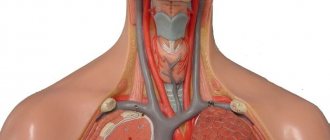
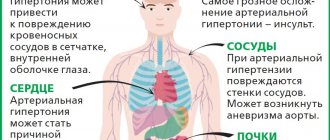
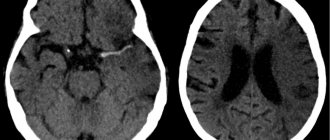
The brain is responsible for coordinating the work of the entire body. A reliable way to obtain information about the structure and functioning of the baby’s brain structures, to conduct NSG / neurosonography / of the brain with determination of the nature of blood flow in the vessels / Doppler ultrasound /
Currently, almost all children undergo NSG in the maternity hospital as a screening method.
To monitor the dynamics of the baby’s development and brain development disorders, repeated examination is recommended in order to exclude congenital or acquired abnormalities. This is especially true for children from the group of premature, low birth weight, immature for gestational age.
Dopplerography or duplex ultrasound scanning of blood vessels in children
Vascular ultrasonography is a major diagnostic field that uses duplex ultrasound scanning to see in real time how blood flows through the arteries and veins in different parts of the baby's body and organs.
Ultrasound examinations (ultrasonography) are a safe and informative method for modern diagnostics of the condition of the blood vessels of a newborn or older child. Ultrasound scanning of blood vessels can be performed without special preparation, right at the bedside. Such diagnostic studies are easily tolerated by the child.
Why is this ultrasound examination called duplex?
Duplex ultrasound scanning is used for visualization and differential diagnosis of various conditions and diseases of blood vessels. The term "duplex" means "double". The fact is that this study combines two types of ultrasound diagnostics: traditional sonography and Dopplerography. On the screen of a duplex scanning ultrasound machine, a double layer of image is simultaneously displayed in real time: visualization of the structure of the examined part of the body in shades of gray and a color Doppler image to visualize the movement of blood in the vessels. At the same time, the computer calculates the speed of blood movement, the volume of blood and the diameters of the vessels through which it flows.
Interpretation of ultrasound results of cerebral vessels
The ultrasound procedure is performed by a radiologist. But often the detected pathology requires additional imaging methods or dynamic monitoring of the condition. Ultrasound studies over time make it possible to determine the effectiveness of treatment and the progression of the condition.
Interpretation
Interpretation of the results of ultrasound of cerebral vessels has certain criteria.
- Each clinic should have interpretation criteria that are used by all members of the technical and medical staff.
- Diagnostic criteria should be derived from the literature or from internal validation based on correlation with other imaging modalities or surgical and/or pathological correlation.
- The vascular ultrasound report should indicate categories of internal carotid artery stenosis that are clinically useful and accepted nationally or internationally and are based primarily on velocity criteria and waveform analysis. Stenoses greater than 50% should be scored with a precision range (eg, 50% to 69%, 70% to near occlusion) or a numerical score (eg, 60% ± 10%) to provide adequate information for clinical decision making .
- Numerous factors can falsely increase or decrease velocities (eg, systemic disease, cardiovascular disease, severe contralateral disease or occlusion, incomplete occlusive stenoses). Simple speed criteria may not be appropriate for younger populations.
- The report should describe abnormal waveforms, if any.
- The report should indicate the direction of vertebral artery flow.
- The report may characterize the plaques depending on laboratory interpretation criteria.
- The report should describe significant nonvascular abnormalities.
- The criteria for stenosis of the common carotid and vertebral arteries differ from those of the internal carotid artery.
- The velocity threshold that indicates external carotid stenosis has not been established. A simple description may be provided indicating stenosis if present. Identification of stenosis may be based on narrowing of the gray and/or color flow, increased velocity of passage of the stenosis, and typical poststenotic waveforms.
- Rate criteria for stenosis after interventions may require different critical indicators.
How does a Doppler ultrasound machine work?
Doppler ultrasound uses reflected sound waves to assess blood flow in different parts of your baby's body. It is important that ultrasound machines do not use any other type of radiation other than ordinary sound.
The mechanism for obtaining images during Doppler sonography is in many ways similar to the mechanisms that nature uses: with the help of ultrasonic waves, dolphins and whales search in the seas and oceans for schools of fish that they hunt. The tip of the Doppler ultrasound machine emits sound waves, like a dolphin, which are partly reflected from organs and tissues and partly absorbed by them. By analyzing the difference in reflected echo waves, the computer builds images of the structure of blood vessels. Structures that reflect sound well appear brighter on the screen, while organs and tissues that absorb most of the sound wave appear less bright than their surrounding environment. Body tissues that completely absorb sound waves (anechoic) appear black.
When the doctor sees on the screen a vessel in which he wants to evaluate the blood flow, he presses a button to turn on the Doppler function. To measure blood flow parameters, an ultrasound machine uses the Doppler effect, which consists of changing the length of the echo wave when reflected from a moving object (moving blood). In this case, the computer measures the change in the wavelength of the echo signal and calculates all the necessary parameters of the heart, blood vessels and blood movement, while building a color image of the blood movement in the vessels on the screen.
Indications for performing NSG and ultrasound examination:
- intrauterine hypotrophy;
- intrauterine infections;
- previously identified brain defects;
- pathology in hypoxic, ischemic, toxic and metabolic disorders of the brain;
- birth injuries of the brain and spinal cord;
- seizures and other symptoms of neurological diseases;
- multiple malformations of organs and systems;
- genetic diseases.
To assess the blood circulation of the brain in children after the “closure” of the fontanel, modern ultrasound techniques are used - transcranial Dopplerography. In some cases, this technique makes it possible to clarify the cause of headaches in children (angiospasm, increased intracranial pressure). Transcranial Dopplerography allows you to examine large vessels of the head and neck, see the lumen of the vessel, the degree of patency of veins and arteries. This method is absolutely painless and has no contraindications, which makes this procedure possible for young children.
We invite you to do a study at our medical center.
Why is duplex scanning of blood vessels performed?
Doppler ultrasound is used to evaluate blood flow through the chambers and valves of the heart. Spectral Doppler ultrasound can measure the size of the holes through which blood flows. In addition, Doppler ultrasound of the heart can accurately detect abnormal blood flow in the heart, which may indicate a hole in the heart septum or insufficiently functioning heart valves.
Vascular Dopplerography allows you to assess the quality of blood flow through central and peripheral arteries and veins. Using duplex scanning, you can identify blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques, underdeveloped vessels, anomalies in position and branching, tortuosity, damage and compression of their walls, narrowing of blood vessels (stenosis) or complete blockage of blood flow (vessel occlusion), assess changes in the course of the vessel, and abnormal tortuosity. Dopplerography helps to identify abnormalities in the development of blood vessels, determine the pathological expansion of the vessel walls (vascular aneurysm), the failure of the valves in the veins, assess the elasticity of the vascular wall and the condition of their internal surface.
Using diagnostic information obtained through duplex scanning of blood vessels, the doctor will prescribe treatment for the child that will prevent the development of possible complications associated with impaired blood flow (up to and including cardiovascular accidents: heart attacks and strokes, which, unfortunately, occur even in young patients).
Duplex ultrasound scanning can detect hemangiomas in a baby - congenital vascular lesions in newborns, most often occurring on the head and neck.
Duplex scanning is also performed before more serious diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in order to accurately determine the position, nature and probable cause of blood flow disturbance in the vessel.
Indications for ultrasound of cerebral vessels
Indications for ultrasound examination of the extracranial carotid and vertebral arteries include:
- Evaluation of patients with hemispheric neurologic symptoms including stroke, transient ischemic attack, and amaurosis
- Assessment of the condition of patients with cervical osteochondrosis
- Evaluation of pulsating massive neck masses
- Preoperative evaluation of patients scheduled for major cardiovascular surgical procedures
- Evaluation of non-empirical or unexplained neurological symptoms
- Dynamic examination of patients with proven carotid artery disease.
- Assessment of the condition of patients after surgery or after intervention after cerebrovascular revascularization, including carotid endarterectomy, stenting
- Intraoperative monitoring of vascular surgery
- Evaluation of suspected subclavian artery steal syndrome
- Examination for suspected carotid artery dissection, arteriovenous fistula, or pseudoaneurysm.
- Evaluation of patients with carotid artery reconstruction after ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) bypass
- Assessing patients with fainting, seizures, or dizziness
- Screen for high-risk patients: atherosclerosis elsewhere, history of head and neck radiation, fibromuscular dysplasia, Takayasu arteritis, or other vasculopathies.
- Neck injury
Indications for transcranial ultrasound examination:
- Assessing sickle cell disease to determine stroke risk.
- Detection and follow-up of stenosis or occlusion in the main intracranial artery or vertebrobasilar system, including monitoring and rationale for thrombolytic therapy in patients with acute stroke.
- Detection of cerebral vasculopathy.
- Detection and monitoring of vasospasm in patients with spontaneous or traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Assessment of collateral pathways of intracranial blood flow, including after intervention.
- Detection of circulating cerebral microembolisms
- Detection of shunts from right to left.
- Assessment of cerebral vasomotor reactivity.
- As an adjunct to the clinical diagnosis of brain death.
- Intraoperative and postoperative monitoring to detect cerebral thrombosis, embolization, hypoperfusion and hyperperfusion.
- Assessment of arteriovenous malformations before and after treatment.
- Detection and follow-up of intracranial aneurysms.
- Evaluation of positional vertigo.
- Assessment of intracranial pressure and hydrocephalus
Preparing for the study
The key to the success of this diagnostic procedure is that the child can lie quietly during the examination. Therefore, it is necessary to feed him 2 hours before the test, and immediately before the study, take him to the toilet or change his diaper. On the day of the study, older children are not recommended to drink tea, coffee, energy drinks or take other drugs that may affect vascular tone.
Only duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta requires special preparation. The study is carried out on an empty stomach. 2 days before the test, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that stimulate gas formation in the intestines: black bread, raw vegetables, legumes, carbonated drinks, fermented milk products. 3 hours before the test, it is necessary to give the child (in agreement with the pediatrician) a drug to reduce gas formation, Espumisan.
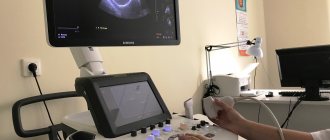
Conducting research
The doctor will place the child in a comfortable position on the couch and apply an acoustic gel, warmed to body temperature, to the surface of the area being examined, which helps sound waves penetrate the body tissue. The doctor will move the tip of the ultrasound machine along the gel, which will make pulsed whistling sounds. The doctor may ask the child to lie down in different positions, take a deep breath, and hold his breath. In some cases, a cardiogram can be taken and pressure in the upper and lower extremities (at the ankle and shoulder) can be measured at the same time. The duration of the study is 30-45 minutes.
How is it carried out?
It is possible to perform an ultrasound of the child’s brain only until the age when the fontanelles close. The examination is carried out through the anterior, lateral fontanelles or foramen magnum at the base of the child’s neck.
During an ultrasound, the diagnostician moves a special sensor over the baby's head. The resulting pulses are sent to the device and displayed on the monitor in the form of images. This is a comfortable procedure that can be done in the clinic, even while the child is sleeping.
You can sign up for ultrasound diagnostics by calling the reception at (495) 951 87 63 or
In our center, infants undergo comprehensive diagnostics (NSH, ultrasound of the hip joints, EEG/video-EEG monitoring) and consultations with a neurologist, orthopedist, geneticist, and ophthalmologist.