With the advent of pregnancy, a radical restructuring of the main and secondary processes of life occurs in a woman’s body. From now on, the work of all structures of the female body is aimed at providing comfortable conditions for the development of the fetus. Also, adaptive changes, the dynamics of which can be tracked based on the results of clinical analysis, occur in the environment of blood cells. In the article we will dwell on the question of how neutrophils behave in the blood during pregnancy.
Neutrophils are the most numerous type of leukocytes. During the gestation period, the leukocyte formula is mobile: for the body of a pregnant woman this is a variant of the norm. The same indicators in a normal (non-pregnant) state of the body usually indicate the presence of pathology. However, under a certain set of circumstances, a shift in leukocyte counts in the blood of the expectant mother is a symptom of a particular disease. Doctors determine the nature of these changes through a comprehensive examination of the pregnant woman.
What it is
WARNING!
The information on the site is provided for informational purposes and cannot be used to make a diagnosis or make treatment decisions. Neutrophils are a group of leukocytes that have antimicrobial activity. Determining the number of these blood cells during pregnancy helps confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis.
This group of white blood cells is formed from progenitor cells produced by the bone marrow. During growth, the bodies go through 2 stages, at each stage they acquire a specific subtype.
- Metamyelocytes are immature cells that do not leave the bone marrow. If it penetrates into the general bloodstream, the doctor may suspect an acute inflammatory process or leukemia.
- Band neutrophils - doctors call them “young” defenders of the body of a pregnant woman and not only.
- Segmented neutrophils are the mature form of blood cells. Based on the name, it is clear that they are subject to division into segments.
The life of this type of leukocyte lasts no more than 14 days. They remain in the bone marrow for 6 days. After this, mature white blood cells are released, gradually spreading throughout the body. 10 hours after release, they begin to die.
Neutrophils during pregnancy: stages of cell maturation
There are 6 stages of maturation in the neutrophil life cycle. From the first to the fourth stage, “young” leukocyte cells are found in the bone marrow. In the period from the fifth to the sixth stage, neutrophils, already “old”, move into the bloodstream, where they fulfill their immediate purpose. If cells of the first four stages of development are found in the blood, then there is no doubt: the body is fighting a severe infection or there is a serious disorder in the function of hematopoiesis.
Types of neutrophils by stage of maturity:
- myeloblasts (primary fractions of neutrophils);
- promyelocytes (cells become overgrown with granules);
- myelocytes;
- metamyelocytes;
- band granulocytes;
- segmented granulocytes.
Neutrophils of the last two stages are the “oldest”. Segmented cells are the first to react to pathogen cells and usually cope with the danger themselves. But if the infection is severe, the segmented neutrophils are joined by band cells, and after some time, immature myelocytes and metamyelocytes. There are no last two types of neutrophils in the blood of a healthy person, since they fully mature in the bone marrow.
For reference. Rejuvenation of the blood, that is, the presence of immature neutrophils in it, is called a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left. When the leukogram shifts to the right, the blood ages: an increased content of mature segmented cells is observed in it.
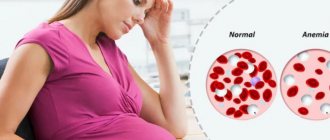
Norms and deviations
When a pregnant woman feels normally, the following ratios are observed in the plasma.
| Name of cells of the leukocyte group | Quantity (%) |
| Segmented | 48 – 72 |
| Lymphocytes | 19 – 37 |
| Monocytes | 3 – 11 |
| Rod | 1 – 6 |
| Eosinophils | 1 – 5 |
| Basophils | 0,5 – 1 |
Increased segmented neutrophils during pregnancy do not always indicate an inflammatory process. When other studies show the norm, this means that the woman is healthy.
Deviations of leukocytes from the norm are often detected during pregnancy. Pathological microorganisms negatively affect the mother’s body, weakened by pregnancy, affecting the child as well.
What is the essence of neutrophilia?
If neutrophils are elevated during pregnancy, this means neutrophilia. This condition is considered normal for a woman if the deviations are not too large from the norm. The organism that develops in utero is initially foreign, in which case the immune system begins to actively produce killers - leukocytes - in huge quantities. This process must be regulated by a special hormone - prolactin. To avoid untimely birth or fetal loss, a woman must constantly monitor her health and be under the close supervision of specialists.
Reasons for the increase
The toxic effect of food, which is observed when consuming low-quality or expired products, affects the results of the study. In cases of food or chemical poisoning, the indicators are increased.
Also, increased neutrophils during pregnancy can be a consequence of negative factors.
- Drinking alcoholic beverages. With systematic consumption of alcohol, the internal organs of the fetus may have an abnormal structure.
- Infectious damage to the body. During gestation, many pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively multiply. Streptococci and staphylococci cause inflammation. Infection occurs only from person to person.
- Sexually transmitted infections. Viruses cause inflammation of the genitourinary system. This is revealed by laboratory tests. An STI test is taken several times during pregnancy upon registration and after 30 weeks.
- Incorrect dosage during vaccination. Women, unaware of their situation, can be vaccinated against infectious diseases. The doctor may incorrectly calculate the dose and give the patient more than necessary. A large number of pathogenic microorganisms are suddenly released into the plasma. There are too many of them, and the body begins to produce protective cells.
- Necrosis of internal organs. Neutrophilic leukocytes, during the development of dead cells, are aimed at suppressing them. Because of this, the level of blood cells increases, as the research results will show.
If a woman has increased band neutrophils by several units during pregnancy, this does not indicate a disease. Elevated values within 10-15 values indicate the development of an inflammatory process.
Neutrophils are low during pregnancy: what does this mean?
The maximum permissible decrease in the level of neutrophils corresponds to 40%. The reasons for the decrease in these blood cells (neutropenia) are the following factors:
- exhaustion of immune system resources due to prolonged struggle with a serious inflammatory response;
- immunodeficiency;
- extensive damage to various organs and systems by fungal microorganisms;
- helminthic infestation or the presence of other parasites in the body;
- a gene mutation that results in hereditary neutropenia;
- frequent x-ray examination of the body, chemotherapy, interaction with irradiation equipment on duty;
- the presence of chemical toxins and poisons in the blood;
- unauthorized drug treatment without the knowledge of the doctor;
- the course of malignant processes in the red bone marrow.
Features of diagnosis for neutropenia
The presence of neutropenia obliges the expectant mother to regularly take blood tests. The dynamics of the level of neutrophils allows the doctor to judge the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment: if the number of protective blood cells increases, the therapy is selected correctly, otherwise the course of treatment will be changed.
It happens that laboratory tests show a decrease in neutrophils and a simultaneous increase in lymphocytes. This indicates the presence of a viral infection in the body. To find out the origin of the inflammatory process, a woman is prescribed a blood test for the total number of lymphocytes and their absolute content.
Consequences of low neutrophils during pregnancy
Neutropenia is not a disease, so this condition in itself cannot harm the fetus. The danger comes from a disease that causes a decrease in neutrophils. In this regard, the greatest threat to the intrauterine development of a child is posed by viral pathologies such as measles, rubella, and chickenpox. From their exposure, the fetus acquires various congenital diseases, anomalies and gene mutations. Under such circumstances, the woman is advised to terminate the pregnancy.
The next group of potentially dangerous factors during pregnancy are toxins. In case of food poisoning, special medications will help eliminate the malaise. The fetus will be protected from harmful toxins by the placental barrier. The situation is completely different in case of poisoning with salts of heavy metals and chemicals, since the placenta is not able to contain the attack of their breakdown products. As a result, the fetus runs the risk of developing various deformities, congenital malformations, and insufficient performance of some internal organs.
Treatment of low neutrophils during pregnancy
As part of the treatment of the root cause that caused the imbalance of leukocyte cells during pregnancy, the expectant mother is prescribed:
- Local preparations to eliminate signs of viral infection. Antiviral drugs are contraindicated for pregnant women.
- Sorbents to eliminate the consequences of food intoxication. At the same time, pregnant women are advised to drink plenty of fluids.
- In the presence of a tumor or serious damage to the red bone marrow, doctors cannot initiate active treatment, given the delicate position of the patient. If it is decided to continue the pregnancy and wait for the baby to be born, the expectant mother will undergo various laboratory tests until the birth, which will allow doctors to closely monitor the dynamics of the development of the disease.
Note! No matter what disease and no matter what drugs a pregnant woman is treated for, it is necessary to very carefully monitor the development of the fetus. Everything is important: how quickly he grows, whether his heart beats normally, whether his organs function correctly. Since the active components of some drugs are able to bypass the barrier in the form of a child’s seat, there is always a risk of harming the child. If the danger of therapy is confirmed, it is immediately canceled. Women usually begin direct treatment of diseases after pregnancy.
Changes in the balance of neutrophils during gestation are an important diagnostic indicator. Something has gone wrong in the body of the expectant mother, which her body is in a hurry to report by an instant “rearrangement” of blood cells. The sooner this or that symptomatic picture is deciphered, the faster the expectant mother will receive qualified medical care.
Reasons for the downgrade
With a significant decrease, doctors talk about the formation of neutrophilia during pregnancy. The diagnosis is made based on test results when 1.6*109 per liter or less is detected in plasma. The main reasons for the decrease in these leukocytes are:
- complicated viral and infectious pathologies (influenza, rubella, measles);
- bone marrow pathologies susceptible to serious drug therapy;
- blood diseases (forms of leukemia, anemia, etc.).
During pregnancy, women are required to report their health to their doctor every time. And if you feel unwell, you should visit the residential complex unscheduled.
Diagnostic methods
The first thing they do is take blood for ABS. This test reveals the number of cells per liter of plasma. The doctor compares the results obtained with normal values. Situations are considered severe when values exceed 20/109 per liter of blood.
Relative analysis is often prescribed. After the quantitative comes the qualitative: doctors analyze the number of immature cells. If they are detected, doctors may suspect a serious pathology that requires immediate treatment.
After the initial tests, additional tests are prescribed. They allow you to determine the reasons for deviations from the norm. It is important to exclude the presence of a toxic process in the body of the expectant mother. To do this, a urine test is performed, and rarely a venous blood test.
Neutrophils are increased during pregnancy: what does this mean?
If there is a marked increase in neutrophils, the pregnant woman is diagnosed with neutrophilia. Most often, the titer of leukocyte cells increases due to an increase in the number of segmented particles. And since neutrophils detect any potentially dangerous changes in a woman’s body, there are many reasons for this increase.
Why do abs neutrophils increase during pregnancy?
First of all, the number of protective cells increases due to infectious agents penetrating into the internal environment of the body: fungi, coccal flora, viruses, encephalitis infection. To secure their “territory,” neutrophils leave the bone marrow en masse and stop the source of inflammation. When the percentage of dangerous microorganisms decreases to the maximum permissible level, the number of neutrophils returns to normal.
Other factors that provoke a sharp change in the parameters of segmented cells include:
- destructive processes in tissues (burns, internal hemorrhages, bruises, bone fractures);
- surgical operations or surgical procedures of a diagnostic nature;
- tissue death as a result of gangrene, stroke, etc.;
- intoxication of the body of food, chemical or medicinal origin;
- diabetes;
- autoimmune diseases (eg, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis);
- formation of benign and malignant tumors;
- acute allergic reaction;
- hormonal therapy.
If there is a rapid increase in the number of band neutrophils, it means that the body “declares” war on the reactive inflammatory process. In such a situation, inflammation covers the tissues so quickly that mature cells cannot effectively stop it, so young band neutrophils are used.
The number of rod particles is increasing for the following reasons:
- neoplasms in internal organs;
- trophic ulcers;
- suppuration in subcutaneous, muscle or bone tissues;
- myocardial infarction;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- oversaturation of blood with carbon dioxide;
- loss of large amounts of blood;
- pronounced psycho-emotional experiences;
- pneumonia;
- skin diseases.
How is neutrophilia diagnosed?
To objectively assess the condition and number of neutrophils in a pregnant woman, an abs blood test is performed, which will display their number per 1 liter of blood. The reason for immediate treatment of the expectant mother is a condition when the abs neutrophil levels significantly exceed the permissible threshold and amount to 20 x 10⁹ per liter.
If necessary, the blood of the expectant mother is also subjected to a relative analysis, the result of which will show how many young neutrophils are in her body. If they are present in the blood, and even in large quantities, there is evidence of a serious pathology that requires immediate treatment.
To check whether a pregnant woman’s body is being exposed to a toxic attack, the diagnosis includes a urine test and a blood test from a vein. If there are signs of specific diseases, the expectant mother is also prescribed an ultrasound.
Consequences of elevated neutrophils during pregnancy
If the level of the body's protective cells does not exceed the upper limit of normal, the fetus is safe. In this case, such a picture only demonstrates an adequate response of the female body’s immune system to the birth of a child. However, if the indicators increase excessively, the likelihood of bleeding and elimination of the embryo increases. Only emergency treatment measures can save a pregnancy.
Treatment of elevated neutrophils during pregnancy
There is no specific treatment for neutrophilia, and there is not always an urgent need to correct this condition. If the reason why neutrophil counts exceeded the norm does not pose a great danger to the mother and fetus, all therapeutic measures are postponed until after childbirth, or even until the natural end of lactation.
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at eliminating the root cause, which led to changes in blood cell counts:
- To suppress the infectious process, antibiotics are used that are not able to penetrate the placenta to the fetus. The safest period for drug therapy is the 3rd trimester, when all the vital organs and systems of the child are fully developed.
- If there is a benign or malignant neoplasm in the body, women wait for the birth of the child or terminate the pregnancy immediately. Antitumor drug therapy has a teratogenic effect on the fetus.
- In the event of a burn or any injury, the actions of doctors are aimed at eliminating their destructive consequences.
- If endocrine abnormalities are detected in the expectant mother’s body, the dosage of medications that the woman most likely began to take before pregnancy must be adjusted.
Is treatment necessary?
Therapeutic measures prescribed for pregnant women depend on the reasons caused by the deviations.
- When the cell level is at the upper limit, there is no need for therapy. Thus, the mother's immune system responds to the development of the fetus. But with large deviations, medication support may be required.
- Therapy of infectious diseases. Antibacterial treatment is used. Medicines are selected taking into account the woman’s current situation. Antibacterial medications should not cross the placenta. Doctors recommend using this kind of treatment only at the onset of the 3rd trimester, when all the baby’s organs are formed.
- When a benign or malignant neoplasm is diagnosed, the woman is advised to terminate the pregnancy or have a premature birth.
- Therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating injuries after they have occurred.
- Control of endocrine disorders with the help of conventional medications that were used before conception. It is possible to adjust the dosage level.
Most medications can cause complications for the growth and development of the fetus or the woman's condition. Therefore, during treatment, ongoing diagnostic tests are carried out and the dosage of medications is adjusted.
During pregnancy, blood counts often change. An excess of neutrophils by a couple of units is a variant of the norm for the state of gestation. All methods of therapy must be agreed with the attending physician so as not to harm the fetus.