CRP – indications for examination
CRP is assigned:
- if the patient is at risk of a bacterial infection;
- For patients recovering from surgery, if CRP values remain elevated three days after surgery, a bacterial infection may be suspected;
- newborns with signs of infection;
- patients with signs of sepsis: fever, chills, rapid breathing and palpitations;
- when a health condition needs to be assessed, such as lupus or arthritis;
- to check the effectiveness of inflammation therapy - during it, the level of CRP should decrease;
- to study body damage and consequences after operations, organ transplants and burns, for early detection of possible infection.
The CRP test can help with:
- assessing the severity of the inflammatory process;
- early detection of postoperative complications;
- detection of transplant rejection;
- monitoring the success of antibiotic treatment for bacterial infections;
- monitoring patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases.
Thus, the most common use of the CRP test is to determine its level when inflammation caused by a bacterial infection is suspected.
This is especially useful for distinguishing viral from bacterial infections. Since in viral infections - inflammations accompanied by increased sedimentation and an increase in the number of leukocytes, the level of CRP remains in a lower range than in the case of a bacterial infection. And in this case his growth is much higher.
An increase in CRP is present in the following cases:
- with inflammation;
- after operation;
- in the presence of malignant diseases;
- for allergic reactions;
- for chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
Treatment
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women
If signs of rheumatoid arthritis appear in a woman, treatment should be prescribed immediately after diagnosis, taking into account the data of the examination. Prescribed:
- a diet with sufficient animal protein and calcium - dairy products, lean meat and fish, vegetables, fruits, cereals; spicy foods and sweets are excluded;
- correct daily routine with alternating sleep and wakefulness, eliminating stress;
- drug therapy and traditional methods of treating rheumatoid arthritis in women;
- physiotherapeutic procedures, physical therapy (physical therapy), massage;
- methods of gravitational blood surgery - hemosorption, plasmapheresis;
- orthopedic correction methods;
- surgical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women.
High CRP and disease diagnosis
During an acute inflammatory reaction, the concentration of CRP increases many times over. It begins to grow 6 to 9 hours after the onset of inflammation and reaches a maximum after 48 hours. Protein returns to baseline levels within 7 to 10 days after stopping treatment.
| SPB level | Meaning | What does it indicate? |
| <5 mg/l | Normal | No inflammation |
| 0-40 mg/l | Slightly elevated | Mild inflammation |
| 40-200 mg/l | Increased | Acute inflammation |
| 200 and above mg/l | High | Severe bacterial infection |
Testing the concentration of C-reactive protein often reveals problems in the proper functioning of the body at an early stage before symptoms appear.
| Type of infection | SPB level |
| Gram-negative bacteria – Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Helicobacter pylori and others | 500 mg/l or more |
| Gram-positive bacteria – staphylococci, streptococci, tuberculosis or parasites | up to 100 mg/l |
| Viruses | up to 50 mg/l |
Results above 50 mg/L are a sign of serious infection, injury, or chronic disease, which will require additional testing to determine the cause.
In such situations, rapid identification of the bacterial pathogen is especially important to determine targeted antibiotic therapy.
Stages
Any form of arthritis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
There are 4 clinical stages of the development of rheumatoid arthritis in women:
- Initial
– lasts for 6 months, the first signs are somewhat erased, but remain constant; sometimes there is an acute onset; - Early
– the development of pathology in the first year of the disease, the symptoms appear clearly. - Expanded
– the first two years of the disease, the signs are bright, the course is progressive, possible impairment of joint mobility. - Neglected
– more than two years, symptoms of joint deformation and persistent impairment of limb function appear, which becomes a cause of disability.
From stage to stage, there is a clear tendency for arthritis to progress in the absence of treatment. Therefore, it is very important to promptly identify the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in women and immediately begin treatment.
What can a CRP test show?
C-reactive protein manifests itself as a protective reaction of the body. Its function is to participate in the immune response, which consists in inactivating the inflammatory factor and stimulating the function of immune cells.
Quantitative CRP testing has less diagnostic value in the case of chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatic diseases, since the CRP value can vary from 10 to 1000 mg/L. However, diagnostically important is the fact that the level of CRP is associated with the degree and activity of the inflammatory process. Monitoring changes in the concentration of C-reactive protein - decrease or increase - informs about the stage of inflammation, its extinction or failure of therapy.
Before taking a CRP test, it is recommended that you consult with your doctor in advance to discuss any medical conditions that may affect the results.
It is important that your consultation with your doctor takes into account lifestyle risk factors, other medical conditions and family history. If there is a risk of cardiovascular disease, an echocardiogram, computed tomography of the coronary arteries, a stress test, cardiac catheterization or an electrocardiogram may be prescribed.
How to achieve lasting remission
In order to forget about exacerbations of rheumatoid arthritis, you need to:
- Healthy food;
- move more, do exercise therapy, swim, walk;
- get rid of stress, overload at work and at home, heavy physical work;
- no smoking;
- promptly identify and treat hormonal disorders;
- regularly carry out courses of maintenance treatment prescribed by your doctor.
Rheumatoid arthritis in women is treated at any stage. The specialists of the Moscow Paramita clinic know this well.
Literature:
- Nasonov EL, Karateev DE, Balabanova RM. Rheumatoid arthritis. In the book: Rheumatology. National leadership. Ed. E. L. Nasonova, V. A. Nasonova. Moscow: GEOTAR-Media; 2008. pp. 290–331.
- Folomeeva O. M., Galushko E. A., Erdes Sh. F. Prevalence of rheumatic diseases in adult populations of Russia and the USA. Scientific and practical rheumatology. 2008;46(4):4-13. DOI:10.14412/1995-4484-2008-529.
- Leandro G, Mangia A, Hui J, et al. Relationship between steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Gastroenterology 2006;130(6):1636-42.
- Rubbia-Brandt L, Quadri R, Abid K, et al. Hepatocyte steatosis is a cytopathic effect of hepatitis C virus genotype 3. J Hepatol 2000;33(1):106-15.
- Hezode C, Roudot-Thoraval F, et al. Different mechanisms of steatosis in hepatitis C virus genotypes 1 and 3 infections. J Viral Hepat 2004;11(5):455-8.
Themes
Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 04/14/2020 Date of update: 03/12/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 4.5 / 5 (4)
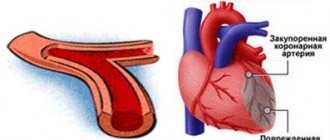
CRP and cardiovascular disease
Recently, CRP protein levels have also been taken into account in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. It is used to assess the risk of myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke and sudden cardiac arrest. It turns out that there is a relationship between the risk of coronary heart disease and the level of CRP in the patient’s blood.
Low levels of CRP accompany mild inflammation, which medicine associates with atherosclerosis because the inflammatory process plays a key role in the detachment of atherosclerotic plaques, the formation of local blood clots and blockage of blood vessels. CRP levels are also associated with hypertension, low good cholesterol, and metabolic disorders leading to abdominal obesity.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, a non-profit multidisciplinary academic medical center (Ohio, USA), the CRP test can be used to identify the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases:
| CRP value | Risk of developing cardiovascular diseases |
| below 1 mg/l | Short |
| from 1 to 2.9 mg/l | Moderate |
| exceeds 3 mg/l | High |
However, the CRP test does not provide a complete picture of the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Other causes of elevated CRP
If the reading is above 10 mg/L, this may be a signal for further research to answer the question of what is causing the inflammation.
Such a high CRP value may indicate:
- osteomyelitis or bone infection;
- tuberculosis;
- inflammatory bowel diseases;
- lupus;
- connective tissue disease;
- some kind of autoimmune disease;
- exacerbation of autoimmune arthritis;
- pneumonia;
- type 2 diabetes;
- cancer – with a special indication for lymphoma.
Increased levels of CRP may occur in women:
- taking birth control pills;
- in pregnant women - this condition may indicate complications, so additional tests should be carried out to be sure.
CRP and cancer
The highest concentrations of CRP are observed in patients with malignant neoplasms, especially neoplasms of the hematopoietic system. Sometimes these are three-digit numbers or more. If the CRP blood test results show a high level of C-reactive protein, doctors immediately begin looking for a neoplastic process that, in addition to the elevated CRP level, has not yet caused any symptoms other than an altered ESR level.
However, keep in mind that the CRP test is not useful in diagnosing cancer. Too many other factors influence its level. A low level of CRP does not exclude the presence of a neoplasm, and its elevated level should direct the diagnosis primarily to infectious and inflammatory diseases. Moreover, the CRP protein is a very plastic molecule: the rate can increase up to a thousand times in 24 or 48 hours - this happens during acute bacterial or viral infections and after serious injuries.
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women in our clinic
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women in the clinic
At the Moscow clinic “Paramita” they approach the treatment of female forms of rheumatoid arthritis with special care. To do this, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out, identifying hormonal disorders and concomitant diseases that contribute to the development and maintenance of the autoimmune inflammatory process. Correction of these disorders is necessarily part of the complex therapy of a woman suffering from rheumatoid arthritis.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
The doctors of our clinic have at their disposal a wide range of the latest European and traditional oriental healing methods. In our practice we use:
- drug therapy, combining the administration of the most effective modern drugs, medicinal herbs and homeopathic remedies; this allows you to quickly relieve pain and significantly reduce the drug load on the patient’s body;
- physiotherapeutic procedures - their skillful combination with drug therapy according to modern regimens leads to a rapid improvement in a woman’s condition;
- kinesitherapy, taping, exercise therapy and massage courses are selected strictly individually, preventing the development of ankylosis and joint deformities;
- PRP therapy is a unique modern method of stimulating the regenerative abilities of tissues by introducing the patient’s own platelets, processed using a special technique;
- reflexology (RT) - influence on acupuncture points (AP) on the human body, reflexively connected with various organs and systems; our specialists have been trained in RT in China and Tibet, they are proficient in all methods of RT - acupuncture, cauterization with wormwood cigarettes, acupressure, etc.; in skillful hands, the effectiveness of RT can be equal to the effectiveness of drug therapy;
- pharmacopuncture – introduction of modern medicines into AT; one of the most effective ways to treat RA.
This approach to the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women allows patients to constantly be in a state of remission. They regularly undergo courses of maintenance therapy in our clinic, lead an active lifestyle, forgetting about painful exacerbations and the prospect of disability.
Elevated CRP – is this always a pathology?
In adults, an elevated CRP value exceeds 5 mg/l, with the exception of smokers, people with obesity or hypertension, for whom the norm is less than 10 mg/l.
In older children, elevated CRP values are considered to be greater than 10 mg/L. As with adults, interpretation of the result should be left to the pediatrician. He will evaluate the result in the context of the child's condition and medical history.
Slightly elevated CRP values up to 40 mg/l may be observed in older people and during pregnancy.
Therefore, when interpreting the results and drawing up a medical report, it is necessary to take into account other laboratory parameters, such as a complete blood count (CBC) with a leukocyte formula.
Effect of drugs on CRP concentration
Taking acetylsalicylic acid or aspirin, even in high doses, does not affect the quantitative level of CRP. This is somewhat surprising since aspirin is known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
Patients with high cholesterol who take statins are less likely to have a heart attack because statins not only lower lipid levels but also have anti-inflammatory properties. This is very important because high CRP and low cholesterol are more dangerous than high cholesterol and low CRP. The level of CRP is also reduced by drugs from the group of fibrates and beta-blockers, but less effectively than by statins.
Complexes with this research
Men's check-up No. 1 39 studies for an annual preventive examination 18,570 ₽ Composition
Women's check-up No. 1 38 studies for an annual preventive examination 19,290 ₽ Composition
Joints 2,620 ₽ Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause RUB 12,630
- Male anti-aging diagnostics RUB 13,300
- Inflammation of joints 860 ₽
- For those at risk of COVID-19 RUB 4,510
- Rheumatoid arthritis RUB 3,720
C-reactive protein and ESR
ESR or Birnatsky reaction is a measurement of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in a test tube with blood. It is expressed in millimeters per hour. ESR is an indirect indicator of the inflammatory response. However, the ESR test is less specific than CRP.
In addition to inflammation, an increase in ESR is also affected by:
- Obesity. Adipose tissue is a source of interleukin 6. This is one of the proteins involved in the formation of inflammation.
- Kidney failure. In end-stage renal failure and in the case of nephrotic syndrome, patients have significantly increased ESR values.
- Hemoglobin concentration. Anemia speeds up the decline of red blood cells.
- Shape of red blood cells. Determination of ESR is unreliable in diseases with abnormal red blood cells, such as sickle cell disease.
If there is a disproportion between CRP concentration and ESR, the first step is to consider the possibility of a false measurement due to the above factors or laboratory error, such as taking too long from collection to delivery to the laboratory or storing the tube in inappropriate conditions.
CRP levels respond more dynamically to increased inflammation than ESR. In the case of, for example, lupus erythematosus, the ESR value may be elevated when the level of CRP in the blood is low. This is caused by high levels of type 1 interferon, which suppresses the liver's production of CRP.
References
- Kishkun, A.A. Immunological and serological studies in clinical practice. - M.: Medical Information Agency, 2006. - 536 p.
- Sarapultsev, P.A., Sarapultsev, A.P. The role of c-reactive protein in the acute phase response in myocardial infarction. Cytokines and inflammation, 2013. - T.12. - No. 4. - P. 18-24.
- Biasucci, M., Liuzzo, G., Colizzi, C. et al. Clinical use of C-reactive protein for the prognostic stratification of patients with ischemic heart disease. Italian heart journal: official journal of the Italian Federation of Cardiology, 2001. - Vol. 2(3). — P. 164-171.
- Russell, A., Cunninghame, G., Shepherd, C. et al. Polymorphism at the C-reactive protein locus influences gene expression and predisposes to systemic lupus erythematosus. Human molecular genetics, 2004. - Vol. 13(1). — P. 137-147.
- Mevorach, D., Mascarenhas, J., Gershov, D. et al. Complement-dependent clearance of apoptotic cells by human macrophages. The Journal of experimental medicine, 1998. - Vol. 188(12).