Heart cancer is a malignant tumor that affects the heart muscle and pericardium. An extremely rare disease. Even in the world's largest oncology clinics, such patients are encountered no more than once a year.
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
There are primary and secondary malignant tumors of the heart. Most often, it is secondary cancer, which is nothing more than metastases. In this case, the cancerous tumor first develops in another organ, for example, the lungs or kidney, and then is carried through the bloodstream to the heart, where an additional focus is formed.
The primary malignant tumor, which initially affects only the heart, is sarcoma. There are several types of neoplasms:
- Angiosarcoma arises from the cells lining blood vessels and accounts for up to 40% of malignant heart tumors.
- Fibrosarcoma - the substrate is connective tissue cells.
- Liposarcoma - develops from adipocytes, fat cells.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma - develops from myocytes.
- Leiomyosarcoma develops from smooth muscle cells.
- Undifferentiated sarcomas. The cells are so altered that they cannot be classified as any tissue. Such sarcomas account for 25% of cases.
Another type of malignant heart tumor is pericardial mesothelioma. It affects mainly men.
Sarcoma of the heart is even less common than its metastatic lesion. It's all about the characteristics of the heart tissue. As we know, the heart consists of special muscle cells - myocytes. They stop dividing quite early, even in childhood. And further growth of the organ occurs due to an increase in cell size. Actually, this aspect is the most important protection against cancer, because malignant tumors are characterized by excessive proliferation, i.e., uncontrolled cell division. And more often they affect actively dividing tissues, for example, epithelium.
On the one hand, the lack of regeneration creates a kind of protection against malignant tumors, and on the other hand, it leads to serious cardiac problems. For example, during myocardial infarction, a disruption in the nutrition of a muscle area occurs, and its cells die in this place. Because they do not repair themselves, scar tissue forms instead. It cannot perform the functions of myocytes, and accordingly a number of problems arise.
Kinds
Types of heart cancer are:
- Sarcoma. Among malignant tumors, the most common one usually affects patients in middle age (around 45 years). There are many types of sarcomas and their characteristics.
- Pericardial mesothelioma. A rare type of cancer, most often affects men, the age of patients varies greatly. Capable of metastasizing to the spine, brain, and nearby soft tissues.
- Primary lymphoma. An even rarer type of tumor is more often observed in patients with various types of immunodeficiencies. This type of heart cancer grows very quickly.
Other types of cancer can also affect the heart and cause heart damage. For example, melanoma, breast or lung carcinoma, kidney cancer - all of this can metastasize to the heart. Leukemia and lymphoma have similar properties. But here we are not talking about heart oncology itself, but about the fact that oncology of another localization invades this organ.
Pathogenesis
All processes that occur in the heart are characterized by an excessively high rate, which is explained by the increased work of the organ. Cells practically do not divide, so heart cancer is rare. However, the inability of cells to divide does not prevent the formation of malignant tumors. When the heart muscle is damaged, it becomes scarred rather than repaired. If oxygen does not enter the changed area, it becomes necrotic and dies. The exact pathogenesis of the development of heart cancer is still unknown, but there are certain prerequisites that can provoke uncontrolled cell division and mutation. The initiation and growth of a tumor can be triggered by certain factors.
Symptoms
The issue of symptoms is very complex. In the first stages, the disease usually has no symptoms. And when heart cancer symptoms and signs begin to appear, they can easily be confused with signs of other diseases. Therefore, patients often seek help in late stages or even die without knowing that they had such a diagnosis (sudden death). Possible symptoms of the disease include:
- cough;
- joint pain and fever;
- blue color of fingers when pressing them;
- swelling of different parts of the body: legs, abdomen, face;
- bloating of veins;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, fatigue;
- dizziness, fainting;
- rapid heartbeat, irregular heart rhythm;
- feeling of a lump in the chest, creeping pain;
- noise in ears.
Heart problems are constantly getting worse, increasing - and the patient’s well-being is deteriorating. It is by no means necessary that even if the listed signs are present, we are talking about symptoms of heart cancer - cardiologists can diagnose a completely different problem, but going to a consultation and getting a diagnosis is very important.
Heart tumor: when is it necessary to sound the alarm?
The most terrible disease of any human organ is a tumor, benign or malignant. Heart tumors are quite rare, but still occur in oncological practice.
Classification and types of tumors
Neoplasms in the heart can affect both the pericardium and the tissue of the heart muscle itself. Such a pathology is not often found in oncology due to the good blood supply to the organ and the rapid metabolic process.
Heart tumors are: primary (develop from the myocardium itself) and secondary (formed from cancer cells coming to the heart through lymph and blood from organs with cancer).
Most primary formations are benign, but in 15% of cases malignant processes are also diagnosed.
8
24/7
Benign heart tumors include 7 types:
- Myxoma. Occurs in 78% of cases among all myocardial tumors. The tumor grows into the cavity of one of the atria. Myxoma is more often diagnosed in women during the postmenopausal period.
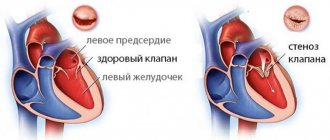
- Papillary fibroelastoma. A type of tumor that is quite common. The location is the papillae of the aortic or mitral valve. The specific location of the tumor prevents complete closure of the valve during ventricular contraction.
- Rhabdomyoma. The tumor is formed from cardiac muscle tissue. Occurs in 12% of cases. The location is the left ventricle. Provokes conduction disturbances in the heart muscle. More often diagnosed in children.
- Fibroids mainly affect the heart valves. It can provoke stenosis between the ventricle and the atrium, pericarditis.
- Lipoma. Neoplasm from adipose tissue cells. The location can be any part of the myocardium. Usually it does not manifest itself, but if it is large in size it can provoke disruptions in the functioning of the heart.
- Hemangioma. A tumor of the heart vessels, which is diagnosed very rarely. Does not affect the functioning of the myocardium if it does not grow into the sinus node. In such a case, the heart rhythm may become disrupted, and severe cases can lead to death.
- A teratoma is a cardiac cyst that develops from embryonic cells. The tumor can be located under the heart, on the side or above it.
Sarcomas are considered the only type of primary malignant tumors of the heart. It is divided into the following types:
- angiosarcoma: formed from cells of blood and lymph vessels, most often affects the right atrium, in most cases it is diagnosed in men;
- fibrosarcoma: develops from the soft tissue of the myocardium;
- liposarcoma: originates from a collection of cells of predominantly mesodermal origin (mesinchem);
- Rhabdomyosarcoma: forms in the striated muscles, sometimes grows through the entire heart, causing symptoms of myocardial infarction.
Secondary heart tumors provoke metastases of cancer developing in other organs. These include cancer of the kidneys, lungs, breast, stomach, and thyroid gland.
Causes
The cause of tumors in the heart area is quite difficult to determine. Thanks to long-term clinical studies, doctors and scientists have discovered common risk factors for the development of this pathology. These include:
- heart surgery after injury or clinical problems;
- blood clots;
- infectious diseases;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- toxins;
- obesity and overweight;
- metastases of cancer of other organs;
- atherosclerosis of blood vessels and brain;
- constant stressful situations that lead to weakened immunity;
- genetic predisposition.
Symptoms
In the early stages of a heart tumor, there are no symptoms. A person may not even realize that they have cancer. In addition, its symptoms are very similar to other diseases.
A cancer patient may experience a slight increase in low-grade fever, which persists throughout the entire period of cancer development. There is weakness, fatigue, joint pain. Unreasonable weight loss and numbness in the fingers also indicate illness.
Depending on the location of the tumor, patient complaints may differ.
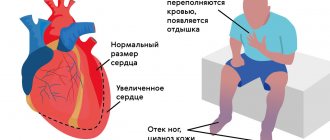
For example, if a tumor has grown in the myocardium, it manifests itself as heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias) and other serious disorders. The patient develops:
- dyspnea;
- swelling of the legs;
- accumulation of fluid in the lungs;
- weakness.
8
24/7
Heart tumors have the ability to masquerade as heart defects. Then the following symptoms are present:
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- physical labor is difficult to bear.
A sharp deterioration in the condition can be caused by tumors that have grown into the cavity of the heart. With this pathology, myocardial conductivity decreases, heart failure develops with attacks of suffocation (cardiac asthma).
It is worth noting that if the patient has tumors in the heart, the fingers become like drumsticks. The finger itself becomes thinner, and its tips, on the contrary, thicken.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing heart tumors seems to be quite a difficult task. Neoplasms have many morphological forms. To determine the type, stage and location of the tumor, diagnostic methods are used:
- collecting anamnesis and assessing the patient’s complaints;
- chest x-ray;
- electrocardiogram;
- angiocardiography;
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- probing of the heart cavity;
- pericardial puncture;
- biopsy;
- echocardiography;
- blood chemistry.
All of the above measures will help determine the presence of cancer, the number of metastases, and the extent of their growth into other human organs and tissues.
Treatment at different stages
Doctors consider heart tumors to be the most complex cancer diseases. They cannot be cured. If cancer is detected in the early stages, surgery is performed, provided that the tumor is primary. However, there is still no guarantee of a complete cure. According to statistics, out of 10 people, four have cancer that returns during the first 2 years after surgery to remove a heart tumor.
Cardiac oncology requires complex treatment. This includes radiation and chemotherapy. To eliminate defects that have arisen due to the growth of the tumor, a symptomatic course of treatment is prescribed. Therapy aimed at maintaining and restoring the body is also necessary. Medicines are selected by the attending physician.
If a tumor is detected at later stages, surgical treatment is not advisable. In such cases, it makes sense to use therapy aimed at alleviating the symptoms of the disease and improving the patient’s quality of life – palliative care.
The surgical technique itself includes several stages:
- opening the chest (thoracotomy);
- connection to a heart-lung machine;
- cutting the heart chamber;
- suturing the incision site;
- disconnection from the heart-lung machine.
Also in surgical practice to remove heart tumors, a gamma knife is used. It is used in cases where surgical intervention is not possible for certain reasons. This type of tumor removal is a good alternative if the patient has severe illnesses for which conventional surgery is contraindicated.
After undergoing surgical treatment, patients are advised to monitor the condition of the myocardium using ultrasound.
Forecast
The prognosis after removal of single tumors is favorable. Life expectancy increases by 5-10, sometimes more years. Patients need to be constantly monitored by a cardiologist and cardiac surgeon in order to identify a possible recurrence of oncology in time.
As for the heart tumor – myxoma, the prognosis after the operation is very good. Many patients never experience it again. Relapses are observed in patients with hereditary tumors or with incomplete excision of the myxoma attachment site.
Almost no deaths were recorded during or after surgery. The majority of patients who get rid of the pathology in a timely manner experience a complete recovery. Clinical manifestations and hypertension disappear completely.
An important factor for a successful outcome is strict adherence to the doctor’s recommendations and maintenance therapy after the intervention.
Disease prevention
There are no specific preventive measures as such. However, doctors advise following general preventive standards.
First of all, you need to get rid of bad habits (smoking, excessive drinking), lead a healthy lifestyle, and eat right. It is necessary to pay attention to contraindications and side effects when choosing medications.
Timely treatment of infectious diseases serves as a preventive measure. Their chronic stages and inflammation should not be allowed. All these factors contribute to the formation of cancer cells in the body. Don't forget about strengthening your immune system.
It is recommended to visit a cardiologist once every 6 months, undergo an ultrasound and ECG of the heart.
It is important to remember that it is better to prevent the disease and consult a doctor in time than to later look for optimal ways to treat it. A heart tumor detected in the early stages is the key to a good prognosis in treatment and complete relief from the disease.
8
24/7
Causes and risk factors
The causes of heart cancer in men and women, as in many other cases, are not 100% identified. But there are a number of factors that increase the risk of developing the disease. These include the following:
- serious immunity disorders;
- chemical, radiation and UV effects on the body;
- genetic predisposition;
- degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one;
- weakening of the body against the background of various negative factors: alcohol abuse, smoking, drug use, poor quality nutrition, sedentary lifestyle, etc.
As already mentioned, cancer in the heart may not be primary - that is, it develops in the form of a subsequent lesion due to oncology in another area. In this case, it is considered secondary, and the cause of the development of oncology is considered to be the primary disease.
General information: does heart cancer happen?
Heart tumors are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that grow from the membranes and tissues of the heart. Neoplasms can occur at any age and develop from any tissue. Tumors can invade the pericardium, myocardium, and damage the valve apparatus and septum of the heart. During pregnancy, tumors in the fetus can be diagnosed at 16-20 weeks of intrauterine development using fetal echocardiography . The most common are metastatic tumors , which are secondary in nature, less often - primary. Absolutely all neoplasms are potentially dangerous and carry a high risk of developing deadly complications. Wikipedia contains a detailed description of cardio-oncology.
Diagnostics
To diagnose heart cancer in women or men, it is necessary to carry out a set of measures and studies:
- Examination and interview at an appointment with a cardiologist.
- X-ray examination.
- Angiocardiography. The method is used to study the thoracic veins, other large vessels, and chambers of the heart.
- ECG, MRI, CT, EchoCG.
- Echoscopy with Doppler examination. It is performed in one of two ways: through the chest, like a regular ultrasound, or through the esophagus.
- Coronary angiography (one of the X-ray methods).
- Several laboratory tests: tumor markers, histological analysis, as well as a number of blood tests (ESR, leukocytes, platelets, hemoglobin, C-reactive protein).
A thorough investigation is very important, as signs of heart cancer may end up pointing to a completely different diagnosis that has a much better prognosis.
Forecast
The three-year survival rate after removal of single benign cardiac tumors is 95%. After surgical treatment, patients are observed by a cardiologist and cardiac surgeon with mandatory annual echocardiography monitoring for timely diagnosis of tumor recurrence. When multiple tumors are present, the five-year survival rate is only 15%. For metastatic and primary cardiac tumors, the prognosis is considered unfavorable. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy have no effect on the prognosis, and surgical treatment is considered ineffective.
Treatment
For symptoms of heart cancer and an accurate diagnosis, the following treatment options are offered:
- Radiation therapy. In this case, brachytherapy is often used - this is when a radio source is injected directly into the tumor.
- Chemotherapy is usually used to control metastases in other organs.
- Surgical intervention. It is performed extremely rarely in the treatment of heart cancer - only if the heart is affected and other organs are not yet affected.
- Maintenance therapy. The patient is prescribed medications that alleviate his condition and support the body to fight the disease.
Forecasts
This type of heart cancer has a poor prognosis in men and women. If the problem is detected early and treated effectively, survival of five years is possible. But most often the disease is found late, so the survival time is much shorter.
Two-year survival rate at different stages is possible in the following percentage:
- Stage 1 - 8.3%.
- Stage 2 - 3%.
- Stages 3 and 4 - 0.9%.
If metastases have not spread to the spinal cord and brain, even in the last stages the prognosis is more favorable - 11-14% survival rate over two years.
The situation is more complicated with sarcomas - these are aggressive types of cancer in men and women, which on average give the following survival rate:
- Angiosarcoma: 6-11 months.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma: 2 years at stages 1 and 2, less than a year at stages 3 and 4, provided the primary tumor is removed and chemotherapy is used.
- Liposarcoma: 6-8 months.
As you can see, the prognosis will depend on the characteristics of a particular heart cancer, and it can only be determined after a thorough diagnosis.
Symptoms and signs of heart cancer
The clinical picture is largely determined by the type of tumor, its size, location and ability to decay. Extracardiac tumors are characterized by:
- chills;
- fever;
- rashes on the skin;
- arthralgia;
- weight loss.
When the tumor compresses the coronary arteries and cavities of the heart, chest pain and shortness of breath occur. As the tumor grows and bleeding develops, a life-threatening condition can develop - cardiac tamponade .
A neoplasm with intramyocardial growth ( rhabdomyoma , fibroma ) is characterized by compression and growth into the conduction system of the heart, which manifests itself in the form of paroxysmal tachycardia , atrioventricular and intraventricular blockades.
Intracavitary neoplasms obstruct the flow of blood from the chambers and disrupt the function of the valves. Characteristic phenomena are tricuspid and mitral stenosis and insufficiency. The main symptoms appear when changing body position, which is associated with hemodynamic overload.
Often the first symptoms of heart cancer are thromboembolism in the pulmonary arteries and arteries of the systemic circulation. Tumors growing from the right side of the heart are characterized by:
- pulmonary hypertension;
- pulmonary embolism;
- cor pulmonale.
Tumors growing into the left side of the heart are characterized by:
- stroke or transient ischemic attack;
- ischemia ;
- myocardial infarction.
A heart tumor can be suspected when infarctions of internal organs are detected in young people in the absence of congenital and acquired heart defects, infective endocarditis , or atrial fibrillation .
Statistics
It is difficult to provide global statistics on this disease. But there is one interesting fact. One of the largest research centers in the world, the private Mayo Clinic in the USA, notes that per year they see no more than one patient who shows signs of heart cancer.
But such statistics should not justify a negligent attitude towards the previously listed symptoms. In addition to oncology, there are many other heart-related problems that, if left untreated, can lead to death.
Diagnosis and treatment of heart cancer in Moscow
The Institute of Nuclear Medicine (Moscow region, Khimki, Klyazma quarter) has all the necessary equipment for the diagnosis and treatment of malignant tumors of the heart. Patients are received in a modern outpatient diagnostic complex, built taking into account the latest advances in oncology and radiology.
Prevention
The development of a malignant neoplasm in the heart can be prevented by following certain rules:
- do not neglect physical activity, gymnastics, keep yourself in good shape;
- carry out timely treatment of infectious diseases, preventing them from becoming chronic;
- monitor your weight;
- avoid eating carcinogenic, fatty and unhealthy foods;
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- control cholesterol and blood sugar levels;
- annual medical examination.
Reasons for development
A heart tumor can develop, according to doctors, for one of the following reasons:
- abnormal regulation of cell division;
- immune disorders in the body;
- radiation;
- viruses;
- extreme sun exposure;
- smoking;
- poisonous mushrooms;
- benzene, etc.
The highest probability of death, according to statistics, is observed in cases where the tumor is caused by tobacco use. Scientists also confirm a hereditary factor - approximately 10%. Women are more susceptible to the disease.
Painkillers
The symptom that most clearly indicates the development of a malignant tumor is pain. An actively growing tumor most often causes pain. Pain can be caused by damage to the nervous tissue, the development of an inflammatory process in the tumor. To alleviate the patient's condition, pain medication is administered. It is prescribed individually, taking into account the patient’s condition, and can significantly reduce the intensity of pain. Pain relief for stage 4 cancer:
- If mild pain occurs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
- pain of moderate intensity is treated with combination drugs: ketorol and other potent drugs.
- severe, debilitating pain is treated with the help of strong drugs containing narcotics - fentanyl, morphine, promedol.