Gangrene
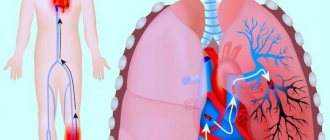
- This is the death of a part of the body. The cause of gangrene can be frostbite, burns, trauma, infection, but most often it occurs when there is insufficient blood supply to the organ (this condition is called ischemia). Most often, blood circulation is disrupted in the lower extremities and leads to necrosis of the fingers, foot or entire leg. Ischemic gangrene of the upper extremities and internal organs is less common.
There are several types of gangrene:
1. Dry gangrene
. This type of gangrene is the least dangerous for the patient. Develops gradually against the background of ischemia. The tissues mummify (dry). Sometimes the outcome is self-amputation. There is no development of infectious processes.
2. Wet gangrene
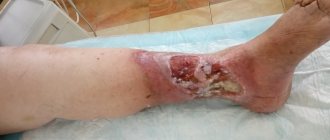
. This type of tissue necrosis is accompanied by the addition of an infection with rapid proliferation of bacteria, which is accompanied by severe intoxication and can lead to blood poisoning. Wet gangrene requires urgent measures to be taken to eliminate it; in the absence of urgent treatment, it can lead to death.
3. Gas gangrene
. It happens rarely, is a type of wet gangrene, caused by infection with bacteria of the genus Clostridia. It has a lightning-fast course, severe intoxication and requires emergency amputation of the affected limb.
Causes of gangrene of the lower limb
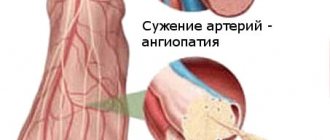
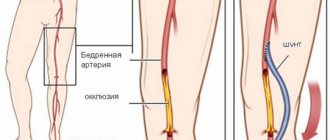
1. Obliterating atherosclerosis of the arteries of the lower extremities
. The most common cause of ischemia (lack of blood supply). In this case, the disease develops gradually. First, pain and cramps in the legs may appear when walking, then at rest. If the pain in the leg becomes constant and becomes unbearable (the pain can be reduced by sitting, hanging the leg down), the leg becomes cold, pale (when walking, the color may change to bluish-purple due to swelling of the veins), this condition is called critical ischemia and requires urgent treatment. As a rule, at this stage, drug therapy is ineffective and surgical restoration of blood flow is necessary to save the leg.
2. Diabetes
with foot damage (diabetic foot syndrome) is also often the cause of gangrene of the lower limb. In this case, gangrene may be limited in nature, affecting the fingers and parts of the foot, or it may develop as a wet gangrene with the progression of the infectious process and rapid spread. Treatment should be comprehensive and include fighting infection, restoring impaired blood flow, and controlling disorders caused by diabetes. If not treated in a timely manner, loss of a leg and blood poisoning with serious consequences are possible.
3. Acute ischemia
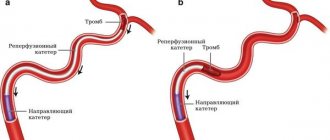
. Develops with thrombosis of the arteries supplying the leg or embolism from the cavities of the heart with atrial fibrillation, aortic aneurysm cavity or iliac arteries. Develops suddenly and requires emergency surgery to remove the blood clot.
4. Obliterating endarteritis (Buerger's disease), Raynaud's disease
. Chronic diseases characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the arteries of the extremities, gradually progressing throughout life, can lead to gangrene in the terminal stage. There are therapeutic treatment regimens that slow down the pathological process. In case of severe ischemia, microsurgical methods of restoring blood flow are used.
Causes of gangrene of the legs in diabetes
The patient’s reduced sensitivity to pain very often becomes the reason for the patient’s delay in seeking help. Gangrene develops, body tissues become infected with cadaveric substances, but there is no pain, and the person continues to not notice the deterioration. Signs indicating the imminent occurrence of gangrene:
- calf pain, foot deformity;
- constant feeling of tired legs;
- discomfort in the foot (tingling, itching);
- change in the normal color of the foot to red or bluish;
- numbness of the legs;
- calluses.
Symptoms of gangrene:
- strong purulent discharge;
- lack of blood supply to the affected area;
- nausea (due to intoxication of organs with cadaveric elements);
- elevated temperature;
- the skin around the affected area becomes purple or black;
- constantly increasing pain in the affected area.
Treatment methods for gangrene of the lower limb
Treatment of gangrene must be comprehensive, using both surgical and conservative methods. Conservative methods are aimed, first of all, at suppressing the activity of infection, improving the general condition of the patient, and treating diseases against which gangrene has developed. The goal of surgical treatment is to separate viable tissue from dead tissue and remove the latter. In this case, maximum efforts are made to preserve the limb.
The Hospital provides therapeutic and surgical treatment for critical ischemia, incipient gangrene of the lower extremities, diabetic gangrene, including in cases where the patient was refused to save his leg by other medical institutions. If it is impossible to stop gangrene on the foot, and amputation is inevitable, everything possible is done to preserve the knee joint, which in the future facilitates prosthetics and prolongs the patient’s active life.
Surgery
The following surgical treatment methods can be used:
- surgical sanitation of the gangrene focus;
- balloon angioplasty and stenting of the arteries of the lower extremities;
- endarterectomy (removal of atherosclerotic plaques from the lumen of the vessel)
- bypass;
- amputation (if other treatment is not possible).
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Surgical method
Surgery is necessary for wet gangrene because it is the only way to save the patient’s life. During surgery, the surgeon removes the infected tissue and all tissue located near the affected area. When using the surgical method, the following operations are also performed:
- blood transfusion;
- detoxification therapy (use of antibiotics).
Surgical intervention for gangrene of the legs involves amputation of the limb
Along with the treatment of gangrene, actions can be taken to eliminate other complications:
- microsurgical bypass surgery, which makes it possible to save the foot if gangrene of the toe is diagnosed;
- treatment of ischemia, aimed at reducing pain during the development of wet gangrene;
- stenting allows you to reduce the severity of surgery, and sometimes avoid amputation;
- removal of blood clots using a probe.
Wear only comfortable shoes to avoid the appearance of blisters
Mechanism of diabetic foot
Nerves are affected, tissue sensitivity is dulled, so a person may faintly feel pain from cracks on the soles, small ulcers on the skin of the foot. This phenomenon is called diabetic neuropathy, and it is extremely insidious.
Minor injuries take a long time to heal, but the patient does not take them seriously, as the level of pain decreases. By the way, this prevents many diabetics from feeling that they are wearing the wrong shoes, which injure their feet. Only over time do the growing ulcers and cracks begin to interfere with walking.
Due to deterioration of tissue nutrition:
- the skin of the foot becomes darker;
- ulcers form on it;
- the shape of the nails changes;
- bones are deformed;
- joints work poorly.
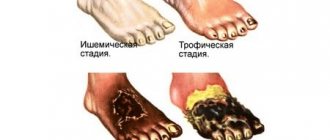
As a result, any bruise threatens to form a wound into which infection and bacteria can easily penetrate. In turn, they soften the tissues - the wounds grow into trophic ulcers, the cells begin to die, forming black necrotic areas. The process affects the subcutaneous fat, muscles, and then penetrates the ligaments and bones. Eventually, gangrene, abscesses, and phlegmon develop from the ulcers.
Causes
Often, diabetic foot syndrome is a consequence of diabetes mellitus, which is accompanied by atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension, smoking, and alcohol abuse.
However, a diabetic leg ulcer can also be caused by a seemingly harmless cause. People suffering from diabetes may not pay attention to calluses, corns, cracked heels, or ingrown toenails that appear due to tight shoes. Meanwhile, these small injuries provoke the disease.
Diabetes mellitus negatively affects the functioning of the entire body, but the lower extremities suffer the most (especially since they bear a serious daily load). Saturation of the blood with excess sugar and glucose destroys blood vessels - large and small (a distinction is made between macro- and microangiopathy in diabetes), bones and muscles. Due to anatomical features, blood circulates in the legs of any person worse than in other parts of the body, so it is the feet that are the first to suffer from total circulatory problems in diabetes.
How to treat diabetic foot?
- If the patient’s condition does not require hospitalization and the disease is not advanced, the doctor makes nutritional adjustments in order to achieve the correct balance of carbohydrates and the release of the required amount of hormones in the body.
- If diagnostics reveals problems with blood pressure, systemic drug therapy with beta blockers, inhibitors, diuretics, etc. is prescribed.
- Treatment of diabetic foot is inextricably linked with therapy for diabetes mellitus. Therefore, the patient takes insulin and medications in strictly adjusted doses to stabilize blood sugar and glucose levels.
- To combat the expansion of ulcers due to the proliferation of microbes, antibiotic therapy is carried out. The patient takes antispasmodics, Actovegin, and a-lipoic acid preparations.
- If there are suppurations or ulcers on the foot, treatment by an orthopedist is necessary. Special orthopedic devices, bandages, insoles, motion restraints, etc. are used.
- Wounds and ulcers are treated with antiseptics and antibacterial agents. If necessary, the surgeon excises necrotic tissue and removes potentially dangerous calluses and corns.
- Severe vascular lesions are treated by a vascular surgeon. Modern medicine offers a wide range of low-traumatic methods: stenting, bypass surgery, angioplasty, thromboembolectomy, etc.
- If the foot is gangrene and cannot be treated, amputation is performed.
Signs of diabetic foot
- An ingrown toenail occurs if the corners are not trimmed correctly. They can grow into tissues, and in these places inflammation occurs and pus forms, which is fraught with more serious consequences.
- A darkened nail indicates hemorrhage underneath it. Most often the reason is uncomfortable shoes. The consequences are the same - inflammation, pus, ulcer.
- A thickened nail can be the result of a fungal infection. Due to the irregular shape of the nail, the tissue under it is injured, and it can put pressure on neighboring fingers. In general, diabetics need to be careful about preventing fungal diseases.
- Calluses and corns are a common sign of the onset of diabetic foot. It is in them that invisible hemorrhages occur and pus is formed. Most patients “treat” these formations with patches and ointments, only worsening the problem.
- Cuts occur due to various factors, but in any case they should be carefully treated, since the wounds can be attacked by infection.
- Cracked heels are directly related to dry skin in neuropathic diabetic foot. Cracking leads to the formation of ulcers and bleeding.
- Deformation of the joints and bones of the foot provokes the formation of calluses and wounds on the skin.
Stages of pathology development
Regardless of the form of the disease, it develops sequentially. When moving to a new stage, existing symptoms become more acute and new ones are added.
The course of diabetic foot, regardless of classification, is as follows:
- Initial stage. It is characterized by changes in the shape of the foot, bone deformation, and the formation of blisters and calluses.
- Stage 1. Accompanied by the formation of ulcers and necrotic wounds, while the deep structures of the skin are not damaged.
- Stage 2. Ulcerative and necrotic skin lesions deepen into the dermis, affecting muscles, joints, and tendons.
- Stage 3. The ulcer deepens to the bone tissue, and in the vast majority of cases a wound infection is associated. An abscess and osteomyelitis develop.
- Stage 4. It is characterized by the formation of limited gangrene on the supporting part of the foot. The tips of the fingers turn black, the destructive process has smooth and clear edges. At this stage, the limb can still be saved through surgery.
- Stage 5. Accompanied by a significant increase in the area of tissue death. Gangrene affects the lower leg. In this situation, the process is irreversible, and the only option to save the patient’s life is amputation.
Preventing diabetic foot symptoms
- Particular attention to prevention should be paid to people with extensive diabetic experience. In addition to preventive measures for diabetes (monitoring nutrition, blood glucose levels, etc.), there are specific recommendations:
- wearing special shoes without seams, with orthopedic insoles;
- performing foot exercises and self-massage;
- careful foot hygiene, careful pedicure;
- treating the skin with creams recommended by a doctor.
Prevention of gangrene in diabetes mellitus
Pain in the lower extremities often accompanies diabetes mellitus. To avoid complications, you need to remember simple preventive measures:
- when a corn forms, do not use adhesive plasters; when removed, the top layer of skin may be damaged and a wound may form, which may become infected;
- use socks only made from natural ingredients, buy loose shoes, this will help you prevent the occurrence of calluses. During hot periods, shoes should be washed and changed frequently;
- It is necessary to wash your feet in water whose temperature does not exceed 33 degrees;
- it is necessary to examine your feet every day for the appearance of wounds and cracks, not forgetting to closely examine the skin between the toes;
- regularly apply natural vegetable oils to your feet, which help stimulate the protective function and heal cracks well;
- get rid of bad habits, they can lead to impaired blood flow and cause atherosclerosis.
Gangrene is a serious disease, and a person with diabetes is strongly advised to be careful about their health and not neglect preventive measures.