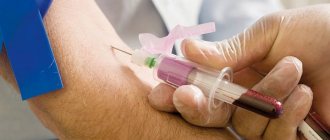
Troponin test is a biochemical analysis of blood composition, which makes it possible to detect the presence of the protein troponin (Tn) in it. This protein leaks into the bloodstream from cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells) that die during a heart attack.
In the blood plasma of a healthy human body, the concentration of troponin protein is very low, which is practically undetectable during diagnosis. This protein is present only in myocardial cells.
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is necrosis of areas of muscle tissue of the heart organ, in which myocardial cells die without the right to be restored. At the moment of cell death, Tn enters the bloodstream, and its concentration can reach several thousand units.
The cardiac troponin index may be an indicator of myocardial infarction in the diagnostic study of heart attack.
What is troponin?
During a heart attack, not only this protein enters the bloodstream, but also other substances are found in the blood, but only troponin is associated with the cells of the myocardial tissue. The troponin protein complex in myocardial cells contains isoforms that interact with each other: T, C and I.
Each type of troponin protein has its own functional responsibilities: some perform their function in the ability of the heart muscle to contract, others are responsible for the condition of the heart tissue. All types of troponins differ from each other in molecular weight.
Troponins T and I, which are contained in isoforms, have 3 types:
- Cardiomuscular type
- Cardiomuscular slow type,
- Cardiomuscular type is fast.
Isoforms T and type I are most specific to myocardial muscle, therefore they are called cardiac troponins
.Damage and destruction of myocardial cells leads to the fact that the troponin complex disintegrates. Its individual isoforms penetrate into the blood plasma within a few minutes. At this time, their concentration can be diagnosed using modern equipment (laboratories and rapid troponin test).
The troponin test for heart attacks has been used for 10 years. The sensitivity of the biochemical analysis for the protein troponin is about 100.0%.
The troponin test indicates one isoform of the protein in the blood plasma, this is T, or I. For diagnosis, venous blood is taken in a volume of several milliliters. Protein concentration is determined in blood plasma or serum.
Standard indicators
In every healthy organism, during the physiological process of myocardial cell death, the plasma level is determined to be quite low.
The standard indicator of troponin type T which, without the presence of pathologies of the cardiac organ in the body, ranges from 0.010 ng/ml to 0.10 ng/ml. The unit of measurement for troponins is nanogram/liter (ng/L).
The protein index increases not only during a heart attack, but also for the following reasons:
- After surgery on a cardiac organ,
- Acute coronary syndrome,
- Damage to skeletal muscle cells
- Sepsis,
- Inflammatory process in the pericardium, pericarditis,
- Inflammation of the myocardium, myocarditis,
- Injury to the heart muscle
- Hypovolemia accompanies cardiogenic shock, hypovolemic, as well as septic shock,
- Reduced level of blood pressure (BP) in the bloodstream,
- Supraventricular type of tachycardia,
- In case of atrial fibrillation with atrial fibrillation,
- Left ventricular hypertrophy caused by hypertension
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,
- Hemorrhagic stroke,
- Ischemic stroke,
- Vasculitis of the coronary arteries,
- Severe anemia
- Endothelial dysfunction of coronary vessels without cardiac ischemia,
- Dissection of the aortic walls, aortic insufficiency,
- Disorders of the aortic valve,
- Amyloidosis and sarcoidosis.
One of the reasons why protein levels increase.
Extracardiac pathologies that cause an increased troponin index in the blood:
- Therapy with medical chemicals,
- Overdose of catecholamines,
- Intoxication of the body due to snake bites,
- Toxins from a scorpion sting,
- State of myxedema coma,
- Severe large-scale burns,
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pulmonary hypertension,
- Bleeding inside the cerebral cortex,
- Chronic renal failure,
- Alcohol intoxication in acute and severe form.
Bleeding inside the cerebral cortex.
If the pathology of the cardiac organ occurs in a typical form, then an ECG (electrocardiography) can be done to determine it, but if the disease develops in an atypical form and the cardiogram does not provide accuracy in the examination, then to diagnose a heart attack, it is necessary to use a troponin test through a biochemical blood test.
A quantitative troponin test is carried out only in laboratory conditions, and the result of its study will be a specific digital result.
Troponin test with normal troponin I protein:
| Concentration up to 0.50 µg/l | Myocardial infarction in acute form is not established |
| From 0.50 mg/l to 2.0 mg/l | Acute myocardial infarction is confirmed |
Troponin test with a normal troponin T index:
| Concentration less than 0.40 µg/l | Myocardial infarction is not diagnosed and a repeat test is ordered in a couple of hours |
| From 0.40 µg/l to 2.30 µg/l | Acute myocardial infarction is confirmed, but requires additional research |
| More than 2.30 µg/l | Proven infarction in the acute stage of the disease |
Causes of increase and methods of treatment
We can name 8 provoking factors.
Myocardial infarction
Classic pathological process of the cardiac profile. Accompanied by a sharp disruption in the nutrition of the entire heart muscle. Or a separate fragment of it. It is considered a type of acute coronary insufficiency.
The condition is urgent. If you do not provide first aid to the patient in a timely manner and then do not start therapy, there is only one prospect - death from complications. Arrhythmias and critical disorders begin, and cardiac arrest develops. Urgent correction is needed.
Troponins increase during a heart attack due to the fact that part of the myocardium is destroyed - the cells disintegrate and release the substance, the concentration increases rapidly and reaches a peak in a matter of hours.
Treatment. The acute condition is first eliminated, and then the symptoms resolve in the hospital. Strictly. Perhaps even in intensive care. Special cardioprotective drugs are prescribed. Constantly monitor the state of things.
Then, as soon as the person recovers from the acute condition, treatment with Mildronate and Riboxin is continued. They fight against violations of the rheological properties of blood. It thickens, it is liquefied, but with great care. Antiplatelet agents based on aspirin and other drugs are used to prevent blood clots from forming.
Myocarditis
Inflammation of the heart muscle. It is quite rare. This is mainly the result of a previous infection. The causes are always pathological.
The patient experiences a group of unpleasant manifestations. From acute chest pain to rhythm disturbances. If nothing is done, the consequences will be the same as with a heart attack. At a minimum, some of the heart cells will die. At the maximum, the organ’s functioning will stop, asystole.
Therapy is carried out strictly in a hospital setting. Sometimes it ends up in intensive care because urgent medical attention is needed.
Troponin increases gradually, since during myocarditis the cells die in parts. The peak occurs in the middle of the disease. There is no need to artificially reduce them. This is just a marker of the problem. The underlying condition must be dealt with.
This is where antibiotics, glucocorticoids, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs come to the rescue. Average course. If necessary, the duration of therapy is increased.
Angina pectoris
Coronary insufficiency in the chronic or subacute phase provokes a gradual increase in troponin. The same as with myocarditis. However, this does not always happen. Because death of heart tissue does not necessarily develop with angina.
The question is complex. However, if coronary insufficiency is suspected, a test is always prescribed.
Treatment. Depends on the specific condition. As a rule, stable angina is corrected with the help of protectors. Mildronate, Riboxin. Monitor blood pressure levels. Unstable form must be constantly monitored. Surgical treatment is indicated if necessary.
Arterial hypertension at an advanced stage
When target organ damage is present. Eye, heart, kidney, brain. The question is what is the origin of the pathological process. If you don’t know this, then you won’t be able to lower troponin.
Treatment of arterial hypertension is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist. A group of drugs is prescribed: beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, calcium antagonists, centrally acting agents, and other substances like sartans.
The question remains with the specialist. You need to choose the right combination.
Sometimes the problem is in the kidneys (renovascular hypertension). Then it is necessary to treat the underlying nephrological disease (not to be confused with a neurological one). For example, pyelonephritis or autoimmune tissue damage.
Mechanical heart damage
As a rule, they are iatrogenic in nature. That is, the violation is associated with the actions of doctors. Usually the operation is to blame.
Cardiac surgery in general is a risky and time-consuming field. Therefore, the likelihood of such an outcome developing is quite high. Fortunately, this condition does not pose a serious danger. Moreover, the patient is under the supervision of doctors all the time after the operation.
Treatment. No special correction is needed. Dynamic observation and maintenance therapy with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and cardioprotectors are sufficient.
It is important not to miss the moment if complications develop. The patient should talk about all his feelings to the treating specialist.
Pulmonary embolism
It develops after a blood clot rich in fibrin forms on the vascular wall. And then it breaks off and begins to migrate along the bloodstream.
Almost always such a “journey” ends in tears. Develops against the background of coagulopathies and excessive coagulation. This is possible after operations, with dehydration and other pathological processes.
Treatment is carried out immediately. In the acute phase, the patient dies without even understanding what happened (read more about PE in this article). If the blockage of the vessel is not so serious, the clot must be removed. For this purpose, minimally invasive techniques are used.
After surgical treatment, antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are used to reduce the likelihood of recurrence of the pathological process. By the way, relapses are quite possible.
Pericarditis
Inflammation of the membrane that encloses the heart. The process is accompanied by severe pain in the chest.
With prolonged disorder, effusion may form. Liquid transudate that accumulates in the pericardial sac. This extremely dangerous condition is called hydropericardium. As soon as the pressure outside becomes equal to that in the structures of the muscular organ, cardiac arrest occurs. Therefore, the disorder is considered critically dangerous. Therapy is needed.
Treatment. Loading doses of broad-spectrum antibiotics are used. Glucocorticoids like Prednisolone are required. It is also possible to prescribe more powerful medications in this group. When the effect is insufficient.
On the other hand, the formation of effusion is constantly monitored. If it comes out, the liquid must be pumped out. For this purpose, the puncture method is used.
Overall, the recovery prospects are quite positive. The survival rate is almost 79-93%. According to various estimates. The main thing is to see a doctor in time. Troponin will decrease on its own.
Cardiac markers
In the first few hours of the progression of a heart attack, it is quite important to determine the situation and establish an accurate diagnosis of the attack. The life of the patient depends on the efficiency of doctors.
Previously, the doctor received information through instrumental research:
- The picture of clinical symptoms is severe and burning pain in the chest,
- Results by ECG method,
- Biochemical indicators myoglobin, creatine kinase index, lactate dehydrogenase index.
Recently, the mechanism of diagnostic studies of heart attack has changed. The first analysis that is done during an attack is a troponin test and an instrumental ECG method.
Using this examination strategy, it is now possible to recognize myocardial ischemia in the first couple of hours from the moment the first signs of pathology appear, which allows for a timely diagnosis with minimal damage to the heart muscle.
The sooner a troponin test is performed, the sooner drug therapy for a heart attack is started, and the greater the patient's chance of survival.
The specificity of the method for studying the troponin test in the pathology of the first myocardial infarction is 100% and this is its advantage over other methods. During the second attack of a heart attack, Tn do not react strongly to it, although they have an increased level.
In the second case of infarction, more information can be obtained from the MV QC indicator. MB is myoglobin, and CK is creatine kinase.
Reason for performing a troponin test
Reasons for performing a troponin test are symptoms consistent with myocardial infarction. The procedure is carried out on the condition that rapid laboratory tests are not possible. The rapid test provides instant information and saves precious time allocated to save the patient.
Testing for troponins is most necessary for atherosclerotic patients, overweight people and those suffering from angina pectoris. The reasons for the test are:
- Sudden pain inside the chest, on the left side, which radiates to the left shoulder, collarbone, ear, and is also noted in the neck and between the shoulder blades.
- Sharp fluctuations in blood pressure.
- Changes in heart rate.
- Choking, pallor of the patient, dizziness. sweating
- Weakness, nervous disorders.
Troponin complex
Troponin is not just a single-celled substance that takes part in the work of the heart, it is a whole complex containing 3 units. Each component has its own distinctive characteristics in terms of amino acid composition, weight, and location in the myocardium.
According to its functions in the heart muscle:
- Tn type T properties of this molecule bind to tropomyosin, with the help of which the regulatory complex is attached. In the cells of myocardial tissue (cardiomyocytes), troponin T is 2 times more than troponin I. Tn I has a different amino acid composition and is found in myocytes of other myocardial tissues,
- Tn type I is a substance that puts pressure on ATPase activity. Although this troponin is in lower concentration in the myocardium, its sensitivity is much higher than Tn T,
- Tn type C. This marker is not involved in diagnosis, because the Tn T and Tn C markers in the myocardial muscles are identical and there is no way to decipher it. This troponin binds to calcium molecules.
Troponin molecules.
Troponin is a regular complex of protein molecules that are found in the blood in small quantities in a healthy normal body.
In the damaged state of the muscle tissue of the heart, the troponin complex is quickly broken down, and releases troponin protein molecules from the damaged and collapsing heart muscle during necrosis. During a heart attack, troponins increase in plasma several hundred times.
A troponin test is used for diagnostic study of indicators during a heart attack.
The troponin test can also be used during therapy to monitor drug treatment and adjust it as necessary.
Prevention is better than cure
Any highly effective tests and therapy in prestigious medical institutions are not comparable to full health. No matter how high the achievements of modern medicine, myocardial infarction continues to cripple human lives.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle significantly reduces the risk of myocardial infarction
Preventive measures that are not difficult for anyone can significantly reduce the possibility of the manifestation of this pathology:
- Increased physical activity.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Balanced diet.
- Optimism.
- Timely rest and healthy sleep.
- Consultations with a family doctor.
- Prevention of diabetes and hypertension.
Even if a person has never experienced heart failure before, at the slightest suspicion of a heart attack, you should immediately call an ambulance. Self-medication and loss of time are fraught with fatal consequences.
How to do a troponin test?
In case of a heart attack, the main thing is not to miss the time for emergency treatment, so the ideal solution would be to use the rapid troponin test method. This heart attack testing can be performed by the patient himself or by an emergency doctor. The rapid troponin test is a qualitative method for diagnosing troponin.
Quantitative diagnostics of troponin in the blood can only be done in a clinical laboratory. This is quite a long time compared to quick and emergency express diagnostics. The rapid troponin test is performed in 12 minutes to 20 minutes.
Test procedure.
The mechanism of action of this express is very simple. On the test device, according to the instructions for use, it is necessary to apply a few drops of blood to the application area where antibodies are present, upon touching which the molecules react and a complex is formed. Within 15 minutes the reaction reveals the presence of troponins, if present.
According to this test, red blood cells are separated, and plasma with markers enters the detection zone, in which there is a signal line where the protein streptavidin is applied, as well as a control line with immobilized troponin. The control line is with antibodies.
A change in color on the troponin express test indicates the presence of troponin molecules in the plasma. When the control line is colored, this indicates that the testing was carried out according to the rules.
Explanation of testing using the express method:
- 1 band stained negative, no troponin detected in plasma,
- 2 stripes are colored positive, there is troponin in the blood,
- If no stripes appear at all, then the test is not suitable for use.
Price for systems for determining troponin
Express tests for determining Tn type I in serum, plasma and blood.
Available in all pharmacies:
- Troponin express test kit for identifying Tn I molecules from the manufacturer Wondfo.
- Express Test for troponin from the manufacturer Formed.
- Troponin express test for measuring troponin in blood, plasma and serum, from .
Each troponin test kit includes:
- Test - cassette, tightly packed in foil,
- Pipette for collecting and dispensing blood,
- Instructions for using the test.
Testing blood for troponin in the laboratory
Tn T or Tn I is studied by taking a blood sample into a test tube. This analysis can be performed immediately, or the blood sample can be frozen.
Testing method:
- Tn type I and type T can be used for diagnosis. They are both useful markers of infarction and give the same clinical indicators,
- It is impossible to use the troponin test from different manufacturing companies in diagnosis, because such comparisons cannot be made. The result of a comparison study, the troponin test Tn T and Tn I, will not be correct in this situation, even if they have the same reference limits,
- Compare in one analysis: you can only test from one manufacturer, from one production lot number. Only in this case can you be 100% confident in the result of biochemistry,
- Troponin T is studied according to a developed system of standards, troponin I does not have such a system,
- The first time blood is taken for a sample at the first symptom of a developed heart attack, if the troponin level is not determined, it is necessary to repeat the diagnosis after 2-3 hours,
- With such precision in the technique, it is possible to timely track the development of a heart attack, as well as monitor the dynamics of recovery.
Causes of high troponin concentration coronary syndrome
Troponin test is a method for studying blood composition during a heart attack.
And it involves determining the plasma level of troponin concentration:
- Troponin T (Tn T) in coronary syndrome appears in the blood 2-6 hours after blockage of the coronary artery occurs. The increased index is maintained for up to 14 calendar days, and sometimes up to 21 calendar days,
- Troponin I (Tn I) is one of the earliest markers that can be diagnosed 2 hours after the onset of symptoms of coronary syndrome; activity manifests itself during the first day and this troponin continues to be in the blood for up to 7 calendar days.
Troponin type I
The etiology of troponin I in the blood, in the composition of plasma and serum, is in the first place coronary syndrome caused by myocardial infarction. Also to destroy the troponin compound complex and release Tn I into the blood.
There are other reasons:
- IHD (coronary heart disease) in chronic form,
- Damage due to muscle trauma on the skeleton.
Cardiac ischemia
For these reasons, the concentration of troponin Tn I in the serum is only 10% less than during a heart attack and coronary insufficiency. Kinetics shows the yield of a given protein molecule as a two-phase line curve, on which the concentration in the serum increases within 2 hours.
The maximum concentration accumulates 16–20 hours after the first symptoms of the pathology (this is the first maximum phase). After this, the concentration decreases and after 60 hours, a repeated surge in the accumulation of troponin in the blood appears (the second phase of accumulation).
For other reasons, Tn I increases only once. Troponin returns to normal levels after 7 calendar days; in rare cases, there is a delay in the body for up to 14 calendar days.
Dynamics of the main cardiac markers during myocardial infarction
Troponin type T
Troponin type T is a cardiac marker that has less specificity for myocardial infarction. The marker reacts not only to pathologies of the cardiac organ, but also to non-cardiac causes. Therefore, the etiology of this marker is much broader than that of Tn I. In addition to acute coronary insufficiency syndrome, as well as heart attack.
This troponin increases when:
- Angina pectoris
- Small focal infarction,
- After coronary artery bypass surgery,
- Angioplasty of coronary arteries,
- Heart transplant (noted until 3 calendar months),
- Myocarditis.
With these pathologies, there is an increase in the composition of the blood, or in the blood plasma, of troponin, but the level of molecules of this protein will not be as high as with a heart attack.
Differences in the dynamics of troponin levels in acute MI and unstable angina
Write to us
About the test
The CardioBSFA rapid test is a test system for the rapid bedside determination of elevated levels of the early cardiac marker cardiac fatty acid binding protein (cFABP) in venous whole blood.
The use of the CardioBSJK rapid test helps in the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction, especially in the first 12 hours from the onset of clinical manifestations
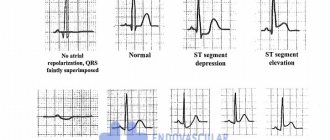
- with an atypical clinical picture;
- in the absence of clear electrocardiographic criteria (absence of ST segment elevation, against the background of bundle branch blocks and cicatricial changes in the myocardium).
Areas of application:
- Examination of the patient at home
- Reception of a patient at the clinic
- In the ambulance
- Hospital emergency room
- Laboratory
- Any medical department (BRIT, department of cardiology, therapy, surgery, etc.)
- First aid stations, first aid stations
Setting up the test and evaluating the results
Before starting to use the test, please read the instructions for use carefully.
- 100-150 μl of heparinized whole venous blood is added to the oval window of the tablet.
- The test result is assessed visually in a rectangular window of the tablet after 20-25 minutes as positive (two stripes) or negative (one strip):
Analytical characteristics of the “CardioBSJK” express test
*The sensitivity of the CardioBSJK tests is tested using recombinant cardiospecific BSZHK (human) produced by NPO BioTest LLC.
| Time from the onset of clinical manifestations | 1-3 hours | 3-6 hours | 6-12 hours | 12-18 hours |
| Sensitivity | 86% | 92,4% | 94,5% | 100% |
| Specificity | 87,5% (93,1%*) | |||
| Accuracy of the method | 91,7% (93,3%*) | |||
| Positive predictive value | 94,6% (97,2%*) | |||
| Negative predictive value | 87,4% | |||
Based on the results of a clinical study of 108 patients consecutively admitted to the hospital with suspected acute myocardial infarction. The diagnosis of myocardial infarction was confirmed or removed based on a summary analysis of troponin I indicators, CK-MB series, ECG dynamics, and echocardiography. The results obtained were correlated with the results of the CardioBSJK test. *Analytical characteristics when excluding patients with previously diagnosed stage III-IV chronic renal failure from the sample.
Functional and technical characteristics of the “CardioBSJK” express test
| Operating principle | Immunochromatography |
| Blood sample volume | 120-150 µl |
| Analysis result | Quality, yes-no |
| Evaluation of results | Visual, within 5-25 minutes |
| Hardware | Not required |
| Sensitivity | 15 ng/ml |
| Portability | Compact dimensions 94x20 mm |
| Storage conditions | 4 - 20(degrees) |
| Shelf life | 18 months |
| Package | ETC1-10 individual sealed packages with desiccant in a cardboard box. ETC2 - 10 individual sealed packages with a desiccant in a cardboard box, 10 individual Pasteur pipettes, 10 stickers for the medical history. |
Cardiac marker sBSFA
Cardiac fatty acid binding protein (cFABP) is a cardiac-specific cytoplasmic low molecular weight protein (15 kDa) that binds and transports fatty acids within the cell. A small amount of sBSFA constantly circulates in the blood of healthy people. The upper limit of normal is 6 ng/ml, with background levels fluctuating depending on age, gender and circadian rhythm. sBSFA is excreted from the body by the kidneys, therefore, in patients with renal failure (creatinine > 200 µM), there is a steady increase in the background level of sBSFA in the blood, against the background of a decrease in glomerular filtration.
sFAFA is an early cardiac biomarker. With the development of myocardial necrosis and destruction of the cell membrane, cytoplasmic sFAFA immediately enters the intercellular space. Due to its low molecular weight, it quickly diffuses through endothelial clefts into the vascular bed and enters the bloodstream. The dynamics of the release of sBSFA is single-phase and similar to the dynamics of myoglobin. A diagnostically significant increase in the level of sFAFA is observed 1-2 hours after the onset of pain. The level of sFAFA in the blood reaches its maximum values 6 hours after myocardial necrosis and returns to normal values after 12-18 hours for Q-negative and 24-72 hours for Q-positive acute myocardial infarction (AMI) (Graph No. 1.). The amount of sBSFA in the blood increases in proportion to the extent and depth of the infarction zone, and reaches a level of more than 200-300 ng/ml with a diagnostic level of myocardial necrosis of 15 ng/ml using the immunochromatographic method.
Schedule No. 1. Dynamics of cardiac biomarkers in myocardial necrosis
In the first hours of myocardial infarction, the early cardiac biomarker sFAFA is superior to troponins and MB-CK in sensitivity, and myoglobin in specificity. The “diagnostic window” with a late increase in the bloodstream (5-8 hours) and a late time of maximum increase (11-30 hours) makes the standard cardiac biomarkers CF-CK and troponins uninformative for the early diagnosis of AMI (Table No. 1).
Table No. 1. Dynamics of the level of cardiac biomarkers during myocardial infarction
| Cardiac biomarkers | Detection time from the onset of clinical manifestations, hour. | Time of maximum increase, hour. | Time to return to baseline |
| sBSJK | 1 | 6 | 24-72h |
| Myoglobin | 2 | 6 | 24-39 h |
| MV-KFK | 5 | 14 | 72-120 h |
| Troponin T | 7 | 19 | 7-14 days |
| Troponin I | 6 | 18 | 5-10 days |
Clinical studies conducted earlier by Ishii 1997, Glatz 1997, Okamoto 2000, Ghani 2000, Nakata 2003, O'Donoghue 2006 confirmed the higher diagnostic value of sBSFA in comparison with myoglobin in patients admitted to the hospital with chest pain syndrome and suspected AMI . In all studies, the area under the characteristic ROC curve of specificity and sensitivity for sFAFA is significantly greater than that for myoglobin, which is a result of the high cardiac specificity of sFAFA.
The high cardiac specificity of sBSFA is explained by its maximum concentration in cardiomyocytes (0.5-0.6 mg/g), which significantly exceeds its concentration in other tissues. In addition to myocardial tissue, sBSFA is found in skeletal muscles, the small intestine, some parts of the brain and, according to some data, in the proximal and distal tubules of the kidneys, adipose and other tissues (Table No. 2).
Table No. 2. The content of sFAFA in various tissues (Glatz JFC, Van der Vusse GJ. Cellular fatty acid-binding proteins. Their function and physiological significance. Prog Lipid Res 1996;35:243-82)
| Fabric type | sBSFA content, µg/g |
| Myocardium | 540-600 |
| Striated muscles | 20-170 |
| Brain | 16-39 |
| Small intestine | 2-5 |
An increase in the level of sFAFA , like any other cardiac marker, is a reflection of myocardial necrosis of both coronarogenic and non-coronarogenic origin. The main cause of elevated sFASH levels is acute myocardial infarction. In addition, the increase may be a consequence of the destruction of cardiomyocytes during inflammation, trauma, surgical interventions, intoxication, etc. The level of sFAFA increases with atrial fibrillation, after EIT, with stage III-IV chronic renal failure, acute strokes, and extensive muscle injuries.
Therefore, an assessment of the level of sFAFA should be carried out by a doctor, taking into account all anamnestic and clinical data. Determining the level of sFAFA in a patient with chest pain syndrome in combination with a competent analysis of the clinical case provides significant assistance in the early diagnosis of AMI, especially in the first 12 hours of the disease.
As a result of numerous studies of the diagnostic aspects of the use of this protein, in 2007 the Society of Clinical Laboratory Biochemical Medical Practice of the United States included sBCFA in the list of recommended biomarkers of myocardial necrosis, which is a prerequisite for the use in clinical practice of available diagnostic tests that determine this cardiac biomarker.
Recommendations for use
Before starting to use the test, please read the instructions for use carefully.
- Collect heparinized blood according to the standard method
- Open the individual packaging and place the test on a dry, flat surface.
- Add 120-150 µl of blood into the oval window (Fig. 1)
- Interpret the result after 5-25 minutes. (Fig.2)
| Fig.1 Adding a blood sample for testing | Fig.2 Interpretation of test results |
Interpretation of test results (Fig. 2)
Positive: If the test result is positive, two purple lines appear in the result reading window - test and control. The control line certifies that the plates are working correctly. The color intensity of the control and test lines may be different. The concentration of sFAFA in the blood is higher than the diagnostic level of myocardial necrosis.
Negative: Only one purple line appears - the control line. The concentration of sFAFA in the blood is below the diagnostic level of myocardial necrosis.
Indeterminate: If the control line does not appear, the test results are invalid. In this case, it is recommended to repeat the test using a new test tablet.
Attention! The presence of a test line of any intensity indicates a positive result.
Test evaluation examples
Possible errors when performing the test and ways to eliminate them
1. There are no bars in the rectangular results viewport
| Cause | Elimination methods |
| Insufficient volume of blood sample applied | Take a new test and add a blood sample of 120-150 µl |
| Violation of test storage conditions | Take a new test that has been stored in accordance with the storage conditions, open the individual test package immediately before adding the blood sample |
| Blood viscosity too high | Perform analysis using another method |
2. The appearance of a red background in the window for viewing results
| Cause | Elimination methods |
| Excessive volume of blood sample applied | Take a new test and add a blood sample of 120-150 µl |
| Entering a blood sample into the window to view the results | Take a new test and add a blood sample to the foramen ovale for sample depositing |
| Hemolytic blood | Take a new blood sample or test using another method |
Comparative kinetics
If we compare all three troponins in the same proportions and under the same conditions, then we can see that troponin T has its own clear and characteristic differences.
Comparative kinetics of Tn T with Tn I and with Tn C:
- After the development of pain, TnT accumulates in the blood within three hours. This indicator is determined by the state of the blood flow system in the ischemic area,
- Over the next 72,100 hours, the TnT level rises and increases its concentration from the initial one, by at least 40-50 times, and sometimes even higher. The maximum concentration occurs after 100 hours, then this index stops and continues for 7 calendar days,
- After 7 calendar days it begins to decline. The decrease occurs slowly and this marker is detected in the blood for up to 20 calendar days.
Tn T indicator during thrombolytic therapy
During emergency and intensive thrombolytic therapy, troponin T in the blood changes 2 times within 100 hours:
- The first phase of peak concentration occurs 14 hours after the first symptoms of damage to the myocardial heart muscle,
- The second phase of high concentration occurs after 100 hours of therapy and this troponin value is lower than during the first surge.
Also, with favorable dynamics of healing of acute myocardial infarction, a decrease in troponin levels occurs on the 5th day and after a week from the moment of the heart attack is completely reduced.
Advantages of biochemical analysis for the detection of troponin
The basis for conducting a biochemical analysis for troponins (troponin test) is the suspicion of the beginning of the formation of foci of necrosis in the heart muscle in acute coronary syndrome.
The troponin regulatory complex is the first marker for determining large-focal and small-focal infarction in the heart muscle, because the molecules of the complex are one of the first to begin to disintegrate during necrosis and enter the bloodstream.
A troponin test can be performed in the following situations:
- An acute attack of myocardial infarction, with a non-specific increase in markers,
- Subacute form of heart attack. Troponin testing is ideal as a late marker, since by the time of the study the CK markers and the CF-CK marker have already reached standard values,
- During thrombolysis and to evaluate its results,
- To determine the extent of ischemic damage to the heart muscle,
- To determine an asymptomatic attack of a heart attack before surgical intervention in the heart muscle,
- For acute coronary syndrome, which may be caused by a heart attack,
- To control treatment with drugs of the heparin group.
Acute coronary syndrome
Methods for testing cardiac troponins are being improved, more highly sensitive antibodies are being developed, which makes it possible to quickly determine the level of myocardial damage.
It is possible to determine an accurate diagnosis already 2 hours after the first signs of a heart attack using the troponin test. And for coronary syndrome and heart attack, time is the main indicator in saving human life.
Specificity of cardiac markers in myocardial infarction
In patients with an attack of coronary syndrome and myocardial infarction, the first test, a troponin test, may give a negative presence of troponin protein molecules in the blood. This happens with repeated large-focal, as well as small-focal infarction. Therefore, it is necessary to know the dynamics of growth and apply timely repeated testing.
| Troponin T has its own specific dynamics | the cardiac marker has the properties of increasing the index after 3 hours and up to 8 hours, |
| reaches a maximum concentration from 12 hours to 100 hours, | |
| the normal value occurs after 14 calendar days. | |
| Troponin type I has its own specificity in growth dynamics | the cardiac marker has the properties of increasing the index after 4 hours and up to 6 hours, |
| reaches its maximum concentration in the first day - from 12 hours to 24 hours, | |
| the norm occurs in 10 - 21 calendar days. |
Troponin test in action
Troponins during myocardial infarction make themselves felt almost immediately after the incident. Their influence is reflected in the breakdown of the protein complex into molecules and subsequent penetration into the blood. This phenomenon has been used in medicine for more than a decade and has successfully proven itself in modern diagnostic methods.
If, when a patient visits the cardiology department, he has symptoms of myocardial infarction, but the ECG readings do not give confidence in the latter, a quantitative troponin test is prescribed. This procedure involves accurately determining the amount of troponins in the patient's blood. The measurement is in nanograms per liter. The value of a quantitative test in monitoring the dynamics of changes in cardiac protein content. Thus, the method makes it possible to identify relapses of pathology and provide the patient with more intensive therapy. The disadvantage of a quantitative test is its complexity and the requirement of special equipment. In addition, its implementation takes quite a lot of time.
Standard Troponin Test Kit
Troponin rapid test does not require such high qualifications from a medical worker as other methods. Externally, the product resembles a household pregnancy test. It is represented by a strip with marked divisions. To get the result and draw a definite conclusion about the presence of heart pathology, one drop of blood placed in a special compartment is enough. The procedure takes 15 minutes. The appearance of one strip indicates the normal state of the body. Two stripes indicate that the troponin T level in the blood is exceeded and the patient needs emergency help.
If no stripes appear during the test, this means that the product has expired and the procedure must be repeated using a new test.
The value of the troponin test is in the accuracy and speed of determining myocardial infarction. Even with an atypical form of pathology, which complicates other types of diagnosis, this test will almost certainly indicate the presence of troponin in the blood.
Today, the troponin test can be found on pharmacy shelves. It is almost always included in the products found in ambulances. Relevant personnel are familiar with its use.
It should be remembered that the rapid test is not a 100% guarantee of the presence or absence of myocardial infarction. Even with a negative result, but symptoms of the disease appear, more serious laboratory tests or a repeat test, performed 3-4 hours after the first, are necessary, since the maximum concentration of troponins in the blood is observed only 6-8 hours after damage to the myocardial muscle.