Have you ever asked yourself the question “How much is a person worth?”, or “How much do human organs cost?” The question is ambiguous, but interesting. Oddly enough, human organs are considered one of the most popular goods, both in Russia and the world. In the article we will talk about how much body parts are sold for, as well as how legal it is and whether it can be done.
Let's figure out together how much human organs cost
How much is a person worth in general?
Man, by his nature, is a unique creature, although he is an animal by nature. People, unlike animals, have the ability to take a creative approach to the process of work. Human organs have a liquid value and are in high demand. When estimating how much human organs cost, according to data from various sources, different criteria are used, and therefore the cost differs. According to one information, the cost of human organs is approximately 1 million US dollars; according to other sources, the total cost of organs reaches almost 4 billion rubles. It is important to note that the final cost depends on the lifestyle of the person that the donor led, and also, as a consequence, the quality of the organs being sold.
Hence, the logical question is “How can you sell a person?”, or how can you sell organs. Let's talk about this later in the article.
How much human organs cost depends on the quality of life of the donor himself.
What determines the price of a heart and how much it costs
The heart is one of the most important human organs that cannot be removed during life. Therefore, its cost is very high. It depends on factors:
- is a complex transplant (heart + lungs) necessary?
- urgency of the operation;
- place of purchase of the organ: the black market or an agreement with the relatives of the person killed in an accident or at work.
By making an agreement with the relatives of a person who has already died, it will be possible to obtain a human heart for only a few hundred thousand. If a person is in a coma and further resuscitation does not lead to results, then intermediaries can contact relatives; they set a price from 8 to 13 million per organ. There are black transplantologists who are ready to help find a donor for 3-4 million rubles.
Total cost of human organs
The value of human organs varies. However, by comparing information from various sources, a price segment is compiled for each organ:
- Two kidneys – 50 thousand US dollars according to some sources, and up to 140 thousand US dollars according to others;
- Liver – prices start from 120 thousand US dollars;
- Pancreas – 70-120 thousand US dollars;
- Lightweight (2 pieces) – from 40 to 200 thousand US dollars;
- Heart – about 250 thousand US dollars;
- Bone marrow – 23 thousand US dollars per 1 gram (an adult man contains up to 2.5 kg of the substance, which in monetary terms is up to 60 million US dollars);
- Cornea - information varies greatly. According to some sources, prices are about 5 thousand US dollars, according to other information from 300 thousand US dollars. It is difficult to determine a single average price;
- Male or female gonads – up to 15 thousand US dollars;
Prices are approximate and are not final. It is also worth noting that the organs of a living person are 2 times more expensive than those of a dead person.
Without compromising health, we sell renewable
It's not just vital organs that are sold. There is also a high demand for renewable parts of oneself. The current situation in the world with COVID-19 is also recalled. The blood of people who have been ill is valued, as it has antibodies. Renewable products that are sold without harming one’s own health include:
Hair
Blood
Sperm
Ovules
The cost of renewable human parts is lower than that of non-renewable organs.
How much does sperm cost?
Semen donation is quite common. Single women often turn to artificial insemination services, and therefore there is a demand for sperm. An adult male between the ages of 18 and 35 can become a donor. Before becoming a donor, you will need to take a bunch of different tests: hepatitis, HIV test, general blood test, and DNA test. You will not have to pay for tests from the list; clinics will cover the costs themselves. The price for delivery is different: starts from 1.5 thousand rubles and up to 4 thousand rubles. Before donation, you will need to comply with certain restrictions: abstain from sexual intercourse for 3-5 days, do not use drugs, tobacco and alcohol, and it is also prohibited to visit baths and saunas.
You can donate biomaterial no more than 6-8 times a month. But clinics do not always need such a quantity of material.
Men have the opportunity to donate their biomaterial for a fee
How much will the hair cost?
There are hair transplant operations. This requires real human hair, not artificial hair. Hair is in good demand. It is important that only long hair is suitable for sale; the length must be at least 50 cm, so in most cases only women can sell hair. The most valuable hair is considered to be hair that has not been dyed and also has a light shade.
For a kilogram of light and healthy hair they can offer up to 100 thousand rubles. Shades close to light brown are estimated at 40-60 thousand per kilogram. Dark, split ends and dyed hair are valued much lower and can cost around 10-20 thousand per kilogram.
How much do eggs cost?
Women experience various illnesses that can lead to infertility, but such women still want to give birth. For such cases, there is egg donation. Any woman who is in the age range of 18-30 years and has given birth to at least one healthy child can sell her eggs. Before taking the exam, you will have to undergo numerous medical examinations and tests. In the Russian Federation, they pay from 50 to 80 thousand rubles for one egg. You can take it no more than once every three months and no more than 6-8 times in your entire life.
How much does it cost to donate blood?
The easiest way to sell a part of yourself is to become a blood donor. Blood is needed for transfusion, for people who, for example, have experienced large blood loss. The blood donation option is available to men and women over the age of 18 and weighing more than 50 kg. You can donate no more than 400 ml at a time. They pay either 3,500 rubles or 550 rubles and a food ration. You can take it no more than 5 times a year, and therefore receive no more than 20 thousand rubles. By donating blood regularly over several years, you can earn the title of honorary donor and receive additional vacation days and additional payments.
Donating blood is the easiest and most legal way to make money from your own body.
Lifestyle after transplant
The patient’s lifestyle in the postoperative period after a heart transplantation procedure consists of the following components:
- Nutrition. It is important for the patient to switch to a healthy lifestyle, completely stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking. It is necessary to follow a diet, excluding harmful foods (smoked, fried, fatty, etc.) from your diet.
- Physical activity. During the first month after surgery, the patient must strictly adhere to the restrictive regime. However, normal daily activity should still be present. After a couple of months, the patient is allowed to return to driving a car, and after a few more, begin light physical activity (walking, gymnastics, etc.).
- Protection against infections. The patient should try to avoid visiting public places for several months after transplantation and contact with people suffering from infectious diseases. It is equally important to wash your hands thoroughly before eating, drink only boiled water, and eat food that has been well heat-treated. This is due to the fact that due to suppressed immunity, the likelihood of the patient becoming infected with viral, fungal, and bacterial diseases increases after the start of immunosuppressive treatment.
- Use of medications. This part of a heart transplant patient's life is the most important. The patient must carefully observe the time of taking medications and strictly follow the dosage prescribed by the doctor. As a rule, we are talking about the use of hormonal drugs and cytostatics, the action of which is aimed at suppressing one’s own immunity, which attacks foreign tissue of the heart muscle.
In general, it should be noted that the patient's life after surgery undoubtedly changes significantly, but the quality of life without swelling, palpitations and shortness of breath changes for the better.
Harmful, but not fatal - Organ donation
Even if you meet all the medical criteria and express a desire to become an organ donor, you may still encounter obstacles. Each country has its own laws and regulations in this regard. Thus, in Russia only a relative can become an organ donor during their lifetime. And if you decide to become a donor in the absence of a relationship, then this will be considered a criminal offense and fall under Article 120 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. There is no direct ban on the purchase and sale of organs in Russia, but there are precedents for problems arising, both for the donors themselves and for the doctors treating such cases.
What is the cost of a liver
The liver is one of the most vital organs in the human body. The liver takes on all the damage that we cause to the body by drinking alcohol, fast food and other unhealthy treats. Thus, due to excessive alcohol consumption over a long period of time, liver cirrhosis occurs. The liver must be protected; it performs many important functions: it is responsible for processing food, regulating the body’s temperature, and also removing toxic substances.
The entire liver or part of it can be donated. It is important to note that a whole liver is not required for the normal functioning of the body; only a part will be sufficient. The cost of the entire liver will cost 120 thousand US dollars, part of the liver is half the cost of the whole one, i.e. at 60 thousand. The liver can be taken from a living patient or from a deceased one, but according to most studies, the liver of a living person adapts to the recipient’s body much faster.
It is important to understand that donation during your lifetime can significantly affect your physical condition.
Bone marrow prices
When answering the question “How much does a person cost”, it is important to focus on one of the most important organs – the bone marrow. In this case, we are not talking about the brain that is in our head, but about something a little different. The bone marrow is responsible for most of the blood processes in the body.
The functioning of the bone marrow largely determines the condition of the body, and in case of disturbances it can lead to leukemia or other diseases. If a person does become ill with one of the blood diseases, a bone marrow transplant may be required.
The process of bone marrow collection is completely harmless to the donor. Elements of the donor's bone marrow help patients fight cancer. Bone marrow is a very expensive element - the cost is approximately 23.5 thousand US dollars per 1 g.
How much does it cost to sell a kidney?
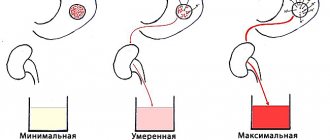
According to statistics, the majority of organ transplants involve kidneys, namely 75%. For normal life, a person needs 1 kidney. An operation, even the simplest one, is always a risk, because you can never say with 100% probability that everything will be successful and the transplanted organ will take root in the human body. However, modern medicine uses the most advanced technologies and methods, and therefore the chances of an unsuccessful outcome are virtually minimized. The prices for a human kidney are quite immodest. The average global price for a kidney is 70 thousand US dollars. In the Russian Federation, the price starts from 2.5 million rubles and reaches 6 million rubles.
Department of surgical treatment of congenital heart defects (CHD)
Congenital heart defects (CHD) are a large group of anomalies of the intrauterine development of the heart and large vessels flowing into or leaving its cavities, varied in formation and anatomy.
CHD incidence statistics
According to various sources, the incidence of congenital heart disease varies from 2 to 15 cases for every 1000 newborns. In 2021, among more than 1.3 million newborns, about 12 thousand children with congenital heart disease were registered.
Compared to statistics 10 years ago, the frequency of detection of congenital heart disease in newborns has increased from 6 to 9 cases per every 1000 infants born, which is apparently due to improved means of early diagnosis of this serious and often life-threatening group of diseases in childhood.
Despite the fact that modern methods and technical capabilities of ultrasound examination (echocardiography) will make it possible to detect congenital heart disease in the fetus starting from 12-14 weeks of pregnancy with a high degree of probability (up to 96%), nevertheless, cases of late detection of this pathology are recorded both among children, as well as among adults.
At the end of 2021, more than 573 thousand patients (children and adults) with an established diagnosis of congenital heart disease were registered in Russia (population of about 147 million people). However, there is a high probability that the actual number of such patients may be higher, and the number of annually registered cases of this diagnosis will increase.
Survival prognosis
Undoubtedly, the natural (without medical intervention) course of the vast majority of various congenital heart diseases, as a rule, has an unfavorable prognosis and leads to a reduction in the duration and quality of life of the patient, often quite significantly. Up to 90% of newborns with so-called “critical congenital heart disease” do not survive beyond 1 year. Many of them die within the first weeks of their lives. According to statistics, congenital heart defects account for about 10% of the causes of infant mortality in Russia.
Causes of congenital heart disease
Among the most likely causes of the formation of congenital heart disease are genetic and chromosomal aberrations, viral infections of the mother during pregnancy, chronic endocrine and metabolic diseases, bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, etc.), teratogenic and mutagenic adverse environmental factors.
There are a great many congenital anomalies of the development of the heart and great vessels. Conventionally, the entire set of congenital heart disease can be subdivided depending on the age at which clinical manifestations (symptoms and consequences) are most pronounced and prognostically significant.
| Types of congenital heart disease | Age at which surgical treatment is usually necessary |
| Newborn period |
| First year of life |
| Over a year old |
Some congenital heart diseases are characterized by severe disturbances of central hemodynamics soon after birth, forcing surgical treatment to begin already in the neonatal period (for example, simple transposition of the great arteries or obstructive forms of total anomalous drainage of the pulmonary veins).
Transposition of the great arteries
Total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage
Other congenital heart defects occur with clinical compensation in the first few weeks or months of life, manifesting closer to the second half of life (ventricular or aortic-pulmonary septal defect, atrioventricular canal, SBUG).
Common atrioventricular canal
Ventricular septal defect
Common truncus arteriosus
There are congenital anomalies that do not appear clinically for a long time and are benign, which makes it possible to delay their surgical treatment until the second year of life and even later (atrial septal defect, partial anomalous drainage of the pulmonary veins).
Atrial septal defect
Moreover, there are a number of congenital heart defects, the correction of which is advisable to delay within the duration of the clinical compensation period in order to achieve better treatment results (corrected transposition of the great arteries, compensated forms of Ebstein's anomaly, moderate coarctation of the aorta).
Coarctation of the aorta
It should also be noted that the same nosological form of congenital heart disease, depending on the specific anatomy, can become a reason for surgery at different age periods. For example, a simple transposition of the great arteries forces an arterial switch operation to be performed in the first two weeks of life, whereas in combination with a large ventricular septal defect, the same anomaly can be operated on at the age of two months or older. Extreme forms of Ebstein's anomaly with hemodynamic atresia of the pulmonary artery and ductus-dependent pulmonary blood flow are “critical congenital heart disease of the newborn period.”
“Critical defects of the newborn period” account for about 30% of identified congenital heart defects and require immediate surgical care in the first weeks, or even days, of a child’s life.
Previously, this group of diseases was identified with a pathology incompatible with life. However, the capabilities of modern medicine have made it possible to achieve impressive early and long-term results in the treatment of many of this group of congenital heart diseases.
Critical UPS
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Pulmonary valve atresia
Tricuspid valve atresia
It is important to remember that a number of congenital heart abnormalities cannot be eliminated immediately, within the framework of one surgical operation. In such cases, to achieve optimal treatment results, it is divided into several stages, or phases, each of which is performed at different ages, starting from infancy. Also, it is almost never possible to exclude the possible need to perform additional surgical intervention even after a previously performed radical (that is, definitive) correction of a heart defect.
All operations for congenital heart disease can be divided into 4 categories:
| Radical operations (corrections) | When complete and final elimination of congenital heart disease is achieved and the child’s heart acquires an anatomical structure corresponding to a healthy heart or close to normal anatomy. Intracardiac circulation after such operations naturally becomes physiological (that is, normal). After treatment, the patient’s rate of development, quality and life expectancy does not differ from healthy peers and usually only needs preventive outpatient monitoring. As a rule, disability is removed. |
| Hemodynamic corrections | When the intracardiac circulation, as well as the anatomical structure of the heart, upon completion of treatment cannot be called “corresponding to a healthy heart.” However, such a correction ensures hemodynamics close to physiological, allowing the child to live, develop, and in the future, successfully adapt to society and create his own family. A person’s physical capabilities may be somewhat limited, but the disability is not completely removed. |
| Preparatory (intermediate) palliative operations | They are interventions that aim to prepare the heart and the body as a whole for subsequent radical or hemodynamic correction. There may be several such operations. Patients after such operations can be temporarily discharged from the hospital, but require systematic outpatient monitoring in order to monitor the clinical condition, correct drug therapy and determine the timing of the next hospitalization for diagnosis and continuation of surgical treatment |
| Definitive palliative (life-prolonging) operations | Currently, they are very rare and are performed on patients with incurable (inoperable) complex forms of cardiac anomalies or their incurable complications. Such operations are sometimes called a “bridge” to heart transplantation. |
From a prognostic point of view, all congenital heart defects can be divided into anomalies with a favorable prognosis and defects with an unfavorable prognosis.
. The latter most often represent a combination of multiple congenital heart defects (often combined with malformations of other organs, multiple manifestations of dysembryogenesis and syndromic forms of genetic anomalies), which are not subject to radical correction and predetermine, even if hemodynamic or palliative surgery is performed, a low quality of the patient’s future life, limitation of its duration, deep disability and limited social adaptation. Patients with such anomalies are potentially considered candidates for heart or heart-lung transplantation. In cases of early prenatal (intrauterine) diagnosis of congenital heart disease with an unfavorable prognosis, the possibility of terminating the pregnancy for medical reasons should be considered in connection with the detection of a congenital heart defect incompatible with life in the fetus.
Classification of congenital heart disease
CHD can also be classified into simple (the patient has a single anomaly) and complex (a combination of several anomalies). In the WHO International Classification of Diseases, some frequently combined anomalies of heart formation are often combined into one nosological unit with appropriate coding, for example, “hypoplastic left heart syndrome” or “tetralogy of Fallot.”
Tetralogy of Fallot
Clinical manifestations (symptoms) of congenital heart disease
are not only very diverse, but also have a characteristic spectrum inherent in a specific age period of their natural course. For example, a large ventricular septal defect usually does not cause symptoms in the first few months of life due to the physiology of the lungs in newborns and infants. By six months of life, the child develops symptoms of heart failure (frequent colds, poor appetite, decreased exercise tolerance, shortness of breath, underweight, anemia, sleep disturbances) caused by excess blood flow in the lungs and overload of the left chambers of the heart. However, later, by 2-3 years of age and older, as irreversible dangerous sclerotic changes develop in the small vessels of the lungs, these symptoms spontaneously regress - a period of imaginary well-being begins. During this period, the patient is either conditionally operable or not operable at all. Subsequently, the clinical picture is characterized by symptoms of right ventricular circulatory failure and secondary deficiency of pulmonary blood flow against the background of sclerosis and obstruction of small vessels of the lungs.
Division of defects into “pale” and “blue” (cyanotic)
, widespread in popular scientific literature and online resources, is very conditional in nature, since it does not have a clear correlation with the hemodynamic patterns of the natural course of congenital heart disease and does not carry any prognostic value. Thus, two anomalies “simple transposition of the great arteries” and hypoplastic right heart syndrome are cyanotic congenital heart disease, but in the first case the possibility of radical correction predetermines a favorable prognosis, in contrast to the second of these congenital heart disease.
Congenital heart disease in adult patients is included in a special group
— corrected or uncorrected congenital heart disease in persons 18 years of age and older.
They are usually divided into primary and secondary. Primary
- a set of anomalies with a relatively favorable natural course, allowing one to survive childhood, first identified at the age of over 18 years or identified in childhood, but recognized as incurable (incurable).
This is a smaller cohort of patients. Secondary
– in the so-called “GUCH-patients” (the larger of the two cohorts). They are represented by a wide range of congenital heart anomalies previously operated on in childhood.
On the basis of the clinical departments of our Center, specialized in the treatment of patients with congenital heart disease, all types of open surgical, minimally invasive surgical (thoracoscopic) and X-ray endovascular interventions (including hybrid) are performed for a wide variety of congenital anomalies and tumor diseases of the heart and great vessels .
The center is equipped with all the necessary modern equipment for timely and complete diagnosis of congenital heart disease, including prenatal (intrauterine) diagnostics. Every year, about 3,500 patients with congenital heart disease receive the necessary surgical care at our Center. More than 900 X-ray endovascular procedures are performed for congenital anomalies of the heart and great vessels.
How much does a brain cost?
Probably, the brain is the most complex substance in the human body, responsible for a combination of various processes, conducts mental activity, and gives commands to the rest of the body. The capabilities of the human brain are still not fully understood and are the subject of debate and controversy. Due to the complexity of the structure, there have been no precedents for human brain transplantation, so it is impossible to talk about the cost of this organ. At the moment, perhaps the cost should be described as “priceless.” There is a possibility that somewhere on the black market you can find a human brain, but this is already an illegal trade in organs and a very immoral activity. I think that over the coming years medicine will actively develop and soon we will learn about the possibility of human brain transplantation.
There are currently no cases of human brain transplantation
Contraindications for transplantation
Such surgical intervention is contraindicated in the following situations:
- Severe form of pulmonary hypertension (presence of high pressure in the pulmonary artery).
- A severe form of diabetes mellitus, in which there is damage to the retina, kidneys, and blood vessels.
- Active tuberculosis process, HIV infection.
- Acute forms of infectious diseases.
- Severe forms of liver and kidney failure.
- Systemic diseases of an autoimmune nature (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, others).
- Severe degree of chronic obstructive disease.
- Drug and alcohol addiction.
- Oncological diseases.
- Acute stages of mental illness.
We talked about the cost of a heart transplant in Moscow.
The price of a lung
The lungs perform the respiratory function in the human body. They supply oxygen to all organs. In modern society, where there are many factories, factories and industries that emit vapors into the atmosphere and, as a result, the air becomes dirty. People breathe this poisonous air and develop lung diseases. Lung donation is not an easy process, since after the death of a person the lungs are suitable for transplantation for only 2 hours, after which they die after the carrier. In this regard, it is necessary to act quickly and the cost of the operation, including two lungs, increases - from 20 to 30 thousand US dollars.
Heart transplantation from a religious perspective
Previously, when the field of transplantology was just beginning to develop, representatives of almost all religions had mixed opinions in relation to heart transplantation. For example, representatives of Christianity believed that such an operation was not a godly act, since a person’s still living heart was actually taken away. In addition, it is believed that theoretically a person can emerge from a comatose state after a few months. But due to the fact that doctors clearly differentiate the state of coma and brain death, more and more clergy in recent years have begun to say that saving someone else’s life after one’s own death is the true purpose of a believer, since the basis of such an action is sacrifice. And giving your heart is a benefit to other people.
We looked at the cost of a heart transplant in Russia.
How much is a heart worth?
The heart is the epicenter of many processes in the body. As a result, it is more vulnerable to disease, as the diet of where the disease can come from increases. In adulthood, many people's hearts begin to fail and may require surgery or even a heart transplant. After a heart attack or stroke, a person’s heart cannot cope with the load and therefore the body may need a new one. But even after performing a heart transplant, most often it does not save patients, because most heart transplant operations end in death. If the operation is successful, the patient’s life expectancy is increased by no more than 5 years. Despite this, heart transplant operations are carried out in many countries, because if a heart transplant is not performed, then an alternative option to maintain the patient’s life is to connect him to a stationary machine. Based on all these facts, the cost of a heart and its transplant surgery increases significantly. Prices average 250 thousand US dollars or from 17 million rubles.
Heart surgery and heart transplantation are very common in transplantology
Method of performing transplant surgery
The heart transplant procedure in Moscow begins with the removal of the donor organ from the body and placing it in a container with a cardioplegic solution for no more than 4-6 hours. During this time, preoperative preparation of the recipient is carried out (premedication - sedative and analgesic drugs are administered). Then, in the operating room, using general anesthesia, the recipient's anterior chest wall is cut, large vessels are connected to a machine that performs artificial blood circulation (ACB), which will perform the function of an artificial heart during the operation.
Then the left and right ventricles of the heart are cut off. The atria are preserved. Preserving your own atria allows you to leave the sinus node active, which sets the rhythm of heart contractions and is the pacemaker.
The donor's atria are then sutured to the recipient's atria and a temporary pacemaker is placed to maintain adequate heart rate after transplantation. The chest is sutured and an aseptic bandage is applied. This operation takes several hours, usually no more than 6.
The next stage of surgical intervention is cardiotonic (supporting cardiac activity) and immunosuppressive treatment. Immune suppression (usually through the use of cyclosporine) is required to eliminate rejection reactions and successful graft engraftment.
What is the price of a head
There are cases when organ transplantation is not able to help a person and death is inevitable. In this case, we can talk about transplanting a person’s head onto another, healthy body. As of today, such operations have not been performed on humans, but one American doctor performed a similar operation on experimental animals. His plans include carrying out a similar operation on a person; a person has already been found who agrees to the operation. According to the surgeon himself, the cost of the operation will be 12 million US dollars, of which 5 million will go to the donor’s body.
Possible complications after transplantation
Among the complications that can occur in the early period after surgery are bleeding from the wound and infectious lesions. The first can be treated quite successfully by reopening the wound and suturing the source of bleeding. To prevent infectious (viral, fungal, bacterial) complications, the patient is prescribed antibiotic medications and an adequate immunosuppression regimen.
In the long-term period after surgery, the development of rejection of the transplanted heart, as well as dysfunction of the coronary arteries, accompanied by myocardial ischemia of the donor organ, is likely.
Bones and ligaments
Athletes often experience problems related to bones and ligaments. Numerous sprains, fractures, tears, tears, and so on, all this is normal for athletes. Often, fractures and sprains heal with the help of conservative treatment methods. In some cases, the ligaments are cut out, because the body can continue to function normally without them. So, for example, a fairly common injury among football players is a serious injury by sports standards - a cruciate ligament rupture.
If the conservative method cannot be used, and removal does not create the desired effect, then the ligament or bone is replaced. The advantage of ligaments and bones, compared to other human organs, is that they do not have a shelf life. The cost is not the same as other organs and depends on the part of the person's body. Thus, a cruciate ligament costs about 5.5 thousand US dollars. The cost of the brush will be approximately $350.
Leather
Leather also has value. Skin grafting operations are required for people who have suffered skin damage, severe burns - thermal, electrical and chemical. If possible, skin is transplanted from another part of the victim’s body. If the first option is not possible, then they resort to donor assistance. As a rule, donors are deceased people who have agreed in advance to donate their skin for the benefit of others. Leather costs $10 per square inch.
The skin is not such an expensive organ; its cost compared to other organs is insignificant
Is this legal?
According to Russian law, a person cannot be bought or sold. The rule also affects internal organs and is regulated by Law No. 120 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. However, organs are one of the most popular commodities in the world.
People suffer from diseases and need replacement of individual organs. The waiting list for organ transplants reaches decades, and therefore people are willing to pay a lot of money to receive organs from private individuals. A black market is emerging where organs are also sold. Nevertheless, in most countries of the world the practice of buying and selling organs is legal and actively functioning. Only in order to sell your organs will you need the approval of close relatives or will another condition be imposed, depending on the country.
The most expensive organs are the bone marrow, liver, lungs, heart and cornea of the eye.
How much does an organ transplant cost?
The price of the heart includes the services of people who will remove it and deliver it to the transplant site. That is why, with a formal agreement, the cost of an organ can reach up to 13 million rubles.
It also includes the use of high-quality materials during surgery and the use of high-quality medical equipment at all stages.
The operation can be performed in one of the following ways:
- heterotopic – the patient’s own heart is not removed, the donor organ is placed above it on the right;
- orthotopic – the patient’s heart muscle is removed and replaced with a new one.
Most often, doctors perform orthotopic surgery; it is considered classic.
Its cost can increase to 60 million rubles if the patient requires not only a human heart, but also lungs. In this case, relatives will have to pay up to 50 million rubles just for transporting organs and paying compensation. A normal operation, when they work on only one organ, costs from 13 to 20 million. The final price of the intervention depends on the urgency and how complex the procedure will be. There are several factors that can increase it to 100 million rubles:
- age of the donor and the patient;
- both have serious diseases that cause complications during transplantation;
- urgency.
The most expensive will be an immediate transplant; this is required if the donor has already died, and the patient cannot wait for a transplant for a few more days, for example, with artificial support of his life.
Conclusion
In the article we answered the question “How much does a person cost” and “How much do organs cost?” Theoretically, we have confirmed that in the modern world it is possible to sell a person. Such a sale does not correspond to the sale of goods, since the transfer of organs and body parts requires the consent of the donor and appropriate legislative permission to conduct such “trade”. In general, even in Russia there is an opportunity to make money by transferring individual parts of the body, which allows a person to make good money.
Types of transplantation
Today, two main methods of performing the operation are known. They are heterotopic transplantation , in which the patient's own heart is not removed, but the donor is placed under it on the right side, and orthotopic transplantation , as a result of which the donor heart is replaced with the recipient's heart. This method is recognized as the most common.