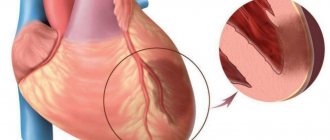
What is a heart attack
A heart attack is one of the types of coronary heart disease. The attack occurs due to insufficient or completely stopped blood supply to the myocardium. The most common cause of this effect is blood clots that form in blood vessels.
Acute pain in the heart area can be completely sudden. Depending on the degree of localization, the human body is able to return to life or coronary death occurs. As a result of the pain syndrome, the heart muscles die, which affects the further functioning of the cardiovascular system.
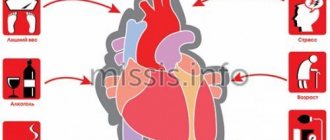
Those at risk are mainly elderly people, active and passive smokers. Concomitant diseases such as alcoholism, diabetes, obesity, and blood vessel diseases can also cause a heart attack. According to statistics, heart attacks most often affect men and people leading a sedentary lifestyle.
What should a patient do during a heart attack?
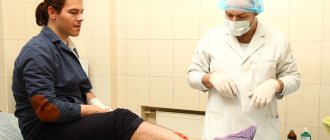
Unfortunately, during an attack there are not always people nearby who could help. Therefore, it is important to know what to do if the disease strikes a person at a time when no one is nearby. The first rule is don't panic. Panic can make the situation worse. A person must understand that first aid for a heart attack can be provided to oneself. Naturally, first of all, you need to call a doctor, explain how to get into the house or apartment and leave the front door open just in case. Next, it is necessary to ensure the presence of fresh air in the room. To do this, you can open the windows or turn on the air conditioner. Nitroglycerin should be placed under the tongue, which, once it penetrates into the blood, will relieve painful sensations. Aspirin can also help in the first minutes of an attack. The drug helps thin the blood and alleviates the symptoms of the disease. For faster action of the drug, the tablet must be chewed.
A person should sit down or lie down so that the upper part of the body is slightly higher than the lower part. Legs should be bent at the knees. It is this position of the body that maximizes blood supply. Next, you need to wait for emergency medical attention.
Symptoms of a heart attack
Harbingers of a heart attack can be a wide variety of pain that occurs not only in the heart area, but under the shoulder blades, in the stomach or throat. Nagging pain in the limbs may also indicate problems with the functioning of the heart.
The main symptom of a heart attack is sharp, unbearable pain in the chest. The attack may last several minutes or not go away for hours. A heart attack can be primary (spontaneous) or repeated at regular intervals.
In medicine, there are five main types of heart attack, each of which manifests itself with different symptoms. A typical form of heart attack develops with a sharp burning pain in the heart area.
In the asthmatic form, a sudden attack of suffocation occurs. The patient does not have enough air, his breathing quickens several times. The eyelids, fingers, lips and nose area acquire a rich blue tint. The underlying skin suddenly turns pale. Such a heart attack may be accompanied by hemoptysis, coughing and noisy, uneven breathing.
The arrhythmic form is directly related to changes in heart rate. The patient's pulse quickens, the heartbeat becomes visually noticeable, and blood pressure decreases several times. This form of heart attack most often leads to clinical death.
The cerebral form is accompanied by a sudden loss of consciousness. Moreover, the initial signs of a heart attack are very similar to a stroke. The patient cannot pronounce words coherently, his speech becomes incomprehensible, coordination of movements is impaired, and sharp pain occurs in the chest area.
The abdominal form of heart attack is considered the rarest. Pain in this case does not occur in the heart area, but in the abdominal cavity closer to the stomach. According to some signs, such an attack resembles an exacerbation of an ulcer or gastritis. A heart attack is accompanied by profuse sweating, rapid heartbeat, tachycardia, arrhythmia, nausea and vomiting.
Main signs of a heart attack
Close signs of an imminent heart attack are more aggressive and vivid in nature. The imminent development of acute ischemic heart pathology can be determined by the following close warning signs of a heart attack:
- by the appearance of moderate pain in the left side of the body, chest or shoulder, sensations of moderate compression or tightness in this area;
- development of severe shortness of breath without serious physical exertion, difficulty breathing;
- a drop in blood pressure below working values;
- increased sweating;
- detection of slight numbness of the limbs, which may not occur with this condition.
Sometimes short-term manifestations of a heart attack can be accompanied by a strong attack of unreasonable fear of death, panic attacks, the so-called angina attack.
Detection of such symptoms definitely requires contacting a doctor as early as possible and receiving specific treatment - treating such attacks at home is IMPOSSIBLE and can be life-threatening!
First aid, what to do before the ambulance arrives
When characteristic signs appear, it is important to calm the patient down, limit physical activity if possible, and sit him on a chair or sofa. The most acceptable body position is sitting, leaning on the back of the sofa or reclining with your knees drawn up to your body. Loosen clothes that cause discomfort, remove the tie.
First aid for a heart attack:
- Give the patient a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue, but only if there is high blood pressure. Taking nitroglycerin with low blood pressure can increase the workload on the heart, thereby making you feel worse. Nitroglycerin can lower blood pressure, thereby causing collapse.
- In the absence of allergic reactions to aspirin, the patient is given 300 mg of acetylsalicylic acid to chew. If the patient takes aspirin regularly, the dosage should be increased to 600 mg. Aspirin must be chewed, which will significantly speed up the expected effect.
- In severe cases and extensive lesions, the patient may experience cardiac arrest. Signs of cardiac arrest include fainting and lack of breathing. In this case, cardiopulmonary measures are performed, increasing the likelihood of patient survival. Previously, cardiopulmonary resuscitation was used in the absence of a pulse; now, loss of consciousness and breathing difficulties are enough.
To treat the consequences of a heart attack, we recommend contacting qualified cardiologists at our medical center.
Share the article on social networks:
Typical course
To be able to avoid the most severe complications of a heart attack, it is advisable to know and remember the classic symptoms of the development of this pathology.
These symptoms usually include:
- sudden development of acute chest pain, with a burning, often pressing or squeezing character;
- irradiation of pain to the pericardial region (irradiation to the left side of the chest, left arm or under the left shoulder blade);
- situations when the described pain is accompanied by a panic attack, acute fear of death.
It is important to remember that the slightest suspicion of the development of myocardial infarction should force the patient to urgently consult a doctor to receive specialized treatment aimed at opening a narrowed, closed (stenotic) vessel to prevent the development of extensive necrosis of the heart muscles.
Although a heart attack is always an unexpected heart attack, it is not difficult to recognize. Its symptoms cannot be confused with any other disease. Do not forget that a heart attack is life-threatening. Timely help can save a person, but its absence will lead to death. An ambulance must be called as quickly as possible.
Clinical picture of atypical cases
Unfortunately, sometimes a heart attack develops in a non-standard way, complicating its diagnosis and early detection.
For example, some patients may experience the following hidden symptoms of narrowing of the coronary arteries:
- sensations of pain in the lower jaw, left arm or even leg, left side;
- the occurrence of pain in the epigastric region, with the addition of nausea, bloating, vomiting;
- some patients may simply not have enough air, in the absence of other symptoms.
Somewhat less frequently, during the attacks in question, symptoms similar to manifestations of completely different ailments may occur:
- an attack of the asthmatic type with the development of bronchospasm, pulmonary edema, severe shortness of breath, etc.;
- an attack similar to an exacerbation of pancreatitis - with the occurrence of nausea, profuse vomiting, general weakness, and abdominal pain;
- an attack of a neurological type, with the development of neurosis, a panic attack, with disorders of consciousness, vision, with the appearance of dizziness, headaches.
The described clinical picture should also force the patient to urgently call an ambulance - independent treatment in such cases is prohibited!
First aid for heart attack
Filippova Tatyana Sergeevna Cardiologist,
More about the doctor
Myocardial infarction is a pathological crisis condition in which significant ischemia of the heart muscle is observed. Lack of oxygen leads to the death of cardiomyocytes, and an area of necrosis appears on the surface of the heart. The greater it is, the less chance of a favorable outcome after an attack. Also, the likelihood of recovery decreases in the presence of one or more combined factors:
- age of the patient - in people over 70 years of age, heart attacks often end in death, even with timely pre-medical and medical care;
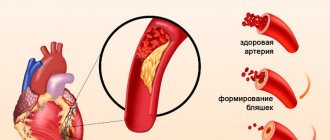
- the presence of chronic diseases that aggravate the situation - atherosclerosis , hypertension , diabetes mellitus , obesity significantly worsen the condition of blood vessels and are risk factors for myocardial infarction;
- atypical clinical picture of the attack - in the absence of characteristic symptoms, the patient may not be aware of the development of a heart attack. At the same time, the time for providing first aid will move away, and the area of necrosis will grow;
- a combination of ischemia with arrhythmia, especially extrasystole, which can lead to atrial or ventricular fibrillation. In this case, sudden death often occurs, the patient cannot be helped, and resuscitation measures are not successful.
Symptoms
You can suspect the onset of an attack based on several characteristic signs:
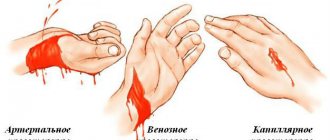
- pain on the left side, behind the sternum. It can radiate to the arm, shoulder blade, neck. The character is sharp, pulsating. In addition to pain, patients describe a burning sensation and pressure on the chest. Often elderly patients do not experience discomfort or pain at all, which complicates diagnosis and delays the provision of assistance;
- shortness of breath - difficulty breathing when inhaling or exhaling can be associated with tachycardia, characteristic of a heart attack, panic, which often affects patients;
- nausea;
- severe weakness, accompanied by cold sweat, possible loss of consciousness.
There are also quite atypical signs of a heart attack - different localization of pain, which at first glance is not related to the heart, dizziness. Very often, a heart attack is combined with a hypertensive crisis . Then the symptoms are accompanied by a severe headache and spots before the eyes.
Helping a patient with myocardial infarction
If you suspect a heart attack, you must urgently call an ambulance. Next, the patient is seated on a stable chair with a back, a shallow, fairly high chair. Remove all tight, tight clothing and accessories - tie, scarf, massive jewelry from the neck. Provide maximum flow of fresh air into the room by opening vents or windows. It is important that the patient does not sit in a draft.
The patient needs to be reassured as much as possible, saying that the ambulance is on its way and he will be helped. Excessive worries raise the heart rate and increase the load on the heart. In case of severe pain, you can give the patient a validol tablet with nitroglycerin. It is important to remember that nitroglycerin can increase the flow of oxygen to the heart by rapidly dilating blood vessels, but it can also cause headaches. You need to be prepared for this effect. Validol partially relieves the side effects of the drug.
Emergency resuscitation
If the patient loses consciousness, stops breathing or has a heartbeat, it is necessary to immediately begin chest compressions and perform artificial respiration. To do this, the patient is placed on a flat, hard surface and rhythmically pressed on the chest at a speed of 100-120 compressions per minute. At the same time, air is exhaled into the patient’s open mouth at a frequency of one breath per 15 presses. Current first aid guidelines for cardiac arrest state that lay resuscitators should focus only on chest compressions without artificial respiration. Assistance continues until the ambulance arrives or the moment when the patient begins to breathe on his own and the heartbeat is restored.
First aid
In order to promptly independently determine the possible development of the pathology in question, it is very important to pay attention to:
- intensity and nature of pain. a heart attack is characterized by squeezing, pressing, burning sensations;
- localization of pain. location of pain in the left side of the body, just behind the sternum, in the area of the shoulders, shoulder blades;
- irradiation of pain to the arm, side, neck.
But in order to really help a patient with an angina attack, the first thing that is very important to do is, of course, to call a medical team. The sooner doctors have the opportunity to begin their work, the greater the patient’s chances of surviving and avoiding the sad complications of the primary problem.
The first pre-medical treatment or simply assistance to the patient should be as follows:
- It is important for the patient to take a comfortable body position; he can be laid down or seated comfortably, allowed to lean back on the pillow;
- unbutton tight clothes;
- provide air flow, open windows;
- You can give the patient one tablet of nitroglycerin or aspirin.
Further actions should be carried out by the resuscitation team. Unfortunately, it is extremely difficult to teach people without medical education to perform chest compressions and artificial respiration, which may also be urgently needed by patients in such situations.
Rubric “Conversation with a specialist” Acute myocardial infarction - symptoms and first aid
The joint article was prepared by three specialists at once - cardiologist, anesthesiologist-resuscitator of Health Academy LLC Konstantin Nikolaevich Bozhesku, functional diagnostics specialist of Health Academy LLC (formerly an employee of the Nizhny Tagil emergency medical service team), Gennady Andreevich Puzanov and paramedic of the highest category of the team intensive care of the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution SO "City Emergency Medical Care Station of Nizhny Tagil" by Dmitry Vasilievich Subbotin.
Timely pre-medical and emergency medical care during an attack of myocardial infarction in most cases is the key to the patient’s successful recovery. It is the absence of such activities that often becomes the cause of death even for young people who have encountered this acute cardiac pathology. Cardiologists recommend that all patients with coronary artery disease know the first signs of myocardial infarction and the rules for providing first aid. It is also important to know what treatment the patient will be prescribed in the hospital in order to prepare for a conversation with the attending physician and ask him the necessary and important questions.
When is it necessary to start performing first aid? The answer to this question is always clear – immediately. That is, already when the patient began to show the first signs of myocardial infarction. Its onset is signaled by the following typical symptoms:
intense chest pain; irradiation of pain to the left arm, shoulder blade, teeth or neck area; severe weakness; fear of death and severe anxiety; cold clammy sweat; nausea. With atypical forms of heart attack, the patient may experience other symptoms:
stomach ache; digestive disorders; vomit; dyspnea; suffocation, etc. First aid in such situations should begin with calling an ambulance. When talking with the dispatcher of this service, you must:
report the symptoms observed in the patient; express your assumption about the possibility of myocardial infarction; ask to send a team of cardiologists or resuscitators. After this, you can begin to carry out those activities that can be performed outside the medical institution.
First aid The patient must be carefully placed on his back and given the most comfortable position (semi-sitting or a cushion placed under the back of his head).
Ensure a flow of fresh air and the most comfortable temperature conditions. Remove clothing that interferes with free breathing (tie, belt, etc.).
Convince the patient to remain calm (especially if the patient exhibits signs of motor agitation). Talk to the victim in a calm and even tone, do not panic or make sudden movements.
Give the patient a Nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue and a sedative (Corvalol, motherwort tincture or valerian).
Measure blood pressure. If the pressure is not more than 130 mm. rt. Art., then it is advisable to re-take Nitroglycerin every five minutes. Before the doctors arrive, you can give 2-3 tablets of this drug. If the first dose of Nitroglycerin caused a severe throbbing headache, then the dosage should be reduced to ½ tablet. When using this drug in the form of a spray, its single dose should be 0.4 mg. If the patient's first dose of Nitroglycerin caused a sharp decrease in blood pressure, then this drug should not be used further.
Give the patient a crushed Aspirin tablet (to thin the blood).
Count the patient's pulse. If the heart rate is no more than 70 beats/minute and the patient does not suffer from bronchial asthma, then he can be given one of the beta blockers (for example, Atenolol 25-50 mg).
You can put a mustard plaster on the area where the pain is located (remember to keep an eye on it so that there is no burn).
During the provision of first aid, the patient’s condition may be complicated by the following conditions:
fainting; heart failure. If fainting occurs, it is necessary to remain calm and ensure the normal functioning of the respiratory system. The patient must be placed in a horizontal position, a cushion placed under his shoulders and dentures (if any) removed from the mouth. The patient's head should be in a tilted position, and if there are signs of vomiting, it should be turned to the side.
In case of cardiac arrest, artificial respiration and chest compressions must be performed before the medical team arrives. The frequency of compressions on the midline of the chest (heart area) should be 75-80 per minute, and the frequency of blowing air into the airways (mouth or nose) should be about 2 breaths every 30 compressions on the chest.
Emergency medical care and principles of treatment in a hospital Emergency medical care for myocardial infarction begins with the relief of acute pain. For this, various analgesics (Analgin) and narcotic drugs (Promedol, Morphine, Omnopon) in combination with Atropine and antihistamines (Diphenhydramine, Pipolfen, etc.) can be used. For a faster effect, painkillers are administered intravenously. Seduxen or Relanium is also used to eliminate the patient's anxiety.
Then, to assess the severity of the heart attack, the patient is given an electrocardiogram. If hospitalization is possible within half an hour, the patient is immediately transported to a medical facility. If it is impossible to transport the patient to the hospital within 30 minutes, thrombolytics (Alteplase, Purolase, Tenecteplase) are administered to restore coronary blood flow.
A stretcher is used to transfer the patient to the ambulance, and during transportation to the intensive care unit, humidified oxygen is inhaled. All these measures are aimed at reducing the load on the heart muscle and preventing complications.
After arrival at the intensive care unit, to eliminate pain and agitation, the patient is given neuroleptanalgesia with Talamonal or a mixture of Fentanyl and Droperidol. In case of a prolonged angioedema attack, the patient can be given inhalation anesthesia using a gaseous mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen.
Next, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
Nitroglycerin, Isosorbide dinitrate, Isoket - in the acute period of a heart attack, these drugs are used to reduce the myocardial oxygen demand, first they are administered intravenously, and after stabilizing the patient's condition - orally and sublingually.
Beta blockers (Anaprilin, Inderal, Obzidan, Propranolol) - help slow the heart rate and reduce the load on the heart.
Antiplatelet agents (Aspirin) thin the blood and prevent the development of a new heart attack.
Anticoagulants (Heparin) - used to prevent recurrent heart attacks and reduce blood clotting.
ACE inhibitors (Ramipril, Captopril, Enalapril, etc.) are used to lower blood pressure and reduce the load on the heart.
Sedative and hypnotic drugs (Diazepam, Oxazepam, Triazolam, Temazepam, etc.) are used when it is necessary to limit the patient’s activity and for sleep disorders.
Antiarrhythmic drugs (Novocainamide, Rytmilen, Lidocaine, Difenin, Amiodarone, etc.) are used for cardiac arrhythmias to stabilize cardiac activity and reduce the load on the myocardium.
Other pharmacological drugs can be used to treat myocardial infarction, since the tactics of drug treatment of the patient depends on the general condition of the patient and the presence of other pathologies (diseases of the kidneys, blood vessels, liver, etc.).
Also, for the treatment of myocardial infarction, modern medicine uses various instrumental, highly effective techniques to restore coronary blood flow:
balloon angioplasty; coronary artery bypass grafting. Such surgical techniques allow patients with severe forms of myocardial infarction to avoid serious complications and prevent the high risk of mortality from this cardiac pathology.
Motor activity of a patient with myocardial infarction All patients with myocardial infarction are advised to limit their physical activity, since this regime contributes to a more rapid replacement of the infarction area with scar tissue. In the first days, the patient must observe strict bed rest, and from 2-3 days, in the absence of complications and signs of heart failure, his motor regimen begins to gradually expand. Initially, he is allowed to sit on a bedside chair 1-2 times a day and sit on it for about 15-30 minutes (the frequency and duration of these actions is determined by the doctor).
These days the patient can eat on his own. He also needs to be washed and cleaned, and he must use a bedpan to defecate (the use of a bedside toilet seat is permissible only with the permission of a doctor and only for patients with a stable heart rhythm).
Starting from 3-4 days, the patient is allowed to sit on a chair for about 30-60 minutes twice a day. In case of an uncomplicated heart attack, the patient is allowed to start walking between 3-5 days (this time is determined by the doctor). The time of such walking and the distances over which the patient moves increase gradually.
In an uncomplicated form of myocardial infarction, the patient is discharged from the hospital on days 7-12, and in complicated cases it can take place only after 3 weeks or more. In the future, the patient must undergo a course of rehabilitation, which can be performed in specialized institutions or at home. During this period, the intensity and duration of physical activity gradually increases depending on health indicators.
Nutrition of the patient during myocardial infarction In the first week after myocardial infarction, the patient is recommended to have a low-calorie diet with limited salt, animal fats, liquids, foods with nitrogenous substances, excessively coarse fiber and cholesterol. The diet should include foods that are rich in lipotropic substances, vitamin C and potassium salts.
In the first 7-8 days, all dishes should be pureed. Food is taken in small portions 6-7 times a day.
The diet may include the following foods and dishes:
wheat bread crackers; semolina, oatmeal, buckwheat and rice cereals; lean veal; low-fat varieties of fish; chicken meat; protein steam omelette; low-fat cheese; fermented milk drinks; butter; salad of fresh grated carrots and apples; vegetable soups; boiled beets and cauliflower; pureed fruit; compotes and fruit drinks; rosehip decoction; weak tea; honey. During this period, the following foods and dishes are prohibited:
dough products (pancakes, donuts, cakes, pies); smoked and marinated dishes; pickles; fried foods; sausages; fatty dairy products; salty and spicy cheeses; caviar; fat meat; boiled and fried eggs; fish and mushroom broths; pasta; cooking fat; mushrooms; legumes; sorrel; turnip; grape; tomato juice; spices; chocolate; natural coffe. 2-3 weeks after a heart attack, the patient is recommended the same set of products and list of restrictions, but the food may no longer be pureed, prepared without adding salt and taken about 5 times a day. Subsequently, the patient's diet expands.
Remember! Myocardial infarction is a serious and dangerous pathology that can cause many serious complications and even death of the patient. Be sure to follow all the rules for providing first aid during an attack of this acute condition, call an ambulance in a timely manner and follow all the doctor’s recommendations during treatment in a hospital.
You can make an appointment with a cardiologist, as well as undergo an electrocardiogram at our Medical Center. Make an appointment by phone 8(3435) 230-500
We care about you!
Always yours, Medical
Diagnostics
After the ambulance arrives, the patient, as a rule, undergoes an urgent electrocardiogram, according to the readings of which the development of a heart attack can be determined. At the same time, doctors collect anamnesis, analyzing the time of onset of the attack, its duration, pain intensity, its localization, irradiation, etc.
The following changes can be considered electrocardiographic criteria for the development of an attack:
- damage or arched growth of the st segment, which can merge with a positive t wave or even turn into a negative t wave;
- the appearance of a pathologically altered q wave with a decrease in the amplitude of the r wave. sometimes there may be a complete disappearance of the r wave with the formation of qs;
- the appearance of a negative, often symmetrically located T wave.
In addition, acutely occurring bundle branch block may be indirect signs of the development of a heart attack. Also, the diagnosis of myocardial infarction is based on the detection of markers of damage to the muscle tissue of the heart.
Today, the most convincing (obvious) marker of this type can be considered the troponin level in the blood, which will be significantly increased when the described pathology occurs.
Troponin levels may rise sharply in the first five hours after a heart attack and may remain elevated for up to twelve days. In addition, to detect the pathology in question, doctors can prescribe echocardiography.
Cardiologist Mikhail Tashnik: “In acute myocardial infarction, the first 2 hours are decisive!”
Interventional cardiology Apr 07, 2016
Myocardial infarction is a condition that occurs suddenly, and the urgency of treatment is critical. The patient can fully recover after a myocardial infarction, provided that he receives the correct professional assistance as soon as possible. The Myocardial Infarction Center is the only center in the country that provides a full range of medical services, both therapeutic and surgical, for acute myocardial infarction, specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular pathologies according to international standards, therefore NKMS has entered into a contract with the Myocardial Infarction Center in order to receive emergency cardiovascular conditions. Here, every patient receives the best care and emergency intervention, ensuring the best chance of recovery. It is extremely important that each of us is able to recognize the manifestations of a heart attack, and, if symptoms are detected, call an ambulance immediately in order to save our own life or the lives of loved ones.
What is acute myocardial infarction?
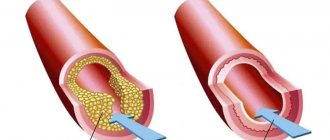
When one or more branches of the heart's arteries become blocked or narrowed for various reasons (eg, atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots), blood cannot reach the area of the heart muscle, which will therefore not receive the oxygen it needs to function. In such cases, it is said that ischemia of the heart muscle occurs. Myocardial ischemia (the heart suffers from a lack of oxygen) can manifest itself as angina pectoris (typical cardiac chest pain) within a short time. However, after 20 minutes of ischemia, the heart muscle cells begin to die, causing a myocardial infarction, known as a heart attack and acute coronary syndrome. Myocardial infarction impairs the contractile function of some areas of the heart (depending on the affected vessels).
Causes of acute myocardial infarction
The reasons for the decrease in coronary blood flow, as a rule, are atherosclerosis - the progressive thickening of artery walls due to cholesterol deposits. Sometimes, myocardial ischemia is caused by an increased need for oxygen at the cardiac level, for example, during physical activity, when some coronary vessels are severely narrowed.
What are the risk factors for acute myocardial infarction?
Risk factors increase the chances of developing atherosclerosis, and therefore the risk of death or disability as a result of a myocardial infarction. These factors fall into 2 categories:
- Constant - that is, not subject to influence, such as gender, age or heredity. Some families have a greater risk of exposure to acute myocardial infarction. The likelihood also increases with age (especially after 65 years), and men are more at risk of experiencing a myocardial infarction than women at a younger age.
- Changeable - it is very important to know them, because they can be eliminated with the help of medications or giving up bad habits. Unfortunately, cases of myocardial infarction are becoming increasingly common among young patients (30-40 years old), for whom the only risk factor is smoking. Stress, the disease of this century, should be kept under control before it has an adverse effect on health. Other risk factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyle, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus and kidney failure can be corrected with healthy lifestyle and treatment
Sometimes just one of the above factors is enough to increase the risk of coronary disease. Thus, we once again draw your attention to the importance of timely contacting the Medpark Cardiology Center.
How can you prevent the disease?
Preventing a heart attack is the best thing a person can do for their heart health. It's never too late to give up habits that are bad for your heart. This means that it is necessary to undergo regular medical examinations and reduce coronary risk factors.
A patient suffering from heart pain is always at high risk of developing myocardial infarction, therefore periodic examinations, exercise tests, ultrasound of the heart, diagnostic coronary angiography, identify coronary pathology in the early stages and help prevent the development of myocardial infarction.
How does acute myocardial infarction manifest?
Acute myocardial infarction remains barely recognizable to most people. Considering that providing medical care in the first 2 hours can mean a complete recovery, it is necessary to pay attention to alarming symptoms.
Typically, patients complain of severe or pressing chest pain with the following characteristics:
- localization - most often retrosternal (in the middle of the chest), radiating to both arms, often to the left shoulder and arm (sometimes with tingling in the fingertips), neck and lower jaw, in other cases to the epigastrium (in the stomach area), less often to the back ;
- character – when pressed, deep, burning, pressing, squeezing or itching over a large surface, varying in intensity, from mild to severe pain;
- duration - from 20 minutes to several hours, not stopping for a short time after taking nitroglycerin tablets under the tongue (3 tablets taken at intervals of 5 minutes);
- combined symptoms - anxiety, shortness of breath, sweating, pallor, fainting and sometimes nausea and vomiting;
- provoking factors - in more than 50% of patients at least 1 provoking factor can be identified, most often it is physical activity, emotional stress, surgery; Precursors (sometimes) – a few days or weeks before a heart attack, less intense and prolonged chest pain may appear more often during exercise or at rest
Atypical symptoms of a heart attack
There are cases where the symptoms are atypical, such as epigastric pain, indigestion, stabbing chest pain, general unexplained weakness, increased sweating, dyspnea, irregular heartbeat, nausea or other non-specific symptoms. Most often, atypical symptoms appear in young patients (25-40 years old), elderly (over 75 years old), women, patients with diabetes mellitus, renal failure or dementia.
When should you see a doctor?
Don't waste a minute! Seek help immediately! Remember the clinical signs because it could save someone's life. There is a tendency to deny the presence of myocardial infarction! This leads to untimely initiation of treatment, which is unfavorable. Even if you are not sure that you are experiencing symptoms of a myocardial infarction, still call a doctor immediately! Not all chest pain means the development of a myocardial infarction, but most often, severe, long-term chest pain requires a visit to the doctor for a consultation and an electrocardiogram, as well as some additional tests. There are many risks due to ignoring the warning signs of myocardial infarction: sudden death, severe forms of arrhythmia, angina pectoris, which further increases the patient's risks during heart failure. However, timely and adequate treatment significantly reduces the risk of any of the complications.
Treatment of acute myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is a complex emergency condition, the only treatment for which is the rapid restoration of blood circulation in the affected area, that is, the release of a blocked vessel as early as possible (in the first hours), in order to reduce the area of necrosis of the cardiac muscle tissue to prevent complications. If pain occurs, if there are nitroglycerin tablets on hand, the patient should place one under the tongue. If the pain does not go away, you can take 2 more tablets with an interval of 5 minutes. The disappearance of pain against the background of nitroglycerin in a short time after taking it indicates that the pain is of cardiac origin. Requesting an ambulance as soon as possible, which will take the patient to the Medpark Myocardial Infarction Center is a chance to save a patient with a heart attack.
At Medpark-e, at the Emergency Center, a diagnosis is made using a clinical examination and ECG, venous catheters are installed, blood is taken for analysis, special medications are prescribed: sublingual nitroglycerin and intravenous drip, analgesics, aspirin and, ultimately, clopidogrel, heparin . In the case where myocardial infarction is confirmed by the ECG, the patient's clinical picture and positive tests for degrading cardiac cells (troponin and CK-MB), the patient is urgently transported to the cardiac catheterization room.
Modern treatment of myocardial infarction is based on a minimally invasive interventional approach using diagnostic coronary angiography. If a coronary block is detected, angioplasty will be performed, the vessel will be restored either with a balloon or a stent, which normalizes blood flow. Prompt implementation of the procedure to restore blood circulation reduces the negative effects of acute coronary syndrome on the heart. Coronary angiography is performed by inserting a thin tube into the artery, and through it a catheter to the arteries of the heart, then a contrast agent is injected, which allows you to see the location of the coronary arteries. Coronary angiography is performed under local anesthesia in order to minimize discomfort during the procedure. The patient remains conscious and talks with the doctor throughout the procedure, watching the details of the procedure on the screen. If necessary, a stent (a small metal frame) is inserted into the diseased coronary artery through the same pathways and catheters, which restores blood flow to the heart, or the artery is uncorked using a balloon that is inflated inside the vessel. The consequences of a heart attack depend on the speed at which a patient contacts the Medpark Myocardial Infarction Center. If a patient with a myocardial infarction undergoes angioplasty within the first 90 minutes of the onset of pain, complications are minimized, and the patient can return to their usual lifestyle and previous activities. In case of late presentation (as usually happens), the effectiveness of angioplasty is minimal, the patient will experience restrictions in activity and a decrease in the level of endurance and stress.
Another approach to acute myocardial infarction, in centers with coronary angiography labs, is to dissolve clots by fibrinolysis: substances that dissolve clots throughout the body, including the arteries of the heart, are injected into the blood. This procedure is much more unsafe, with many associated risks, but is often the only solution in areas without access to modern cardiac services.
Recovery after acute myocardial infarction
After restoration of coronary circulation, the patient with myocardial infarction will undergo gradual recovery under the strict supervision of doctors. The myth that a patient must remain in bed for several weeks after a heart attack is not true and can lead to adverse consequences. A patient who has survived a myocardial infarction, depending on the damage to the heart, requires regular and constant use of special drug treatment prescribed by the attending cardiologist, in accordance with international standards. The presence of a stent requires antiplatelet therapy prescribed by a cardiologist. Since the stent is a foreign body, the body will try to cover the stent with blood clots for at least 6-12 months, so it is necessary to take two types of antiplatelet drugs simultaneously, such as aspirin and clopidogrel (at least 6 months in the case of metal stents or 12 months in the case of medical ones), which will prevent them from being blocked.
Attention! If the patient does not comply with the prescribed instructions and interrupts the medication for at least one day, there is a risk of recurrent myocardial infarction due to blockage of the stent. It is necessary to understand that angioplasty and stenting are effective only when the patient simultaneously treats coronary risk factors (weight loss, smoking cessation, reduction of lipids and glycemia, blood pressure control). Otherwise, there is a risk of narrowing of the dilated artery.
Medpark Myocardial Infarction Center
Medpark is the only private medical institution in the Republic of Moldova that has developed, based on international standards, a center of excellence dedicated to the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular pathologies - the Myocardial Infarction Center. In 2013, the Ministry of Health included the Medpark Myocardial Infarction Center in the National Program for the Control of Cardiovascular Pathologies. Thus, 3 days a week (Sunday, Monday and Wednesday) our Center receives patients from all over the country with acute myocardial infarction admitted from Emergency Medical Services. In these cases, our specialists perform a coronary angiography procedure and, if necessary, stenting. Assistance is provided on the basis of a compulsory health insurance policy issued by the National Health Insurance Company (CNAM).
The Myocardial Infarction Center deals with the diagnosis and modern methods of treatment of ischemic cardiopathy, as well as invasive cardiology, unique for the Republic of Moldova, available daily and around the clock, within the framework of which urgent myocardial revascularization is carried out in the case of acute coronary syndrome with or without ST segment elevation.
Why choose the services of Medpark Cardiology Center:
- We are the only center in Moldova that has everything necessary for all stages of diagnosis and treatment of heart diseases, including cardiac surgery;
- We have the best cardiac surgeons and interventionalists, both in the country and abroad;
- We have a specialized consultation department where you can get the necessary advice about your heart health at any time;
- We have the most modern medical equipment, which allows for quick and accurate diagnosis, and as a result, correct treatment;
- International accreditation by Joint Commission International guarantees the safety of medical practice and the best results;
- We are at your service 24 hours a day, 7 days a week and can come to your aid at any time for any cardiac emergency.
A gift from the heart from Medpark
All cardiac treatments begin with a visit to a cardiologist, therefore, Medpark gives you a unique offer for your heart: until April 15, 2021, you have a 50% discount on a consultation with a cardiologist and a 20% discount on all subsequent tests recommended by the best specialists at the Medpark cardiology center. We are waiting for you for a consultation. Sign up by number 0 22 40 00 40
* * *
Author: Mikhail Tashnik, cardiologist, head of the Medpark Emergency Center with more than 5 years of experience in the field of cardiology.