- What symptoms of a microinfarction do women experience?
- What symptoms of a microinfarction do men experience?
- General signs of microinfarction
- Causes
- What complications does a microinfarction lead to?
- How to act if you suspect a small focal infarction
- Therapy
- Prevention for people with heart disease
- General methods of prevention
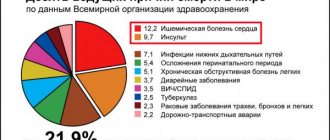
“Microinfarction” is the popular name for the disease - small-focal myocardial infarction. Often the symptoms of the disease are attributed to fatigue or a cold, so many do not attach importance to the ailments they experience during an attack.
The cause of myocardial infarction is disruption of blood flow to the heart muscle due to a blood clot that blocks a coronary artery.
A heart attack can be recognized by chest discomfort, fever, weakness and aching bones.
What symptoms of a microinfarction do women experience?
The disease is very “insidious”, since the symptoms of a microinfarction in women are not always noticeable. Because of this, the diagnosis is made after the fact when other diseases occur.
One of the first symptoms is sudden chest pain. Pain may be present in the left side of the shoulder girdle, shoulder blade and jaw.
According to statistics, women are less likely to pay attention to the symptoms of a heart attack, as they are less sensitive to pain. Also, microinfarction often goes unnoticed by patients over 55-60 years of age and diabetics.
Post-infarction state
After the symptoms of a microinfarction subside, the patient’s condition stabilizes, and he is discharged from the hospital. The complex of symptoms and complications that can develop after the first heart attack is called the post-infarction state. During the recovery period, there is a high probability of developing a second heart attack.
The most common manifestations of the post-infarction state:
- Dressler's syndrome. Develops 2-6 weeks after MI. The typical form is characterized by various combinations of pericarditis, pleurisy, pneumonia, and polyarthritis. The atypical form is characterized by inflammation of the joints, skin lesions, shortness of breath, cough, and symptoms of peritonitis.
- Post-infarction angina. Attacks of chest pain occurring 1-14 days after a heart attack. Dangerous due to the possibility of developing a new MI.
- Chronic heart failure. Develops with multiple or extensive heart attacks due to the inability of the heart muscle to cope with the current load. Its characteristic symptoms: shortness of breath, swelling, weakness, fatigue.
What symptoms of a microinfarction do men experience?
Men experience microinfarction less often and usually do not endure it on their feet. The first sign is chest pain, however, unlike women, men feel radiating pain in the abdomen. There may be a sensation of a foreign object in the chest. In men, the symptoms are more pronounced. During an attack, the patient may experience cold sweat, increased anxiety, bluish lips and an increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees.
Despite the fact that the risk of a small-focal heart attack is lower in men, the likelihood of encountering a real heart attack in the stronger sex is higher, since they are more susceptible to stress.
Characteristics of the pathology
Fine-focal damage to myocardial cells followed by necrosis occurs as a result of:
- incomplete closure of the lumen of the vessel;
- the presence of collateral blood flow pathways;
- complete blockage of small arteries.
All these factors lead to subtle changes that rarely lead to complications. But with a repeated attack or disruption of the patency of several small-caliber vessels at once, the pathology can develop into a large-focal process with severe symptoms and serious consequences.
There are two types of microinfarction: intramural (located deep in the myocardium and does not affect the inner and outer layers) and subendocardial (on the inner lining of the heart). In the first case, a negative T wave is recorded on the ECG in the area of the disorder. In the second, the ST segment shifts below the isoline, as can be seen in the photo:
General signs of microinfarction
Since the symptoms of a microinfarction can easily be confused with a regular illness, it is important to pay attention to the appearance of several signs at the same time.
What symptoms indicate a microinfarction:
- increased temperature, which causes necrosis of cardiac tissue;
- feeling of pain and aches in the joints;
- dizziness, weakness, possible loss of consciousness;
- swelling;
- sudden pain in the chest, radiating to the stomach, shoulder, shoulder blade;
- the appearance of shortness of breath, acute lack of air;
- pain in the solar plexus area;
- cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, lips.
Usually the attack lasts 40 minutes, and if no serious consequences occur, the symptoms go away. But this does not mean that they can be ignored. If signs of a microinfarction appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
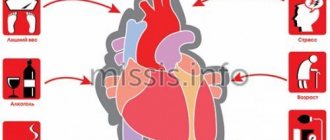
Causes
In 95% of cases, myocardial infarction is associated with blockage of an artery by a blood clot. The cause of illness is a lack of oxygen and nutrients in the heart muscle.
The supply of oxygen in the heart cells lasts for 10 seconds. Over the next 30 seconds, the muscle remains viable, after which the pathological process begins. 3-6 hours after the onset of the attack, the heart muscle in the damaged area dies. If a small area has died, then the infarction is considered small-focal.
The clinical picture of the disease is varied, which makes diagnosis difficult, and it can be difficult for specialists to confirm the disease in a short time.
The diagnosis is based on 3 indicators:
- medical history, complaints of pain typical of a heart attack;
- ECG indicators;
- results of a biochemical blood test.
If the doctor has doubts, he may prescribe additional studies, for example, identifying the lesion using the radioisotope method.
Case from practice
A 54-year-old woman came to the clinic with complaints of weakness and nausea.
The problem was associated with malnutrition. During the interview, it turned out that she had been experiencing angina pectoris for 10 years; attacks occurred several times a month and were relieved with Nitroglycerin. The ECG shows signs of acute ischemia along the lower wall of the left ventricle, without the formation of a Q wave. Diagnosis: Small focal infarction.
The woman completed a full course of treatment in hospital, her condition improved, and she was discharged under the supervision of a local cardiologist. Recommended: following a diet, taking Aspirin Cardio, Metoprolol, Atrovastatin.
How to act if you suspect a small focal infarction
The first thing to do is call an ambulance. Pre-medical care for the patient consists of creating conditions of maximum comfort in order to alleviate the condition.
The patient needs to take a lying or semi-lying position, ensure a flow of fresh air into the room (avoid drafts). Eliminate light and sound stimuli. If necessary, remove the patient from restrictive clothing. For medications, you can use nitroglycerin (dissolve under the tongue) or Corvalol (30-40 drops).
Rehabilitation activities
Rehabilitation begins in the hospital.
Initially, the patient begins to move the arms, eyes and upper body in a supine position, as bed rest is indicated. After about 5-8 days, the patient can slowly get up and move around. After a person is discharged from the clinic, he should go to a specialized medical and recreational facility for further recovery.
Rehabilitation includes the following activities:
- Physical therapy under the strict supervision of an instructor. The loads are initially minimal, but over time they gradually increase. An individual complex is developed for each patient. After completing rehabilitation in a sanatorium, the patient will have to do the same gymnastics at home for a long period of time. Swimming, massage and an exercise bike help very well.
- The patient must follow the diet prescribed by the doctor after discharge from the hospital. Basically this is diabetic table number 10.
- A person should completely eliminate the consumption of alcoholic beverages and quit smoking.
- Every day you will have to take walks in the fresh air. Every day the instructor will add a few meters. As a result, a person will be able to easily walk 2 or more kilometers.
- During the rehabilitation period, drug therapy is not canceled. Unfortunately, the patient will be forced to take medications for quite some time, but this will ensure a full recovery. These are mainly statin and thrombolytic drugs.
Therapy
The patient is taken to intensive care, where complex therapy is carried out. When treating a heart attack, the speed of reaction is very important: the faster the patient gets to the hospital and receives proper care, the higher the chances of a positive outcome and the absence or minimum number of complications.
Doctors use drugs that help dissolve a blood clot, painkillers, and medications to lower blood pressure and reduce blood circulation. Also, as part of treatment, it is necessary to achieve a decrease in heart rate, which is achieved by taking beta-blockers.
The rehabilitation period after inpatient treatment is no less important than the therapy itself. The recovery period lasts up to 6 months. The patient may be prescribed medications that must be taken constantly. Also, to maintain normal condition, it is necessary to follow a diet, in particular, eliminating fatty and fried foods from the diet, as well as stopping smoking and drinking alcohol.
If the doctor's recommendations are followed, the patient can count on a long and fulfilling life.
Consequences
The main thing is to recognize a mini-heart attack in time and undergo therapy to avoid a large one, which often follows a small one after some time. You may not be too worried about the micro-infarction you suffer while on the run, but an echocardiogram will definitely show that it happened. At the same time, the risk of 2 micro-infarctions remains, or that the heart is extensively affected. You urgently need treatment.
- The first signs of diabetes in women after 40 years: photos and symptoms
There are no universal solutions in such situations. Therapy includes several main areas.
- Medicines from the group of antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs. They are used in combination or separately from each other. After an attack, the patient must take them regularly throughout his life. They are needed to prevent recurrent attacks.
- If the lipid spectrum has been disturbed, a course of statins is prescribed. They help fight atherosclerosis.
- Taking diuretics and drugs to lower blood pressure is important for hypertension. Used as an auxiliary therapy.
- The problem of cardiac arrhythmia is eliminated with appropriate antiarrhythmic drugs. Prescribed individually if there are relevant violations.
- Symptomatic remedies. Here the doctor takes into account what diseases and symptoms accompany the patient, selecting appropriate medications or giving recommendations for their elimination.
Having survived a micro-infarction, people have to keep the situation under control throughout their lives. A large list of medications prescribed by the doctor is recommended for them to take as prescribed. Any deviations from the instructions can result in a new attack, but this time it will be extensive. Most people, after a blow, are aware of the danger of recurrent pathology. Therefore, we are always and everywhere ready for relapses. To do this, do not forget to take with you medications that can save your life or minimize the consequences of a new attack.
Prevention measures
After MI there is always a risk of a second attack. To prevent it, you must follow some rules for prevention. There is nothing complicated about them, but they can cost a person his life.
- Change your approach to nutrition. Heavy, coarse, fatty and unhealthy foods are a source of increased stress on the cardiovascular system. By refusing such food, you will normalize your condition and allow your body to work as efficiently as possible. It is better to consult a nutritionist individually about your diet.
- Don't lead a sedentary lifestyle. Yes, you will have to forget about sports achievements and world records. But you can’t completely give up physical activity. Special massage, exercises and physical therapy will help maintain muscle tone and provide the heart with oxygen. This will have a positive effect on the state of the cardiovascular system, plus it will improve your mood.
- Follow the prescribed course of preventive medications. Some are taken in courses with breaks, others need to be taken regularly, trying not to miss the time for taking it.
- Healthy sleep, protection from stress. Simple but very effective tips for people after micro-infarction attacks.
Compared to a major attack, the prognosis after a microinfarction is more favorable. But statistics indicate that about a third of patients after MI experience a relapse within the first year
Therefore, it is extremely important to improve your health as much as possible and adhere to all the rules that your doctor told you about. Although microinfarctions are less dangerous, this pathology affects the heart muscle and leads to partial necrosis
Therefore, it must be treated extremely carefully and seriously.
Subscribe, leave comments, ask questions and don’t forget to tell your friends about us!
- Precursors and signs of a heart attack, first aid and treatment
Prevention for people with heart disease
People with chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system need to undergo an annual medical examination in order to receive timely and adequate medical care.
As a preventive measure, patients with coronary heart disease are prescribed an assessment of the condition of the coronary arteries, during which the degree of narrowing and localization of atherosclerotic plaques will be identified. If necessary, the vessels are expanded from the inside using angioplasty. Another method is to implant a metal frame into the artery. It will prevent the passage from narrowing.
Some patients are prescribed coronary artery bypass grafting. During the operation, additional vessels are transplanted to the aorta, which go around the narrowing site and create additional pathways for blood flow to the heart.
What to take for treatment
The immediate goals of treatment are to relieve pain and improve circulation and heart function. Long-term goals of microinfarction treatment: prevention of complications, management of risk factors, reduction of the likelihood of recurrent heart attacks. A combination of medications and surgical procedures is used to achieve these goals.
Depending on the patient's condition, medications for acute and/or long-term therapy may include:
- thrombolytics, which dissolve a blood clot that has blocked an artery;
- analgesics, including narcotics, to relieve pain;
- nitroglycerin, which temporarily dilates the coronary arteries;
- antiplatelet drugs to prevent future blood clots;
- beta blockers, which slow down the pulse, reduce blood pressure and stress on the heart;
- ACEIs that improve blood circulation;
- angiotensin receptor blockers that control blood pressure;
- statins, which reduce the amount of cholesterol in the blood and stabilize atherosclerotic plaques.
If technically possible, angioplasty can be performed, during which a thin tube, a stent, is inserted into the affected coronary artery. If a patient has suffered many microinfarctions and constantly has angina attacks, he may be offered coronary artery bypass surgery.
- Dyspnea in heart failure, the treatment of which is complicated by the underlying disease