What awaits a conscript diagnosed with tachycardia? Let's try to figure it out in this article. If you feel your heart racing, this does not mean that you are seriously ill. In completely healthy people, tachycardia manifests itself as a reaction to the release of adrenaline into the blood and due to increased excitability of the nervous system. Normally, elimination of the action of stimulating factors leads to the disappearance of increased heart rate and the return of heart rate to normal values. Can they be drafted into the army with tachycardia and how can they be released from service? It is impossible to unequivocally answer the question of what awaits a conscript diagnosed with sinus tachycardia - exemption from conscription or military service, because this is not an independent disease, but a symptom (sign) of pathology of the cardiovascular system or other organs and systems.
In general, tachycardia is an increase in heart rate from 90 beats to 160 beats per minute; it is easy to determine when measuring the pulse. The following types of tachycardia are distinguished:
- physiological is a normal reaction of the body in response to fear, stress, taking coffee and some medications, and physical activity. This type does not require examination or treatment and is accepted into the army.
- pathological is a manifestation of diseases and requires additional examination. The issue with the army will depend on the identified disease.
Categories of suitability for military service
There are 5 main categories of suitability for service.
| Category | Description |
| "A" | A conscript is fit to be sent to serve in any army without restrictions. |
| "B" | The conscript is suitable for military service with restrictions. |
| "IN" | A citizen is exempt from conscription in peacetime. To be added to the reserve. |
| "G" | Deferment (6 months - 1 year) for medical examinations or treatment. |
| "D" | A citizen does not belong to the draft. |
A military ID is issued to citizens who have been assigned categories “B” and “D”. It is worth noting that from the moment the medical re-examination is cancelled, there is no need to confirm and re-establish your military unfitness in the future.
Conscripts recognized as partially fit for military service (category “B”) are distributed among the troops, taking into account individual limitations and health conditions in accordance with the table of additional requirements for the health of citizens.
Diagnostics
Traditionally, arrhythmia is diagnosed by a cardiologist. This specialist must not only identify the disease, but also determine its etiology, type and degree of neglect. The following studies are used for this:
- ECG. This is a standard procedure that allows you to determine the possible causes of arrhythmia, monitor the frequency of ventricular contractions and record the heart rhythm.
- Daily Holter monitoring. This is a painless test that records the work of the heart and deciphers the data obtained on a computer. Such an examination allows us to identify hidden interruptions in the functioning of the heart that occur during excitement, walking, or rest.
- Thyroid examination. Used for differential diagnosis.
- Ultrasound of the heart.
- Exercise test.
Is the disease a contraindication to service?
Abnormal heartbeat can often indicate the presence of serious pathologies. Arrhythmia is divided into the following types:
- tachycardia - rapid heartbeat;
- bradycardia – slow heartbeat;
- extrasystole - extraordinary heart contractions.
Independent sinus arrhythmia most often is not a reason for determining unfitness, but the conscript has the right to undergo an examination, with which a temporary category “G” is assigned - a deferment for a period of 6 to 12 months. The final category of eligibility will depend on the associated abnormalities, frequency and severity of attacks.
As a rule, even if dangerous arrhythmic conditions are detected, you will not be able to immediately obtain a military ID. The conscript will be able to receive it after two or three calls with the same complaints. One of the determining factors will be the presence of old records of the disease in outpatient records.
What is a contraindication
If the arrhythmia occurs as a result of a complication of another disease of the cardiovascular system, there is a high probability that military service is contraindicated with the underlying disease. If attacks of arrhythmia are accompanied by persistent severe pain in the chest or obvious deviations of the vegetative-vascular system, the medical commission of the military commissariat is obliged to issue the conscript with an examination certificate to determine the root cause of heart rhythm disturbances.
Diseases that can trigger the appearance of arrhythmic syndrome:
- cardiac ischemia;
- hypertonic disease;
- heart defects of various types;
- rheumatism;
- cardiosclerosis;
- VSD;
- asthma;
- acute heart failure;
- diabetes mellitus of the first and second types;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- acute infections, etc.
Important! Most major diseases with concomitant arrhythmia and its complications (frequent attacks, acute pain, dysfunction of the heart, blockades) completely exclude the young man’s suitability for service.
If there are any complications of arrhythmia, it is necessary to report the symptoms to the medical commission. According to article No. 44 of the disease schedule, fitness categories “B” and “D” are assigned when:
- atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal arrhythmia with complications;
- polytopic extrasystole (with several ectopic foci).
What is not a contraindication
Those citizens who are at risk of developing functional complications are exempt from conscription, while the main types of arrhythmias are often not contraindications to service. If the diagnosed arrhythmia is not a consequence of an underlying disease of the cardiovascular system, the conscript will receive fitness category “B”.
Independent types of arrhythmias that are not grounds for disqualification :
- tachycardia, in which the pulse ranges from 90 to 140 beats per minute;
- bradycardia, the cause of which is not endocrine, cardiovascular or nervous system diseases;
- monomorphic extrasystole (with one epicentric focus).
Will arrhythmia become an obstacle to service in 2021?
Everyday life in the army, filled with increased physical and psychological stress, becomes a serious test for some.
For young men aged 18-27 years who have pathologies associated with cardiac activity, the question of fitness is especially relevant during the conscription campaign.
The disease is divided into different types, depending on the classification: the recruit will go along with the rest of the army or will receive a deferment.
What is taken into account when assigning a fitness category to a young man diagnosed with arrhythmia:
- the degree of the disease;
- frequency of recorded attacks;
- stage: persistent remission, exacerbation;
- undergoing the necessary diagnostics;
- detected concomitant diseases and complications.
It is worth noting that it will be possible to completely avoid service only in case of serious violations that are documented.
In any case, hoping to receive a non-conscription category, it is better for a young man to take care in advance of collecting medical certificates, extracts, research results, including an ECG.
Identifying heart problems in a conscript
During the medical commission, after a conscript complains of arrhythmia, the military commissariat issues a certificate of medical examination for a certain period. During the specified period, the conscript is obliged to undergo a full medical examination, provide the doctors with the issued certificate to fill out, and return to the medical commission with the results of the examination - the verdict and documents of all studies.
According to the act on identifying arrhythmia, the conscript must:
- register with his local physician with symptoms of arrhythmic syndrome;
- donate urine and blood for general analysis;
- register with a cardiologist;
- undergo a course of daily blood pressure monitoring by a therapist for 5-14 days;
- undergo an examination by an endocrinologist to identify endocrine diseases.
Based on the conscript’s complaints, the cardiologist should issue referrals for the following studies:
- An electrocardiogram (ECG) to monitor your heartbeat.
- ECG using Holter method – daily monitoring. Electrodes are placed on the chest for 24 hours while a portable device, usually kept in a small shoulder bag, continuously records an electrocardiogram. The interpretation of this study is carried out by a doctor and is provided in the form of a brief report with the main indicators.
- 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM). It is carried out to identify hypertensive or hypotensive diseases.
- Ultrasound of the heart area.
- Bicycle ergometry (VEM) is carried out to monitor performance during physical activity. This study is especially important because it will show the conscript’s tolerance to different degrees of load, on the basis of which it will be possible to draw a conclusion about his suitability for the loads of service.
After completing all the studies and submitting the report, the medical commission can immediately issue a verdict that the young man is subject to conscription if studies have shown that the detected arrhythmia does not pose a danger to his general health.
Otherwise, the conscript will receive a temporary deferment . During the deferment period, the conscript must undergo prescribed treatment, as well as constant monitoring of cardiac parameters. Indicators of arrhythmia must be noted within two to three calls for the arrhythmic syndrome to be recognized as stable. Before the final verdict (usually on the third conscription), the conscript may be assigned to undergo in-patient observation, in which all indicators must be confirmed.
Probability of avoiding service with arrhythmia
Except for cases where pronounced symptoms indicate a complex disease or the presence of concomitant diagnoses, evading military service is not so easy.
Attempts to mislead members of the medical-military commission are fraught with trouble: the law provides for serious punishment for “deviators,” ranging from impressive amounts of fines to criminal liability.
Verbal complaints about rapid rhythm without documentary evidence can be ignored and considered as a result of excitement. It is pointless to pretend in front of experienced doctors, and you should also not look for illegal ways to “slope” in the form of buying a military personnel or other dubious options.
Not wanting to undergo the tests of difficult everyday life in the army, a rational solution would be to turn to professionals in this field.
What troops can you serve in?
If a conscript with a mild form of arrhythmia is declared fit without restrictions, assignment to the troops will be made randomly.
If limited fitness has been assigned, next to the main category a number must be indicated indicating the group of troops to which this category applies. Categories “B” are as follows: “B-1”, “B-2”, “B-3” and “B-4”.
Arrhythmia almost always falls into the “B-3” category. This is the most extensive category of fitness, because it includes most conscription diseases without significant impairment of functions. With fitness category “B-3” they are called to:
- drivers of infantry fighting vehicles and armored personnel carriers;
- missile launch installations;
- internal troops of the Ministry of Internal Affairs;
- pipeline troops and other chemical work;
- control and operation of anti-aircraft missile systems.
Causes and risk factors
Before you find out whether someone with heart arrhythmia is recruited into the army, it is important to note that the reasons for this deviation in a person can be different (related to heart disease or arising from other diseases).
Most often, the development of this deviation in patients is facilitated by:
- Heart diseases. This may be myocarditis, an organ malformation, a history of heart attack, or coronary heart disease.
- High blood pressure.
- Abuse of strong alcoholic drinks and frequent drinking of coffee.
- Smoking.
- Stress and chronic nervous overstrain.
- Impact of a number of medications.
- Diabetes.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Excess weight.
Procedure for passing a medical examination
The pathological form of tachycardia is one of the common problems encountered in young men of military age.
A conscript who knows that he has health problems must come to the military registration and enlistment office, bringing with him the entire list of documents confirming the presence of the disease. Important documents include certificates, clinical tests, examination results, confirmation of periodic visits to the doctor.
The examination at the military registration and enlistment office is carried out in accordance with the available documents. If controversial issues arise, as well as in the absence of the necessary medical certificates and the conclusion of the attending physician, the conscript is sent for additional examination. The results of the re-examination and examination are considered final for the medical commission to make a verdict.
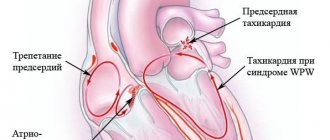
Paroxysmal tachycardia
Attacks always occur suddenly and stop just as suddenly. The rhythm remains correct, but the heart rate is around 150-300 beats per minute.
There are 3 forms:
- Atrial (supraventricular) – occurs quite often, can occur during stress, feelings of fear and shock;
- Ventricular (the most dangerous form) – occurs when the functions of the heart muscle are impaired;
- Nodal.
Paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia, like ventricular fibrillation, is classified as suitable for CGM. If a conscript has frequent paroxysms of supraventricular tachycardia (3 times a year or more often), then the NGI fitness category is assigned.
Diagnostics includes: electrocardiography (ECG), daily Holter ECG monitoring, echocardiography (Echo-CG).
Ventricular fibrillation is characterized by chaotic and irregular contraction of the heart muscle (140-600 beats per minute). It may be a complication of myocardial infarction or a continuation of the development of paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia.
To confirm the diagnosis and fitness category, the conscript should contact a specialist. In the case of tachycardia, for the possible detection of a disease that could result in a rapid heartbeat.
What is tachycardia, its types
In medicine, tachycardia is understood as a rapid heart rate that exceeds 90 beats in 60 seconds if a person is in a lying position, or 100 beats when a person is standing.
There are pathological and physiological tachycardias. The first talks about pathological changes in the body, the nature of which is important to find out in order to help a person in a timely manner. Physiological tachycardia is natural for anyone, because it shows the presence of a reaction to various external stimuli.
Physiological tachycardia does not exempt you from service, but pathological tachycardia provides grounds for a more thorough examination of the health of a young man applying to become a recruit in the army.
The final decision is made depending on what diagnosis is made by cardiology doctors.
This is the only way to 100% count on being written off to reserve.
Problems with exemption from the army may arise for those young people who previously, before the medical examination, did not consult a doctor because they had a disease. The position of the conscript against the opinion of the military commissariat may turn out to be weak if the young man does not have documents from the medical institution where he was observed before passing the commission from the military registration and enlistment office.
If this is the case, then it is better for the conscript to seek help from lawyers in order to undergo an examination with doctors recommended by legal experts before the medical examination so that they can make the correct diagnosis. With this diagnosis, the military commissariat will definitely send the conscript for additional examination in order to confirm it and assign the failed recruit a fitness category and write him off to the reserve.
Cases where the rights of conscripts declaring their diagnosis at a medical examination are violated occur in judicial practice. If the interests of a young man are represented by a lawyer, the lack of documents proving early visits to a doctor will not be an obstacle to obtaining a military ID. It is only important to have time to take advantage of this opportunity to protect your civil rights.
Diseases and secondary arrhythmia
It should be noted that often arrhythmia is a sign of developing dangerous diseases that can cause release from service. Such pathologies may be:
- diseases of a rheumatic nature;
- disruption of the heart (including acute heart failure);
- heart disease;
- mitral valve prolapse;
- chronic myocardial pathologies;
- endocrine and hormonal disruptions.
In this case, the conscript should undergo a full examination and identify the cause of the arrhythmia. The diagnostic results must be documented and presented during the medical examination at the military registration and enlistment office.