Antispasmodics are a group of medications that can relieve spasms of internal organs and the associated pain syndrome.
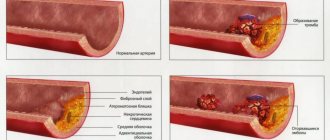
Internal organs with a tubular structure (vessels, uterus, bronchi, ureters and bladder, intestines, bile ducts, etc.) contain a smooth muscle matrix - a layer of muscles located in the wall of the organ. Under physiological conditions, this smooth muscle regulates the lumen of the organ and is in constant tonic contraction.
Smooth muscle is involuntary. This means that we cannot control it using consciousness, such as striated muscles. We can voluntarily raise or lower our hand, but we cannot, through an effort of will, expand the bronchi or stop the contractions of the intestines. The smooth muscles are controlled by the autonomic nervous system. Autonomous because its functioning does not depend on our will.
The nerve endings of the autonomic nervous system do not adhere tightly to the smooth muscles; there is always a gap between them and the muscle, called a synapse. When the autonomic nerve is excited, under the influence of its impulse, a special substance called the mediator acetylcholine is released. This substance diffuses (penetrates) from the nerve ending to the muscle and activates the acetylcholine receptor on the smooth muscle cell membrane. At the same time, it is reduced. This is a normal physiological process.
In cases where the tone of the autonomic nervous system increases, for example, when the ureter is irritated by the spines of a kidney stone, more acetylcholine is produced, and the contraction of smooth muscles becomes excessively strong or chaotic. This leads to a painful sensation - spasm.
Spasm is a tonic, cramp-like contraction of internal organs that have smooth muscles and is manifested by specific pain. Spasm usually occurs due to inflammatory damage to the internal mucous membrane of a tubular organ.
During a spastic contraction of an organ, sensitive nerve endings and blood vessels are mechanically pinched, which leads to impaired circulation in the organ and pain. The pain syndrome caused by spasm is called colic.
Content:
- Detox and overcoming withdrawal are the main tasks in the treatment of binge drinking 1.1. Anti-binge drugs with detoxification activity 1.2. Anti-binge medications that relieve withdrawal symptoms
- How to restore the nervous system after binge drinking
- Medications to help prevent relapse after withdrawal from binge drinking
By binge drinking, narcologists mean a condition when an alcohol addict drinks alcohol in large quantities for more than a day. Breaking out of binge drinking is a very responsible procedure. It is in no way connected with the use of cucumber and cabbage pickles, as many people think. Special medications must be used here to neutralize ethanol toxins and improve the functioning of internal organs.
The wisest thing to do to get out of binge drinking is to seek help from experienced narcologists. Doctors will draw up an individual rehabilitation plan that will minimize the damage to health. Self-medication for severe alcohol poisoning is dangerous.
Neurotropic agents
Psychoactive substances have a diverse effect on the central nervous system at any level of central nervous system functioning: molecular, synaptic, cellular, systemic. In general, any such influence is accompanied by a change in metabolism at the level at which this influence occurs.
Psychoactive substances can enter the body in a variety of ways; common methods are:
- orally, when swallowed through the digestive system,
- parenterally - by injection intramuscularly or intravenously,
- through the mucous membranes, including intranasally - through the nasopharynx, by inhaling crushed substances,
- through the lungs - by smoking or inhaling vapors.
A psychoactive substance goes through a complex path in the body, depending on its structure, method of use, state of the excretory systems, and can be processed by the body into derivatives with different activities. Getting into the blood, passing through the blood-brain barrier, they affect the transmission of nerve impulses by neurons. By influencing the balance of neurotransmitters of different influences (activating and inhibitory) in the brain, drugs thus change the functioning of the entire nervous system.
Tolerance
The higher the tolerance of the substance used, the larger doses it needs to obtain the expected effect. Typically, tolerance is developed by taking substances whose activity declines over time. Tolerance develops quickly for caffeine and opiates. The more often and more a substance is used, the faster tolerance grows.
Classic psychedelics (LSD, psilocybin, mescaline) have a peculiar tolerance - when taking one of these substances, tolerance increases very quickly, literally a few hours after the onset of action, but subsides completely in about a week. Moreover, psychedelics are characterized by cross-tolerance; for example, taking psilocybin the day after taking LSD, depending on individual sensitivity and the amount of substance, will either have no effect at all or the effect will be significantly reduced and short-lived. Cross-tolerance to psychedelics also completely disappears in about one week.
It has been noted that some substances, such as salvinorin, a natural dissociative found in the Mexican sage Salvia divinorum, may exhibit reverse tolerance, meaning the phenomenon that with long-term use, less of the substance is required to achieve the same effect.
Formation of addiction and withdrawal syndrome
Typically, the formation of addiction is associated with the abuse of psychoactive substances and its systematic use. Although the effect of substances on a person is very individual, it can be said that among the most common substances, addiction develops most quickly when taking heroin, nicotine, psychostimulants cocaine and amphetamine can also be distinguished, causing mental (but not physical) dependence.
Physiological dependence is formed when the body gets used to the regular exogenous intake of substances involved in metabolism into the body and reduces their endogenous production, thus, when the intake of a substance into the body ceases, a need for this substance arises due to physiological processes. Physical dependence differs from psychological dependence in that as a result of replacing one’s own neurotransmitters with exogenous ones, their production in the body [12] (or the number of receptors for them) decreases.
The mechanism of addiction formation can be associated both with the substance itself and with its metabolites, for example, heroin, by removing acetyl groups, is metabolized into morphine, which acts on opioid receptors. Alcohol affects the nervous system by directly binding to GABA receptors[13]. Nicotine and amphetamines stimulate the release of endogenous adrenaline [ source not specified 3062 days
].
Psychological dependence is associated mainly with pleasant sensations from substances that stimulate a person to repeat the experience of using them. Under the influence of opiates, a person may not feel pain or anxiety; one of the ways in which stimulants act is to increase self-esteem and energy. However, addiction can also form when using other substances, for example, dissociatives that cause a collapse of consciousness (trip reports even report experiences of death under their influence); The experiences and visual effects of psychedelics often cannot be described as pleasant at all, however, with frequent use, these substances can cause a break with reality associated with the escapist nature of the psychedelic experience. Cannabis intoxication helps with depression[14], while constant use of marijuana or its substitute mixtures develops a number of psychosocial problems[15].
Psychoactive substances and relevant targets
| Exogenous ligands | Endogenous ligands | Receptors |
| Hemp (cannabinoids) | Anandamide 2-arachidonylglycerol | Cannabinoid |
| LSD | Serotonin Dopamine Adrenaline | Serotonin Dopamine Adrenergic Receptors |
| Cocaine Amphetamines | Dopamine Norepinephrine Serotonin | Dopamine Adrenergic receptors Serotonin |
| Opiates (Morphine, Heroin, etc.) | Endorphins Endomorphine | Opioid |
| Alcohol Sleeping pills | Gamma-aminobutyric acid Dopamine Norepinephrine Serotonin Beta-endorphin | GABA receptors Dopamine Adrenergic receptors Serotonin Opioid |
| Nicotine | Adrenaline Acetylcholine Dopamine | Adrenergic receptors n-cholinergic receptors Dopamine |
| Caffeine | Adenosine | Adenosine |
Detox and overcoming withdrawal are the main tasks in treating binge drinking
Anti-binge medications are used to bind and utilize ethanol metabolites, dangerous toxins. It is thanks to them that doctors are able to quickly improve the mental and physical condition of the addict.
Anti-binge drugs with detoxifying activity
Detox therapy is a set of measures to relieve an alcohol addict from nausea, vomiting, headaches, muscle pain, and tremors. Detoxification also reduces the craving for alcohol-containing compounds. During it the following are used:
- Absorbents . Designed for accelerated removal of all types of poisons and harmful compounds from the body. The drug treatment service has a large selection of drugs in this group. The most affordable and popular of them is activated carbon. “Polysorb” and “Smecta” have also proven themselves well.
- Diuretics . Needed to speed up the elimination of poisons.
- Means for the correction of disorders in alcoholism based on metadoxine. They protect the liver from toxic damage and help its cells renew themselves at an accelerated rate. At the same time, they reduce the desire to take another dose of alcohol.
Anti-binge medications that relieve withdrawal symptoms
Withdrawal syndrome occurs only in people with extensive drinking experience. It is always very painful, so most often addicts cannot overcome it without qualified drug treatment help. Doctors use anti-binge drugs from pharmacological groups such as:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , which include salicylic acid. With their help, you can quickly reduce combat symptoms, make the blood more fluid and thereby prevent thrombosis of small vessels.
- "Medichronal" . Composition including glucose, aminoacetic acid and other active substances. It reduces the concentration of toxic acetaldehyde in the drinker’s body, supports the functions of the nervous system, and increases the level of vital energy. At the same time, it has a central inhibitory effect and calms the patient, putting many metabolic reactions in order.
- Detoxifying medications , including sodium dimercaptopropanesulfonate, calcium pantothenate. With their help, it is possible to obtain a pronounced antioxidant, hepatoprotective, and detoxification effect. They bind and neutralize acetaldehyde and speed up regenerative reactions.
- Metabolic agents based on citric and succinic acid . Indicated if it is necessary to restore healthy tissue metabolism, increase the overall reactivity of the body, increase intellectual and physical endurance, and reduce the toxic effect of alcohol and its breakdown products.
It is very important that a doctor selects medications to help alcohol addicts break from binge drinking. Self-medication for severe alcohol poisoning very often turns out to be ineffective or further aggravates the patient’s condition.
Psychotropic substances prohibited in Russia
In Russia, the group of prohibited substances includes the following:
- Ephedrine is a raw material for the production of amphetamines. The substance is produced from coniferous trees.
- Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), isolated from hemp. In the USA and European countries, the drug is approved for relieving side effects of radiation therapy, in the treatment of AIDS, etc. The drugs Nabilone and Nabiximols have been developed on its basis.
- Dimethyltryptamine is isolated from the Mimosa legume plant grown in Brazil. A psychedelic that causes an altered state of consciousness is more often used in religious or psychedelic practices.
- Morphine, extracted from the opium poppy, was used as an anesthetic.
- Codeine is an opium alkaloid. In a number of countries it is used as an analgesic and antitussive.
- DMT (dimethyltryptamine) (from plants Mimosa hostilis, Psychotria viridis, etc.).
- Kavain is produced from intoxicating pepper. The name of the plant itself indicates the effect it has. – the substance relieves tension, anesthetizes, and causes mild euphoria.
This list contains addictive substances, which is why they are prohibited in Russia. Not all psychotropic drugs are narcotic, that is, addictive. But all narcotic substances are psychotropic to one degree or another. Drug addiction treatment is the first step towards getting rid of this harmful addiction, which must necessarily be followed by a period of rehabilitation. In order to get advice or find out information of interest, call the hotline number indicated at the top of the page or write to us via chat.
How to restore the nervous system after binge drinking
Since multi-day drinking sessions almost always bring the addict out of balance, making him aggressive and anxious, when withdrawing from binge drinking, medications are used that improve the functioning of the nervous system. Usually these are sedatives, which:
- normalize sleep;
- relieve overexcitation;
- relieve unreasonable anxiety;
- normalize blood pressure.
Medicines containing:
- Glycine. The product has neurotropic properties. Improves mental activity, relaxes. Positively affects the patient's intellectual abilities.
- Bromodihydrochlorophenylbenzodiazepine. This is an anxiolytic component. It is characterized by muscle relaxant, central, hypnotic and sedative effects.
- Diazepam. Anxiolytic and antiepileptic component. Reduces the likelihood of seizures, helps the patient cope with anxiety and fear. Perfectly relaxing.
If, during an examination of a person who is in a state of prolonged heavy drinking, a narcologist sees severe overexcitation and inappropriate actions, then he may decide to include tranquilizers and antipsychotics in the therapeutic program . The use of such drugs is allowed only under constant medical supervision , so the alcohol addict will have to go to a drug treatment hospital.
Medications to help prevent relapse after withdrawal from binge drinking
To minimize the likelihood of repeated drinking after binge treatment, narcologists sometimes use drugs that cause individual intolerance to alcohol-containing drinks. Such medications should never be combined with alcohol. They are administered upon completion of detoxification. The patient must be warned about this.
Compositions containing disulfiram have proven themselves to be excellent. When combined with ethanol, they provoke nausea, vomiting, increased blood pressure, severe weakness and other unpleasant symptoms. Knowing that the administered drug is incompatible with ethanol, the patient consciously restrains himself from participating in another drinking session.
Since all disulfiram-containing products exhibit a pronounced aversive effect, their use must be treated with maximum responsibility. They should never be secretly mixed into the patient’s food or drinks. They are also not prescribed to persons with a history of stroke, myocardial infarction, or those prone to hypertension.
For unadvanced alcoholism, doctors sometimes prescribe the medicine Proproten-100 . It belongs to the pharmacological category “Medicines for the correction of disorders in alcoholism, toxicity and drug addiction.” Contains antibodies to brain-specific protein S-100. The drug is available at the pharmacy without a prescription, but it is clear that you cannot use it without first obtaining medical advice.