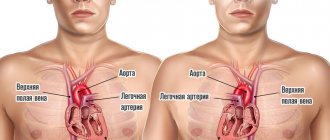
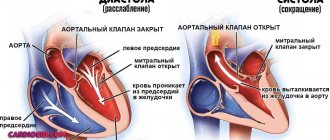
The structure of the heart contains tendon threads called chords. Normally, they are attached to the valve flaps through which blood flows, and prevent them from sagging under the influence of gravity. However, sometimes an additional chord may be detected during diagnosis. This is a structural feature of the heart, which does not always indicate an anomaly. But in some cases it can be dangerous to the health and even life of the patient.
What is an accessory chord in the heart?
The chordae are tendinous threads of equal thickness and size, consisting of muscle and connective tissue and connecting the valve apparatus and the ventricle. When they contract, they pull the valve leaflets towards themselves, which promotes the formation of a gap and the release of blood from the atria. During relaxation, the passage is closed. The additional (false) chord does not perform its intended functions. It has an atypical structure and can connect to the ventricle or valve at only one end.
The abnormal chord has a code according to the ICD (International Classification of Diseases) 10th revision Q20.9. It stands for Congenital Abnormalities of the Heart Chambers. “False chord” is not considered as an independent pathological process. It is divided according to its location in the cardiac cavities as follows:
- Direction: transverse;
- diagonal;
- longitudinal
- right ventricular;
- single;
- basal;
An extra chord in the heart usually does not pose a particular danger, but whether this is so depends on the hemodynamic significance. Transverse tendon threads can disrupt the flow of blood, which will lead to various consequences (stroke, arrhythmia, heart block). Multiple chordae are no less dangerous, as they are perceived as a sign of genetic pathologies.
In most cases, a single left ventricular filament is detected in newborns during an ultrasound examination of the heart. Sometimes it is noticed in the fetus in the womb during routine diagnostics. In adults, its detection is associated with a medical examination or the occurrence of cardiac symptoms.
False tendon filaments in infants are often combined with other minor anomalies of the heart structure:
- excess trabecula;
- open oval window;
- insufficiency of valve apparatus.
Unlike other anomalies, the patent foramen ovale closes with age. Only in rare cases does it remain forever.
A well-known pediatrician, E. O. Komarovsky, commented on the presence of “false chords” in babies. According to the expert, the baby will not experience any discomfort. This anomaly is more an individual feature than a serious defect. Only in exceptional cases, in the presence of many tendon threads, is it possible that hemodynamic disturbances may occur. Treatment will be aimed at stabilizing the heart. Single chords do not require any treatment regimen or restrictions regarding the type of activity, sports or diet.
Danger of SVC syndrome
SVC syndrome, manifested by attacks of tachycardia, reduces the patient’s quality of life. Loss of consciousness during paroxysms can lead to serious injuries and accidents.
In addition, reciprocal AV tachycardias in WPW syndrome belong to the category of prefibrillatory arrhythmias. This means that frequent attacks of the disease can lead to more dangerous and complex atrial fibrillation, which in turn can transform into ventricular fibrillation and lead to death.
Causes
An additional chord in a child’s heart appears in the womb due to certain factors:
| Cause | Description |
| Hereditary predisposition | The presence of false tendon threads or other heart ailments in one of the parents is the main cause of abnormalities in their baby. |
| Bad habits | A woman who drinks alcohol, drugs and smokes cigarettes during pregnancy significantly increases the likelihood of developmental defects in the unborn child, affecting not only the heart. |
| Poor environmental situation | Polluted air and water contribute to the formation of abnormalities in the baby during intrauterine development. |
Clinical picture
One extra chord in the left ventricle rarely manifests itself. The situation is different if the filament is located transversely in the right ventricle, or if there are quite a lot of them. The patient begins to experience discomfort associated with impaired hemodynamics and heart function in general:
- fast fatiguability;
- irregular heartbeat;
- stabbing chest pain;
- mood swings;
- general weakness;
- dizziness.
Signs are most often detected during adolescence. The child begins a stage of intensive muscle and bone growth, which puts additional stress on the heart. If they are detected, it is necessary to register with a cardiologist so that he can monitor the development of the situation and take timely measures to stabilize the condition.
Diagnostic methods
A cardiologist should be involved in identifying excess chordae and drawing up a treatment regimen. They are detected using instrumental diagnostic methods and by auscultation (listening to noises):
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) allows you to visualize the structure of the heart and examine hemodynamic features.
- Auscultation helps to hear diastolic murmurs arising from the accessory chord.
- Electrocardiography (ECG) displays the electrical activity of the heart and allows you to see possible impulse conduction abnormalities.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe daily ECG monitoring and bicycle ergometry. The first examination helps to obtain accurate data on the work of the heart muscle throughout the day. The second test is carried out to evaluate her response to physical activity.
An identified extra chord in a child’s heart may gradually “disappear.” The baby is actively growing, which leads to a displacement of the anomaly. Instrumental diagnostic methods will confirm its absence. A treatment plan will not be drawn up. In conclusion, the doctor will indicate that the heart is without pathologies.
Course of therapy
In the absence of symptoms of disruptions in blood flow, there is no point in treating the anomaly. A person will have to undergo an ultrasound and ECG annually and, with the results obtained, make an appointment with a cardiologist to monitor the condition of the heart muscle.
If the clinical picture of a hemodynamic disorder is still present, then drug therapy is prescribed:
- Preparations rich in B vitamins (“Neurovitan”, “Superum”) are involved in nervous regulation, increase cellular metabolism and stop the development of atherosclerosis.
- Tablets containing magnesium and potassium (Asparkam, Orocamag) help stabilize blood pressure, vascular tone and neuromuscular transmission.
- Antioxidants (“q-Protect”, “Resveratrol”) prevent the development of atherosclerosis, normalize heart function and stimulate metabolic processes in the myocardium.
- Medicines with nootropic effects (Aniracetam, Semax) are used to improve cognitive abilities and increase tolerance to stress (physical, mental). They are also used to relieve signs of VSD against the background of severe disruptions in hemodynamics.
Antiarrhythmic and other cardiac medications are prescribed by the attending physician depending on the patient’s condition. To complement the therapy regimen, you should follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- create the right diet;
- spends more time outdoors;
- take breaks while working;
- exercise;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- sleep at least 7-8 hours a day.
With the development of various life-threatening conditions, the patient must be hospitalized. They are usually the result of multiple or transverse accessory chordae. In a hospital setting, a detailed examination will be carried out and treatment will be prescribed.
Surgery is required if the accessory tendon thread disrupts the conduction of impulses and leads to severe disruptions in blood flow. Doctors will perform a procedure of cryodestruction (destruction of tissue by exposure to cold) or excision of the chord.
What treatment is needed
An additional chord of the left ventricle, if it does not have any clinical manifestations and does not interfere with myocardial function, does not require specific treatment. However, it requires regular visits to a cardiologist and periodic preventive examinations (ECG, echocardiography).
If any symptoms occur, drug therapy may be prescribed. Most often, vitamins are prescribed, the purpose of which is to improve the nutrition of the layers of muscle tissue of the organ. This can be thiamine (B1) and riboflavin (B2); nicotinic acid (vitamin PP) is often prescribed. If it is necessary to improve metabolism in cells, antioxidants (for example, cytochrome C) are used.
If an additional chord of the transverse direction is found in the LV cavity, and its presence affects the functioning of the organ, then hospitalization with a more detailed examination is necessary.
In rare cases, an operation to excise the anomaly may be prescribed, or it may be limited to cryodestruction (this is the name of the cold treatment method).
Get a treatment program
Possibility of complications
It is impossible to predict in advance whether an additional chord will lead to the development of disruptions in the functioning of the heart or not.
The most favorable prognosis is in the presence of an anomaly in the left ventricle.
In most cases, it does not lead to pathological changes and does not require treatment. The use of medications to improve the functioning of the heart muscle significantly reduces the likelihood of complications. The only thing to be wary of is transverse and multiple tendon strands. They have the most unfavorable prognosis.
Symptoms of WPW syndrome
Symptoms of SVC syndrome are usually mild. These include heart rhythm disorders:
- atrial flutter;
- atrial fibrillation;
- reciprocal supraventricular tachycardia;
- ventricular tachycardia;
- ventricular/atrial extrasystole.
In turn, attacks of rapid rhythmic/irrhythmic heartbeat are accompanied by:
- “fluttering”/fading heart;
- attacks of suffocation (feeling of lack of air);
- dizziness;
- increased heart rate;
- arterial hypotension;
- weakness, loss of consciousness.
Deterioration of the patient's condition may occur after drinking alcohol, emotional or physical stress.
In most cases, paroxysmal arrhythmia in SVC syndrome can be stopped by taking a deep breath and holding the air. Prolonged attacks require emergency hospitalization and treatment under the supervision of a cardiologist.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Military service
In the presence of a single false chord, young people who have reached the age of 18 are still drafted into the army for service. Representatives of the medical commission believe that it will not have any effect on well-being during the next year of life. The conscript does not need to undergo treatment in a hospital setting. He will be able to follow orders and engage in physical training on an equal basis with other military personnel. A contraindication to service in the armed forces is an abnormal heart rhythm and other severe complications caused by the anomaly.
Excess chords in the ventricles of the heart muscle are perceived by specialists as a minor anomaly that does not require treatment and does not limit human life. It is enough to do an ultrasound every year to monitor its development. If signs of disruption in hemodynamics and arrhythmia occur, drug therapy is prescribed. If it does not help to achieve relief of the condition, then surgical intervention will be required.
Doctor's advice: how often to do echocardiography with false chord
For a standard check-up for a minor cardiac anomaly, it is enough to undergo an echocardiography once a year. The examination is scheduled unscheduled if:
- the patient has complaints, including those not directly related to cardiology;
- you notice that the child is growing rapidly;
- there was a sharp weight loss;
- a chronic disease has been diagnosed, such as asthma, gastritis, nephritis;
- the child goes to kindergarten, school, university;
- there is a question about the sports section;
- stress occurred: an exam, the loss of one of the family members, conflict in the children's team and at home;
- pregnancy is planned or determined.
Single LVDC is not considered a pathology. Experts consider them as an anatomical feature of a person. The presence of an additional chord is not a contraindication to attending physical education classes. Young men with abnormal cords can be drafted into the army if they do not have complications or concomitant pathologies. It is only important to clearly tell the child about his condition and warn him that he needs to be attentive to his health.