What is systolic pressure and what does it determine?
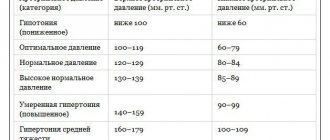
Blood pressure (BP) numbers are determined by two indicators: systolic upper SBP, diastolic lower DBP.
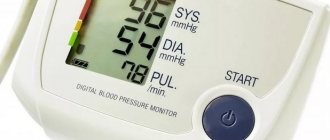
Measured with a tonometer in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). For a healthy adult, the norm is 120/80 mmHg. up to 100/70 mmHg Low numbers may be a variant of the norm if such pressure is observed throughout life and is “working”. The exception is situations of sudden or prolonged decrease in blood pressure and deterioration of general condition, which may indicate pathology of the heart, kidneys, psycho-emotional fatigue, metabolic disorders, and hormonal imbalance. To understand the problem of low systolic pressure with constant normal diastolic pressure, you need to understand what this condition may indicate.
Upper pressure is the moment the heart chambers contract and blood is pushed through the arteries during systole. Low upper pressure may indicate congenital or acquired cardiac pathology, which is taken into account when prescribing an examination plan, treatment regimen and further monitoring of the patient.
What does a low diastolic reading mean?
After a series of studies, doctors found that the nature of the pathology in different people can differ significantly. There are three types of deviations that help to understand what problems are in the body's functioning. Types of arterial hypotension:
- Orthostatic. This type of pathology may mean that the human body cannot quickly and correctly regulate indicators. This disease is characterized by a sharp drop in blood pressure (blood pressure) downwards after a change in position. At the same time, the head may become dizzy, and in some cases the person loses consciousness. The main reasons: pregnancy, dehydration, use of certain groups of medications.
- Postprandial hypotension. The main symptoms are a sudden rush of blood to the lower extremities after eating. This type of malaise indicates disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, mental disorders (neurasthenia, neurosis, etc.), organic changes in the brain (Alzheimer’s disease may threaten).
- Vegetative-vascular. This diagnosis means that the cardiovascular system is developing or functioning incorrectly. Often diagnosed in teenagers.
Reasons why the upper figure may decrease
In the modern rhythm of life, factors such as stress, insufficient rest during intense workload, psycho-emotional experiences, and untimely treatment of underlying diseases lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
Other causes of low upper blood pressure are listed below:
Vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypotonic type.- Pregnancy period, especially the first trimester, and in patients with severe toxicosis.
- Hormonal disorders, diabetes, hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency.
- Consequences of injuries to the head, neck, spine.
- Physical fatigue, especially among professional athletes.
- Congenital or acquired cardiac pathology, valve defects, incorrect selection of medications for hypertension.
- Neurosis, depressive disorder, chronic fatigue syndrome.
- Frequent changes in time zones and climate.
- Sudden change of weather.
- Dehydration, fatigue, consequences of infectious diseases, injuries, operations, blood loss.
Reduced systolic with normal diastolic: why does this happen?
Upper pressure decreases as cardiac contractility decreases. This can happen when:
- damage to the heart and large vessels due to atherosclerosis, rheumatism;
- decreased vascular tone;
- heart failure;
- dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system;
increased secretion of the hormone acetylcholine and decreased adrenaline;- taking sedatives that slow your heart rate.
However, it should be remembered that it is almost impossible to distinguish low systolic pressure from high diastolic pressure on your own. A single measurement of blood pressure at home is not enough to make a correct diagnosis. Cardiologists, therapists and neurologists focus patients’ attention on the need for examination by a specialist. Within the walls of a medical institution, special instrumental diagnostics are carried out to detect low SBP.
Factors influencing the decrease in pressure
There are 3 main factors that influence the pressure indicator:
- cardiac output (the rate at which blood flows out of the heart);
- volume of blood in the blood vessels (low amount of blood in the body is called hypovolemia and leads to hypotension).
- parameters of blood vessels (their internal diameter, wall density).
Heart pressure changes throughout the day and depends not only on the above factors, but also on the age and body type of the person. Low heart pressure that is asymptomatic in healthy, active people is considered natural and does not require treatment.
Low blood pressure sometimes occurs in young people
But if small tonometer readings are accompanied by the above unpleasant symptoms, then it is likely that the following reasons provoked hypotension:
- dehydration due to loss of fluid or excessive sweating in very hot weather;
- overdose of drugs used to treat hypertension, angina, depression;
- pulmonary embolism, weakening of the heart muscle after a heart attack;
- anemia (reduced number of red blood cells or lack of hemoglobin, the red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body);
- Addison's disease, or dysfunction of the adrenal glands, which normally secrete hormones involved in blood pressure control;
- pregnancy;
- immobility (bed rest for a long period due to illness or injury);
- significant blood loss;
- septic shock (acute infection).
How to solve the problem?
If low SBP is caused by chronic fatigue, insufficient rest or emotional distress, to improve the condition, taking vitamins and sedatives based on Valerian, Motherwort, Peppermint and Melissa is indicated to normalize night sleep. For neurological disorders, B vitamins with Magnesium and ascorbic acid are recommended. However, it should be understood that such treatment is more preventive and cannot eliminate hypotension. Without a doctor's examination, it is impossible to independently identify the true cause of the disorder and raise the upper pressure. Alternative therapy for low systolic blood pressure is not recommended, since taking such medications can mask the manifestations of hypotension, while the underlying cause of the disease will not be identified.
Diagnostic methods
All patients with low blood pressure undergo:
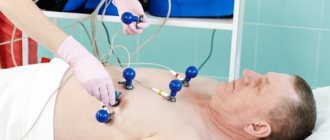
- Electrocardiogram to assess heart rhythm and detect bradycardia.
- Three-time measurement of blood pressure on both arms to assess the difference in pressure, counting heart rate and pulse.
- Holter 24-hour monitoring. Allows you to identify peaks of the lowest and highest SBP over a period of 24 hours, and other deviations.
- Ultrasound with Doppler, Echocardiography. Evaluates the condition of the cavities of the heart, large and small vessels, blood flow, and the functioning of the valve apparatus.
- Listening to the work of the heart with a phonendoscope.
Additionally, laboratory diagnostics are carried out: clinical blood and urine tests, hormones taking into account symptoms, biochemical markers of the lipid spectrum, kidney and liver tests.
What drug therapy is most often prescribed in such a case?
With low upper pressure, treatment is prescribed after receiving the conclusions of all examinations. It is extremely important to identify the cause of the disorder in order to choose the right treatment regimen.
Currently, the following are indicated to raise blood pressure:
| 1. | Medications. | Caffeine, Pantocrine, Citramon, Etilephrine, Rodeola tinctures, Leuzea. |
| 2. | Dosed physical activity. | Walking, stretching, jogging, gentle exercise 30 minutes a day. |
| 3. | Physiotherapy. | Cryomassage, acupuncture, magnetic therapy. |
| 4. | Rejection of bad habits. | Smoking, alcohol, energy drinks. |
| 5. | Normalization of work schedule, sleep and rest, nutrition. | Night sleep is at least 8 hours, daytime sleep is 30 – 60 minutes. Airing the room before going to bed. |
Drug treatment regimens include:
For vegetative-vascular dystonia, take general strengthening and tonic drugs based on herbal components, caffeine, tinctures from the roots of Ginseng, Schisandra.- For chronic fatigue and depressive disorder, antidepressants, sedatives, and sleeping pills are indicated to correct persistent insomnia.
- To improve blood flow, massage of the body, neck, and head is recommended.
- For diabetes, glycemic control, regular use of glucose-lowering drugs are indicated, and for hormonal disorders, appropriate hormone therapy.
- If another concomitant pathology causing hypotension is detected, pathogenetic therapy is prescribed.
Diagnostics
With low blood pressure, some patients have pronounced symptoms such as dizziness and weakness. In other situations, the problem may be discovered accidentally during a medical examination. The first step to make a diagnosis is to take blood pressure readings while lying down and sitting. In some cases, the causes are obvious in the form of blood loss due to injury, after surgery, or as a result of stress. Such factors are identified quite easily based on a patient interview.
A diagnostic examination involves an integrated approach and consultation with a wide range of specialists, including a neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, and oncologist.
The survey includes the following types of research:
- determination of blood composition, anemia due to bleeding or an increased level of white blood cells due to infection may be detected;
- urine examination to diagnose the presence of urinary system infections, sepsis;
- determining cortisol levels to diagnose dehydration and kidney pathologies;
- chest x-ray to detect respiratory diseases, heart pathologies and other disorders;
- electrocardiogram, echocardiogram to assess the state of the cardiac and vascular system.
If indicated, the patient may be prescribed an ultrasound examination of the veins in the legs and chest area. Such measures can identify the problem of thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
In difficult cases, the doctor prescribes Holter monitoring. Such a study will show episodes of blood pressure problems, which is often impossible to do using standard tools. Such a monitor records the patient’s vital signs for 24 hours.
How does a constant decrease in SBP affect the patient's life prognosis?
The prognosis for low upper pressure is determined by the cause of hypotension. In the absence of serious concomitant cardiac pathology, kidney disease, or endocrine disorders, the prognosis is relatively favorable.
If low SBP is detected before the age of 25 years, there is a high probability of normalizing blood pressure using lifestyle correction. At older ages, patients are recommended to undergo a more thorough examination by a cardiologist, therapist and neurologist, drug therapy and physiotherapy.
conclusions
Hypotension is determined when the pressure drops below 120/80 mmHg; it can be either normal or pathological. There are possible cases when only one indicator decreases - SBP, while the upper pressure is low and the lower pressure is normal. Symptomatically manifested by general weakness, increased fatigue, attacks of headache and dizziness. Often occurs after physical or psycho-emotional fatigue. It may be a sign of a cardiac or concomitant disease, and requires a comprehensive examination. Based on the conclusion, the doctor prescribes drug therapy and gives recommendations on normalizing the daily routine and rest.
Symptoms that require you to see a doctor
The list of manifestations can be presented as follows:
- Headache of any degree and nature.
- Dizziness, especially regular dizziness that does not go away on its own.
- Changes in heart rate such as acceleration or deceleration (both conditions are dangerous).
- Weakness, drowsiness, lack of desire to work or do anything.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting without signs of relief, often repeated.
- Heaviness in the legs.
- Chest pain for no apparent reason. Accompanied by severe arrhythmias.
- Irritability.
- Sharp darkening of the eyes when moving.
- Tinnitus, hearing loss.
- Changes in the nature of potency in men. Possible decrease in libido. Hypotension is associated with an increased risk of erectile dysfunction.
- Menstrual cycle disorders such as delay.
- Fainting, syncope.
- Paresthesia, paralysis, speech, vision and hearing disorders are possible. These are the most dangerous manifestations. Shortness of breath or suffocation.
Attention:
In all cases, you should consult a doctor or call an ambulance. The consequences can be unpredictable. It's not worth risking your health.