest injuries
Chest injuries usually include fractures or bruises of the ribs. Fractures are characterized by ruptures of bone tissue and cartilaginous joints of one or more ribs. Depending on the injury, pain symptoms may be constant, aching, or acute and intense.
Bruises are characterized by mild pain, which is accompanied by swelling and the appearance of a hematoma in the area of injury. As a rule, pain symptoms disappear after seven to ten days. Fractures require mandatory diagnosis in order to exclude the possibility of injury to the soft tissues of the lung or other internal organs. Depending on the side of the injury, the pain can be localized on the right or left under the ribs or between them. Its intensity and duration depend on how severe the injury was.
Intercostal neuralgia
Pain between the ribs along the nerves can occur due to the following diseases:
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine;
- vertebral protrusion;
- intervertebral hernia.
Attacks in the form of shooting pain, similar to an electric shock, occur due to pinched or irritated nerve roots, and their appearance can be triggered by the following factors:
- hypothermia;
- penetration of infection;
- exercise stress;
- getting a back injury.
The pain becomes stronger with strong inhalations/exhalations or attempts to change body position.
Costochondritis
Costochondritis (or, as it is also called, Tietze's syndrome) is a disease in which thickening of the cartilage tissue of the ribs occurs, leading to their pain. Pain is not localized in one place and can spread to the entire sternum. They can be quite strong and appear brighter with sudden movements, deep inhalations/exhalations or coughing. Pain may be accompanied by:
- local edema;
- an increase in temperature in the area of the pathological process.
It appears suddenly and in its manifestations is comparable to an angina attack.
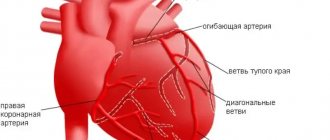
Angina pectoris
Angina is characterized by constant, pressing pain behind the sternum and sometimes between the ribs. It is localized in the retrosternal region and can spread to the left side of the neck, left arm and left side of the chest and may be accompanied by:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- feeling of fear.
Other reasons
In addition, pain in the ribs can occur with the following diseases:
- malignant neoplasms (in particular, osteosarcoma of the ribs) are characterized by dull pain at the beginning of the disease, which becomes more and more pronounced as it develops;
- fibromyalgia - pain occurs when trying to raise your arms or turn your torso;
- pleurisy - pain symptoms manifest themselves with coughing and deep inhalations/exhalations;
- herpes zoster - characterized by intense pain under the ribs in the right or left side, which is accompanied by itching or burning.
Another reason is hypertonicity of the pectoral muscles, which occurs as a result of intense physical activity. The pain in this case increases and is localized in the intercostal space.
More about fibromyalgia
Why might my right side hurt?
The causes of this symptom are usually associated with internal organs. “This is a sign that something located on the right side of the abdomen is suffering,” says Bulat Yunusov, a surgeon at GMS Clinics and Hospitals. “The cause of damage to these organs can also be different, for example, inflammation, oncological processes, trauma, consequences of previous operations, neurological disorders.”
However, this symptom may have other reasons. “An unpleasant sensation in the right side can be muscular in nature, especially if it occurs after physical activity. If a person falls on their right side, the pain may be associated with muscle contusion or injury, such as myositis. Gallstones can also cause an uncomfortable tingling sensation in your side. The stones close the ducts, which leads to swelling of the bladder and, as a consequence, to the occurrence of calculous cholecystitis, that is, an inflammatory process. All this, of course, is accompanied by pain,” commented an invited specialist from another medical center. Let's look at the main causes of pain in the right side.
Diagnosis of rib pain
If you are suffering from rib pain, contact the CELT Pain Clinic. We employ doctors of various specialties who will use the entire arsenal of diagnostic and treatment capabilities of our multidisciplinary clinic to solve your problems. Since there are many reasons that cause pain in the ribs, it is very important to correctly diagnose. This is the only way to correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
If you experience pain, contact one of our specialists:
- therapist;
- neurologist;
- traumatologist;
- pulmonologist;
- cardiologist.
Diagnosis in our Pain Clinic, in addition to examination by a doctor and medical history, may include:
- laboratory research methods;
- cardiography;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging.
Conservative therapy
The most common treatment option is conservative therapy with anticoagulants. Drugs used for inferior vena cava syndrome include the anticoagulant warfrin or Xarelto. Detralex or phlebodia are used to improve blood flow from the legs. The main means of conservative treatment is the constant wearing of compression tights of compression class 2-3. They need to be changed every 3 months, as they lose their properties with prolonged wear.
Treating the symptoms of inferior vena cava syndrome with medications and compression can reduce chronic venous insufficiency. Considering the technical complexity of surgical treatment, conservative methods are predominant in modern medical practice.
Treatment for rib pain
Treatment of rib pain is primarily aimed at eliminating the original cause that caused it. In case of severe pain, symptomatic therapy is used. It involves the use of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If we are talking about diseases for which thermal procedures are indicated, ointments with a warming effect are used, if the pain occurs due to muscle spasms - antispasmodics.
Physiotherapeutic procedures, massage and manual therapy can relieve pain in the ribs due to osteochondrosis and hypertonicity of the pectoral muscles. After the pain goes away, the patient may be prescribed physical therapy.
In case of chest injuries, the specialists of the CELT Pain Clinic will recommend a state of rest, in which not only the injured area, but also the patient as a whole should remain. This way, healing will be much faster. Can use a chest bandage that prevents sudden movements and deep inhalations and exhalations.
By contacting the CELT Pain Clinic, you can count on professional treatment that is sure to be successful!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Diseases of the urinary system
Often the side on the right side hurts due to the organs of the excretory system. “These include urolithiasis and pyelonephritis,” says Bulat Yunusov.
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory disease of the kidneys, in which, in addition to pain in the right side, weakness, nausea, vomiting, “jumping” pulse, dry mouth, and high temperature may also occur.
Pain in the side due to urolithiasis can be constant or wave-like, dull or sharp, it can only bother you at rest or intensifies when walking. It depends on the location of the stone, but sometimes the pain may first be felt in the lumbar region (so-called “renal colic”), and only then “settle” in the right side.
Pain in the right side not associated with internal organs
Abdominal pain with depression
. Depression is accompanied by increased anxiety and increased levels of norepinephrine and cortisol. They cause spasms of smooth muscles, including the intestines. The person experiences symptoms characteristic of indigestion. Moreover, this is not associated with eating low-quality food. Abdominal pain cannot be relieved by medications because it is psychosomatic in nature.
A severe and persistent cough also causes abdominal pain
. This is due to the increased load on the abdominals, which not everyone has trained and strong. Often coughing, the patient strains the muscles, they stretch and put pressure on the diaphragm, causing a dull pain. It goes away on its own after the cough is cured.
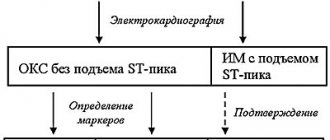
How is diagnosis carried out in patients who often experience heart pain?
An ECG is the most important initial diagnostic procedure for frequent chest pain. Abnormalities detected by an ECG help doctors determine the type of treatment needed. Abnormalities on the ECG also help determine where the heart muscle has been damaged. If several ECGs recorded over a period of several hours are completely normal, doctors consider a heart attack unlikely.
Measuring levels of certain substances (called cardiac markers) in the blood also helps doctors diagnose abnormalities. These substances are usually found in the heart muscle, but only enter the bloodstream when it is damaged or dead. The most commonly measured are heart muscle proteins called troponin I and troponin T, and an enzyme called creatine kinase. Blood levels rise within 6 hours of a heart attack and remain elevated for several days. Levels of cardiac markers are usually measured upon admission to the hospital and at 6 to 12 hour intervals over the next 24 hours.
When ECG and cardiac markers do not provide sufficient information, echocardiography can be performed. It may show decreased mobility of part of the left ventricular wall. This suggests damage due to a heart attack. Other tests are used to determine whether a person needs additional treatment or is likely to have heart problems. For example, a person may have to wear a Holter monitor, which records the heart's electrical activity over a 24-hour period. This procedure allows doctors to determine whether a person has an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) or episodes of poor blood flow without symptoms (silent ischemia).
An exercise test (electrocardiography done during exercise) before or shortly after discharge can help determine how well a person is doing after the attack and whether ischemia continues.
During an exercise tolerance test (stress test), a person walks on a treadmill at an accelerating pace. A blood pressure cuff monitors your blood pressure throughout the procedure. The video monitor displays the pulse and ECG. The results help determine the presence of coronary heart disease.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis of abdominal pain on the right, the doctor prescribes the following tests.
Blood tests
A clinical blood test reveals signs of inflammation (increased leukocytes, accelerated ESR). Appendicitis is characterized by a sharp increase in the level of leukocytes to 15x109/l. Liver tests evaluate liver function.
Analysis of urine
A general analysis and, if necessary, urine culture exclude/confirm kidney inflammation and the presence of stones.
Stool tests
The coprogram diagnoses gastrointestinal diseases. If an intestinal infection is suspected, a stool culture is performed. A test for occult blood is prescribed when bleeding is suspected (for example, in Crohn's disease). Children who complain of abdominal pain are tested for dysbiosis and worm eggs.
Instrumental methods
Ultrasound (including Doppler mode) is the safest method for examining the abdominal cavity, pelvic organs and kidneys. The study is carried out for abdominal pain of any location in adults, pregnant women and children of all ages. If you suspect a disease of the stomach and gallbladder, it is advisable to undergo an FGDS. Pathology of the small intestine is diagnosed using x-rays. For colitis, colonoscopy is prescribed. However, the doctor receives the most accurate information about organic changes in the gastrointestinal tract using CT/MRI.
Abdominal pain on the right side in men
Dull abdominal pain in men most often occurs due to an inguinal or umbilical hernia. The reason is excessive physical activity. A bulge in the groin often develops in boys under 1 year of age due to weakness of the ligamentous apparatus, so babies should not be allowed to cry angrily for a long time. Umbilical and inguinal hernias are eliminated with plastic surgery (suturing the hernia opening or strengthening it with a special mesh). Without timely surgical intervention, strangulation of the hernia is highly likely. The pain increases, spreads to the entire abdomen, patients note frequent vomiting, stool retention and bloating. The surgery is performed on an emergency basis.
Pain in the lower back, radiating to the groin and leg, is characteristic of protrusion and herniation of the intervertebral disc. Patients often complain of weakness and numbness in the legs. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe an effective course of anti-inflammatory drugs. If necessary, a therapeutic blockade or surgery is performed.
Diseases of the genitourinary system in men (cystitis, prostatitis, prostate adenoma) are manifested by pain in the lower abdomen, which subsides after defecation and urination. However, sometimes the pain is worse on the right or left.
With orchitis (inflammation of the testicle) and vesiculitis (an inflammatory process that develops in the seminal vesicles), the temperature suddenly rises, a sharp or dull pain radiates to the groin and perineum, and intensifies when walking down the stairs and physical activity. The damaged testicle swells. Inflammation of the testicles often complicates the course of sexually transmitted diseases and is fraught with infertility.
Varicocele (varicose veins of the spermatic cord) is diagnosed in every fourth man under the age of 30. The disease is often asymptomatic and is diagnosed during clinical examination of adolescents. Only in severe cases does aching pain occur on one side of the scrotum and in the groin. Pain increases with overheating, physical exertion and during sexual intercourse.
When testicular torsion occurs, a sharp pain suddenly occurs in the scrotum on one side, radiating to the groin, perineum and lower back. In young boys, the disease is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Palpation reveals a higher position of the testicle in the scrotum. The pathology is eliminated urgently.
Important! If you suspect prostatitis, prostate adenoma or testicular disease, you should contact a urologist-andrologist.