Repeated ischemic stroke occupies one of the first places among diseases leading to disability and death. If life expectancy after the first stroke averages eight to nine years, then a second acute cerebrovascular accident can reduce it to two to three years. Therefore, in modern neurology clinics, one of which is the Yusupov Hospital, a large role is given to secondary stroke prevention.
It is proper prevention and treatment that can prevent the recurrence of a vascular accident, because, according to statistics, the probability of a second stroke within a year after the first is about 15%, and after a few years - up to 30-40%.
Who's at risk
After a primary stroke, the body retains mechanisms that provoke the following development of events: intravascular thrombus formation, vascular atherosclerosis. The patient, as a rule, also has a number of concomitant diseases, often in advanced forms: hypertension, diabetes mellitus, arrhythmia, heart failure and others. Preventing recurrent ischemic stroke in such cases is a rather difficult task, but thanks to the efforts of qualified specialists at the Yusupov Hospital, it is feasible.
Repeated ischemic stroke sometimes threatens even patients who are unaware that they have already suffered a vascular accident: patients with short-term disturbances of cardiac or cerebral circulation, the so-called transient ischemic attacks, manifested by the sudden onset of headache, dizziness, numbness of the arm or leg - symptoms which are often ignored, despite the fact that they are the first alarm bells preceding a stroke. The threat of vascular attack increases even more with transient loss of vision, speech, weakness in the upper or lower limb, sudden amnesia and other symptoms.
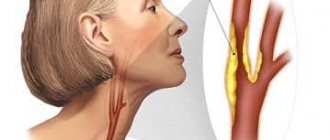
In this case, the patient should not hesitate; it is recommended to seek medical help as soon as possible at the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital to obtain a doctor’s consultation. You will undergo the necessary examinations: ultrasound examination of large vessels (first of all, it is necessary to examine the carotid arteries), an electrocardiogram, ECHO-CG, detailed blood tests for the lipid profile and the tendency to form blood clots, the level of homocysteine - an amino acid that causes early atherosclerosis and thrombus formation, as well as several times increasing the risk of stroke and heart attack.
A similar examination is also recommended for patients who have suffered a hypertensive crisis, attacks of angina pectoris (pain in the heart area), or arrhythmia. These conditions often precede a stroke and are manifestations of transient ischemic attacks.
Make an appointment
Types of strokes
A stroke, or cerebrovascular accident, occurs as a result of a deterioration in the blood supply to the brain. This occurs when there is a decrease or complete disruption of the patency of the vessel (ischemic stroke) or a violation of the integrity of the arteries (hemorrhagic stroke) supplying the brain.
In other words, a stroke is an acute cerebrovascular accident (CVA), accompanied by a sudden disorder of brain function. ACVA is always a complication of acute or chronic human diseases.
If symptoms last less than 24 hours and then disappear completely, it is a transient cerebrovascular accident or transient ischemic attack (TIA). In such a situation, cerebrovascular accident ends with complete restoration of impaired functions, and all sudden symptoms disappear within 24 hours.
Small stroke (micro-stroke) - restoration of affected functions occurs from 24 hours to 3 weeks. The causes of minor stroke are atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension.
There are two types of strokes: hemorrhagic (bleeding in the brain)
and
ischemic (cerebral infarction)
.
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke
is a serious, life-threatening disease that develops due to sudden hemorrhage into brain tissue. This is one of the most severe forms of acute cerebrovascular accident.
One of the most common causes of hemorrhagic stroke in elderly patients is arterial hypertension, followed by atherosclerosis.
Up to 40 years of age, aneurysms (congenital local dilatations of blood vessels) and malformations (congenital disorder of the structure of the vessel) predominate among the causes of hemorrhagic stroke.
Due to the differences in the causes of the disease in different age groups, early and most accurate diagnosis of the pathology comes first. Manifestations of hemorrhagic stroke
All manifestations of brain pathology are usually divided into several groups:
General symptoms
- Severe headache, which patients often describe as “a blow to the head.” It occurs suddenly and is accompanied by dizziness, does not go away on its own and is not relieved by painkillers.
- Vomiting without previous nausea due to cerebral edema and increased intracranial pressure.
- Loss of consciousness followed by the possible development of a coma. This symptom may be the only manifestation of a hemorrhagic stroke. Information from people who were close to the patient and saw what happened can help in diagnosis.
- Stunnedness, causeless drowsiness. At the same time, at the initial stage of development of hemorrhagic stroke, increased emotional and motor excitability is often observed, which is then replaced by inhibition.
- Signs of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system: cold sweat, feeling hot, dry mouth.
- An increase in body temperature to high values can be observed in severe cases.
Specific neurological symptoms
Focal manifestations are a group of symptoms characterized by a number of specific neurological signs that occur depending on the location of the lesion.
The most common manifestations are:
- weakness in the arm/leg/half of the body, up to paralysis;
- violation of the movement of facial muscles, due to which the eyelid does not rise, the corner of the mouth drops and the cheek “sails” when exhaling;
- impaired skin sensitivity;
- pathology of speech, vision, hearing;
- exotropia;
- swallowing disorder;
- spatial disorientation of varying severity - staggering, tilting and turning to the side when walking, inability to assume a vertical body position.
It should be noted that the described clinical manifestations can be seen with small hematomas. However, when it is significant in size, cerebral edema rapidly increases and the patient’s condition becomes so severe that it becomes impossible to identify focal symptoms.
Symptoms of irritation of the meninges
The most typical sign is rigidity (inflexibility) of the muscles of the back of the head, when the patient cannot press the chin to the chest when lying down.
Brudzinski's sign is another sign of irritation of the meninges when the patient bends his knees while checking for rigidity.
Diagnosis of hemorrhagic stroke
In order for a person without medical education to be able to promptly suspect the initial signs of a stroke in a relative or friend, special recommendations have been developed.
Test " Face-hand-speech"
"implies detection of the most typical clinical manifestations of the disease:
- Detection of facial asymmetry.
- The patient needs to extend both arms in front of him. If one of them involuntarily descends, then there is a possibility of a vascular accident.
- The patient is asked to give his full name, address, time of year to determine speech impairment and the person’s orientation in space and time.
There are simplified versions of tests, for example, UZP - “smile, speak and raise your hands”
. If there are noticeable deviations in these actions, an ambulance should be called and emergency measures should be taken to transport the patient to the hospital.
Before prescribing effective treatment, the doctor must answer two questions:
- Is there a stroke?
- If yes, what type of stroke occurred?
Determining the nature of brain damage is only possible with CT or MRI. Without these highly accurate research methods, the diagnosis of stroke is incomplete.
There are signs that are more likely to indicate the occurrence of a hemorrhagic stroke:
- The patient had previously been diagnosed with arterial hypertension, but the medications did not have the desired effect or the patient simply did not take them.
- Deterioration of the condition is associated with a peak in physical activity or emotional stress.
- A sharp and significant deterioration in health with pronounced cerebral and focal symptoms (specific neurological signs, see above).
Ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke (cerebral infarction)
occurs due to a complete or partial cessation of blood flow to the brain through any vessel as a result of thrombosis, embolism, vasospasm, pathology of the main (main) vessels or a sharp drop in blood pressure.
Atherothrombotic ischemic stroke
- occurs as a result of blocking of a vessel by an atherosclerotic plaque or a thrombus that has broken away from it.
Thromboembolic ischemic stroke
- develops in the case of blockage of a vessel by an embolus (thrombus) that entered the brain from a peripheral source - most often from the heart during atrial fibrillation.
The most important risk factors for developing ischemic stroke:
- Arterial hypertension
is the most important correctable risk factor for the development of both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. There is a direct relationship between blood pressure levels and the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD): the higher the systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure, the higher the risk of developing both stroke and myocardial infarction. - Heart diseases (including atrial fibrillation)
– these include previous myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, atrial fibrillation, heart failure. On average, the risk of developing a stroke with heart pathology increases 2-3 times, its probability becomes even higher in the presence of left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy and heart failure.More than half of all cases of cardioembolic stroke are atrial fibrillation (AF)
. Thus, AF without damage to the heart valves increases the risk of developing ischemic cardioembolic stroke by 5 times, and in the presence of valvular disease - by 17 times. About half of the attacks of AF are asymptomatic, of which 30% last more than 48 hours, which poses a real threat to the formation of blood clots in the atrium with subsequent blockage of cerebral vessels and the development of stroke. Thus, at least 20% of ischemic strokes are associated with AF.
AF-related strokes are particularly severe and are associated with higher rates of disability. About half of patients die within the first year. In addition, AF can cause cognitive (mental) dysfunction, incl. dementia (dementia). In patients with AF, the quality of life deteriorates, exercise tolerance decreases, and left ventricular dysfunction often appears and/or progresses with the development of heart failure. In approximately 25% of cases, arrhythmia can be asymptomatic and detected incidentally during a medical examination.
The A90 is the smallest and easiest to use automatic upper arm blood pressure monitor in the Microlife product line. One-button operation ensures efficient and convenient operation even while traveling.
Comfortable cuff 22-42 cm. For all common shoulder sizes. PAD technology for detecting cardiac arrhythmia. One button operation. Easy to use.
- Transient ischemic attacks (TIA - transient cerebral circulatory disorder)
. Approximately 30% of patients with TIA of any origin will develop a stroke over the next five years. More than 20% of them - within the first month after the first TIA and about 50% - within the first year. The likelihood of developing a stroke after a TIA strictly correlates with the age of the patient (in each subsequent decade of life, the likelihood of developing a stroke is 1.45 times higher than in the previous one) and the incidence of TIA. The duration of clinical manifestations of TIA in most cases does not exceed 10-15 minutes, and often lasts only 2-3 minutes. For this reason, patients who have suffered a TIA do not always seek medical help. In order to identify a history of TIA, a targeted unified questioning of the patient is necessary. - Smoking
. On average, smoking increases the risk of stroke by 40% in men and 60% in women. This is one of the most powerful risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries and coronary artery disease. Quitting smoking leads to a gradual reduction in the risk of stroke. This point is of vital preventive importance for those who have already suffered ischemic cerebrovascular accidents or TIA. - Diabetes mellitus (DM)
is one of the serious risk factors for the development of strokes. At the age of over 40 years, strokes occur in patients with diabetes 1.5-2 times more often, and at the age of under 40 years, 3-4 times more often than in the population. Those suffering from diabetes have a much higher mortality rate from stroke. - Lipid metabolism disorders and atherothrombosis
. High levels of cholesterol (CH) in the blood are one of the leading risk factors for vascular diseases of the brain. High levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) reduce the risk of vascular disease, and high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), high levels of triglycerides (TG) contribute to the development of cerebral artery atherosclerosis and are an important factor development of stroke. - Other factors that play a role in the development of stroke:
- Alcohol abuse;
- Physical inactivity (chronic lack of physical activity);
- Nutritional pattern: excessive salt consumption, predominant consumption of animal fats, etc.
- Excess body weight;
- Oral contraceptives (a cause of stroke in women), especially in combination with smoking or arterial hypertension, promote blood clots. These drugs should be prescribed with caution to women who already have the above risk factors;
- High psycho-emotional stress, chronic traumatic situations, some personal characteristics and reactions to stress, type of behavior – desire for competition, intolerance, aggressiveness and hostility;
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
The most obvious and first harbinger of ischemic stroke is a sharp increase in blood pressure
, which is why it is so important to control blood pressure. It is recommended to measure blood pressure twice a day at the same time. According to international recommendations from cardiologists, an automatic tonometer would be the best choice for home use.
Further symptoms of ischemic stroke develop very quickly.
This type of stroke develops more often at night or in the morning
.
There is also a connection with previous increased emotional (stress factor) or physical activity, alcohol consumption, blood loss, or progression of an infectious process or somatic disease. The most typical symptoms of ischemic cerebral stroke:
- loss of speech clarity;
- lack of coordination in space;
- muscle weakness.
Disturbances in the musculoskeletal system signal damage to the brain, which occurred due to blockage of a cerebral artery.
In addition to typical symptoms, the patient may experience
:
- sudden and severe headaches;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- dizziness.
Speech and coordination disorders occur rapidly. They are often used to diagnose a disease, the treatment of which should begin immediately.
Distinctive feature of hemorrhagic stroke from ischemic
– increasing impairment of consciousness with unchanged motor and sensory pathology. This may be a sign of an enlarged hematoma (a limited accumulation of blood in the tissues, forming a cavity containing liquid or clotted blood).
Differential diagnosis is vital because treatment for different types of stroke can vary dramatically.
Causes
There are several reasons for the development of a recurrent stroke, including factors beyond a person’s control that provoke the development of a recurrent stroke:
- Patient's age
- Hypertonic disease,
- Alcohol, drug addiction, smoking,
- Poor nutrition
- Failure to follow doctor's recommendations
- Stress,
- Obesity,
- Sedentary lifestyle,
- High cholesterol levels
- Increased irritability
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system,
- Improper work and rest schedule, night shifts, disturbed sleep,
- Diabetes.
The most common type of vascular disorder is ischemic stroke, which accounts for up to 85% of cases. This type of stroke is caused by blockage of blood vessels supplying the brain or their critical narrowing.
The development of ischemic stroke is caused, first of all, by a person’s destructive lifestyle, which means: alcohol abuse, heavy smoking, poor diet, physical inactivity (lack of physical activity). Such habits lead to a deficiency of oxygen in the brain, associated with inadequate heart function, the loss of the vessels’ elasticity and ability to expand, due to which the blood flow increases, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the central nervous system.
Repeated ischemic stroke occurs due to a number of main reasons:
- psychological and emotional stress;
- excessive stress, heavy physical labor (most often, relapses occur during the summer season, if the patient spends a long time in an uncomfortable position, upside down, and also under the scorching sun, as a result of which dehydration occurs, increasing the risk of vascular accident);
- deterioration in quality of life;
- deterioration of the environmental situation;
- indifferent attitude towards one’s own health (neglect of prevention, poor lifestyle).
ALCOHOL
Alcohol abuse leads to an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding in the brain). Reduce the amount of alcohol you consume to a minimum.
OBESITY
Excess weight negatively affects the functioning of your heart and blood vessels. People who are overweight or obese often have high blood pressure and diabetes. These factors significantly increase the risk of developing a recurrent stroke. To reduce the risk, measures to correct body weight are necessary, which your doctor can suggest for you individually.
Symptoms and consequences
The symptoms of a second stroke are not always the same as those of the first stroke, and they are sometimes quite difficult to determine. Therefore, at the first manifestations of discomfort, it is advisable to turn to professionals - to the neurology center of the Yusupov Hospital, where the patient will quickly undergo a comprehensive examination and be prescribed immediate treatment, thereby minimizing the risk of developing severe complications. Our specialists will organize transportation of the patient to the hospital.
The main symptoms that should cause alarm in a patient who has previously suffered a first stroke:
- the muscles of the face, body or limbs become paralyzed or numb;
- vision deteriorates sharply, vision decreases, blindness occurs;
- speech abilities are impaired;
- consciousness is disturbed: slight drowsiness is felt, fainting occurs, coordination of movements is impaired;
- Nausea and vomiting occur.
The severity of the attack depends on the volume of the affected part of the brain and the location of the affected area. Among the likely consequences of repeated ischemic stroke in the absence of adequate medical care are the following:
- loss of control over the senses;
- loss of ability to think;
- impairment or loss of motor function;
- death (in patients who have suffered a recurrent ischemic stroke, survival is significantly reduced).
Patients suffer a repeated ischemic stroke much more severely than the first, and it is sometimes impossible to predict what consequences it will accompany. In some cases, the nature of the resulting pathologies becomes irreversible. Therefore, the main role belongs primarily to stroke prevention.
First aid
When the first symptoms of a stroke appear:
- Place the patient on the bed.
- Call an ambulance.
- Place the patient on his back or side if vomiting begins or he loses consciousness.
- Unfasten clothes and belt.
- Open the window to allow fresh air into the room.
- Place a cold wet towel or ice in a bag wrapped in cotton cloth on your head.
- Measure the patient’s blood pressure, pulse, and monitor blood pressure and breathing until the doctors arrive.
- If necessary, give medications that were previously prescribed by the attending physician.
- Constantly talk to the patient, try to get answers to questions from him, and do not lose contact.
Memo on providing first aid to the elderly for ischemic stroke
At the first manifestation of symptoms of an ischemic stroke, it is necessary to call a team of doctors to provide emergency medical care. The effectiveness of further treatment directly depends on the timeliness of these actions. While the ambulance is traveling, you should prepare the elderly patient and take certain actions:
- The victim should be laid so that the shoulders and head are located above the body, this will help reduce blood pressure on the vessels of the brain. You cannot move or shift an elderly person - this can only make him worse.
- You should not give the patient anything to eat or drink while waiting for doctors because of the likelihood that the usual swallowing function will be disrupted; the person will choke or choke.
- It is strictly forbidden to give any medications before the ambulance arrives; you may not alleviate, but, on the contrary, aggravate the condition of an elderly relative.
- The oral cavity must be cleared of any secretions and objects (saliva, blood, mucus, food).
- Provide all conditions for free breathing: increase access to fresh air, remove tight clothing.
- If a person has lost consciousness but is breathing on his own, he must be turned on his side, his head resting on his arm and slightly tilted forward, and his leg bent at the knee so that it does not allow him to accidentally roll over.
- If there is no breathing, the elderly person is placed on his back and given artificial ventilation. If there is no pulse, cardiac massage is added to this procedure. For every two breaths there should be 30 heartbeats (2/30). These measures should be carried out only if you have the necessary skills and abilities until the victim begins to breathe on his own or until the ambulance arrives.
The development of ischemic stroke in older people occurs very quickly, which is why it is so important to provide qualified medical care literally in the first minutes and hours of the disease. Treatment must necessarily take place in the intensive care unit, where all efforts will be devoted to carrying out the necessary medical procedures. The faster this happens, the more favorable the prognosis and outcome of the disease. The optimal time for first aid and treatment is 2–4 hours from the onset of an attack. If you manage to carry out the necessary therapy in this short period of time, you may be able to avoid many complications.
Forecast
As is already known, the five-year survival prognosis is disappointing. Loss of intellectual and motor abilities after a second stroke can be lifelong. Most patients after a relapse suffer from irreversible changes and pathologies in the cerebral cortex.
After lesions, patients usually experience disability. In more than half of patients, after suffering a recurrent stroke, a coma occurs, which does not allow the doctor to give a positive prognosis about recovery from it.
Rehabilitation of patients after repeated ischemic stroke in the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is based on traditional, latest and original methods for the recovery of patients who have suffered a stroke.
Thanks to the extensive practice and rich knowledge of the clinic’s specialists in the field of rehabilitation medicine, comprehensive rehabilitation of patients is carried out at the highest level, meeting international standards.
For optimal rehabilitation, patients are provided with comfortable conditions of stay: cozy rooms, good nutrition and attentive attitude of the staff.
Call by phone and the coordinating doctor will answer all your questions.
Make an appointment
Life after ischemic stroke
If the patient experiences an acute period of stroke, then residual disorders are possible in the form of:
- complete immobilization;
- paralysis on one side of the body;
- partial paralysis of a limb;
- paresthesia (numbness with loss of skin sensitivity);
- speech and swallowing disorders;
- vestibular disorders;
- hearing loss;
- pelvic paralysis with inability to control bowel and bladder movements;
- decreased intelligence;
- changes in psyche and character;
- impossibility of self-service.
Recovery of various impaired functions in patients with ischemic stroke occurs at different rates. Thanks to the use of innovative techniques in the rehabilitation clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, movement disorders go away faster, and it may take longer to restore speech. After discharge from the hospital, patients need support from loved ones and continued rehabilitation under the supervision of specialists from the Yusupov Hospital.
Prognosis in older people
In patients with ischemic stroke, age is one of the most important factors that influence the prognosis and quality of life after the acute period of the disease. In older people, ischemic stroke is much more severe than in younger patients. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital take an individual approach to the treatment of elderly patients; when prescribing medications, they use doses recommended for a certain age. When using innovative methods of kinesitherapy, the age characteristics of the body are taken into account.
The prognosis after an ischemic stroke suffered by an elderly person is influenced by the following factors:
- localization of the ischemic focus;
- prevalence of cerebral infarction zone;
- a disease that caused a stroke;
- severity of neurological symptoms.
Coma caused by cerebral edema is the most severe neurological manifestation of a stroke, sharply worsening the prognosis.
Factors that positively influence the results of rehabilitation of elderly patients and improve the prognosis are:
- a small lesion confirmed by computed tomography;
- maintaining the patient's full consciousness;
- minimal number of neurological damages;
- absence of pronounced atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels according to the results of Dopplerography of the arteries of the head and neck;
- the patient's profession requiring constant mental stress;
- normal blood pressure;
- absence of arrhythmias and other heart diseases.
Methods for diagnosing stroke
CT scan
(CT) is the "
gold standard
" for detecting cerebral hemorrhage. This study is distinguished by its accessibility, information content and short scanning time. A CT scan performed in the first hours of the disease helps to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI) has greater sensitivity for small foci of hemorrhage and helps to more accurately determine the stage of the process. However, in order to verify the hemorrhagic nature of the stroke, an MRI scan must be done 24 hours after the onset of the disease. Even many years after a stroke, an MRI of the brain will reveal pathology.
To determine the cause of hemorrhagic stroke, MRI is preferable because it shows brain structures in more detail than CT. In any case, each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, so before using them, you need to be examined by a specialist - a neurologist.
Since the patient’s further well-being depends on the time of initiation of treatment, primary diagnosis is usually carried out using CT. Later, after the necessary therapy or surgical treatment has begun, an MRI will help clarify the cause of the stroke.
Treatment
A patient with a recurrent stroke most often ends up in the intensive care unit. At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors begin treatment and early rehabilitation immediately after diagnosis. The prognosis is most favorable when patients are admitted to the neurology clinic within the first 4 hours from the appearance of the first signs of acute cerebral circulation. Doctors at the neurology clinic prescribe adequate treatment, thanks to which the nerve cells around the ischemic site completely restore functional activity.
The use of thrombolysis therapy by neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital for elderly patients significantly improves the prognosis. As a thromolytic agent, doctors at the neurology clinic use the most effective drug - tissue plasminogen activator. After the clot dissolves, blood flow through the affected vessels is restored, the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the ischemic area and the area around the cerebral infarction improves. The outcome of ischemic stroke is improved by the use of ancrod (an enzyme from snake venom) in the first 3 hours after the development of acute cerebrovascular accident and for five subsequent days.
To prevent further formation of blood clots and re-embolism, elderly people are given:
- direct anticoagulants (sodium heparin or low molecular weight heparin);
- antiplatelet agents;
- drug from the thienopyridine group Ticlopidine.
If there are contraindications or a high risk of complications from taking these drugs, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe Clopidogrel to patients. Drugs with neuroprotective and neurometabolic effects improve the plasticity of nerve cells. The tone of cerebral arteries in elderly people increases under the influence of vasoactive drugs.
In elderly people, ischemic stroke often occurs against the background of severe arterial hypertension. During the 7-10 days of the acute period of stroke, cardiologists at the Yusupov Hospital when the patient’s systolic blood pressure is less than 200 mm. rt. Art. do not carry out antihypertensive therapy, since hypotension worsens the oxygen saturation of brain areas susceptible to ischemia. In patients with systolic blood pressure above 200 mm. rt. Art. it is reduced very slowly to numbers of 10 mm. rt. Art. exceeding the pressure to which the patient is adapted. After the acute period, cardiologists select individual antihypertensive therapy.
Our information
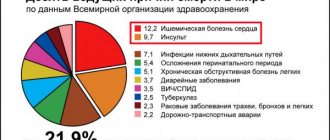
Of the 500 thousand strokes that are registered annually in our country, ischemic ones, caused by blockage or narrowing of the vessels supplying the brain, account for the vast majority - 85%.
Hemorrhagic strokes with hemorrhage in the brain or under its membranes as a result of rupture of the vascular wall are much less common - in 10-15% of cases, but are more severe and destructive in consequences. Fortunately, since machines for measuring blood pressure have become a staple in our families, there have been fewer hemorrhagic strokes. And the number of ischemic cases, on the contrary, has increased. Why? There are many mechanisms for the development of ischemic stroke. Among them is a destructive lifestyle with bad habits, poor nutrition and physical inactivity (lack of movement).
***
If a person close to you exhibits the signs of transient cerebrovascular accident described above, you should put him or her to bed and measure his blood pressure. If it is above 160 mm Hg. Art., you must definitely call an ambulance and give the patient his usual blood pressure-lowering drug. You can also give aspirin. Simple or soluble is better: medications in special forms that prevent stomach irritation act more slowly.
Rehabilitation
Early rehabilitation significantly improves the prognosis after a stroke. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital begin to carry out rehabilitation measures from the first day the patient is admitted to the neurology clinic. The intensity of the rehabilitation program depends on the patient’s condition and the degree of his disability. At the Yusupov Hospital, the department for seriously ill patients is equipped with special multifunctional beds. Using the devices of a multifunctional bed, medical personnel can periodically change the patient’s position, carry out hygiene procedures, and care for the patient. Changing your posture helps avoid the formation of bedsores and congestion. To reduce the risk of developing contractures, joint pain, pneumonia, and deep vein thrombosis at the Yusupov Hospital, specialists carry out passive rehabilitation from the first days of treatment.
To improve the prognosis of older people, rehabilitation specialists at the Yusupov Hospital after a stroke use the following innovative methods for restoring impaired functions:
- PNF;
- Voita therapy;
- minor manual therapy;
- Castillo-Morales method;
- kinesio taping;
- Mulligan concept;
- Bobath therapy.
Recommendations after a recurrent stroke
All patients who have suffered a stroke are at risk of relapse of the disease. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital give recommendations to patients on nutrition and prevention of recurrent stroke:
- Dieting. Refusal of spicy, smoked, fatty and sweet foods, alcohol, caviar, eggs, liver. The menu includes more vegetables, fruits, and grains.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Refusal of heavy physical labor, night shifts, and work with high psycho-emotional stress.
- Sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- During the rehabilitation period, measure blood pressure every day, after completion of rehabilitation at least 3 times a week.
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor in a timely manner and strictly on time.
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations.
- Do the recommended therapeutic exercises daily.