Raynaud's syndrome is a serious condition that is caused by spasm of peripheral blood vessels. Because of it, blood flow in the small vessels of the legs (at the level of the feet) and hands is disrupted. This syndrome is usually one of the symptoms of many other diseases. For example, it occurs in rheumatism, endocrine disorders, psychopathy, etc. Only sometimes it is impossible to determine the underlying disease, so Raynaud's disease may be considered independent.
Most often, this syndrome affects young and mature women, as well as residents of regions with cold climates.
Provoking factors
The underlying causes of Raynaud's syndrome have not been identified, but there are a number of factors that, according to doctors, contribute to its development. These include:
- hereditary tendency;
- permanent injury to fingers and toes;
- endocrine system disorders: diabetes, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, etc.;
- disorders associated with hematopoietic functions;
- constant contact with cold water;
- some diseases of the spine;
- alcohol dependence, drug addiction;
- unstable mental state;
- heavy metal intoxication;
- serious stress;
- constant contact with chemicals;
- certain autoimmune diseases.
The disease in an advanced state can manifest itself even without provoking factors - then they talk about spontaneous attacks of Raynaud's syndrome.
Causes of Raynaud's syndrome
Raynaud's syndrome can be a consequence of the following diseases and factors:
- various autoimmune connective tissue pathologies (systemic scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus);
- inflammatory diseases of blood vessels - systemic vasculitis (granulomatosis or Wegener's disease, polyarteritis nodosa, drug-induced vasculitis, cryoglobulinemic vasculitis);
- blood diseases (thrombophlebitis, thrombocythemia, cryoglobulinemia, leukemia);
- diseases of the endocrine system (pathology of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland);
- hypothermia, stress, emotional overstrain;
- long-term use of medications that have a vasoconstrictor effect (migraine medications).
Symptoms, manifestations
Symptoms of Raynaud's disease include:
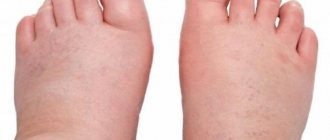
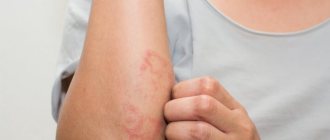
- whitening of the skin on the fingers;
- feeling of coldness, numbness;
- burning, pain, feeling of fullness;
- swelling, cyanosis;
- formation of ulcers and necrosis (over time);
- nail dystrophy;
- curvature of fingers.
The attacks begin with the skin turning white, then the situation gradually worsens. The attacks themselves become longer, and the damage becomes more obvious. This depends on the stage of Raynaud's syndrome.
Are you experiencing symptoms of Raynaud's syndrome?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Raynaud's disease treatment, how to treat Raynaud's disease
Treatment of Raynaud's disease, an isolated and slightly disabling Raynaud's phenomenon, requires simple measures, such as limiting exposure to cold, wearing gloves, avoiding smoking, drinking strong coffee, tea, avoiding taking beta-blockers, clonidine, and ergot alkaloids. The diet must include foods containing polyunsaturated fatty acids (arachidonic, linoleic, linolenic). Vibration should be avoided and stressful situations should be avoided.
Stages
At the angiospastic stage, the patient experiences slight tingling, goosebumps, and chilliness. The skin becomes pale, sensitivity in the fingers is lost, and an aching sensation of pain may appear. After this, hyperemia occurs - that is, the vessels become overfilled with blood, slight swelling and redness appear.
At the angioparalytic stage, exacerbations occur that last longer, cyanosis (blue discoloration) and severe swelling occur. The pain gets worse. Often the patient may experience a fever, cold sweats, and even a feeling of fear and anxiety.
In the third, trophoparalytic stage, the pain becomes less, but if Raynaud's disease is not treated, the consequences for the fingers are much worse. These are the appearance of ulcers, areas of necrosis - the fingers are literally destroyed, and the patient becomes disabled. The condition is serious both from a physical and psychological point of view.
It is the third stage that is truly dangerous, and the first two only lead to it. But treatment and observation by a doctor should begin as early as possible in order to prevent complications.
Official website of Valery Nikolaevich Fokin
Raynaud's disease
Raynaud's disease (Raynaud's phenomenon) is a condition that results in a disturbance in the coloring of the fingers and/or toes due to sudden changes in temperature (cold or hot) or emotional events. The discoloration occurs as a result of a pathological spasm of blood vessels, as a result of which a limited amount of blood is delivered to the tissues. At the beginning, the fingers hurt precisely because a very small amount of blood flows to the tissues. Then the fingers turn blue due to lack of oxygen. Eventually, the blood vessels open again, causing a strong rush of blood and the fingers turn red. This three-color sequence (white-blue-red), which occurs in most cases due to cold weather, is Raynaud's phenomenon.
Most often, this phenomenon occurs in women, especially in the second, third, and fourth decades of life. People can suffer from this phenomenon alone or in combination with other rheumatic diseases. When such a phenomenon occurs alone, it is usually called simply "Raynaud's phenomenon", or "initial Raynaud's phenomenon". If the phenomenon occurs along with other diseases, it is most often called a “secondary phenomenon.”
THE REASONS FOR THE APPEARANCE OF THE PRIMARY AND SECONDARY PHENOMENON ARE UNKNOWN.
Factors such as pathological disturbance of nerve control over blood vessels and pathological nervous excitability at cold temperatures can be considered as conditions due to which this phenomenon occurs. Signs of discoloration of the fingers are partly caused by the fact that the blood vessels narrow, due to spasms in the tiny muscles of the vessel walls, which then tend to suddenly dilate. Small arteries located in the tissues of the fingers have a microscopic thickening inside, which also leads to pathological narrowing of the blood vessels.
SYMPTOMS OF RAYNAUD'S PHENOMENON
depend on the severity, frequency and duration of spasms of blood vessels. Many patients with a mild form of the disease notice only a slight change in skin color as a reaction to cold air temperature. Such patients may experience a slight tingling and numbness in the area of the fingers. The numbness and tingling will go away as soon as the coloring of the fingers returns to normal. Once the spasms of the blood vessels become longer, the sensory nerves become irritated due to lack of oxygen and this can cause pain in the affected areas of the fingers. Rarely, insufficient oxygen supply to tissues can cause finger ulceration. Ulcerations on the fingers may be associated with infection. If the lack of oxygen continues, it can lead to gangrene. Raynaud's phenomenon can also affect areas of the body such as the nose, ears and tongue. Ulcers rarely appear in these areas of the body, but numbness and pain may occur.
For patients with a characteristic sequence of color changes on the skin of the fingers, identified as a reaction to cold air temperature, it is not difficult to predict the phenomenon. Sometimes, by certain patterns of capillaries of blood vessels that are adjacent to the nail plates, Raynaud's phenomenon can be determined. There is no blood test that would help a doctor clarify and verify his diagnosis. The doctor may recommend certain blood tests to rule out rheumatic diseases and thyroid pathologies.
HOW IS RAYNAUD'S PHENOMENON TREATED?
To avoid getting Raynaud's disease, you need to protect your fingers and toes from cold, injury and infection. Medicines can only make the situation worse, causing even greater spasm of the blood vessels, so patients with Raynaud's phenomenon should avoid taking medications. For those patients whose symptoms are persistent, only those medications that dilate the walls of blood vessels can be prescribed. For patients who have no other symptoms other than discoloration, steps can be taken to prevent other complications. Regardless of the severity of the disease, measures to prevent complications should be taken in both the primary and secondary stages of the disease. The best remedy is to keep your feet and hands warm to prevent hypothermia. Dishes must be washed using rubber gloves. Don't go barefoot. Compressive bandages, rings and shoes are absolutely not advisable.
Patients should protect their arms and legs from injury and wounds. Any wounds or infections should be treated immediately to prevent complications. You should also avoid emotional stress.
Both active and passive smoking should be avoided, because the chemicals contained in tobacco constrict blood vessels and lead to hardening of the arteries, which can subsequently lead to a lack of oxygen supply to the tissues. Pedicures and manicures must be done carefully so as not to damage your fingers or cause any infection. Ointments that help open blood vessels (nitroglycerin ointment) are sometimes applied to both surfaces of the fingers that are most damaged in order to increase blood flow and speed up recovery.
Medicines that can worsen the symptoms of Raynaud's phenomenon by causing blood vessel spasms include cold and weight loss medications. Medicines used to treat high blood pressure and heart disease can also make the disease worse. Patients with persistent, painful symptoms may benefit from oral medications that dilate the walls of blood vessels.
For some patients with persistent symptoms, a medicine called Trental may be prescribed to help improve blood circulation.
In acute Raynaud's phenomenon, gangrene may occur with subsequent loss of fingers. In rare, very complex cases of this disease, a surgical procedure called a sympathectomy may be required. To prevent further spasms of the blood vessels, the sympathetic nerves are surgically removed. Usually the operation is performed on the fingers of both hands. Small cuts are made into the blood vessels in the fingers and tiny nerves are removed. This procedure is called digital sympathectomy.
If the upper extremities are affected, the following types of exposure are included.
- Classic massage: Upper back massage.
- Upper limb massage.
1st option:
V11 (Th1 – Th2) ± 1.5 cun
V15 (Th5 – Th6) ± 1.5 cun
GI5 (on the radial side of the dorsum of the hand, in)
MS6 (2 cun above the proximal wrist fold, in the middle of the flexor fold)
P9 (between the proximal and distal radiocarpal folds, on the radial artery)
MC8 (in the center of the palm between the 2nd and 3rd metacarpal bones)
GI11 (midway between the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and the radial end of the elbow crease)
GI4 (in the middle of the protruding part of the first dorsal interosseous muscle with the thumb attached)
2nd option:
V11 (Th1 – Th2) ± 1.5 cun
V15 (Th5 – Th6) ± 1.5 cun
V23 (L2 – L3) ± 1.5 cun
VG14 (between the spinous processes of the 7th cervical and 1st thoracic vertebrae)
MS6 (2 cun above the proximal wrist fold, in the middle of the flexor fold)
C7 (on the proximal radiocarpal fold, in the gap between the pisiform and ulna bones)
GI11 (midway between the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and the radial end of the elbow crease)
TR5 (on the dorsum of the forearm, 2 cun above the proximal wrist fold)
GI4 (in the middle of the protruding part of the first dorsal interosseous muscle with the thumb attached)
P1 (in the clavipectoral triangle, between the 1st and 2nd ribs, 1 cun below the lower edge of the clavicle, in the recess between the deltoid muscle and the pectoralis major)
When the lower extremities are affected, the following types of influence are used.
- Classic massage. Massage of the lumbar region.
- Massage of the pelvic area.
- Massage of the lower extremities according to generally accepted methods.
V40 (in the center of the popliteal fossa, at the lateral side of the popliteal artery)
V57 (in the center of the back of the leg, 7 cun below the middle of the popliteal fossa)
VB39 (3 cun above the center of the lateral malleolus, at the anterior edge of the fibula)
V60 (in the depression midway between the center of the lateral malleolus and the calcaneal tendon)
P 9 (between the proximal and distal radiocarpal folds, on the radial artery)
E36 (3 cun below the lower edge of the patella and the width of the middle finger lateral to the anterior edge of the tibia)
VB34 (on the lateral side of the tibia, in the depression at the anterior inferior edge of the head of the fibula, 2 cun below the lower edge of the patella)
F5 (on the inner surface of the tibia, 5 cun above the center of the medial malleolus, at the posterior edge of the tibia)
F4 (anterior and lateral to the medial malleolus, in the depression above the tubercle of the scaphoid)
F2 (in the depression anterior to the space between the 1st and 2nd metatarsophalangeal joints, 0.5 cun proximal to the border of the skin membrane between the 1st and 2nd fingers)
VB43 (0.5 cun proximal to the edge of the skin fold between the 4th and 5th toes)
E44 (in the gap between the 2nd and 3rd toes, in the cavity distal to the 2nd and 3rd metatarsal joints)
RP4 (on the inside of the foot, in the depression at the anterior inferior edge of the base of the first metatarsal bone)
The course of treatment is 12 sessions.
© Doctor of Pedagogy, Professor V.N. Fokin, 2009—2015
Diagnostics
As a rule, diagnosing Raynaud's disease is not particularly difficult for professionals, but a comprehensive examination is still required. After examination, cold tests and history taking, patients are prescribed:
- blood biochemistry;
- hemogram;
- coagulogram;
- general urine analysis;
- immunogram;
- Ultrasound – examination of internal organs;
- spine tomography;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels, as well as some other studies.
An important goal is to rule out other diseases that may cause similar symptoms.
Amen's test
1) Amen's test to detect occlusion of the branches of the radial artery or ulnar artery distal to the wrist. The patient clenches his fist to force the blood out of the hand. The doctor clamps the ulnar and radial arteries. The patient unclenches his fist, the hand remains pale. The doctor stops compressing the radial artery while continuing to compress the ulnar artery. If the radial artery distal to the site of clamping is patent, the hand quickly turns pink. If the patency of the radial artery is impaired, the hand remains pale. The patency of the distal branches of the ulnar artery is examined in the same way.
Treatment
Since stress, as the diagnosis of Raynaud’s syndrome shows, is one of the possible factors in the development of the disease, treatment will be aimed both at working directly with the vessels and at improving the overall quality of a person’s life.
To restore physical condition, vasodilators, antispasmodics, glucocorticosteroids, cytostatics and other medications are used. If medication and additional recommendations do not give the desired result, surgery is prescribed. The endoscopic method makes the operation more gentle when it comes to correcting the functioning of blood vessels. But in extreme cases, patients may require amputation of a limb or part of it.
At the same time, as already mentioned, other methods of work are used to treat Raynaud's syndrome:
- psychotherapy. It aims to reduce stress levels, as well as discover the hidden causes of suppressed stress, if any;
- different types of physiotherapy. These are magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, paraffin baths, etc.;
- physiotherapy;
- mud treatment;
- a diet focused on healthy eating;
- special massages and much more.
As an aid, after consultation with a doctor, for Raynaud's syndrome, you can use some folk recipes, for example, pine baths.
Treatment, as a rule, is long-term, and therefore requires patience from the patient and strict adherence to all recommendations of the attending physician.
Prevention
To make the consequences of Raynaud's syndrome less likely to affect you, you should think about prevention, which includes:
- protection of hands and feet in the cold season. It is also necessary to avoid regular contact with cold water;
- rejection of bad habits. Smoking has a particularly strong effect on the functioning of blood vessels;
- careful health monitoring, timely treatment of any diseases;
- a healthy lifestyle, including adequate and balanced nutrition;
- avoiding any injury. This also applies to the correct choice of shoes - they should not be small, they should not rub or injure the foot;
- proper skin care. You should avoid aggressive liquid soap, lubricate your hands and feet with nourishing, moisturizing creams, and also protect your hands when working with household chemicals;
- reduction of stress factors. A calm life without unnecessary worries is also an important component for health.
If a person observes all of the above, and is also treated for all the diseases that have already been detected in him, there is a high chance of not encountering the symptoms of Raynaud's disease.
Treatment of Raynaud's disease in Saratov, treatment of Raynaud's disease in Russia
Sarklinik provides comprehensive conservative treatment of Raynaud's disease in Russia on an outpatient basis. Treatment of Raynaud's disease in Saratov includes a variety of reflexology techniques.
Complex differentiated treatment of patients with Raynaud's disease in Russia at Sarklinik with the widespread use of new reflexology techniques allows one to achieve satisfactory results even with a severe clinical picture of the disease.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Millymanz | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system treatment in Saratov
Migraine, migraine treatment in Saratov, symptoms, how to treat migraine, headache
Raynaud's syndrome, Raynaud's disease, symptom, phenomenon, treatment in Saratov, how to treat the disease
Solarite, solar plexitis, treatment of solaritis in Saratov