The acid-base balance in the blood is a vital parameter. Its normal values range from 7.35 to 7.45 on the pH scale. If the pH drops below 7.35, the patient has acidosis. If it rises above 7.45, this means that the patient has alkalosis.
Alkalosis and acidosis are metabolic (metabolic) and respiratory (respiratory). It depends on the reasons for their development.
Respiratory acidosis develops when a lot of carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood, forming carbon dioxide when combined with water. Because of this, the acidity of the blood increases. This condition can develop with respiratory disorders that cause decreased pulmonary ventilation.
1.General information
As is known, the human body maintains homeostasis - the constancy of a number of internal conditions, biochemical and biophysical parameters necessary to ensure normal life activity.
One of the most important is the pH value, or the “acid-base reaction pH” (pH), which is remembered from school chemistry lessons. A shift in this indicator in one direction or another grossly disrupts the functioning of all major organs and leads to the development of a serious, and if measures are not taken in a timely manner, a life-threatening condition. “Acidification”, i.e. An abnormal decrease in blood pH is called acidosis. Accordingly, alkalosis is a shift in pH to the alkaline side, i.e. excess pH level = 7.35 7.45.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Principles of diagnosis and treatment of alkalosis
If the development of alkalosis is suspected, the specialist not only carefully examines the patient, listens to his heart and lungs, but also refers him for laboratory and instrumental examinations.
An ECG with alkalosis reveals low-voltage waves and indirect signs of a decrease in potassium in the blood. A biochemical blood test determines a decrease in the concentration of chlorine, potassium, and calcium. No pathological impurities appear in the urine, but it changes the reaction to alkaline. Mild forms of alkalosis, as well as respiratory disorders due to nervous feelings, hysteria, and neurosis can be eliminated at home. Along with drug therapy, the patient will be advised to follow a diet limiting alkaline drinking, milk, and fermented milk products. Steamed or boiled vegetables are recommended, as well as fruits, lean meats, and grains.
Mild respiratory alkalosis can be eliminated quite simply. In most cases, to normalize the acid-base balance, it is enough to reduce the frequency of respiratory movements. If you have anxiety or a panic attack, you should calm down and try to slow down your breathing. In addition, experts recommend breathing into a paper bag, which increases the proportion of carbon dioxide in the inhaled air mixture. As carbon dioxide in the blood increases, signs of alkalosis disappear and health returns to normal.
For metabolic alkalosis and severe forms of respiratory alkalosis, hospitalization and treatment in a clinic are indicated, where inhalation of carbogen containing up to 8% carbon dioxide is established. For convulsions, intravenous calcium chloride is indicated. Severe agitation with hyperventilation can be eliminated with the help of Relanium; for pulmonary edema, morphine is indicated, which depresses the respiratory center and reduces the frequency of respiratory movements per minute.
Disorders of electrolyte metabolism are corrected by prescribing infusion therapy:
- Sodium and calcium chloride drip into a vein;
- Panangin, potassium chloride, K-polarizing mixture intravenously;
- Potassium-sparing diuretics (veroshpiron).
To eliminate the causes of alkalosis, the following are used:
- Metoclopramide - against nausea and vomiting;
- Loperamide, activated carbon, motilium - help eliminate diarrhea and the associated loss of fluid and electrolytes;
- Hemodialysis - for severe intoxication;
- Sedatives and neuroleptics - eliminate hysteria and neurotic disorders (diazepam, aminazine).
For some diseases, surgical treatment can help eliminate alkalosis. In particular, stenosis of the gastric outlet against the background of a chronic ulcer, occurring with metabolic disorders, can be successfully operated on to eliminate the phenomena of chronic alkalosis.
In children, alkalosis requires treatment when the pH level reaches and exceeds 7.5. The first step is to develop a treatment regimen for the underlying pathology - infusion therapy for dehydration, administration of missing microelements, etc. Premature infants are prescribed vitamin C and amino acids (when the administration of sodium and potassium is contraindicated).
Alkalosis is quite treatable, but the prognosis is much better in the case of a compensated course of the pathology or the presence of initial symptoms. Severe forms require hospitalization in the intensive care unit. Regardless of the cause and symptoms, throughout the entire period of treatment the patient needs strict control of water-electrolyte and acid-base balance through biochemical blood tests.
2012-2020 sosudinfo.ru
Go to section:
Blood and its diseases, components, tests, biochemistry
Recommendations to SosudInfo readers are given by professional doctors with higher education and specialized work experience.
One of the leading authors of the site will answer your question in the form below.
2. Reasons
Depending on the specific causes of alkalosis, there are several main types.
Thus, gas (respiratory) alkalosis develops with hyperventilation - excessively intense breathing, when an abnormally high amount of oxygen enters the body. In turn, common causes of this condition include tumors and inflammatory lesions of the brain, intoxication with certain substances of organic and medicinal origin (in case of overdose), febrile temperature, and massive blood loss.
Among non-gas alkaloses, there are three main forms: excretory, exogenous and exchange (metabolic).
Thus, excretory alkalosis develops due to the loss of large volumes of substances with an acidic pH reaction, for example, gastric juice with uncontrollable vomiting, gastric fistulas, etc., as well as with some kidney diseases, hyperhidrosis (pathological sweating), prolonged use of diuretics .
Exogenous (due to external factors) alkalosis occurs, for example, when consuming large doses of baking soda to reduce high acidity in hyperacid forms of gastritis and peptic ulcers.
Metabolic alkalosis, by definition, occurs with etiologically different (hereditary or acquired) metabolic disorders, primarily electrolytes.
Finally, mixed type alkalosis is occasionally observed, in which respiratory and non-gas etiopathogenesis are combined (for example, in severe traumatic brain injuries, when hyperventilation is accompanied by intense vomiting).
Visit our Therapy page
Symptoms of alkalosis
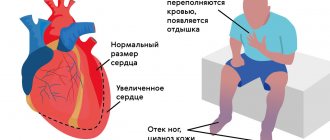
Hypoxia of tissues increases when carbon dioxide is removed from them, which causes symptoms of alkalosis. This is expressed in a decrease in venous tone, a decrease in cardiac output, excessive excretion of water and electrolytes in the urine, and a drop in blood pressure.
A person who develops alkalosis should first pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Frequent dizziness.
- Feeling of crawling on the skin, deterioration of its sensitivity.
- Increased fatigue, excessive weakness.
- Fainting.
- Feeling of lack of air.
- Increased pulse and heart rate.
- Deterioration of cognitive abilities.
Excessive psychomotor agitation, pale or blue skin, increased anxiety - all this may indicate alkalosis. The patient will breathe rapidly (up to 60 breaths per minute) if he develops respiratory alkalosis.
Since the body begins to suffer from oxygen starvation, the heart will beat frequently, in violation of the normal rhythm. Blood pressure decreases. If a person is in a horizontal position, then any attempt to stand up can cause him to fall further. As a result, a person may even lose consciousness.
Disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels and electrolyte imbalance provoke more frequent urination in the patient. This, in turn, increases the likelihood of developing dehydration, which causes seizures. If the patient has another brain lesion, for example, an aneurysm or tumor, then when the acid-base balance increases, the likelihood of an epileptic seizure increases.
Symptoms of metabolic alkalosis are most often transient; moreover, they are compensated by the body's reserves. At peak increases in the alkaline component in the blood, respiratory depression and the formation of edema are possible.
With decompensated metabolic alkalosis, symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, weakness, increased fatigue, thirst, and loss of appetite are observed. In this case, the patient complains of headaches, periodic twitching of the muscles of the face and limbs.
The more calcium removed from the body, the stronger the cramps. Skin that has lost moisture begins to peel and crack, and folds appear on it. Carrying out infusion therapy provokes the occurrence of edema. Unlike respiratory alkalosis, the metabolic form of the pathological condition is accompanied by a decrease in breathing, but the heart rate increases. A person becomes apathetic to the world around him, his drowsiness increases, and coma may develop.
People suffering from stomach ulcers or acid gastritis often try to relieve the pain by drinking milk or drinking alkaline fluids. This causes them to develop Burnett syndrome. Alkalosis becomes chronic, which is expressed in increased weakness and lack of appetite. The patient often feels sick and sometimes vomits, and the skin itches. Calcium salts begin to deposit in the renal tubules, which leads to the development of renal failure.
Respiratory alkalosis leads to deterioration in tissue nutrition, since an insufficient amount of blood reaches them. The pulse becomes faster, muscle tone increases. Mental abnormalities develop when the pH level rises to 7.54. If the cause of the development of respiratory alkalosis is hysteria, then the patient shows severe anxiety, he is very irritated, and aggressive.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
The most common mechanism for the development of the clinical picture is circulatory disorders: blood pressure and blood supply to the heart and brain decrease. Muscle spasms and cramps, fainting, disturbances in intestinal motility, and a significant decrease in mental productivity may occur.
With gas alkalosis, changes in mental status can also be observed: agitation, excitement, etc.; Individuals with lesions of the central nervous system and a predisposition to epilepsy often develop epileptic seizures.
Non-gas types of alkalosis are characterized by severe weakness, increasing fatigue, headache, thirst with lack of appetite, sometimes convulsions or tremors; in chronic forms, skin itching, apathy, and pathological changes in the kidneys may develop.
The diagnosis is suggested clinically and confirmed laboratory.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Alkalosis in a child
Alkalosis is a condition that can affect not only adults, but also children. Moreover, it is children who are more susceptible to this condition, since the functioning of their blood buffer systems is imperfect.
Alkalosis in childhood can be caused by any disease that is accompanied by vomiting: intestinal obstruction, congenital gastric stenosis, trauma received during childbirth, infection with infectious flora. Errors in therapy using alkaline solutions or diuretics can also lead to alkalosis.
Metabolic disorders may be caused by heredity. Metabolic alkalosis in a child due to Barter syndrome develops during the first year of life. This is expressed in severe vomiting, increased body temperature, and delayed physical development. The child urinates a lot and drinks a lot.
Respiratory alkalosis develops against the background of pulmonary hyperventilation. This condition can be provoked by ARVI, pneumonia, skull injuries, meningitis, encephalitis, brain tumors, and disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system. In this case, the symptoms of the underlying disease will come to the fore.
If calcium is removed from the body of a young child, then the manifestation of this disorder will be convulsions and muscle spasms. Tremors of the limbs and increased sweating are also observed. Older children complain of tinnitus, dizziness, and deterioration of sensitivity. If alkalosis has an acute course, then the child may become overexcited and develop coma.
Why does the acid-base balance in the body occur?
The human body is full of mechanisms that regulate the normal state of the buffer system throughout life, launching certain processes to normalize the acid-base balance. The foods you eat every day directly affect your pH.
If the acid-base balance is disturbed, two states of the internal environment of the body are possible - alkalosis or acidosis.
Alkalosis is alkalization of the body. In this case, alkaline compounds will predominate in the liquid system, and the pH will exceed 7.45.
Acidosis is acidification of the body. It is a more dangerous condition, since the body is more resistant to alkalis than to acids. That is why, with any changes, first of all, doctors prescribe a diet that allows you to normalize the pH value.
Treatment
A prerequisite is the elimination of the primary cause of alkalosis. It all depends on the specific provoking factor.
- Vomiting requires the prescription of specific drugs. Metoclopramide, Cerucal.
- Sorbents for intense diarrhea. Be it activated carbon or other medications specifically designed for this purpose.
- Neurotic manifestations with uncontrolled hyperventilation require elimination with the help of sedatives (Diazepam). In complex clinical cases, if the patient is in a psychotic state, the use of antipsychotics will be required. However, this is a relatively rare situation.
As for eliminating the symptoms themselves, other medications are used.
- Panangin, Asparkam. Means for normalizing potassium levels in the body. This is a must. Read about other potassium supplements in this article.
- It is possible to use gentle potassium-sparing diuretics: Veroshpiron, Spironolactone and the like. This group of drugs is described in detail here.
- As a measure for the treatment of alkalosis, Darrow's solution and electrolytic salt mixtures are used.
In the first days after recovery from an acute condition, it is necessary to follow a gentle diet. You need to take as little acid-containing foods as possible.
This includes, for example, fermented milk components, fresh fruits, and vegetables. As support, it is possible to prescribe vitamin-mineral complexes and ascorbic acid.
Treatment of alkalosis in the early stages is carried out in intensive care conditions. After 1-2 days, the person, with a successful course and good dynamics, is sent to the general ward. He should remain under supervision for several more days.
Gas alkalosis
The occurrence of gas alkalosis, as a rule, is caused by a variety of influences and disorders that lead to such an increase in the volume of pulmonary ventilation, in which the excretion of carbon dioxide exceeds the rate of its formation in the body. This in turn leads to a decrease in the partial tension of blood carbon dioxide (pCO2) and the occurrence of hypocapnia.
The reasons leading to the development of gas alkalosis can essentially be divided into two groups: 1) direct stimulation of the respiratory center (similar conditions, accompanied by hyperventilation, occur with brain damage - encephalitis, hypothalamic tumors; with hysteria, severe crying in children, poisoning salicylates and so on); 2) reflex stimulation of the respiratory center due to irritation of peripheral chemoreceptors, as, for example, with hyloxemia (mountain sickness), as well as intrathoracic receptors with various localized lung lesions (pneumonia, pneumosclerosis, lung tumors, and so on). Hyperventilation can be observed during artificial ventilation of the lungs, if the tidal volume and minute ventilation of the lungs increase, as well as with some infectious toxicoses in children, which are therefore called “hyperventilation syndrome” (see below Alkalosis in children).
The compensatory mechanisms of gas alkalosis resulting from hyperventilation consist primarily of a decrease in the excitability of the respiratory center when pCO2 in the blood drops and the pH shifts to the alkaline side, which contributes to a decrease in the respiratory rate and carbon dioxide retention. The presence of such a mechanism prevents the development of pronounced gas alkalosis during spontaneous hyperventilation.
An equally significant role is played by the so-called mechanism. renal compensation. If we take into account that carbon dioxide is a component of the bicarbonate buffer system, then it is natural that a decrease in its concentration leads to a decrease in the dissociation of NaHCO3 in the blood plasma and a relative increase in the concentration of the latter. However, when blood pCO2 falls, the secretion of hydrogen ions by the epithelium of the renal tubules decreases, as a result of which sodium reabsorption and the entry of HCO-3 ion into the blood decreases. Ultimately, the excretion of bicarbonate and dibasic phosphate increases, the urine pH shifts to the alkaline side, and the concentration of plasma bases decreases.
A decrease in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood simultaneously disrupts the Donnan equilibrium between erythrocytes and plasma (see Membrane equilibrium), as a result of which chlorine ions transfer from erythrocytes to plasma, which compensates for the decrease in the number of anions in the plasma. Thus, the primary shift in acid-base balance during gas alkalosis is a decrease in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood, and the secondary, compensatory shift is a decrease in the concentration of bases. Such shifts in the gas and electrolyte composition of the blood during alkalosis have an adverse effect on the body as a whole. In particular, a drop in blood pCO2 causes a disturbance in vascular tone: an increase in the tone of blood vessels in the brain and heart and a decrease in the tone of peripheral vessels, a decrease in blood pressure and a decrease in cardiac output. Such hemodynamic disorders with long-term hyperventilation can lead to the development of vascular collapse.
Excessive compensatory excretion of bases associated with sodium and potassium causes osmotic diuresis and dehydration. Along with this, a decrease in the concentration of hydrogen ions leads to a decrease in the content of calcium ions, which leads to an increase in neuromuscular excitability and the development of tetany in conditions of decompensated alkalosis.
In addition, under conditions of alkalosis, the hemoglobin dissociation curve shifts to the left, increasing the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen, which worsens the dissociation of oxyhemoglobin and contributes to the development of hypoxia.
Therapeutic measures for alkalosis should be aimed primarily at eliminating the factors that caused the development of hyperventilation, as well as ensuring an increase in the level of carbon dioxide in the blood by inhaling mixtures rich in carbon dioxide (carbogen: a mixture of 95% oxygen and 5% carbon dioxide). If hypocalcemic convulsions occur, intravenous administration of a 10% calcium chloride solution is advisable.
Symptoms of the disease
The first signs of gas alkalosis are increased anxiety and overexcitement. The patient becomes dizzy, attention and memory deteriorate, paresthesia of the face and limbs appears, and rapid fatigue from any communication occurs. In addition, drowsiness, dehydration, and pale skin appear (so-called “gray cyanosis” may develop).
Metabolic alkalosis is characterized by frequent headaches, drowsiness, swelling and cramps of the limbs, lethargy, apathy to the outside world, decreased appetite, and digestive disorders. Rashes may appear on the skin, it becomes dry and pale.
Alkalosis: diagnosis of the disease
A diagnosis cannot be made based on external signs and main symptoms. To identify a violation of the acid-base balance in the body, you need to conduct a full examination (donate urine, blood, do an electrocardiogram).
In addition to the standard, a blood test using a micro-Astrup apparatus or a pH meter, and a microgasometric test are indicated. When alkalosis is detected, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment aimed at eliminating the root cause and neutralizing subsequent symptoms.
Description
Acidosis is usually called an increase in the acidic environment in the blood and tissues of the body compared to the norm, while the pH decreases. If the shift occurs by 0.3, acidotic coma develops, and by 0.4, death occurs. If a person refuses to eat, so-called internal nutrition begins to occur using secondary tissues and fats. When the latter are broken down, acetone and oil products are formed. They are not excreted from the body, so the pH of the blood and internal environment changes to the acidic side.
After a while, acidosis reaches maximum levels, ketone cells are converted into amino acids, and an acidotic crisis occurs. Alkalosis is considered to be an increase in alkaline substances in the body with an increase in pH value. If the shift occurs by 0.2, the functioning of all body systems occurs. This process is called uncompensated alkalosis. With compensated alkalosis, the pH is within normal limits (7.35-7.45), but deviations appear in the buffer systems.
Prevention of alkalosis
To prevent pH disorders, you need to carefully monitor your lifestyle. It is important to maintain proper diet and sleep patterns, give up bad habits and get enough sleep. A normal diet with sufficient amounts of fresh fruits and vegetables can quickly normalize the acid-base balance and prevent alkalosis, the causes of which lie in poor nutrition.
You need to know which foods increase the amount of acids and which reduce them (this will allow you to improve your condition faster):
- mineral water, dairy products and green tea help increase the concentration of alkalis;
- Potatoes help reduce the amount of bases in the body;
- the level of acids is increased by tea, coffee, baked goods, sweets, fish and meat, so these products should be consumed in moderation;
- To normalize the pH, it is recommended to take alkaline baths and visit the sauna.
Alkaline baths cleanse the body of toxins and reduce acid levels. Saunas also have a cleansing effect, they affect blood circulation and quickly restore the acid-base balance.
Reasons for the development of alkalosis
Alkalosis develops under the influence of exogenous and endogenous factors. The cause of gas alkalosis is hyperventilation of the lungs. In this case, there is an increased supply of oxygen to the body and, as a result, excessive removal of carbon dioxide.
Alkalosis is often observed in the postoperative period. This is due to the weakening of the body during surgery and under the influence of anesthesia. Gas alkalosis can cause hypertension, hemolysis, rickets in children and gastric ulcers.
The reason for the development of non-gas alkalosis is a lack or excess of gastric juice. Any changes lead to disruption of the acid-base balance.
Metabolic alkalosis is caused by drugs that increase the alkali content in the body. Contributing to the development of pathology are the consumption of foods with a high content of bases or prolonged vomiting, which causes a rapid loss of chlorine.
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out in a hospital setting. The specialized specialist is a hematologist. In most situations you need to act quickly, since there is no time for long-term activities.
An approximate list of ways to assess the condition is as follows:
- Oral interview with a person. It is important to identify all health complaints. This will allow us to draw a picture and put forward basic hypotheses regarding the deviation.
- Anamnesis collection. Previous violations, currently ongoing processes, circumstances of the beginning of the proposed change.
- General blood analysis. It is important to identify baseline indicators. Carried out urgently.
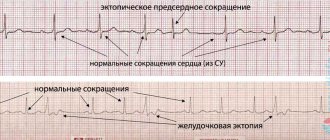
- Electrocardiography is required. The heart suffers first, so it needs to be checked. There are no typical signs of alkalosis, but against the background of the disorder, deviations from the conduction system are observed. First, tachycardia, then the opposite phenomenon with a drop in heart rate and, accordingly, cardiac output.
- Other laboratory tests are ordered if there is time.
Despite the catastrophic limitation of time, it is important to make the correct diagnosis. Otherwise, the effect of help will be zero or, worse, wrong measures will cost a person his life.
Treatment of acidosis
Therapy for gas alkalosis consists of eliminating the cause that caused hyperventilation, as well as directly normalizing the blood gas composition by inhaling mixtures containing carbon dioxide (for example, carbogen). Therapy for non-gas alkalosis depends on its type. Solutions of ammonium, potassium, calcium chlorides, insulin, and agents that inhibit carbonic anhydrase and promote the excretion of sodium and bicarbonate ions by the kidneys are used.
In case of thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries, the patient is hospitalized. With significant hypocapnia, a mixture of oxygen, carbon dioxide and carbogen is inhaled. To eliminate seizures, calcium chloride is administered intravenously. Hyperventilation can be stopped with seduxen and morphine. In a decompensated metabolic state, solutions of calcium and sodium chloride are administered intravenously.
Hypokalemia is eliminated by intravenous administration of a potassium drug - this is Panangin, a solution of potassium chloride along with glucose and insulin, potassium-sparing drugs (Spironolactone). For any type, ammonium chloride is prescribed; Diacarb is used to eliminate excess alkali input. In parallel, symptomatic therapy is carried out aimed at eliminating vomiting, hemolysis, and diarrhea.
Attention! The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials of the article do not encourage self-treatment
Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and give treatment recommendations based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Effective therapy for alkalosis implies the fastest and complete elimination of its immediate causes. Drugs are used that are alkali antagonists and normalize the acid-base balance (solutions of calcium or sodium chloride, insulin, etc. according to indications). Sometimes inhalation of a gas mixture of oxygen and carbon dioxide (the so-called carbogen), sedatives, potassium-containing and potassium-sparing drugs are indicated.
Therapy for gas alkalosis consists of eliminating the cause that caused hyperventilation, as well as directly normalizing the blood gas composition by inhaling mixtures containing carbon dioxide (for example, carbogen). Therapy for non-gas alkalosis depends on its type. Solutions of ammonium, potassium, calcium chlorides, insulin, and agents that inhibit carbonic anhydrase and promote the excretion of sodium and bicarbonate ions by the kidneys are used.
Patients with metabolic alkalosis, as well as with gas alkalosis that developed against the background of serious diseases, such as pulmonary embolism, are hospitalized. Gas alkalosis due to neurogenic hyperventilation in most cases can be eliminated at the point of care for the patient. With significant hypocapnia, inhalation of carbogen is indicated - a mixture of oxygen (92-95%) and carbon dioxide (8-5%). For convulsions, calcium chloride is administered intravenously. If possible, eliminate hyperventilation, for example, by administering seduxen, morphine, and if the mode of artificial ventilation is incorrect, by correcting it.
In case of decompensated metabolic alkalosis, solutions of sodium chloride and calcium chloride are administered intravenously to the patient. For hypokalemia, intravenous potassium preparations are prescribed - panangin, potassium chloride solution (preferably simultaneous administration of glucose with insulin), as well as potassium-sparing drugs (spironolactone). In all cases, ammonium chloride can be prescribed internally, and for alkalosis caused by excessive administration of alkalis, diacarb can be prescribed. Treatment of the underlying disease is carried out, aimed at eliminating the cause of alkalosis (vomiting, diarrhea, hemolysis, etc.).
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=playlist
Therapy in this case should be comprehensive. Treatment should help eliminate the causes of the pathology. Thus, gas alkalosis is treated with mixtures containing carbon dioxide, the patient is given inhalations and Seduxen is prescribed. Non-gas alkaloses are treated depending on their type. Usually they use ammonium, insulin, etc.
The mechanism of changes in the body with increasing pH
In order to respond correctly to changes in your well-being, you need to know why alkalosis is dangerous. It causes hemodynamic disturbances: a decrease in blood pressure, heart rate, cerebral and coronary blood flow. On the part of the digestive system, there is a decrease in intestinal motility, which causes constipation.
Dizziness appears, performance decreases, fainting occurs, and the functioning of the respiratory center is inhibited. Nervous excitability increases, muscle hypertonicity appears, which can reach convulsions and tetany.