Myocardial infarction
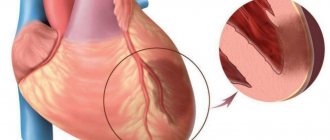
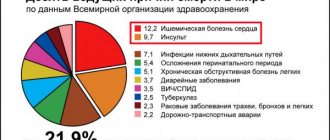
– an extremely dangerous and severe manifestation of coronary heart disease. Myocardial infarction is the death (necrosis) of a section of the heart muscle caused by a critically dangerous deterioration of blood supply in the coronary arteries. Experts note that myocardial infarction most often affects the male half of the population. If previously the conventional age of patients with myocardial infarction was 55-60 years, today cases of such pathology in young people are increasingly being recorded. The risk of death from myocardial infarction is very high. A patient with myocardial infarction requires urgent hospitalization in the intensive care unit. The life of the victim will depend on how quickly he receives the necessary treatment.
Main causes of myocardial infarction
There is a risk group - a population whose likelihood of developing myocardial infarction is higher than the rest of the population. It includes:
- men over 50 years old.
- hypertensive patients.
- smokers and alcohol abusers.
- overweight.
- persons leading a sedentary lifestyle.
- persons who have previously had a heart attack.
The main cause of myocardial infarction
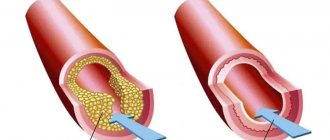
It is considered to be a narrowing of the lumen of the coronary arteries caused by atherosclerotic changes. Increased blood clotting leads to the formation of blood clots that disrupt blood circulation in the heart muscle. The tissues of a vital organ suffer from a lack of nutrients. Myocardial infarction can be triggered by severe emotional and physical stress, the presence of coronary heart disease or angina, as well as diabetes, obesity, addiction to alcoholic beverages and smoking.
Rehabilitation after a heart attack
Rehabilitation is carried out to restore normal heart function and improve health. The rehabilitation program is developed taking into account the emotional and physical condition of the patient. It involves control over risk factors for a recurrent heart attack, lifestyle modification, and psychological assistance.
Restoring quality of life after a heart attack
This part of the rehabilitation program is aimed at restoring normal levels of functional health. To do this, your doctor may recommend:
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- following a diet if you need to lose weight or control high blood pressure;
- moderate physical activity. The quantity, intensity and complexity of physical exercises are increased gradually;
- drug therapy: it is possible to continue taking antiplatelet drugs, ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, statins for some time;
- reducing stress levels;
- control of concomitant diseases, prevention of their complications.
In consultation with your doctor, additional treatment programs can be used during rehabilitation after a heart attack. New technologies can be used in recovery after a heart attack, such as stem cell treatment.
Psychological support after a heart attack
A heart attack is life-threatening and can cause severe psychological reactions. If it is normal, the person maintains control over emotions, but may experience fear of a second heart attack or death. He worries about the consequences of a heart attack, may be prone to caution, and the feeling of fear can be quite strong. For rehabilitation in this case, consultations with a cardiologist, psychological support, and gradual restoration of health are sufficient.
With a pathological reaction to a heart attack, an anxious, depressed, depressed, and tense state may develop. It has a bad effect on your well-being: sweating, rapid heartbeat, and insomnia. The reaction may be depressive-hypochondriacal. This means that a person becomes overly suspicious, he is too focused on the state of his health. Hysterical manifestations are possible in behavior after a heart attack: demonstrativeness, egocentrism, constant attempts to attract attention to oneself.
If a pathological reaction develops, the rehabilitation program is supplemented with psychotherapy. It is possible to prescribe sedatives and tranquilizers that will help stabilize the mental state. Without psychological rehabilitation, the condition may worsen: psychosis, severe behavioral disorders, and night wanderings are possible (in older people).
Stages of the disease and main signs of myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction goes through several stages in its development. The duration and severity of each depends on the size of the lesion, the condition of the blood vessels, concomitant diseases and complications, as well as the correctness of the chosen treatment tactics. There are acute, subacute periods, periods of scarring and post-infarction periods. Many patients noted that the acute period was preceded by some signs of unstable heart function - angina pectoris, arrhythmia.
Acute period
can last up to 10 days. This is the most difficult time for the patient, when all sorts of complications arise and the likelihood of death is quite high. A characteristic clinical picture of the acute period of myocardial infarction is severe pain in the chest area radiating to the left shoulder, collarbone, neck, ear, and shoulder blades. The sensations of spasm can be different - cutting, stabbing, pressing, burning. This condition during myocardial infarction lasts from thirty minutes to several hours. An attack during myocardial infarction occurs in waves. The pain may increase or decrease. It is impossible to stop them with nitroglycerin. At the same time, during myocardial infarction, the patient experiences severe weakness, a feeling of lack of air, and anxiety. Pallor of the skin, cyanosis (acrocyanosis) of the nasolabial triangle, arrhythmia, and profuse sticky sweat are also noted. Possible increase in blood pressure.
Subacute period of myocardial infarction
characterized by the disappearance of pain. Their preservation indicates the addition of pericarditis (inflammation of the outer lining of the heart). Necrotic processes in the area of inflammation can cause fever with a rise in body temperature. The patient is concerned about persistent low blood pressure.
Scarring period
in case of myocardial infarction, it is characterized by gradual healing of the affected area through the formation of scars. The duration of the process ranges from several weeks to several months. The patient's condition improves significantly. Painful symptoms disappear.
Post-infarction period
– time for recovery and return to normal life. It is recommended to avoid moving heavy objects on your own, give up alcohol and smoking, follow a diet, monitor your body weight, monitor your pulse and blood pressure, and avoid prolonged exposure to the sun.
It is important to know that there are atypical forms of myocardial infarction, in which the signs of a life-threatening condition are not always obvious. They make diagnosis and timely provision of medical care difficult. Among the most common:
Sign up for a test for myocardial infarction
Make an appointment
Can the pressure go down?
Can you have a heart attack with low blood pressure? Yes, because during an attack a painful shock develops, which is accompanied by collapse (this condition is characterized by pathological narrowing of blood vessels, including the brain, and a lack of oxygen supply). In such a situation, a person loses consciousness, and blood pressure drops sharply.
Low pressure readings with a rapid pulse indicate an increase in the Algover shock index - this aggravates the picture of the attack and often leads to death due to the centralization of the blood supply. Initially, the heartbeat simply increases, but then tachycardia with a decrease in cardiac output is replaced by uncontrolled contraction of the atria. Ventricular fibrillation develops, which is considered a life-threatening condition.
Complications of myocardial infarction
In the first hours of myocardial infarction, various complications may arise that aggravate the patient's condition. This is the appearance of an aortic aneurysm, myocardial rupture, cardiogenic shock, cessation of cardiac activity (asystole), pulmonary edema. The consequences of a heart attack can accompany the patient for life. These are heart rhythm disturbances, cardiosclerosis and other problems associated with disruption of the cardiovascular system. Experts do not guarantee absolute recovery after a heart attack and recommend following all the instructions of a cardiologist in order to avoid a relapse. The next attack threatens the appearance of a new area of necrosis. It is almost impossible to compensate for such consequences for the heart.
How to recognize an impending heart attack
Doctors understand a heart attack as damage to the heart muscle caused by blockage of the heart artery and deterioration or complete cessation of blood supply to the organ. In such a situation, if the attack is not stopped and normal blood flow is not restored, myocardial tissue will begin to die 30 minutes after the first signs of a heart attack.
In addition to thrombosis of the artery, the attack occurs against the background of its spasm, stratification and penetration of a foreign body into the cavity of the capillary (for example, particles of a tumor). A heart attack is caused by various reasons, but the main ones are obesity, hypertension, heredity, smoking and alcoholism, diabetes, frequent stress, and lack of physical activity.
The risk of developing an attack is higher in people with elevated blood cholesterol levels, diseases of the cardiovascular system, and also after reaching 65–70 years of age. Specific signs of a heart attack include severe pain in the left side of the chest, prolonged signs of angina, panic attacks, cold sticky sweat and shortness of breath. The pain is burning in nature, and an attack of angina pectoris is not controlled by taking Nitroglycerin.
The attack can last two hours or drag on for a day, so at the first symptoms you need to seek medical help.
There are several types of heart attack:
- typical - its symptoms have already been described, it occurs in most cases;
- gastralgic – abdominal pain predominates, overshadowing other symptoms;
- asthmatic – manifested by severe suffocation;
- arrhythmic - it is characterized by a persistent change in the rhythm of heart contractions, which is life-threatening;
- cerebral - resembles a stroke, often occurs against the background of cardiogenic shock;
- asymptomatic - after suffering this type of heart attack, the victim can find out about it only during an ECG during a routine examination by a cardiologist.
It will probably be difficult or impossible to recognize an atypical heart attack on your own - a quarter of patients do not complain at all about squeezing and burning pain in the chest, which complicates timely diagnosis. The main problem with an asthma attack is that discomfort in the heart is masked as an asthma attack, which makes it difficult for doctors to immediately suspect a heart attack. When you press on the sternum and develop sharp pain, the diagnosis can speed up.
Diagnosis and treatment of myocardial infarction
In addition to the clinical picture of myocardial infarction and taking a detailed medical history, a number of additional studies are used to confirm such a serious diagnosis:
If you suspect a heart attack, you must call an ambulance for urgent hospitalization in the cardiac intensive care unit. A patient with myocardial infarction is prescribed strict bed rest, rest and dietary nutrition with the exception of foods that excite the nervous and cardiovascular systems. Therapy is aimed at relieving pain, eliminating arrhythmias and heart failure, restoring normal blood circulation and combating the formation of blood clots. For this purpose, analgesics, neuroleptics, antiarrhythmic drugs, and thrombolytics are used. The list of medications is individual for each patient. It corresponds to the extent of the current disease, the general well-being of the patient and the presence of associated complications. In addition to medications, according to special instructions, surgical treatment methods are used - bypass surgery, excision of an aortic aneurysm, implantation of pacemakers (a device that sets the correct heart rhythm).
Diagnostics
In case of a heart attack, the diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture, the results of electrocardiography and laboratory diagnostics. A heart attack develops quickly, and therefore, if its symptoms appear, you should immediately call an ambulance. Later, when the condition is stabilized, you will need to undergo extensive diagnostics with a cardiologist.
Diagnostic signs of a heart attack are:
- long-lasting chest pain that lasts more than 30 minutes (can be felt as a burning sensation, squeezing);
- leukocytosis and increased ESR in the results of a clinical blood test;
- increased levels of sialic acids, fibrinogen and the presence of C-reactive protein in a biochemical blood test;
- the presence in the blood of markers of ischemic necrosis, cardiac muscle (troponin).
Differential diagnosis may be of some importance during a heart attack. Usually, myocardial infarction is easy to distinguish from other diseases accompanied by pain in the heart (intercostal neuralgia, angina pectoris, pulmonary embolism, pleurisy and others). With an atypical course of a heart attack, diagnosis may become more complicated. The abdominal form can be similar to pancreatitis, peptic ulcers or food poisoning, and the cerebral form can be mistaken for a stroke.
Cost of consultation for myocardial infarction?
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Initial appointment with a cardiologist | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a cardiologist | 1500 rub. |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner | 1500 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment (drawing up an individual treatment regimen) | 1500 - 3000 rub. |
All our services and prices
Prevention of myocardial infarction
Despite all the efforts of modern medicine, mortality from heart attacks will continue to remain quite high. To reduce the likelihood of this pathology occurring, you need to know how to prevent the disease. Expert recommendations:
Sign up for a test for myocardial infarction
Make an appointment
Treatment
Treatment requires hospitalization. Until the condition becomes stable, the person remains in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit. Then he is transferred to the hospital to complete the main stage of therapy. You need to seek medical help and start treatment as quickly as possible. This will improve the prognosis, simplify rehabilitation, and reduce the risk of serious consequences.
Drug treatment
For cardiac infarction, drug treatment is carried out in the following directions:
- anesthesia. For mild pain, analgesics are used. In case of severe pain, in case of pain syndrome, which is accompanied by anxiety, a feeling of fear, sedation and analgesic drugs can be used;
- restoration of blood flow using thrombolytic therapy. It starts immediately and should be carried out within the first 90 minutes after seeking medical help. If pain and changes in the electrocardiogram persist, therapy is continued for 24 hours. Thrombolytic therapy is carried out with caution, taking into account the risk of possible bleeding and other contraindications.
Additionally applicable:
- acetylsalicylic acid. Accelerates the destruction of formed blood clots, improves blood flow;
- heparin. Administered intravenously, it helps restore arterial patency and normalize blood flow;
- beta blockers. Used after completion of thrombolytic therapy and reduce the risk of recurrent myocardial infarction;
- ACE inhibitors. They help normalize blood flow, reduce the load on the heart, and help reduce mortality. They are used taking into account the risk of a possible decrease in blood pressure.
Drug treatment for myocardial infarction is prescribed by a cardiologist, taking into account possible contraindications, health status, and the risk of complications.
Surgical intervention
Surgery for myocardial infarction is aimed at increasing coronary blood flow. To do this, two types of operations are used:
- coronary artery bypass surgery. The narrowing of the artery is bypassed by installing a shunt, creating a new “path” for blood flow;
- percutaneous coronary intervention. Interventions that allow you to restore the patency of the coronary artery. To do this, stenting is performed. It involves the installation of a stent, an intravascular prosthesis that helps restore the lumen of the artery in places of its atherosclerotic narrowing.