Stroke is an acute condition that manifests itself in disruption of cerebral circulation and causes damage and death of nerve cells. The pathology occurs as a result of rupture (hemorrhagic) or blockage (ischemic) of a vessel and can have irreversible consequences for the body.
The main danger of the disease is its unexpected occurrence and rapid development.
Lack of timely medical care can lead to disability and even death.
Therefore, it is very important to know about the first symptoms of a stroke and the actions that need to be taken to prevent possible complications.
Causes of stroke and provoking factors
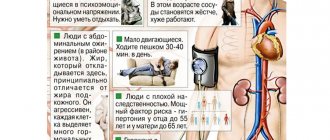
There are a number of diseases and external factors that can trigger the development of a stroke. These include:
- bleeding disorders, hypertension, thrombosis and embolism;
- cerebral aneurysms;
- atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus;
- carotid artery stenosis;
- unhealthy lifestyle (obesity, insomnia, irregular daily routine);
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- depression, fatigue;
- apnea (stopping breathing);
- general hypothermia, injuries;
- hereditary predisposition;
- age over 50 years.
Prevention
Prevention should be aimed at identifying and correcting the main risk factors.
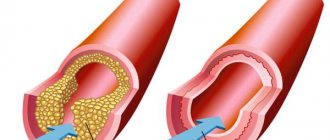
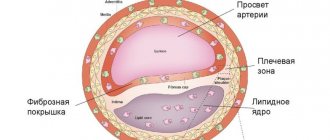
Atherosclerosis
It is necessary to constantly monitor the level of blood lipids - total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, VLDL, TG, CA. If you are prone to high cholesterol, you must follow the prescribed diet. If following a diet does not provide the desired reduction in cholesterol levels, statins are prescribed - drugs that lower blood lipid levels.
Arterial hypertension
If a diagnosis of “Arterial hypertension” is made, you should take all prescribed medications without skipping, even with normal blood pressure values. You need to keep a blood pressure diary, where you should enter your blood pressure and pulse readings. If blood pressure is unstable, there is a tendency to crises, the diary should be filled out 2 times a day - morning and evening. Such a diary will help the doctor choose the optimal therapy.
Rhythm disorders
Rhythm disturbances can be the result of many heart diseases, incl. myocardial infarction. If there are rhythm disturbances in the atria, most often atrial fibrillation, a person may not feel anything; these disturbances can be detected by taking an ECG. Atrial fibrillation causes the formation of thrombi - blood clots that can cause not only strokes, but also heart attacks of other internal organs.
If atrial fibrillation is detected, anticoagulants are prescribed - drugs that prevent thrombus formation. Taking anticoagulants increases the risk of bleeding. Anticoagulants should not be interrupted, and the drug or dose should not be changed without the doctor's permission.
When PMI or stroke occurs in people under 45 years of age without cardiovascular disease, rarer causes should be excluded.
Stroke is easier to prevent than to treat its consequences. In severe cases, patients remain bedridden despite all the efforts of doctors and relatives. In other cases, rehabilitation can take months or years. The network of boarding houses has created special programs for recovery after a stroke in boarding houses, which are aimed at speedy recovery under the supervision of specialists.
Main symptoms and signs of stroke
It is important to know that when the first symptoms of a stroke appear, you should urgently call an ambulance. The main features are:
- a sharp feeling of weakness;
- feeling of numbness in the limbs, weakness;
- speech impairment (“porridge in the mouth”) and blurred vision;
- dizziness and headache;
- nausea, vomiting;
- impaired coordination and balance.
Sometimes the behavior of a person who has had a stroke outwardly resembles the behavior of a drunk. To recognize pathology, pay attention:
- on speech (it will be incoherent and difficult);
- on a smile (asymmetrically located corners of the lips - the first sign of a stroke);
- on hand movements (the handshake will be weak, hands raised up will lower spontaneously).
Call an ambulance immediately at the first suspicion of a stroke. The body cannot cope with the disease on its own.
Features of treatment
Treatment of hemorrhagic stroke today is more in the purview of neurosurgeons than neurologists. The blood has already been shed, and the possibilities of medical assistance are limited. Removal of an intracerebral hematoma can save lives and maintain an acceptable level of health. Surgical removal is more successful the earlier it is performed. Optimally, the patient should be operated on on the first or, in extreme cases, on the second day after the incident.
The main intervention is aspiration (suction) of the hematoma and clipping of the aneurysm. It is only possible when the artery is in an accessible place. There is no way to help with an aneurysm deep in the medulla. In a typical case, the blood is aspirated, a clip is placed at the base of the aneurysm, and the aneurysm is isolated from the bloodstream.
Malformations are excised whenever possible. These are complex operations that require not only the skill of a specialist, but also first-class equipment.
Possible consequences
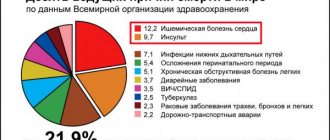
A stroke can result in temporary disability, disability, or even death. Only 20% of people who have had this disease can fully return to work. Every year in Russia, stroke occurs in about 450,000 people. According to statistics of recorded deaths from stroke, this cause ranks second among all deaths in our country. The most common consequences of the disease include:
- impaired movement, weakness in the limbs, numbness of various parts of the body;
- memory, speech, and urination disorders;
- loss of ability to care for oneself independently.
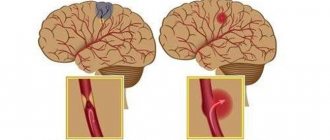
There are two types of stroke:
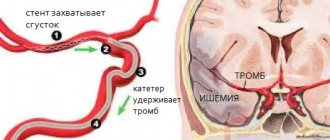
Ischemic – blood vessels in the neck or brain become blocked. More common, it can be triggered by thrombosis, embolism, or arterial stenosis. More often it occurs at night, while clarity of consciousness is maintained. With a mini-stroke, the blockage of blood flow is temporary, but the condition also requires immediate hospitalization.
Hemorrhagic (intracerebral) - occurs in 10-15% of cases, but 30-60% of them end in death. The blood vessel ruptures completely, allowing blood to flow into the brain. Often a stroke is provoked by an aneurysm, in less than 1% of cases - by an arteriovenous malformation (usually congenital). This type of stroke usually occurs during the day, as a result of excessive physical or emotional stress.
Rehabilitation after ischemic stroke
Basic principles
1. Early start of the rehabilitation process - from the first hours of stroke development. At the very beginning, this is primarily:
Correct positioning of affected limbs
To prevent bedsores and the respiratory system, you should lie on both the healthy and paralyzed side. The healthy leg should be straightened, and the paralyzed leg should be brought forward slightly, slightly bent and placed on a pad. Place a pillow under the paralyzed arm.
To lie on the painful side, you should place a pillow under the patient's back to relax the muscles and stabilize him so that he does not roll out of bed. The paralyzed arm should be extended forward. Straighten your arm and place your palm up.
Attention: Do not lie on the paralyzed side for a long time.
The patient can lie with his head elevated for 15-30 minutes 3 times a day, starting from the first day of the disease.
Regularly changing the position of a post-stroke patient in bed
The position of the body in bed should be changed as often as possible. Prolonged pressure on the same areas of the body can lead to the formation of bedsores.
The patient’s position in bed should also be changed to improve bronchial function. If the patient is constantly in the same position, then sputum from some bronchi, under the influence of gravity, flows into the trachea and is coughed up, but from other bronchi, on the contrary, does not flow. And stagnation in any hollow organ leads to its inflammation. Even in the absence of dangerous microorganisms, microbes begin to multiply in the area of stagnation, which leads to pneumonia, which is difficult to cure in a weakened person. Frequent turns in bed help avoid this complication.
Massage
The massage procedure contributes to the overall health of the body, normalization of blood circulation in various parts of the patient’s body, restoration of lost functions or their compensation, normalization of muscle tone, increased joint mobility, elimination of trophic disorders in paralyzed limbs. The pathology of the connection between the muscles of a paralyzed limb and the nervous system leads not only to immobilization of the limb, but also to disruption of tissue nutrition.
Massage after a stroke
Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy)
Exercise therapy is a method of prevention using exercise, often combined with physical therapy and massage.
Exercises for recovery after a stroke
The sooner rehabilitation measures are started, the more lost functions will be restored or compensated.
2. Systematic long-term treatment over many months and sometimes years. Therapy (drug and non-drug) should continue in accordance with the recommendations of the attending physician.
3. Rehabilitation must be comprehensive. It is necessary to combine drug treatment with physical, psychological and speech therapy.
4. Consistency and phasing. At each stage, specific tasks should be set to restore lost functions. After completing the stage, the tasks change as your health improves.
5. Active participation of the patient and his family in the rehabilitation process.
Hyperbaric oxygenation
In diseases when the delivery of oxygen to organs and tissues is disrupted, including ischemic stroke, hypoxia develops - oxygen starvation. The brain is especially sensitive to a lack of oxygen and cannot function normally when it is deficient. In such situations, a modern treatment method, a type of oxygen therapy - hyperbaric oxygenation (HBOT), is used to improve oxygen supply.
Oxygen therapy: treatment and prevention of diseases
Hyperbaric oxygenation is a treatment method using pressure chambers in which the patient breathes an air mixture with an oxygen concentration 5 times higher than normal air. Due to the increased pressure and concentration, oxygen easily and quickly dissolves in the blood and is distributed throughout the body with its current. All tissues of the body are saturated with oxygen, even those in which blood circulation is impaired.
As a result, metabolic processes and blood circulation are improved, the neutralization and removal of waste and harmful substances from the body is accelerated, the functioning of all internal organs is normalized, the body's need for medicinal substances is reduced and their therapeutic effect is enhanced.
In addition, HBO has an anti-edematous effect, promotes the proliferation of blood vessels and restores blood supply to the affected areas of the brain.
Treatment can only be carried out after consultation with a doctor.
Physiotherapy
After a stroke, electromyostimulation, darsonvalization (electrotherapy), faradization (treatment using low-frequency alternating current in pulsed mode), balneotherapy (hydrotherapy), acupuncture, phototherapy and treatment with ionized air are prescribed.
Physiotherapy sessions are held at the Cardiological Sanatorium. The following medical services are also provided: hydrotherapy, inhalations, therapeutic massage, herbal medicine, exercise therapy and drug therapy.
Aromatherapy
The use of the following essential oils is recommended: oil of styrax benzoin, black pepper, eucalyptus, garlic, geranium, ginger, juniper, lemon, tangerine, rosemary, clary sage, thyme.
Oils are used for massage, as bath additives, and to scent the air.
Nausea and vomiting with coronavirus
Severe complications and high mortality with COVID-19 force us to more carefully study the first symptoms of the disease. The difficulty lies in the fact that the virus rapidly mutates, and the clinical manifestations of the disease also change. In 2021, typical symptoms of coronavirus infection were fever, loss of smell and taste, muscle pain, and only then a cough. Only some patients experienced nausea and vomiting a little later. In 2021, the majority of cases are caused by the Indian strain of COVID-19, which is characterized by higher infectiousness and a “stomach” syndrome. Against the background of fever and catarrhal symptoms (runny nose, sore throat, cough), every third patient with coronavirus experiences nausea/vomiting and pain in the stomach. A little later, diarrhea and hearing problems appear, and the sense of smell disappears less often.
The "Delta" strain most often affects young people and children. And previously worked out treatment regimens give a noticeably less effect. This is why vaccination of the population, including those who have previously had coronavirus, is so important. Although a two-time vaccination does not completely eliminate infection, it will help avoid severe disease, complications and death. Among the sick, the percentage of vaccinated people does not exceed 1%.
Important! Nausea after vaccination against coronavirus occurs in every tenth vaccinated person. Vomiting is a rare side effect. All unpleasant consequences of the vaccine disappear within 3 days.
Specific features of nausea and vomiting
To identify the cause of poor health and assess the patient's condition, the duration of nausea and vomiting is important. Acute vomiting (1-2 days) is often caused by medications, infections, poisoning (such as alcohol), kidney damage, and diabetes. Chronic vomiting (more than 1 week) is characteristic of long-term gastrointestinal diseases and mental disorders.
Features of vomiting and nausea
- Vomiting immediately after eating is characteristic of stomach lesions. If the gag reflex occurs 2-3 hours after eating, pathology of the duodenum is possible.
- Nausea and vomiting of acid are observed with gastritis with increased secretion and stomach ulcers.
- Vomiting of bile (greenish-yellow color) is caused by pathology of the hepatobiliary system (liver, gallbladder) or pancreas.
- Bloody vomit (red or brown) indicates gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Vomiting mucus is characteristic of diseases of the respiratory system (smoker's bronchitis), which occurs with a debilitating cough. Patients with alcoholism often complain of foamy vomiting in the morning (on an empty stomach).
- Vomiting with fever indicates the infectious nature of the disease. With a viral infection, the temperature can reach 39-40ºС. Nausea, vomiting and temperature up to 37.5-37.8ºС are more typical for bacterial infections.
- Vomiting with diarrhea/constipation without fever suggests an intolerance or allergy to certain nutrients, such as lactose.
- Constant nausea without vomiting and fatigue often occur with hypothyroidism.
- Vomiting and pain in the upper abdomen makes it necessary to exclude myocardial infarction, but is more often associated with gastrointestinal pathology.
- Fecal vomiting (dark vomit with a characteristic smell of feces) occurs with intestinal obstruction, tumors, and gastrointestinal fistulas.
How to help a person with a stroke
If signs of acute cerebrovascular accident are detected, emergency assistance must be called as soon as possible!
The procedure for providing assistance before the ambulance arrives:
- reassure the victim so as not to aggravate the situation with excitement;
- put the patient on the bed, raise his head 30 degrees; if consciousness is lost, turn your head to the side (vomiting is possible), stretch out your tongue;
- loosen clothes - collar, belt; ensure air flow;
- measure blood pressure and, if it is elevated, give medications to lower it;
- Place your feet in a bowl of hot water or place a heating pad on your feet to help drain blood from the brain.
Prohibited:
- Give the patient vasodilators until the ambulance arrives.
- Give water or food to the patient.
A special case is when a stroke occurs in a car and the victim is driving. Here, not only his life, but also the lives of passengers may be at risk. In this case, you need to stop, call an ambulance, and open all the windows.
Assistance in transporting a patient in an ambulance during a stroke
First of all, no attempt should be made to transport the patient to the hospital by private or public transport. In case of a stroke, a specially equipped ambulance is required, with qualified personnel, medications and a siren. Transportation is carried out to a specialized neurological hospital or to the intensive care unit of the nearest general hospital, where doctors have already been warned in advance.
As a rule, doctors have, at best, an hour and a half to provide care to a patient. Those who were close to the patient during the attack should accompany him to the hospital in order to tell the doctors in detail and constructively about the details of what happened and the first aid provided.
The following measures can be taken in the ambulance:
- Prevention of breathing disorders (if necessary - tracheal intubation, artificial ventilation).
- Smooth decrease in blood pressure.
- Maintaining water and electrolyte metabolism using saline droppers.
- Administration of anticonvulsants.
- When transporting a stroke patient, they are guided by the principle of “transporting with the least loss to the body.”