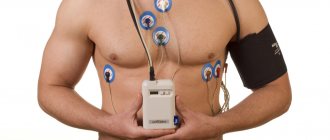
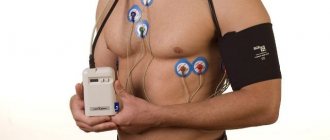
24-hour blood pressure (BP) monitoring is a modern research method. Such diagnostics takes into account the daily rhythm of a person’s blood pressure in his or her usual environment. The data obtained together provide a complete picture of the influence of behavioral factors on blood pressure and reflect the dynamics of the influence of antihypertensive drugs in patients receiving therapy for high blood pressure.
How does the device work?
The essence of the procedure is to measure blood pressure at certain intervals. The measurement takes place regardless of the patient’s activities and his wishes - only the doctor sets the time interval. On average, it ranges from 12 to 30 minutes during the day and every hour at night.
During the entire study, the patient fills out a personal diary throughout the day, in which he enters any changes in his state of health and any symptoms that have arisen. By comparing ABPM indicators (24-hour blood pressure monitoring) and diary entries, the attending physician makes an accurate diagnosis. The diary describes the state of activity, rest, and medications the patient is taking. All this data allows us to evaluate pressure drops in a person who is resting or playing sports.
Content:
- How does the device work?
- When is diagnosis prescribed?
- Contraindications to the procedure
- Preparation for the procedure
- Preparation of documents
- Carrying out the procedure
- Preliminary instructions
- Rules for the patient
- What can you learn using ABPM?
- Decoding the results
Blood pressure and activity are two dependent indicators. The basis of the method is the comparison of data that takes into account the patient’s usual activity. In laboratory conditions, the obtained blood pressure readings are unreliable. The procedure lasts for 24-48 hours, depending on the reasons why ABPM was prescribed. A device is fixed on the human body that automatically measures blood pressure.
Daily blood pressure monitoring - who is prescribed and why, interpretation of results
What is it and how is it done?
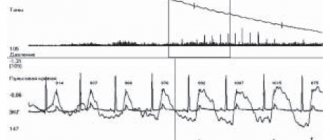
Daily blood pressure monitoring is an instrumental study that monitors this indicator throughout the day. It is carried out like this: a cuff is placed on the patient’s shoulder to measure blood pressure. Using a special tube, the cuff is attached to the recorder. This small device pumps air into the cuff at regular intervals and then releases it. During the day, measurements are usually taken every 15 minutes, at night - after 30 minutes. A sensitive sensor determines the time of appearance and attenuation of pulse waves (as with conventional Korotkoff pressure measurement). The results are recorded in the device's memory. After reading them using a computer program, the functional diagnostics doctor analyzes the results and gives a conclusion.
What will this study show?
The study shows a number of important implications for human health.
- Maximum and minimum blood pressure (systolic and diastolic) during observation in the patient's natural environment, and not in the hospital.
- Average blood pressure during daytime and nighttime hours, which will determine whether the patient has hypertension. This is the main indicator for which the study is conducted.
- Circadian rhythm of blood pressure. Failure to lower blood pressure at night is associated with an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
All this data will help make a diagnosis of hypertension and select the right treatment, and then evaluate its effectiveness.
About self-measurement of blood pressure
Constant self-measurement of blood pressure will provide much less valuable information. It cannot be carried out at night. If a person wakes up on purpose, this leads to an inevitable increase in pressure and distortion of the results.
You need to know that the most accurate results are obtained by measuring the traditional Korotkoff method (determination of tones using a phonendoscope). It is best to use semi-automatic devices with automatic air injection, since manual injection can cause a short-term increase in pressure. Devices that measure pressure on the wrist or finger are much less accurate. We recommend devices that operate on mains power rather than on batteries.
It should be taken into account that in approximately 5% of patients, pressure monitoring indicators differ significantly from self-monitoring data. Therefore, it is very important to carry out control measurements in the diagnostic room immediately after the start of the study.
How to prepare for research?
On the recommendation of the attending physician, certain medications for the treatment of hypertension may be discontinued before monitoring. If there are no special instructions, you must take all medications as usual. It is advisable to wear a light T-shirt with sleeves up to the elbow, and some loose clothing on top, since the recorder will be placed in a bag and hung around your neck, and there will be a cuff on your arm.
In some cases, it is recommended to bring batteries for the device. Alkaline (alkaline) batteries required.
Before the study, you can eat, drink, and lead a normal lifestyle.
How to behave during research?
Detailed instructions are given by the functional diagnostic nurse. She should give the patient a diary in which he will note his actions and sensations during each blood pressure measurement (except for sleep time), as well as taking medications and sleep time.
At the beginning of each measurement, the patient should stop and extend his arm down along the body, relaxing it. After completing the measurement, the subject must make an entry in the diary and continue the interrupted lesson. If the cuff slips, you need to carefully adjust it. The tube through which air is pumped must not be allowed to bend.
The increase in pressure in the cuff is often quite severe, resulting in pain when squeezing the arm. These feelings must be tolerated.
Indications for research
- “Borderline” blood pressure figures identified during repeated measurements using the Korotkov method.
- Monitoring of selected antihypertensive therapy, including to exclude episodes of severe hypotension after taking medications.
- Suspicion of “white coat hypertension”, when high blood pressure is recorded only when measured by medical staff. Suspicion of “workplace hypertension,” when increased blood pressure occurs at work.
- Severe hypertension resistant to treatment.
Who is recommended to undergo the study?
In the presence of the listed indications, especially valuable information can be obtained from the following groups of patients:
- Pregnant women.
- Patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- “White coat hypertension” and “workplace hypertension.”
- Episodes of hypotension.
- Young people with disorders of the autonomic nervous system.
- Older patients.
- Patients suffering from hypertension without treatment effect.
Contraindications for the study
- Exacerbation of skin disease at the site of application of the cuff.
- Disturbances in the blood coagulation system with a tendency to bleeding during exacerbation.
- Injuries to both upper extremities, excluding the possibility of compression by a cuff.
- Impaired patency of the brachial arteries, confirmed instrumentally.
- Patient refusal.
- The study may be useless if there are significant disturbances in heart rhythm, as well as very high blood pressure values (more than 200 mm Hg).
What is Holter?
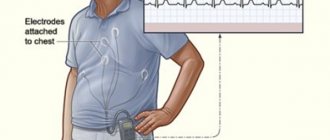
During the examination, a special portable device is used - Holter. Its electrodes are attached to the patient’s chest; they record all changes in blood pressure and record an ECG throughout the day.
The diagnostic device is named after Norman Holter, a famous American biophysicist researcher. In 1961, he developed a monitoring technique and put it into practice for the first time. Thanks to the Holter method, today cardiologists can identify disturbances in the functioning of the heart and various hidden diseases that are not visible on a regular electrocardiogram.
Why do you need daily ECG monitoring (Holter)?
Holter monitoring can be prescribed by a cardiologist or a general practitioner in order to confirm the diagnosis, check the effectiveness of treatment, discontinue medications, clarify details, etc.
The Holter method allows you to identify:
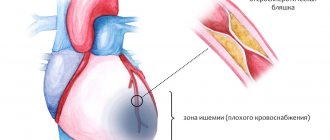
- Ischemic ECG changes.
- Heart rate.
- Type of heart rhythm.
- Heart rhythm disturbances: pauses, ventricular extrasystoles and others.
A regular cardiogram is significantly less informative than 24-hour monitoring, since although it can detect heart disease, it is not capable of assessing the frequency of its occurrence and the severity of its course. It is easier for the doctor to select adequate therapy after analyzing the Holter ECG results.
Who is recommended for 24-hour ECG monitoring (Holter)?
Typically, the electrodes of the device are installed in patients for a day; if nothing could be recorded within 24 hours and no deterioration occurred, then the monitoring is extended (maximum period of 7 days).
Indications for use:
- Coronary heart disease of various forms: silent myocardial ischemia, Prinzmetal angina, etc.
- Studies of heart rhythm disorders: Parkinson's, Wolff's, White's syndrome, atrial fibrillation, as well as ventricular tachycardia and sinoatrial block.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Heart defects.
- Treatment control
- Scheduled preventive examination.
In addition, daily ECG monitoring is prescribed if there are patient complaints of discomfort in the left side of the chest, a feeling of a sinking heart, fainting, or a feeling of lack of air. Diagnostics for frequent dizziness is also indicated.
There are no contraindications for diagnosis, except perhaps skin lesions in the chest area, which will complicate the procedure for attaching electrodes.
How is the examination carried out?
In the diagnostic room, special disposable electrodes in the amount of 5-7 pieces are fixed to the patient’s chest with an adhesive plaster (depending on the Holter model). Using a wire, the sensors are connected to a recording device. The device is in a special case and is hung on the patient’s neck or belt.
The specialist will provide instructions on how to use Holter and give the patient an observation diary. It must indicate all the events that occurred with the person being examined: deterioration and improvement of the condition, taking medications, physical activity, nighttime, as well as daytime rest. Data must be recorded with precise time reference.
To see how the cardiovascular system reacts to stress, during the study the doctor may advise the patient to walk up the stairs. This will help find a connection between complaints and changes in the electrocardiogram.
Important! If the patient experiences any interruptions in the heart’s function within 24 hours, the rhythm increases for no reason, dizziness or other complaints appear, this must be recorded in the diary.
During diagnosis, you cannot undergo magnetic resonance imaging and x-rays of organs. A day later, the doctor removes the electrodes and deciphers the data obtained.
Monitoring - indications, installation, results, harm
Holter monitoring is a method of functional diagnostics that allows for daily monitoring of the electrocardiogram. ECG recording is carried out continuously from 24 hours to three days. To monitor the ECG, a Holter is used - a small portable recorder that records the round-the-clock work of the heart and records data on its work over the course of a day on a computer. These records are subsequently deciphered by a cardiologist.
Holter monitoring was named after researcher Norman J. Holter, who first put this device into practice in 1961.
When installing a Holter monitor, electrodes are attached to the patient's chest. The electrodes, in turn, are connected to a recording device. Of course, the patient experiences certain inconvenience while wearing the device, however, the study itself is very informative and accurate, which allows the cardiologist to determine an accurate diagnosis.
The data processing program provides analysis and determination of all types of heart disorders, in particular attacks of angina pectoris and arrhythmia, which can significantly improve the effectiveness of treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Who is Holter monitoring indicated for?
With the help of a Holter, an ECG is prescribed primarily to determine heart rhythm disturbances - episodes of atrial fibrillation, extrasystoles, etc., which are quite difficult to detect during a short study - a regular electrocardiogram.
It happens that some atypical contractions for a healthy heart muscle appear only during periods of active physical activity, severe emotional shock, or in other situations. In these cases, such disturbances cannot be detected using a conventional electrocardiogram, whereas with Holter monitoring the patient can lead his usual lifestyle: engage in a certain sport, work, take any body position, etc.
Also, using a Holter study, you can determine various disorders of the blood supply to the heart muscle, in particular changes in the ST segment during sports or physical activity.
Can a Holter study negatively affect a patient's health?
Holter ECG does not pose any harm to health. There is also no risk of electric shock.
To avoid damage to the device, it is recommended not to take a bath or swim while wearing it to prevent water from getting inside. It is also not recommended to go through a metal detector while wearing a halter.
How is a Holter monitor installed?
Before the device is attached to the patient's body, he is advised to take a shower, since he will not be able to take a bath or remove the monitor for the next day or more.
The doctor attaches the electrodes to the patient’s chest and adjusts their position. Subsequently, the doctor connects the electrodes to the wiring of the recording device, which is attached to the patient’s body using special belts.
The doctor instructs the patient and teaches him to keep a diary. This is necessary for correct decryption of data received from the device. The patient records periods of sleep, wakefulness, physical activity, rest and all symptoms (chest pain, tachycardia, arrhythmia, etc.) with an exact indication of time.
After installing the device and receiving a list of instructions, the patient can return to his usual rhythm of life and daily routine.
Holter monitoring is an absolutely painless procedure. The patient experiences slight inconvenience only when wearing the device, when the wires and box of the device are hidden under clothing. During sleep, it is not recommended for the patient to turn over on his stomach, as the electrodes may become dislodged, which will disrupt data recording.
Holter study results
The holter is removed directly by a cardiologist or nurse. The patient provides the physician with a diary of activity and symptoms, which the physician examines along with device data.
Depending on the situation, the doctor makes a final diagnosis or sends the patient for additional examination. If the results of a Holter study within a day do not allow the doctor to form a definite picture, he can prescribe the patient to temporarily wear a heart rate recording device, which the patient himself will activate during the onset of alarming symptoms.
Why is ABPM necessary?
Blood pressure is an extremely unstable indicator. It can change during the day, depend on the emotional state, and differ during sleep and wakefulness.
It is worth mentioning the term "EBH", the white coat effect, the essence of which is that some patients experience undue anxiety simply because they are in the doctor's office.
Their blood pressure rises, which does not correspond to the true blood pressure level. A lot of negative factors can influence measurement deviations: a cold stethoscope, crossed legs, excitement. To prescribe the “correct” doses of antihypertensive drugs, it is extremely important to know the exact blood pressure standards obtained in the patient’s usual environment outside the doctor’s office.
An objective picture is provided by 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) using a fully automated device mounted on the patient’s arm. The device records blood pressure values for 1-2 days under normal human conditions.
By analyzing the data obtained, the doctor confirms or denies the presence of hypertension. ABPM has a number of advantages over traditional studies.
The following disadvantages inherent in clinical measurements are excluded:
- the influence of an alarming reaction, which entails overdiagnosis of blood pressure and incorrect medical therapy for patients with EHD;
- rounding the measurement result, usually to tens;
- subjective assessment, when the researcher (doctor) is pre-set on a certain result, which he believes the patient “should have”;
- inability to take into account blood pressure fluctuations within 24 hours.
Daily monitoring is also useful for patients with already diagnosed arterial hypertension, when the study is combined with taking medications
Indications for use
The ABPM technique is indicated for:
- ineffectiveness of antihypertensive treatment;
- high blood pressure numbers in patients without signs of target organ damage (kidneys, myocardium, fundus, brain) and without identified risk factors for arterial hypertension (AH);
- normal blood pressure in patients with established risk factors for hypertension or existing target organ damage;
- high variability of blood pressure during self-measurement or during repeated visits to the doctor;
- frequent episodes of hypotension (low blood pressure) in older patients with type 1 diabetes;
- suspected preeclampsia.
ABPM is used in clinical practice not only in patients with hypertension, but also in patients with cardiac arrhythmias.
Preparatory activities
The first step is to make an appointment with a cardiologist. At the Family Doctor Children's Center for ABPM, you can undergo an examination without a doctor's prescription, but it is better to stock up on a referral, since a specialist must evaluate the results of the examination.
ABPM requires a free machine, so pre-registration is required.
In our center you are accepted without a queue and by appointment, but in public medical institutions you will have to wait several weeks. No special preparation is needed. The device will be installed by a doctor. He will select the “correct” cuff depending on the circumference of the patient’s shoulder.
A cuff that is too short or, conversely, long will distort the readings. The bag with the monitor (reading mechanism) is attached to the patient’s belt. The cuff is placed on the non-working arm: for right-handers - on the left, for left-handers - on the right.
The doctor will check the device for accuracy by alternately measuring blood pressure on one arm with a monitor and on the other with a regular tonometer. If the numbers match, the patient is sent home.
From this moment on, the device will periodically measure your pressure and “remember” the data. ABPM allows you to obtain fairly accurate daily blood pressure dynamics, provided that the patient adheres to the doctor’s recommendations.
The result will be distorted if the patient does not inform the doctor about the medications currently taken.
Who is contraindicated for 24-hour blood pressure monitoring?
ABPM is a non-invasive technique that does not require serious intervention in the body. However, there are a number of contraindications for it.
Diagnosis is not possible if:
- upper limb injury;
- skin diseases localized in the arms and shoulders;
- rigidity of the vascular system, since the accuracy of the test is impaired;
- pregnancy;
- heart disease and other serious pathologies that interfere with diagnostics;
- high blood pressure levels;
- blood clotting disorders.
In these cases, the diagnosis of ABPM will have to be abandoned, turning to traditional blood pressure measurement.
How is it going?
Diagnostics are carried out for a day or two. The first 2 hours are not taken into account as this is the adaptation time. Your doctor will ask you to keep a diary to record your hours of exercise and periods of rest, times you sleep and wake up, medications you take, heart pain, and other symptoms of discomfort if they occur.
Blood pressure registration occurs once every half hour during the daytime and every hour at night, at least. At the appointed time, the patient comes to the clinic and the device is removed from him. The doctor processes the device readings. The results obtained are interpreted by a cardiologist, comparing them with entries in the diary.
During the examination, the patient should follow simple recommendations:
- monitor the position of the cuff. If it has slipped, correct it;
- at the moment of start, the device emits a sound signal and begins to pump air into the cuff. Try to relax your hand at this time. If possible, do not move, so the readings will be more accurate. At the end of the measurement, a repeat beep will sound;
- do not pinch the tubes connecting the monitor to the cuff;
- stay away from electromagnetic devices;
- Avoid stressful situations. Anxious reactions greatly distort the readings of the device;
- temporarily refrain from swimming;
- don't drink alcohol;
- Protect the device from moisture. If there is an urgent need to remove the cuff, carefully disconnect the tubes from the monitor. Otherwise, when air is pumped, they may burst;
- if you notice that the device has stopped working, inform your doctor;
- stop taking antihypertensive medications (with the consent of your doctor);
- don't forget to keep a diary.
The ABPM technique does not prevent the patient from living his normal life, although it does introduce minor discomfort.
The accuracy of the readings largely depends on the patient's behavior during diagnosis. Listen carefully to the doctor’s instructions before conducting the test and try to follow all recommendations.
Decoding the results
During the study, it was possible to obtain 14 reliable measurements during the daytime and at least 7 during the night. Based on them, the doctor calculates the average blood pressure and pulse rate.
Since the interpretation of average values today does not pose a problem and is carried out on the basis of generally accepted standards, the most important are the “additional” ABPM readings:
- circadian rhythm (CR). ABPM is the only non-invasive study that provides a complete picture of this characteristic. The main indicator of SR is the percentage decrease in blood pressure at night. Violation of this value signals dysfunction of the cardiovascular system (CVS) and damage to target organs by hypertension. A practical problem in using the indicator is its low reproducibility, therefore, to confirm the reliability of identified SR failures, repeated monitoring is required, which is not always convenient for the subject. However, this characteristic must be taken into account in the conclusion based on ABPM results, especially if the procedure is performed for diagnostic purposes;
- ambulatory pulse blood pressure. This indicator is directly related to myocardial and vascular problems. ABPM assesses this characteristic more accurately than clinical studies. The “critical” value of ambulatory pulse pressure is 53 mmHg. Higher values indicate a risk of CV complications;
- blood pressure variability. Elevated values of this indicator may indicate incorrect antihypertensive therapy and the need to change the treatment regimen;
- morning dynamics of blood pressure. It is known that at this time the greatest number of heart attacks, malignant arrhythmias and strokes occur, which can cause sudden death of the patient. The morning increase in blood pressure in hypertensive patients is consistently higher than in healthy people, which is fraught with cardiovascular complications;
- assessment of hypotension episodes in the daily blood pressure profile. For an objective quantitative assessment, it is sufficient to take into account only the minimum blood pressure values;
- smoothing index (SI). Since ABPM provides a large amount of information, it can be used to more accurately assess the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs. The indicator is calculated based on the hourly effects of the drug: the ratio of the average effect to the deviation from it. An IP of at least 1.2-1.5 is considered optimal.
The listed additional indicators of ABPM are very important. However, their practical use is still limited. The situation should change with the introduction of new generation drugs for hypertension into clinical practice and the widespread use of chronotherapy methods.
When is diagnosis prescribed?
The most common reason for 24-hour blood pressure monitoring is to assess the effectiveness of antihypertensive therapy, especially in the case of combination treatment using several groups of antihypertensive drugs. Other reasons for prescribing ABPM include the diagnosis of early arterial hypertension, symptomatic arterial hypertension, patients with heart failure, with myocardial hypertrophy, in the presence of brain diseases, and suspected sleep apnea syndrome.
ABPM is used to examine patients suffering from various types of hypotension: constitutional and orthostatic.
ABPM allows you to determine the presence of so-called “office hypertension”, in the diagnosis of which it is necessary to promptly establish a work and rest schedule.
Features of the study in pregnant women
Daily monitoring of blood pressure in the later stages is also not contraindicated for pregnant women. Thus, in the presence of arterial hypertension, which was acquired even before the onset of pregnancy, the examination showed that upper and lower blood pressure decreases significantly during the night.
- What does 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) show and how is it carried out? Is it possible to fool the device?
This result is used to identify problems associated with high blood pressure in expectant mothers.
Contraindications to the procedure
The procedure for 24-hour blood pressure monitoring is a completely safe test and has no absolute contraindications. But there are relative contraindications, which include thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities, acute infectious disease (as a temporary contraindication), impaired motor activity due to the severity of some chronic diseases.
Psychological reasons (phobias and fears) are a contraindication for ABPM.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of 24-hour ABPM monitoring is the ability to accurately diagnose blood pressure problems. This cannot be done through other medical tests.
Pay attention to the comparative characteristics of measurements
A complete list of advantages and disadvantages is given in the table:
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Allows you to identify the smallest fluctuations and timely diagnose problems with blood pressure | Causes disruptions in sleep mode. The device also monitors at night. This may cause discomfort and make you wake up |
| Allows you to determine the stage of the disease, separate latent and temporary hypertension | Inability to fully flex the elbow because the arm is cuffed |
| Easy to use. The patient does not need to set up the device themselves | — |
| Device security. Even children are allowed to use | — |
| High efficiency, precision | — |
Carrying out the procedure
The patient should sit for a few minutes before the procedure. The key to correct diagnosis is the coordination of the actions of the doctor and the patient. The study is carried out:
- with installation of a cuff and tonometer;
- with the obligatory filling out of the diary by the patient;
- with removal of the device;
- with a comparison of the results obtained and the data entered by the patient.
Installing the device takes no more than 15 minutes. The appropriate position for installing the cuff is sitting. The cuff is placed on the right hand of a right-handed person and on the left hand of a left-handed person. It is important to consider which arm the patient has more active. The mark on the cuff should coincide with the most pulsating point on the arm (blood pressure will be measured using it). The point is located on the distal part of the shoulder and is easy to find. Using a special device, the cuff is fixed on the shoulder. A register and a mercury tonometer extend from this device.
What does the ABPM device look like? Rules of conduct during research
To perform the procedure, a compact device is used, which consists of several parts:
- cuffs and devices that pump air into it;
- tubes;
- data logger.
No special preparation is required for the examination. You just need to first agree with your doctor on the list of medications you are taking (you may need to stop taking some medications during the procedure). On the day of the examination, it is advisable to wear a cotton T-shirt or long-sleeve sweater so that the cuff does not rub your arm.
In the doctor's office, a cuff is placed on the patient's shoulder. The recorder is either attached to the belt or placed in a bag. The device records blood pressure readings every 15 minutes during the day and 30 minutes at night.
If ABPM is combined with Holter ECG monitoring, electrodes are attached to the patient's chest.
The ABPM device should not be exposed to negative temperatures (in winter, when going outside, dress warmly).
Preliminary instructions
Blood pressure monitoring will proceed without complications if within two days the patient can meet several mandatory conditions: while measuring blood pressure, the patient must take a comfortable position and, if possible, extend his arm with the cuff. If these recommendations are not followed, you will not be able to obtain accurate results.
Excessive physical activity is not recommended on the day of ABPM. If recording of indicators occurs during work or movement, the patient must stop - this rule guarantees accurate results. If possible, during the period of blood pressure monitoring it is necessary to exclude stressful situations. You should not follow the measurements - such behavior will cause nervousness, which will affect the diagnostic results.
There is no need to worry about the operation of the device at night. As far as possible, the patient does his usual activities - goes to work, does household chores. You cannot limit yourself, otherwise you will not be able to get results in an environment close to the natural environment. If unpleasant symptoms occur, the patient makes notes in a diary indicating the time of day and the load that gave the body a negative reaction.
Features of Holter blood pressure monitoring
The technique assumes that the patient will strictly follow the rules and recommendations of the specialist. Otherwise, the readings will be incorrect, which will negatively affect the diagnosis and selection of drug treatment.
ABPM is a simple procedure. A “cuff” is placed on the patient’s arm with a device in the form of a small box attached to it using wires, to which the results of each measurement will be automatically transferred and recorded in memory.
During the entire period of wearing the cuff, a person is required to keep an observation diary in which he must record all the actions he performs during the monitoring period. It is necessary to write down with the exact time:
- time of falling asleep - waking up;
- any physical activity;
- taking medications;
- development of a stressful situation;
- meal.
The diary must indicate any changes in well-being, for example, the appearance of painful sensations.
The total duration of the study is 24 – 28 hours. The first two hours after installation of the cuff are excluded when constructing the graph as adaptation. Our specialist comes to the patient at the appointed time to remove the device. The specialist then extracts the received data to perform processing. The result is given to the patient. The interpretation is carried out by the attending cardiologist.
Rules for the patient
Correct measurements depend entirely on the patient's behavior. Keeping a diary is a prerequisite that guarantees diagnostic results. The daily routine is entered into the diary: sleep, exercise, psycho-emotional experiences, walks, clinical symptoms that arise during the day, taking medications. Detailed records will allow you to assess the condition of the body and the factors that worsen the patient’s well-being.
If any negative symptoms appear, the patient consults a doctor. Headaches (severe migraines), weakness or nausea are reasons to suspend ABPM. It is recommended to avoid crowded places and places with a lot of noise for two days - it will affect the recorder and prevent you from taking correct measurements. If the edge of the cuff moves, it needs to be corrected - the correct position of the cuff is 2 cm below the elbow. If the patient is concerned about the correct conduct of ABPM, the attending physician will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Hypertension and ABPM
Heart attacks and strokes are considered the scourge of modern society; the fast pace of life and numerous stresses make themselves felt by difficulties with the cardiovascular system. Cardiology of the 21st century has modern methods for identifying and treating these diseases. But such large numbers of sad statistics are caused by the fact that patients wait until the last minute to see a doctor. Many who did not choose to visit medical facilities in time are later transported by ambulance in serious condition.
One of the common reasons for emergency placement on the surgical table is hypertension, or rather its terrible consequences. Hypertension cannot be ignored; it needs control and treatment. ABPM helps diagnose diseases and promptly prevent the development of life-threatening conditions.
Few young people know what ABPM is, mistakenly considering hypertension and circulatory disorders to be the lot of older people. However, unfortunately, hypertension has become “younger” and can pose a danger even for 30-year-olds. But at this age it is not customary to think about blood pressure and problems with its fluctuations, which can be fraught with consequences. After all, hypertension can develop asymptomatically for a long time and can only be detected through regular tests. Therefore, it is useful for people of all ages to know about ABPM and what it is.
What can you learn using ABPM?
To diagnose the disease, the variability of blood pressure values during the day is used. The analysis of the results obtained is carried out on the basis of 4 indicators. Average blood pressure readings differ at night and during the day. During the daytime, normal blood pressure is 130 to 85 mm, and at night – 120 to 70 mm.
The second indicator is the recorded moments of maximum increase in blood pressure - the number of deviations from the norm indicates the complexity of the disease. The daily index is calculated, consisting of systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The last indicator that allows you to assess the patient’s health status is the magnitude of the morning increase in blood pressure.
Preparation
One of the advantages of daily blood pressure measurement is the lack of special training. However, doctors recommend adhering to the following recommendations:
- Be sure to tell your doctor about all medications you take on an ongoing basis. Some medications may need to be stopped several days before the test.
- 5-7 days before the study you must give up alcoholic beverages.
- On the day of the examination, it is recommended to wear loose, cotton clothing that does not restrict movement.
- On the eve of the test, try not to experience any serious physical activity. You should also avoid stressful situations.
Indications and contraindications
Holter monitoring is carried out for the purpose of:
- detection of arrhythmias;
- detection of myocardial ischemia;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
1st class indications:
- unexplained fainting (syncope), presyncope, episodes of dizziness;
- repeated palpitations with unknown causes;
- assessment of the effectiveness of antiarrhythmic therapy in patients (the frequency and characteristics of arrhythmia were accurately determined before the start of treatment
- assessment of the heart rhythm with an implanted pacemaker to program its parameters or identify possible malfunctions of the device.
Class 2 indications:
- episodes of sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, or weakness of unknown cause;
- fainting, presyncope, attacks of weakness or palpitations against the background of identified arrhythmia or treatment;
- condition after a heart attack with impaired left ventricular function;
- chronic circulatory failure;
- idiopathic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy;
- assessment of the possible arrhythmogenic effect of certain drugs;
- fixation of heart rate in patients with atrial fibrillation;
- documentary recording of intermittent arrhythmia;
- assessment of the performance of an implanted pacemaker or defibrillator;
- assessment of the frequency of arrhythmia attacks in patients with an implanted defibrillator or pacemaker;
- suspicion of variant angina;
- patients with chest pain for whom taking an ECG with physical activity is contraindicated;
- patients before and after coronary artery bypass surgery for whom exercise testing is contraindicated;
- patients with diagnosed coronary artery disease and chest pain.
Class 3 indications:
- syncope, pre-syncope, episodes of weakness or palpitations, the causes of which have been previously identified;
- episodic symptoms of cerebrovascular accident: attacks of dizziness, tinnitus, headache, decreased vision;
- chronic heart failure;
- arterial hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy;
- post-infarction state with normal left ventricular function;
- diabetes mellitus (to assess the degree of diabetic neuropathy);
- confirmation of malfunction of implanted devices in situations where other research methods also reveal defects in the operation of devices;
- preventive examination of a patient with an implanted pacemaker or defibrillator.
Relative contraindications:
- injuries,
- chest burns,
- chronic heart failure;
- as well as other violations of the integrity of the skin in the area where the sensors are attached.
- The examination can be difficult if the patient is highly active; sudden movements may cause the sensors to come off.
Cost of HOLTER AD, HOLTER ECG
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Initial appointment with a cardiologist | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a cardiologist | 1500 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment (drawing up an individual treatment regimen) | 1500 - 3000 rub. |
| Taking and interpreting ECG | 2000 rub. |
| HOLTER HELL, HOLTER ECG (staging and interpretation) | 4500 rub. |
| Preparation of medical documents (extracts, certificates) | 1000 rub. |
| Registration of a sanatorium and resort card | 2000 rub. |
| Reception of a specialist with issuance of a sick leave certificate | 3000 rub. |
All our services and prices