According to statistics provided by WHO pediatricians, the rate of cardiovascular diseases among pediatric patients has increased significantly. Arrhythmia in children is recorded among all ages, both in newborns and adolescents, due to hormonal imbalance. Arrhythmia in childhood is manifested by disturbances in cardiac activity, which consists of a change in the normal rhythm, an increase in the frequency and strength of contractile activity of the myocardium. The pathology can be congenital or acquired, depending on which symptoms of circulatory disorders are present in the clinical picture or the disease is asymptomatic. Physiological rhythm disturbances are very often observed when the resulting changes are temporary. What reasons contribute to the formation of arrhythmia and how to recognize the symptoms of true pathology?
Characteristics of the pathology
Arrhythmia in children is a change in heart rhythm that occurs as a result of a disorder of cardiac functions: automaticity, excitability and conductivity. In most cases, pediatric cardiologists diagnose heart rhythm disorders similar to adults. Pathology can develop at any age, but newborns, children from 4 to 5 years old, 7-8 years old, and puberty are most susceptible to it. Due to age-related characteristics, during the examination period, a mandatory consultation with a cardiologist with preliminary electrocardiography is recommended.
In newborns, the pathology is diagnosed in the first days of life
In some cases, even healthy children experience periods of changes in normal heart rhythm, manifested by the following disturbances:
- Automaticity disorder (including sinus arrhythmias, tachycardia, bradycardia).
- Impaired excitability (pathological changes in the atrium and ventricle, manifested by flutter).
- Changes in conductivity (including blockades of all types).
- Combination of functional disorders (At the same time, tachycardia, bradycardia, prolongation of the QT interval may be observed).
A child may have two types of pathology. Pathological, which occurs as a result of interruptions in cardiac activity, accompanied by a violation of the general condition of the child. Physiological is manifested by minor symptoms, which do not have a negative effect on the baby’s body.
Treatment of arrhythmia in children
Arrhythmia in children requires complex treatment, in which parents must work in tandem with the doctor. First of all, it is necessary to establish an appropriate daily routine, devoting enough time to proper rest, mental exercise, physical activity, and avoiding stressful situations.
Depending on the characteristics of the manifestation and cause of the disease, drug or surgical therapy is selected. However, treatment is necessarily aimed at identifying the cause of the disease and getting rid of it. So, for example, if an increased heart rate causes chronic infectious diseases such as adenoiditis, caries and others, then you need to take care of them first.
Reasons for formation
The causes of rhythm disturbances can be various etiological factors, which experts have divided into three main groups:
- Cardiac (primary damage to the heart muscle, which leads to functional disorders in the functioning of the organ).
- Extracardiac (develops against the background of conditions that are accompanied by insufficient oxygen supply to myocardial cells).
- Combined (combine etiological factors of the first and second groups).
As a rule, in childhood, cardiac causes are not primary in the development of arrhythmias, but when pathology is detected, they must be excluded first.
The causes of pathology of cardiac origin are congenital and acquired defects of the anatomical structures of the heart
There are the following causes of cardiac rhythm disturbances:
- Congenital cardiac anomalies (tetralogy of Fallot, atrioventricular communication).
- Acquired heart defects.
- Congenital and acquired myocarditis, pericarditis due to exposure to infectious agents.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Neoplasms in the structural elements of the heart.
- Anomalies in which additional anatomical structures are formed.
- Mechanical damage during invasive procedures in the cardiac region.
- Organ injuries accompanied by hemorrhage.
- Toxic effect of drugs.
In most cases, rhythm disorder is preceded by damage to the nervous and autonomic systems as a result of pathological processes during pregnancy and childbirth, which leads to disruption of the coordinated activity of the myocardium.
Extracardiac etiological factors include:
- intrauterine hypotrophy;
- prematurity;
- pathologies of the central nervous system and VSD;
- endocrine diseases.
During puberty, arrhythmia develops as a result of mental stress when the nervous system is stressed. Adolescents who engage in intensive sports during a period of intense growth of the heart muscle are also susceptible to rhythm disorders.
Pathogenesis
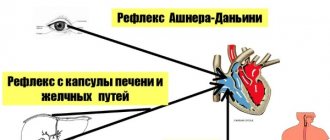
Due to the high activity of the autonomic nervous system during inspiration, the atria become filled with blood, the so-called Bainbridge reflex occurs. It consists of an increase in heart rate in response to an increase in central venous pressure (the sympathetic part of the nervous system is activated).
As you exhale, the tone of the vagus nerves increases, which leads to a decrease in the number of heart beats (parasympathetic fibers of the vagus are turned on). Some authors explain the development of sinus arrhythmia as a compensatory mechanism for improving gas exchange, which reduces the load on the myocardium.
Development mechanism
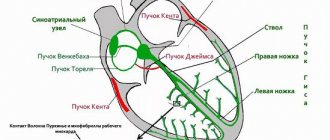
The development of pathology in childhood is facilitated by the peculiarities of the structure and functioning of the heart muscle. Thus, the development of rhythm disturbances is caused by pathological changes in the formation of impulses, the conduction of excitation, as well as their combination.
An important role in the formation of dysrhythmia is played by an imbalance in the ratio of the number of potassium, magnesium and sodium ions inside the myocardium
There are several mechanisms for the development of pathology:
- Due to inhibition of the activity of the sinus node, the pacemaker migrates.
- Disturbances in the spread of excitation as a result of the formed block.
- A disorder of impulse conduction associated with its movement in a circle.
Prognosis of atrial fibrillation
In the Garson study, mortality was 17% in the first 3 years from the manifestation of arrhythmia [5]. The likelihood of an unfavorable outcome increases in children with organic cardiac pathology, with the development of cardiomyopathy, an increase in the size of the atria according to echocardiography, and resistance to drug therapy. Sudden death may be associated with the proarrhythmic effect of drugs. At the same time, the effective use of antiarrhythmics reduces the risk of sudden death by 4 times and the risk of developing heart failure by 2.5 times [5].
Classification of pathology types
Pediatricians use a classification of rhythm disorders, which involves division into the main functional disorders of the heart muscle. According to this provision, the following types of arrhythmias are distinguished:
- violation of impulse formation;
- violation of the wired system;
- combined type.
When the automatic function is impaired, sinus arrhythmia, bradycardia and tachycardia develop. This list also includes fading rhythms and pacemaker migration.
Sinus bradycardia and tachycardia
Sinus bradycardia is characterized by a decrease in the frequency of myocardial contractility with a disorder of impulse conduction. With tachycardia, the heart rate increases with a decrease in the efficiency coefficient of the heart, since the ventricles receive insufficient blood. Tachycardia leads to impaired blood circulation in the myocardium, as the organ suffers from hypoxia. In these conditions, deviations in rhythm changes do not exceed 30 beats/min, taking into account the age of the child.
Heart rate norms in children depending on age
Sinus arrhythmia
As a rule, the condition occurs in adolescence against the background of hormonal changes in the body. In children, the normal number of myocardial contractions is maintained, but the intervals between shock waves increase, that is, the rhythm is disturbed.
Rhythm Source Migration
Displacement of the pacemaker leads to a change in the frequency and sequence of myocardial contractions. In this case, the source producing impulses can migrate through the atria. In children, the formation of pathology occurs as a result of abnormal development and hypoxia.
Rhythm disturbances lead to neurological and autonomic disorders, which manifests itself in delayed physical development. The occurrence of this arrhythmia during puberty contributes to excessive excitability of the nervous system, when concentration and sleep processes are disrupted. The disorder of cardiac muscle excitability includes the following types of arrhythmia: extrasystole, non-paroxysmal and paroxysmal tachycardia.
Extrasystole
The condition is characterized by untimely contraction of the myocardium (extrasystole), which can occur in the ventricles and atria. The pathology occurs without pronounced manifestations indicating its presence. Extrasystole is diagnosed in a child during a routine examination, when the cardiologist prescribes an ECG.
Paroxysmal tachycardia
A heart rhythm disorder is characterized by sudden attacks of tachycardia. Rapid heartbeat is accompanied by specific manifestations on the electrocardiogram. Most often, the condition occurs as a result of panic attacks in both infants and older children.
During an attack, changes in hemodynamics occur, resistance in peripheral vessels increases, blood supply to the brain decreases, which is revealed by a deterioration in the general condition of the child.
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a fairly rare pathology in childhood. Pathology can develop against the background of serious cardiac anomalies. The severity of manifestations depends on the age of the child and the state of the conduction system.
Manifestations
In most cases, the symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia in children are not specific and are detected after an illness or during an examination. Parents may not notice changes in the child’s heartbeat, as they attribute the disturbed condition to other reasons. However, there are some types of rhythm disorders that have striking clinical manifestations that require immediate therapeutic measures to eliminate them. The severity of symptoms depends on the age of the patient and the cause of their development.
Newborns may experience discoloration of the nasolabial triangle and refusal to breastfeed.
The first signs indicating the presence of pathology in infants:
- paroxysmal shortness of breath;
- pale skin;
- restless behavior;
- refusal to eat;
- insufficient weight gain;
- sleep disorder;
- strong pulsation of blood vessels in the neck.
At the first signs of a rhythm disorder in a child, parents should seek advice from a pediatric cardiologist.
In older children, the following symptoms are observed:
- excessive fatigue;
- deterioration of well-being after physical activity;
- discomfort in the heart area;
- decreased blood pressure;
- frequent dizziness;
- fainting states.
After physical or mental stress, the child may experience unpleasant sensations in the chest, which manifest themselves in the form of tremors, freezing or stabbing pain.
When should you see a doctor?
Any diseases in the heart area are dealt with by a pediatric cardiologist. He should be visited as soon as parents notice something in their baby’s condition that worries them, for example, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, frequent fainting and other symptoms. You should not hesitate to consult if the child complains of burning, pain or pressure in the sternum.
It is important to seek help right at the very beginning, because any illness is easier and faster to cure in the initial stages of its development.
Much depends on the doctor’s level of qualification: he must specialize in children, have extensive work experience and have progressive views on treatment methods, that is, be aware of all the discoveries in the world of cardiology and pediatrics.
These are the specialists who work in the pediatric department of JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic), located in the center of Moscow at 2nd Tverskoy Lane, 10, a five-minute walk from the Mayakovskaya metro station. In the immediate vicinity there are also metro stations “Tverskaya”, “Novoslobodskaya”, “Chekhovskaya”.
You can register your child for a consultation with a specialist by calling +7 or using the feedback form. Here you can find out information of interest about the cost of admission and the level of qualifications of all specialists.
Features of pathology during puberty
Very often, adolescent children are susceptible to rhythm disturbances, which is associated with hormonal changes characteristic of this period. Imbalance of hormones affects the functioning of the cardiac and vascular systems, which is manifested by dysfunction of the autonomic system.
According to studies, during examination, 85% of adolescents are diagnosed with respiratory sinus arrhythmia
During puberty, sinus arrhythmia predominantly develops, when the heart rate does not correspond to normal physiological indicators due to the breathing process. The condition develops after physical exertion, stress, mental stress, and while taking medications. This type of respiratory ventricular tachyarrhythmia does not require special therapy, since the condition stabilizes after the normalization of hormonal processes in the body.
True sinus arrhythmia in a teenager is not associated with breathing; it develops as a result of a disturbance in the conduction of cardiac impulses by the pacemaker. A disorder of this function may indicate the presence of cardiac diseases of infectious origin in the child or provoke previously undetected anomalies.
How to treat sinus arrhythmia
If the pathology is severe, then there is a need for drug therapy. Therapeutic methods and cardiac pacing are used. The choice of medications is made by a cardiologist, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
If the pathology is provoked by a stressful situation or emotional instability, then a neurologist can prescribe treatment. For such sinus arrhythmia, sedatives and nootropics are used. In some cases, tranquilizers and antipsychotics are necessary. These drugs are prescribed by a psychiatrist.
If the heart rate is below 50 per minute and pronounced disturbances in central hemodynamics are recorded, then installation of a pacemaker is indicated. This miniature device is inserted under the skin in the collarbone area.
When treating sinus arrhythmia, it is important to avoid physical overload and stress, and adhere to a diet limiting sweets, flour and fatty foods.
If this pathology is detected in a pregnant woman, then the following measures are taken: the patient is registered with a perinatologist and visits him according to a certain schedule, undergoes examinations, takes multivitamins, and adheres to the rules of a balanced diet.
Treatment of sinus arrhythmia in children necessarily implies a rational organization of work and rest. If the pathology is severe, then it is necessary to be treated in pediatric cardiology. The amount of simple carbohydrates in the child’s diet is limited, the emphasis is on vegetables and fruits, which will provide a large amount of fiber. Also an important condition for recovery is the use of psychotherapeutic methods of influence: it is necessary to restore the child’s normal emotional state and protect him from stress. Having diagnosed sinus arrhythmia, the doctor will tell you in detail what it is and explain how to behave to avoid complications.
Research methods
Detection of cardiac rhythm disturbances is not difficult in terms of diagnosis, since already during auscultation the pediatrician can recognize pathological noises and refer the child to undergo additional research methods to clarify the diagnosis.
When collecting anamnesis, the cardiologist takes into account the baby’s genetic predisposition to diseases of the cardiovascular system.
During an objective examination, a specialist can diagnose a rapid heartbeat, irregular myocardial contraction, and a rare pulse compared to the age norm.
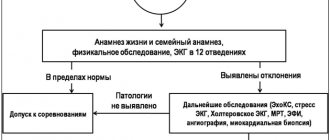
Research plan for detecting cardiac rhythm disorders:
- Electrocardiography. Allows you to identify pathological changes in the pacemaker and disorders of autonomic cardiac regulation. It is carried out in several positions (horizontal, vertical) and after physical exercise.
- Holter monitoring. Detects cardiac fluctuations during the day, carried out by installing a special sensor. The technique is available for both older children and newborns.
- Stress tests. These include bicycle ergometry and drug loading. Allows you to determine the resistance of the heart to various loads, as well as identify hidden conduction and rhythm disorders.
- Drug tests. In pediatrics, atropine and potassium-obsidan tests are widely used, which assess the functional state of the autonomic and conductive systems.
- X-ray of the cervical spine. Assessment of peripheral and cerebral circulation.
- EchoKg. The study is used when there is a suspicion of possible congenital and acquired anomalies in the development of the heart, which provoke dysrhythmia.
The procedure for recording cardiac impulses using an ECG
One of the specific examination methods is a virological study, since experts have proven the ability of viral agents to provoke myocardial damage. A particularly aggressive herpes virus that can remain in the body throughout life.
Diagnosis of the disease in children
For children of different ages, there are established norms for the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle. So, for example, at birth it is about 140 beats made in 1 minute, but per year it already decreases to 120, etc.
It is possible to determine to what extent the situation in a particular child deviates from normal indicators using special diagnostic methods.
First of all, a test ECG is prescribed in three options: in a sitting position, lying down, and then after a slight load. This makes it possible to monitor whether there are rhythm disturbances in a young patient. Additionally, daily ECG monitoring may be prescribed, carried out over 24 hours. The procedure does not complicate the child’s life, does not interfere with his motor activity and can be performed at absolutely any age.
The cardiologist may also recommend stress tests that demonstrate hidden malfunctions in the cardiovascular system, and pharmacological tests.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of functional arrhythmia does not require special methods; parents need to organize proper care for their children and create conditions to prevent the progression of the pathology. To eliminate the clinical form of the disease, conservative therapy and modern surgical techniques are used.
The primary goal of treatment is to eliminate foci of chronic infection that cause worsening cardiac diseases
Drug treatment includes the use of the following groups of drugs:
- Antiarrhythmic drugs (Flecainide, Quinidine, Bepridil).
- Improving myocardial function (Cavinton).
- Neuroleptic drugs (Chloral hydrate, Haloperidol).
- Nootropic drugs (Trental).
- Antioxidants (Vitamin A, E, C, Xidifon).
Dysrhythmias that are resistant to conservative treatment require the use of minimally invasive surgical techniques:
- radiofrequency ablation;
- cryoablation of arrhythmogenic pathological areas;
- implantation of a pacemaker.
Arrhythmia, accompanied by fluttering or flickering of the heart structures, requires immediate hospitalization and intensive care.
Recommendations for parents
During treatment of any type of rhythm disturbance, the cardiologist recommends that parents adhere to special recommendations aimed at stabilizing and preventing the progression of the pathology:
- Compliance with the basics of rational nutrition for diseases of the cardiac and vascular systems (refusal of salty, spicy, fried foods).
- Regular physical activity (to strengthen the heart muscle, long walks in the fresh air and morning exercises are necessary).
- Mode of activity and rest (to ensure normal processes of falling asleep and sleeping, it is important to adhere to a daily routine that will help develop the correct biorhythms).
- Mental and emotional stabilization (it is contraindicated to reboot the child’s psyche; after attending educational institutions, rest in the fresh air is necessary).
For the full development of the cardiovascular system, children are recommended to attend dancing and swimming. It is important for parents to promptly treat acute infectious viral diseases (sore throat, influenza, tonsillitis), since they place a strong strain on the heart. When making a diagnosis, you should undergo preventive examinations from specialized specialists in a timely manner.
In childhood, cardiac arrhythmias require strict monitoring, since clinically significant forms pose a risk of complications. The course of the disease depends on the cause and severity of clinical manifestations.