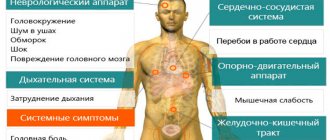
Women rarely experience menstruation without symptoms. Most representatives of the fair sex wait with fear for the onset of premenstrual syndrome (PMS). Most often, women are bothered by abdominal pain, back pain, fatigue, irritability and many other symptoms. So, one of the manifestations of menstruation can be a change in blood pressure. This phenomenon occurs frequently, despite the fact that the cardiovascular system seems to be in no way interconnected with the reproductive system. In this article we will look at the reasons for blood pressure surges in women at different periods of the cycle.
The relationship between pressure and critical days
Menstruation occurs due to the constant production of hormones of the reproductive system. They are responsible for the detachment of the uterine lining. Blood pressure is the force of blood pressing on the vessels. The process of increasing or decreasing blood pressure is regulated by hormonal and nervous factors. Some hormones can affect the condition of blood vessels, so a person’s blood pressure is closely related to the functioning of the reproductive system. During menstruation, a woman’s hormonal background undergoes changes and, as a result, blood pressure jumps.
Pressure changes during menstruation are absolutely normal. There is no need to worry about this, since after menstruation the blood pressure returns to normal.
When to see a doctor
It is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the body if the indicator rises for the first time during menstruation. Hypotension or hypertension can be suspected if pressure surges during menstruation persist on the 4th-5th day of the cycle.
You should consult a doctor immediately if you experience the following accompanying symptoms:
- vomit;
- confusion of consciousness and speech;
- intense bleeding;
- severe pain.
BP before critical days
Before menstruation, the hormone progesterone comes into effect. It is found in the blood, so it can cause vascular imbalance. The substance helps create comfortable conditions for fertilization of the egg and improves blood circulation in the organs of the reproductive system. Changes in a woman's blood pressure during this period are manifested by weakness, apathy and headaches. Development factors may be associated with the individual characteristics of the body or with existing diseases.
Causes of increased blood pressure
The main symptom of high levels before menstruation is headaches . Due to the appearance of discomfort, the woman constantly measures her blood pressure, assuming that it is elevated. However, the doctor notes that there are no disorders in the cardiovascular system. So what are the main causes of high blood pressure before menstruation?
- Depression. In most women, premenstrual syndrome is accompanied by worsening mood, irritability, and depression. All these symptoms are explained by a lack of serotonin in the blood, called the “happiness hormone.” Its deficiency also provokes vasoconstriction, which leads to increased blood pressure.
- Migraine. This symptom is considered a common cause of high blood pressure before menstruation. With this disease, the blood pulsates more strongly, and the blood vessels undergo rapid narrowing and expansion.
- Swelling. If the water-salt balance is disturbed during premenstrual syndrome, disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system occur, in particular, the production of hormones in the hypothalamus region decreases. The consequence of this is additional pressure on the nerve endings. The blood vessels narrow, which leads to increased blood pressure.
Causes of low blood pressure before menstruation
A decrease in pressure on the eve of critical days is more typical for young girls prone to hypotension. Most often they are of asthenic build, melancholic, and prone to depressive moods.
Expert opinion
Daria Shirochina (obstetrician-gynecologist)
A decrease in blood pressure may be associated with the action of progesterone. The same effect is achieved by taking analogue drugs, Utrozhestan, Duphaston and others. Its level increases in the second phase. As you know, it relaxes smooth muscles - the intestines, blood vessels and, of course, the uterus. This is a physiological process aimed at maintaining pregnancy if conception occurs during ovulation.
Also, a decrease in blood pressure may be one of the manifestations of premenstrual syndrome.
Blood pressure during menstruation
Menstruation is a highly individual process. It is known that some perceive this phenomenon as painful, while for others it is almost asymptomatic. The pressure may remain normal, but sometimes changes are observed. Let's look at the reasons for blood pressure surges during menstruation.
High
Blood pressure can rise during menstruation even in people who are not usually bothered by hypertension. Most often, this symptom is the result of hormonal imbalances. During menstruation, high blood pressure is provoked by the following factors:
- pain in the heart area;
- feeling of bladder fullness;
- irritability for no reason;
- nausea;
- bad stool;
- swelling;
- cardiopalmus.
Often, only some of the listed symptoms may be pronounced. All of them affect the functioning of blood vessels and lead to pressure surges.
The next reason for increased blood pressure during menstruation is a disorder of the nervous system. During this period, girls are prone to depression and mood swings. Emotional turmoil leads to undesirable consequences, one of which is high blood pressure.
Low
Low blood pressure is often accompanied by characteristic symptoms: severe abdominal pain, weakness, loss of consciousness. There is a disability; it is difficult for the girl to even get out of bed. The following causes of low blood pressure are noted:
- Heavy menstruation , which can occur due to gynecological diseases of the body. Severe blood loss leads to a lack of hemoglobin, which provokes insufficient oxygen supply to the vessels. At the same time, a woman’s blood pressure during menstruation decreases significantly.
- Hormonal imbalance. If some hormones predominate over others in the blood, a decrease in blood pressure may occur. This phenomenon is observed in thin women and those who abuse bad habits.
- Pain pills. Menstruation rarely passes without the use of analgesics, which women often take uncontrollably. A side effect of such drugs is vasodilation.
- Presence of other diseases. Many pathologies in which medications are taken regularly lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
- Unpleasant sensations. Sharp pain is often observed in girls who have just begun menstruation, since their cycle has not yet established itself.
- Diet. Losing body weight makes the body weaker. During menstruation, a woman needs to consume more resources than usual. The lack of nutrients that enter the body during nutrition leads to a decrease in blood pressure and vascular tone.
Treatment of menstrual migraine
Any headache is a reason to contact a specialist. To establish a primary diagnosis, such a doctor is a neurologist who can prescribe medications to relieve an attack that has already occurred and select a method to prevent new manifestations.
Perennial migraines can be caused by various diseases. For example, after surgery on the ovaries there is an unstable menstrual cycle and acne, then the woman needs to consult a gynecologist and endocrinologist.
Various gynecological diseases can also provoke menstrual migraine or similar attacks. For example, for a benign uterine tumor, headache is often the only external symptom. Endometriosis causes pain not only in the affected organs, but also provokes severe migraines. Adenomyosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, and various inflammatory processes also affect the production of sex hormones and are accompanied by headaches.
Necessary examinations
To make an accurate diagnosis, patients with suspected menstrual migraine are recommended to undergo the following tests:
- general blood test (it is especially important to find out the level of hemoglobin) and urine;
- blood tests for hormones (ovaries, adrenal glands, thyroid gland, pituitary gland);
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs to detect tumors, cysts, inflammatory processes, etc.
In addition, it is possible to prescribe other studies at the discretion of the doctor (ultrasound examination of blood vessels, MRI of the brain, and so on).
Drug treatment
All treatment can be divided into two options:
- preventing the onset of migraines;
- stopping the attack that has occurred.
To relieve attacks, specific anti-migraine drugs – triptans – are considered the most effective. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antispasmodics are also often prescribed. But the use of these drugs (even in large doses) may not give the expected effect due to the specificity of menstrual migraine.
In this case, it is most effective to act proactively to prevent the onset and development of migraine. For preventive purposes, these same drugs are prescribed a couple of days before the expected onset of an attack. Magnesium preparations are also used as part of prevention. The most effective is complex treatment, which begins before the onset of an attack and lasts at least 5-7 days.
Important! Therapy methods and medications can only be prescribed upon examination and consultation with a specialist.
Hormone therapy
Leveling hormonal levels with the help of medications and the use of oral contraceptives and intrauterine devices sometimes leads to the disappearance or reduction in the intensity of menstrual migraines. The use of gels and patches containing estrogen also has a positive effect as a preventative measure.
Blood pressure after menstruation
At the end of menstruation, most often the unpleasant symptoms disappear immediately. However, blood pressure may still be abnormal. This is due to the fact that even after menstruation ends, hormones continue to influence vascular tone. Long-term surges in blood pressure that continue after menstruation may indicate not only a hormonal imbalance, but also serious disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
During menstruation, it is important to closely monitor changes in blood pressure. If the readings deviate from the norm for a long time, you should consult a doctor.
Memo for the patient
Every woman should know:
- You should not self-medicate, but seek help from a doctor if you have severe and regular headaches, as well as if there is a change in its nature and duration. Discomfort during the menstrual cycle and disruption of its flow are an important reason to consult a doctor, regardless of age.
- A healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition are the right decision. You can prevent the development of migraines by following a daily routine, regular walks before bed, maintaining physical activity, and getting enough sleep. In the diet, it is necessary to limit the consumption of “fast” carbohydrates, alcohol and foods that contribute to fluid retention in the body. Maintaining fluid balance is very important for women prone to headaches.
- For effective consultation with a neurologist (and other doctors), it is advisable to keep a diary of health observations, in which you should indicate not only the presence or absence of headaches, but also their intensity. Information about blood pressure, heart rate, and other indicators of well-being will not be superfluous.
- Follow all doctor's recommendations. These can be drugs of various effects, a therapeutic diet, maintenance therapy in the form of vitamin and mineral complexes. You should go for a therapeutic massage of the back and cervical-head region only on the recommendation of your attending physician.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, you can undergo a full examination to identify the causes of headaches during menstruation and prevent the occurrence of migraine attacks. We have highly qualified specialists and the most modern equipment. Our doctors will conduct an examination and prescribe effective treatment.
How to regulate blood pressure during menstruation
The relationship between blood pressure and menstruation has been proven, but an increase or decrease in blood pressure may be a consequence of the influence of other factors. You need to listen to your body during your period. When alarming symptoms of changes in blood pressure appear, it is important to be able to take action and help yourself.
At the first signs of increased blood pressure, you should resort to taking a painkiller. During your period, you should not put stress on your body or engage in excessive physical activity. You should rest more time and remain in a relaxed state.
Quick help with low levels is the use of appropriate drugs to increase blood pressure, for example, analgesics. Citramon helps normalize blood pressure.
Common consequences of blood pressure surges are heavy bleeding and weakness of the body. Rest and healthy sleep will help bring your blood pressure back to normal.
TREATMENT OF PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME IS AVAILABLE IN THE BRANCHES:
Treatment of premenstrual syndrome in the Primorsky region
Address: St. Petersburg , Primorsky district, st. Repisheva, 13
Treatment of premenstrual syndrome in the Petrograd region
Address: St. Petersburg , Petrogradsky district, st. Lenina, 5
Treatment of premenstrual syndrome in Vsevolozhsk
Address: Vsevolozhsk , Oktyabrsky Prospekt, 96 A
Prevention and treatment
If self-help does not bring a positive result, it is recommended to consult a doctor who will examine the patient and refer her for tests to determine hormone levels. If abnormalities are detected, the specialist will prescribe hormonal therapy.
There are many folk methods for normalizing indicators. So, to reduce high blood pressure, drink mineral water with lemon and honey before breakfast for a week. Herbal tinctures, as well as ginger tea, will help increase blood pressure.
An important component of treatment is diet. You should limit your intake of salt and sugar. It is recommended to give up bad habits such as alcohol and smoking, as they often affect blood pressure.
Fluctuations in readings are often a normal process during menstruation. But if the change in pressure becomes regular, then we can assume the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the body. For further treatment you need to consult a doctor.
Risk of delayed or irregular menstrual cycles
In women with a regular menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs every 25-28 days. Although the interval between periods is individual for each woman and may differ, especially during puberty and perimenopause, in any case, menstruation occurs once a month if the woman is healthy.
If a woman stops menstruating, which is called “amenorrhea,” then this is a clear sign that you have some kind of health problem. Primary amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation in girls when they have never had a period, which will begin when they reach the age of puberty. Secondary amenorrhea is when a woman already had a period, but suddenly stopped and has not been present for three months or more.
The presence of regular moderately painful or painless menstruation every month is a sure sign that the hormonal levels are normal and the reproductive system is in order. The opposite picture is observed if irregular menstruation, delayed menstruation, or very painful and intense menstruation are recorded. They indicate that the level of one or more hormones is too high or that one or another hormone is missing altogether. If you have any health problems, chronic stress, poor nutrition, heavy physical activity, frequent delays in menstruation, then such problems should never be left to chance (unless you are absolutely sure that you are not pregnant).
Unfortunately, according to the latest data, many women prefer not to talk to their doctor about frequent delays or irregular periods, which is quite a big risk, since hormonal imbalance and amenorrhea are associated with a number of serious diseases, and also increase the risks of developing osteoporosis, heart disease, and infertility and other hormonal complications.
According to research from the Mayo Clinic's Department of Endocrinology, “amenorrhea may indicate a wide range of anatomical and endocrine disorders. Amenorrhea can lead to decreased fertility. When estrogen levels are low, amenorrhea is often accompanied by an imbalance of minerals, blood glucose and impaired fat metabolism. "Such metabolic changes affect bones and the cardiovascular system, including increasing the risk of osteoporosis and coronary heart disease later in life."
What to do if there are changes at different periods of the cycle?
The algorithm of actions in case of fluctuations in indicators depends on the general condition of the woman, the degree of changes and the main cause.
Minor physiological changes do not require drug correction. If attacks of weakness, nausea, or headache occur, it is recommended:
- active or passive rest (depending on the severity of the condition);
- removing salty, smoked, sour and spicy foods from the diet (more effective with high blood pressure);
- drink a sweet warm drink;
- take a soothing herbal medicine (valerian extract or chamomile decoction).
If pathological signs appear that persist for several cycles (at least 2), or the woman’s condition is serious, a doctor’s consultation is necessary.
It is recommended to contact:
- gynecologist;
- endocrinologist;
- cardiologist;
- psychologist.
After the consultation, the doctor will prescribe the necessary tests (laboratory analysis of a hormonal panel, daily blood pressure monitoring, etc.) and adequate therapy.
Cost of treatment of premenstrual syndrome:
| Services list | Price in rubles | |
| Saint Petersburg | Vsevolozhsk | |
| Initial appointment with a 1st stage obstetrician-gynecologist | 1850 | 1500 |
| Repeated appointment with a 1st stage obstetrician-gynecologist | 1650 | 1300 |
| Primary appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, stage 2 | 2100 | — |
| Repeated appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, stage 2 | 1900 | — |
| MANIPULATION | ||
| Insertion of obstetric pessary | 1500 | 1500 |
| Insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD) | 2500 | 2500 |
| Insertion of the Mirena intrauterine device | 4000 | 4000 |
| Introduction of the implantable contraceptive IMPLANON (without the cost of the contraceptive) | 2500 | 2100 |
| Videocolposcopy | 1700 | 1700 |
| Smear collection (gynecological) | 300 | 250 |
| Instrumental removal of the intrauterine device (IUD) | 2500 | 2100 |
| Intravaginal administration of suppositories (without the cost of medications), 1 procedure | 500 | 500 |
| Therapeutic treatment of the vagina | 700 | 700 |
| Medical termination of pregnancy | 8000 | — |
| Local treatment of the external genitalia | 700 | 700 |
| Removing the obstetric pessary | 1000 | 1000 |
| Removing the intrauterine device (IUD) | 1500 | 1500 |
| Removal of the Mirena intrauterine device | 3000 | 3000 |
| Removal of the implantable contraceptive IMPLANON | 2500 | 2300 |
| Removing a foreign body from the vagina | 1800 | 1800 |
| Line biopsy of the endometrium (pipe diagnostics) | 1500 | 1200 |
| PRP therapy | — | 3500 |
| ULTRASONIC AND FUNCTIONAL DIAGNOSTICS | ||
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (one sensor) | 1600 | 1300 |
| Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (two sensors) | 1900 | 1500 |
| CTG (fetal cardiotocography) | 1800 | — |
| CTG (multiple pregnancy) | 2300 | — |
| LASER SURGERY | ||
| Cervical biopsy + histology | 5000 | 4000 |
| Single cervical cyst | 1500 | 1500 |
| Single papillomas and condylomas of the vaginal walls | 3000 | 3000 |
| Common condylomatosis, papillomatosis | from 6000 | from 6000 |
| Removal of single condylomas, papillomas of the vulva, cervix (for 1 unit) | 600 | 600 |
| Ectopia (erosion) of the cervix (less than 2 cm) | 6000 | 4000 |
| Ectopia (erosion) of the cervix (more than 2 cm) | 9000 | 9000 |
| Endometriosis of the cervix (single lesion) | 1000 | 1000 |
| RADIOSURGERY | ||
| Biopsy of the cervix with a radioknife | 2500 | 2000 |
| Treatment of leukoplakia and vulvar kraurosis using a radiosurgical knife | 5300 | 5100 |
| Treatment of cervical pathology with a radiosurgical knife up to 1 cm | 5000 | 3700 |
| Treatment of cervical pathology using a radiosurgical knife up to 2 cm | 6500 | 6000 |
| Removal of cervical polyps using a radiosurgical knife | 4000 | 2500 |
| Fulguration of cysts, endometrioid lesions using a radiosurgical knife | 3500 | 2200 |
| Electrocoagulation of condylomas on the skin in the perineal area with a radio knife (for 1 unit) | 800 | 800 |
| Electrocoagulation of condylomas, papillomas of the vulva with a radio knife | 1400 | 1400 |
| Electrocoagulation of condylomas, vaginal papillomas with a radio knife | from 3200 | from 3200 |
| OPERATIONS | ||
| Intimate contouring | — | 26000 |
| Surgical defloration | 8000 | 8000 |