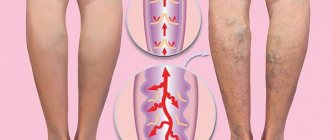
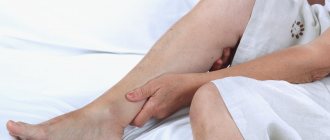
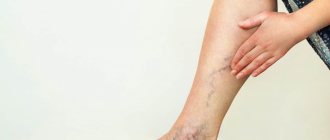
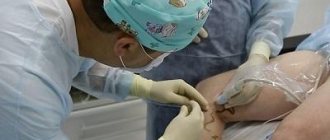
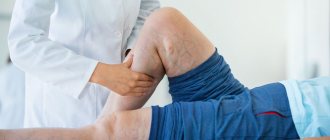
Reticular (network) varicose veins are an enlargement of small intradermal and subcutaneous veins visible to the eye. The problem of reticular varicose veins is given considerable attention in modern phlebology. This is a “cosmetic” type of venous pathology, which is more often observed in women and is manifested by varicose dilation of small intradermal vessels and the appearance of telangiectasis on the lateral surface of the leg and less often along its inner part. Reticular varicose veins cause nothing but a cosmetic defect. Not dangerous, but not pleasing to the eye. The risk group consists of young women. After the first pregnancy and childbirth, a pathological process often develops in their intradermal vessels due to hormonal changes.
What is reticular varicose veins
In the human body, blood circulates through arteries, veins, capillaries, and venules. Arteries are the largest vessels of the circulatory system. They connect to the veins. The smallest vessels are venules. On the lower extremities, superficial intermediate venous vessels are visible under the skin. Their diameter is greater than the diameter of the capillaries, but less than the diameter of the main veins. This venous network is called reticular. In other words, reticular veins are small millimeter-sized vessels that are visible under the skin of the legs.
Every vein has valves. They filter the direction of blood movement and its volume. The reticular vein has only one valve. If it is deformed, the vein expands, twists and carries a larger volume of blood. Venous pressure in the retinal layer of the skin increases due to the accumulation of blood in a certain area. Valve insufficiency develops and reticular varicose veins form - a plexus of small vessels of red, blue, purple color, visible through the skin.
In what places on the legs do spider veins and reticular veins usually appear?
Telangiectasia and reticular veins can appear in any area, but they mainly affect the skin:
- upper thighs;
- above the knee joint;
- supramalleolar region.
Common location of spider veins on the legs
Causes and risk factors for the development of reticular varicose veins
Most often the disease is observed in women. The trigger mechanism is hemodynamic disturbance. Due to the fact that the valve is deformed, blood begins to circulate in the opposite direction. The plexus of blood vessels becomes overcrowded, and the blood stagnates. Because of this, the walls of the blood vessels expand, become brighter and more noticeable through the skin.
This condition may be preceded by:
- Hormonal surge. A decrease in estrogen and an increase in progesterone leads to a loss of venous tone and expansion of the lumen of blood vessels, rapid blood clotting, and a decrease in antithrombin in plasma. Phlebopathy develops. This process is often observed in pregnant women, as well as in women who take oral contraceptives.
- Heredity. Changes in connective tissue are transmitted through the female line, therefore, with varicose veins in a mother or grandmother, the risk of dilation of reticular vessels increases at a young age.
- Load on the legs. In people who work sitting or standing, the diagnosis is made more often. Reticular varicose veins of both extremities are observed in office workers, accountants, loaders, hairdressers, and teachers.
- Frequent air travel. During air travel, due to changes in atmospheric pressure, vascular tone and blood flow in the reticularities change.
The development of the disease is aggravated by smoking, obesity, arterial hypertension, second and subsequent pregnancy, taking corticosteroids, liver cirrhosis, systemic scleroderma.
Signs
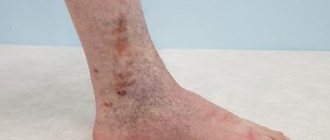
The disease at the initial stage is latent. You can suspect the reticular form of varicose veins of the lower extremities by the bluish color of the skin. Thin veins appear on the legs in the form of:
- tree-shaped (many vessels branch from one base to the left and right);
- cobwebs or stars (vessels extend from the center in different directions);
- lines (even stripes of blood vessels).
Branched veins are especially noticeable at the end of the day after sports, heavy lifting, prolonged static position, running or walking long distances. In the morning the defect on the legs is invisible.
As blood flow worsens, accompanying symptoms worsen:
- discomfort in the calf muscles. Involuntary spasms occur suddenly and disappear after massage of the limbs;
- heaviness and fatigue in the legs;
- burning and itching in the legs and feet.
The clinic is more pronounced during menstruation due to increased blood flow.
Symptoms subside after resting while lying down with legs elevated. Unlike varicose veins of deep veins, there is no pain, swelling and trophic disturbances.
The danger of reticular varicose veins
In many cases, patients do not pay attention to spider veins and do not rush to see a doctor. There are practically no symptoms, so women attribute the visibility of veins to a cosmetic defect.
If treatment is not started at the initial stage, valvular insufficiency of the deep main veins will develop. Reticular varicose veins of the GSV tributaries are especially dangerous. The great saphenous vein runs along the medial side of the legs and connects with the femoral vein. As the GSV valves deform, varicose veins develop.
If the problem is ignored for a long time, the vascular network deepens and the risk of trophic ulcers increases.
Symptoms
With cosmetic (aesthetic) varicose veins, patients' complaints are directed towards the presence of unaesthetic vascular networks, “worms”, “cobwebs”. In most cases, this causes psychological discomfort: women are embarrassed to undress on the beach, in the pool, or simply walk down the street in a short dress. In some cases, with the slightest blow, a hematoma immediately appears at the site of a superficial vessel, followed by the formation of a larger vascular network. In extreme cases, in the presence of reticular varicose veins, patients may feel a feeling of heat and baking at the end of the working day.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
The diagnosis is made by a phlebologist. He examines the patient lying and standing. The doctor needs to distinguish reticular varicose veins from telangiectasia, the initial stage of livedo reticularis, Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome, Maffucci syndrome, Bloom's syndrome, and port wine stain.
Ultrasound in duplex mode is prescribed. Using ultrasound, the condition of the vein valves is assessed. The diagnosis is established if a violation of the reticular blood flow is confirmed, i.e., there is obstruction and reflux of the superficial vessels.
An ultrasound scan is performed. Dopplerography shows the direction of blood movement. During the scan, the doctor asks you to hold your breath, strain, and simulate walking while lying down. An image of green and red vessels is displayed on the screen. The red color shows the extent of the pathological area, and the green color shows the functionality of the venous valve. The direction and speed of blood movement is indicated.
Treatment of reticular varicose veins
When treating the reticular form of varicose veins at an early stage, the outcome is favorable.
First, the phlebologist prescribes drug therapy to improve blood flow along with compression therapy.
Drug therapy includes taking venotonics based on rutoside, heparin, troxerutin, diosmin. They correct the outflow of lymph, strengthen the walls of blood vessels, normalize vascular permeability, increase the tone of the veins, prevent convulsions and the development of trophic disorders.
Depending on the number of reticularities, the doctor selects compression stockings . For saphenous veins on the legs, it is recommended to wear therapeutic tights. If cobwebs appear on the back of your knees, bandaging with an elastic bandage or wearing class A compression tights will do.
If the number of reticularities increases and the vascular network is noticeable even after rest, then they begin to treat the lower extremities using the hardware method.
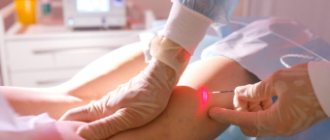
Laser therapy involves exposing a beam of light to the choroid plexus. The laser heats the vein, causing the inner surface of the vessel to collapse. Blood stops flowing through this vein. To achieve results, you need to undergo 2-3 procedures with an interval of 2-3 weeks. After treatment, you should not put any weight on the limb, sunbathe in the sun, take a shower or go to the bathhouse for 12 hours. Laser coagulation has a disadvantage. If the doctor acts on the same area for a long time, you can get a burn. The method is effective for vessel diameters less than 1 mm.
If the veins are dilated by more than 3 mm, sclerotherapy . It consists of introducing a special sclerosant into the lumen of the vein under ultrasound control. The substance glues the walls, due to which the blood supply to the pathological area is stopped. To treat intradermal varicose veins, a substance in the form of foam is used. The procedure is painless, because the injections are made with the finest needles. There may be a burning sensation at the time of drug administration. After the injections, a tight bandage is tightened. You are allowed to take a cool shower and remove compression garments the same day.
Microphlebectomy is not performed for the reticular type of disease.
Treatment will not be effective unless the root cause is addressed. Obese people need to adjust their weight to reduce stress on their legs. Office workers need to pause, get up and walk around every hour. Those who like high-heeled shoes should wear comfortable shoes with a wide last and a heel height of no more than 5 cm.
Treatment of reticular varicose veins at Dr. Gruzdev’s clinic:
Endovasal laser coagulation (EVLC) If you have varicose veins, this does not mean that you will have to have surgery! New medical technologies make it possible to get rid of this disease without surgery.
More details
Sclerotherapy Sclerotherapy is a method of treating varicose veins by injecting a sclerosant (a special medication) into the affected veins.
More details
ECHO sclerotherapy The technique is used in cases where it is necessary to “seal” large veins.
More details
Foam-form sclerotherapy Foam-form technology (foam sclerotherapy) is used to “glue” varicose veins with a diameter of up to 6 mm.
More details
FILM sclerotherapy The newest and unique method of combating varicose veins of any size.
More details
Adhesive obliteration of veins VenaSeal Non-surgical treatment of chronic venous insufficiency and varicose veins using VenaSeal bioadhesive.
More details
Treatment with medications
Treatment of reticular varicose veins of the lower extremities does not allow one to fully cope with the disease and is aimed at eliminating the clinical manifestations of the disease. It is carried out using medications, which also eliminate the risk of complications:
- Detralex tablets - eliminate pain and a feeling of heaviness in the legs;
- Antistax capsules - eliminate venous circulation disorders;
- Venoruton capsules - eliminate the risk of formation of retinal microthrombi, minimize the clinical manifestations of the disease;
- Phlebodia tablets - minimize symptoms;
- ointment "Troxevasin" - minimizes clinical manifestations, used only as prescribed by a doctor if indicated.