Issues discussed in the material:
- What is the reason for the development of congestive pneumonia in older people?
- What are the features of the course and diagnosis of congestive pneumonia in older people?
- What is the treatment for congestive pneumonia in the elderly?
- What measures prevent the development of congestive pneumonia in older people
Hypostatic (congestive) pneumonia in older people proceeds completely differently than in young people. The main reasons are the age of the patient and the weakness of the immune system. It is important to diagnose and properly treat this disease in time to avoid negative consequences. But it is quite difficult to identify congestive pneumonia in older people, therefore, even minor deterioration in health cannot be ignored.
Causes of congestive pneumonia in older people
Older people are more likely to be exposed to factors that worsen their health and suffer from chronic diseases. And, as a rule, such patients are conscious about their well-being, try to constantly visit doctors and treat their ailments.
But congestive complications appear unexpectedly, so it is impossible to diagnose their development in advance. He who is forewarned is forearmed. Therefore, knowing the nature of the origin of hypostatic pneumonia in older people, you can prevent its occurrence.
Over the years, age-related changes are inevitable; they affect all life support systems. In the respiratory system, this is expressed in weakening of the diaphragm muscles, uneven breathing, and a decrease in the elasticity of lung tissue.
However, it is not only advanced years that affect the risk of inflammatory processes. There are a number of other interdependent factors. If several negative causes are simultaneously observed, then it will not be easy to cure pneumonia, and the course of the disease itself will be severe. Consider these factors:
- Recumbent state. An acute form of pneumonia, namely hypostatic, occurs in patients who have suffered a serious illness (heart attack, stroke) or surgery, that is, they are forced to remain motionless for a long time. In such a situation, microbes spread faster, and even a harmless acute respiratory infection becomes a source of inflammation.
- Treatment of other diseases with a large number of drugs, which reduces the body's ability to resist infections.
- Diseases of the heart, blood vessels, genitourinary system, diabetes mellitus, malignant tumors.
- Chronic forms of diseases of the respiratory system.
If an elderly patient has at least two factors, then there is a high risk of congestive pneumonia.
We recommend
“Swelling in the elderly: causes, treatment, medications” Read more
Symptoms
The severity of clinical manifestations of congestive pneumonia depends on the severity of the underlying pathology, the degree of ventilation and hemodynamic disturbances, and the addition of the inflammatory process. But in general, the symptoms of congestive pneumonia do not differ from the symptoms of ordinary pneumonia. Hypostatic pneumonia manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- wheezing in the lungs;
- cough;
- low-grade fever;
- weakness and excessive sweating;
- chills;
- shortness of breath, which worsens with physical exertion;
- a small amount of sputum, there may be purulent discharge, blood in the sputum.
The severity of symptoms depends on the duration and severity of the disease. The danger of congestive pneumonia is the cessation of participation of the affected alveoli and lung tissue in the respiratory process. In a bedridden patient, the cough reflex does not work, sputum does not come out - the patient’s condition worsens, and larger and larger areas of the organ cease to participate in breathing. The active activity of microorganisms leads to intoxication, the patient loses appetite, experiences headaches, pain in muscles and joints.
Congestive pneumonia can be early (in the first 2-3 days of bed rest) and late (from the second to the sixth week). Early congestive pneumonia often occurs under the guise of the underlying pathology. Thus, during a stroke, patients have severe breathing disorders (noisy, bubbling, arrhythmic) and impaired consciousness. In patients suffering from cardiovascular diseases, a manifestation of congestive pneumonia may be an increase in signs of heart failure.
Make an appointment
Consequences of congestive pneumonia in the elderly
Early diagnosis of inflammation and proper therapy reduce the likelihood of serious problems, such as the development of purulent processes. Poor health depends not only on the number of years lived and the duration of development of complications, but also on concomitant diseases. For example, if a patient has diabetes or suffers from alcohol addiction, then the likelihood of negative events occurring increases.
Complications of hypostatic pneumonia can cause breathing problems, which will also affect the cardiovascular system. With an unfavorable course and untimely treatment, negative consequences are possible - the death of the patient.
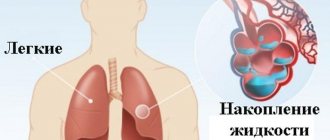
Congestive pneumonia causes inflammation of the outer lining of the heart (pericarditis) or accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity (exudative pleurisy). The disease can damage both the lower parts of the right lung and both organs.
In most cases, the phenomenon of congestive pneumonia is observed precisely in patients forced to lead a recumbent lifestyle.
We recommend
“Senile dementia: causes, symptoms, patient care” Read more
Diagnostics
Due to the low specificity of clinical symptoms and the predominance of the severity of symptoms of the underlying disease, the diagnosis of congestive pneumonia in most cases presents a certain difficulty. The Yusupov Hospital employs pulmonologists, cardiologists, neurologists, and traumatologists who are wary of bronchopulmonary complications in bedridden patients.
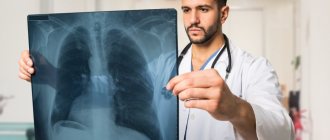
During auscultation of the lungs with congestive pneumonia, hard breathing and moist fine bubbling rales are heard in the posterior lower parts of the lungs. In this case, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe an X-ray of the lungs. It allows you to detect a unilateral or bilateral decrease in the transparency of the lung fields, increased pulmonary pattern, focal and focal shadows, linear shadows in the basal sections, expansion of the shadow of the roots of the lung, hemosiderin nodules.
Using ultrasound examination of the pleural cavity and pericardium, the presence of effusion in the pleural cavity and cardiac sac is determined. Patients with congestive pneumonia must have an electrocardiogram recorded and echocardiography performed. In the blood test for congestive pneumonia, the changes are minimal: there is a slight leukocytosis with a neutrophilic shift to the left, an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. During a microscopic examination of sputum in patients with congestive pneumonia against the background of heart defects, laboratory assistants detect groups of cells containing hemosiderin.
Diagnosis of congestive pneumonia in the elderly
Determining the presence of congestive inflammation in older patients is quite difficult. It happens that doctors do not take into account the manifestations of the disease, but often, playing it safe, they make an unjustified verdict.
To accurately detect pulmonary inflammation you should:
- Undergo an X-ray examination. If there is an inflammatory process, then the image will show an accumulation of fluid.
- Do an ultrasound examination of the space around the lungs. Ultrasound allows you to identify fluid stagnation and where it accumulates in the lungs.
- Listen to the chest with a phonendoscope or stethoscope. Signs of inflammation will be indicated by hoarseness when inhaling and exhaling, as well as gurgling sounds.
Based on the studies performed, the doctor may prescribe additional ones, for example, a blood test, bacterial cultures, etc.
We recommend
“Why blood pressure drops in older people: causes and treatment” Read more
What is hospital-acquired pneumonia
Hospital or nosocomial (another name is nosocomial) pneumonia is inflammation of the lungs that occurs during hospital treatment as a complication.
For pneumonia to be considered hospital-acquired, it must appear no earlier than 2 days after the patient was admitted to the clinic. In addition, the key characteristic of this type of pneumonia is the pathogens. Inflammation is caused by the so-called nosocomial, multi-resistant flora.
Hospital-acquired pneumonia is one of the three most common complications of hospital treatment; most often, only wound suppuration and inflammation of the urinary tract occur.
How is congestive pneumonia treated in the elderly?
A mild form of inflammation can be quickly cured with drug therapy. Hypostatic pneumonia is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the lungs and bronchi, and is therefore treated with other drugs.
Treatment includes the simultaneous administration of bacteriostatic drugs (macrolides) and antibiotics from the class of aminopenicillins or cephalosporins. These medications are prescribed immediately upon detection of the disease, regardless of the results of the bacterial test, since the test readiness period is at least five days. When the exact class of microorganisms is identified, antibacterial therapy is changed if it did not work at the initial stage.
Treatment of congestive pneumonia in older people takes place strictly in a medical institution under the supervision of specialists.
Together with therapy aimed at eliminating the localization of inflammation, treatment is prescribed for the proper functioning of the respiratory system. For this they prescribe:
- drugs that reduce the accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues (diuretics);
- immunomodulatory drugs and antioxidants;
- medicines that facilitate the discharge of sputum.
For the cardiovascular system, glycosides and medications aimed at restoring metabolism are prescribed. Sputum can accumulate not only in the lungs, but also in the bronchi and trachea. To determine it, a special study is performed - bronchoscopy. Based on the examination results, if fluid is present, diuretics are prescribed and punctures are taken.
Along with drug therapy, physical procedures are used: inhalations, massages, oxygen masks, breathing exercises (using the methods of Buteyko and Strelnikova). Elderly patients are also advised to practice deep breathing, which is performed using the diaphragm.
When acute signs of inflammation are relieved and patients feel well, they are allowed to go home, where they are advised to continue treatment with prescribed medications and traditional methods. These include drinking plenty of water: berry teas and decoctions of medicinal herbs (thyme, rose hips).
It happens that a congestive inflammatory process is very difficult: the patient constantly lies down, it is difficult for him to breathe. In such cases, doctors prescribe a puncture of the chest to remove large amounts of sputum.
We recommend
“Vitamins for elderly people over 70: which ones are needed first” Read more
Modern methods of treatment
The main problem in the treatment of this disease is the resistance of hospital microbes to antibiotics used to treat common pneumonia.
Therefore, medications are selected only after studying sputum culture data and determining the sensitivity of bacteria to the drug. Most often, drugs from the reserve group are used - cephalosporins of 3-4 generations, protected penicillins, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones. Sometimes extremely rare drugs are needed. The doctor also recommends:
- move as much as possible so that there is no stagnation of phlegm in the lungs;
- perform simple breathing exercises and exercise therapy;
- drink more fluids (if this is not possible, systems with saline and glucose are installed);
- use antipyretics for fever (Nurofen, Ibuklin, Paracetamol, Fervex, Rinza);
- use medications to thin and remove mucus (Fluimucil, ACC, Ambrobene, Bromhexine, Pertussin);
- wear compression stockings to prevent thrombosis in the legs;
- take vitamins.
Prevention of the development of congestive pneumonia in older people
Hypostatic inflammation in older people develops against the background of other diseases, therefore, to prevent the occurrence of pneumonia, certain preventive measures should be followed:
- Maintain a comfortable temperature in the room: do not overheat and do not overcool.
- Be outdoors often, regardless of the weather. You just need to dress according to the weather conditions.
- Rest more and don't worry.
- Get rid of bad habits: alcohol, smoking.
- Take the right foods that contain essential minerals and vitamins. First of all, this applies to red fish, meat and legumes - these products are rich in zinc.
- During periods of exacerbation of seasonal epidemics, it is necessary to get vaccinated on time.
- For bedridden patients, the following preventive methods are indicated: - do percussion massage for better sputum discharge, avoiding the area near the heart;
- use jars and mustard plasters;- do not lie in bed in one state, constantly change your body position;
- do some physical and breathing exercises. For example, move your arms and legs, inflate balloons;
— keep the room clean (wet cleaning, ventilation).
Congestive complications of pneumonia in older people can be successfully treated without serious health consequences. The main thing in this matter is timely diagnosis and competent therapy.