More than 1.2 million people die from cardiovascular diseases in Russia, despite the high level of cardiology in the country. Timely diagnosis of heart disease allows you to prevent irreversible consequences and thereby significantly prolong your life. One of the accessible and highly effective diagnostic methods, in addition to ECG
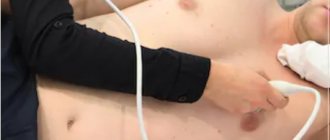
, is an ultrasound of the heart.
How is a heart ultrasound done and what do the results show?
The ultrasound procedure of the heart, which shows the condition of this most important organ, lasts only twenty minutes. To conduct the examination, the patient must undress from top to waist and lie on his back, after which the sonologist applies gel to the chest and examines the organ, passing over the heart area several times. If necessary, the doctor may ask the patient to lie on his side.
A more risky research method is a stress test, which involves physical activity or the administration of a drug that increases the heart rate, which shows on an ultrasound of the heart in an adult the state of the organ “at work.” Preparing a doctor for a cardiac ultrasound in stress test mode implies the availability of equipment and drugs for resuscitation, since heart problems can manifest themselves at any time. In some cases, when serious heart disease is diagnosed, this research method may be contraindicated.
Another research method is transesophageal echocardiography, which can hardly be called a pleasant process: a special scanner is inserted into the esophagus, which examines the organ almost from the inside. This type of study gives more reliable results, therefore it is prescribed if deciphering the results of cardiac ultrasound during a standard procedure is difficult.
What is electrocardiography and the features of its implementation?
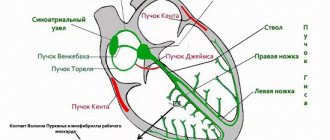
The principle of this examination method is based on recording electronic pulses of the heart that occur during myocardial contraction. The pulses that have arisen are read by the cardiograph, displaying them in the form of a graphic curve on special paper.
Order of conduct:
- Before the procedure, all jewelry should be removed;
- Expose the chest, ankles and hands;
- Lie horizontally and relax;
- Before applying the electrodes, the nurse should treat exposed skin with a cotton pad, which is moistened with water for better conductivity of the impulses.
- Afterwards, 4 electrodes of different colors are applied to the limbs in a certain sequence;
- They are fixed on the chest using suction cups. The number of the latter should be 6 pieces;
- The electrodes are connected to the device, then they are registered.
A cardiogram is necessary when detecting any heart disease; it is also prescribed during a preventive examination.
Using this examination, you can identify such disturbances in the functioning of the heart as:
- Heart rhythm disturbances, for example, tachycardia, arrhythmia, extrasystole;
- Impulse conduction disorder, for example, antiventricular block;
- Myocardial nutritional disorders, for example, heart attack, ischemia;
- Congenital or acquired diseases, for example, disorders in the structure of the fibrous ring, valves, chord;
- Myocardial thickening, for example, atrial ventricular hypertrophy.
Persons who have reached the age of 40 years old must undergo an ECG every year. This will help to identify violations in time at the initial stage.
This study is quite informative, however, despite this, to clarify the diagnosis it is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the heart.
The study is very effective and indicative, but despite this, to clarify the condition of the myocardium, it is necessary to resort to ultrasound diagnostics of the heart.
Pros of the procedure
Among the undeniable advantages are the painlessness of the procedure, safety, and the ability to obtain reliable data. In addition, another advantage is that the procedure does not take much time.
Also, the procedure has no contraindications, and due to the mobility of the device, diagnostics can be carried out outside the clinic.
Disadvantages of the procedure:
The disadvantages of the procedure include the following:
- short recording;
- inability to record heart murmurs;
- impossibility of diagnosing heart defects and various tumors;
- To obtain reliable data, the procedure should be carried out at rest or under load.
Indications for use
Typically, cardiovascular diseases do not manifest themselves clearly and can “masquerade” as other diseases, so doctors prescribe an ultrasound of the heart
even with dizziness, excessive sweating and shortness of breath. What an ultrasound of the heart shows can clarify the clinical picture of identified vascular diseases.
Aortic diseases
The aorta is the largest artery that begins from the left ventricle of the heart, therefore, with ultrasound of the heart, which shows the condition of the aorta, diseases such as atherosclerosis and aortic aneurysm, as well as its dissection and occlusion, can be monitored. Since ultrasound of the heart can be performed frequently in an adult, this is one of the most accessible research methods.
Hypertonic disease
Hypertension affects the condition of all blood vessels, so periodic studies with interpretation of ultrasound of the heart are necessary for the doctor to adjust treatment, depending on the patient’s condition. Common consequences of hypertension are coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, aortic aneurysm, etc.
Myocardial infarction
Ultrasound of the heart shows what is happening to the myocardium as well. The procedure is carried out in a standard manner. Interpretation of the results of cardiac ultrasound during myocardial infarction allows us to identify the focus and degree of myocardial necrosis, as well as its contractility. Also, ultrasound of the heart reveals a pre-infarction state, thereby preventing an attack.
IHD
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is one of the most formidable and serious, and therefore its many symptoms cannot be detected except by ultrasound of the heart. This is the fastest and most effective way. The most effective method to determine IHD is a stress test, as a result of which numerous symptoms of the disease appear.
When is it prescribed?
Ultrasound examination (echocardiography or EchoCG) is an informative and easy-to-use method, without which it is difficult to imagine diagnostics in modern cardiology. With its help, a sonologist (better known as an “uzist” or “ultrasound specialist”) can assess in real time the condition and functions of the organ and its surrounding tissues. Non-invasive diagnostics determines structural abnormalities and changes that can appear in various pathologies and developmental defects.
Thanks to its informativeness and high safety, cardiac ultrasound has become widely used in the diagnosis of cardiac diseases in adults and children. With its help, diseases of the myocardium, heart valves, pericardium, large vessels, including the aorta and pulmonary trunk, as well as other structural units of the cardiovascular and related systems are identified. Other benefits of such research include:
- lack of difficult-to-implement training recommendations;
- the ability to monitor current processes over time;
- affordable cost and high speed of execution;
- availability of mobile equipment for diagnosing urgent cases.
A referral for echocardiography is given to adult patients by a general practitioner or cardiologist, and to children by a pediatrician or pediatric cardiologist. The examination can be carried out for preventive purposes, in the presence of risk factors for the development of cardiac pathologies, for direct indications in the presence of obvious symptoms or diagnosed disorders.
Indications for use
The main advantage of echocardiography is the ability to diagnose pathologies even before the appearance of their first symptoms. But in general, indications for cardiac ultrasound include:
- complaints of shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness, swelling;
- cases of loss of consciousness, rapid heartbeat;
- difficulty breathing, blue fingertips and lips during physical activity;
- severe arrhythmia, so-called chest pain;
- detection of noises during auscultation;
- diseases with a risk of damage to the cardiovascular system, for example, rheumatism;
- often high blood pressure, diagnosed hypertension;
- the presence of changes in the electrocardiogram, for example, myocardial hypertrophy;
- suspicion of congenital defects in children, etc.
In some cases, echocardiography is performed once to confirm or refute existing suspicions, in others repeatedly at certain intervals to reliably track changes.
In addition, thanks to the active development of medical equipment and the expansion of its functionality for cardiac ultrasound, the indications for ultrasound may also be much wider. Thus, many models of modern devices are capable of combining classical ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound. This allows the specialist, during diagnosis, to track the direction and speed of blood flow in the chambers, which is important for a comprehensive assessment of the functioning of the organ and determination of disorders in its valve apparatus.
Contraindications
Along with safety and ease of implementation, another advantageous difference of ultrasound examination is the absence of absolute contraindications. In practice, specialists note only the relative difficulties they encounter when conducting diagnostics. Usually this:
- violations of the integrity of the skin in the area where the sensor is located (wounds, external manifestations of dermatological disorders, etc.);
- pronounced hair growth in the chest area;
- open injuries and deformations of the chest;
- extreme obesity, significant accumulation of fatty deposits in the examined area;
- performing ultrasound of the heart in newborns, etc.
There are no side effects or complications when performing ultrasound diagnostics. The safety of the method allows it to be used several times a week. There are no contraindications for it during pregnancy, since there is no threat to the health of the expectant mother and fetus.
But it is worth considering that some patients, in extremely rare cases, report an allergic reaction to the gel used for smooth sliding and better contact of the sensor with the body. In general, gels for ultrasound diagnostics are hypoallergenic, but exceptions to the rules may still exist. Therefore, when visiting a sonologist, it is better to immediately warn about a possible reaction. You can avoid it by replacing the gel, washing the examined area with soap immediately after diagnosis, or pre-applying baby cream to the skin, which will prevent the gel composition from penetrating the pores.
How to prepare properly?
With transthoracic ultrasound of the heart, preparation for the study is not required. In this case, it is better to quit smoking two hours before the ultrasound, alcohol, caffeine-containing drinks, and medications on the day of the examination.
However, it is worth knowing how to prepare for a cardiac ultrasound using the transesophageal technique: you must refuse to eat 2-3 hours before the procedure. Many young mothers are concerned about whether babies can eat before a heart ultrasound. Doctors recommend skipping one feeding before the ultrasound.
If there are diagnosed diseases, the attending physician gives recommendations to the sonologist on the procedure. Otherwise, preparation for cardiac ultrasound in women, men and children over 1 year of age is no different.
Normal echocardiogram findings
After completing the procedure, the doctor draws up a cardiac ultrasound protocol, which specifies the size and volume of the chambers, local contractility and blood pumping speed. The table shows the permissible values of cardiac echocardiography in men, women and children, which do not require special attention or treatment.
| Index | Men | Women | Children |
| Thickness of the interventricular septum | 6-10 mm | 6-9 mm | 2-3 mm |
| Thickness of the posterior wall of the ventricle | 6-10 mm | 6-9 mm | 2-3 mm |
| Left ventricular myocardial mass (LVMM) | 65-150 g | 65-150 g | 34-85 g |
| LVM index (takes into account the patient’s height) | 49-115 g/m2 | 43-95 g/m2 | 58-74 g/m2 |
| Ejection fraction | 55-70% | 50-55% | |
| Contractility | not violated | ||
If echocardiography readings deviate slightly from normal, it should be understood that the result may be affected by the person's age and health status. In older people, borderline values are acceptable; they are not always associated with heart disease. In childhood and adolescence, indicators can differ significantly, which is explained by the rapid growth of the child’s body.
Only a qualified doctor can decipher the results of an echocardiogram of the heart with normal or altered indicators, who will explain the situation and prescribe the optimal treatment. To confirm the diagnosis, electrocardiography (ECG), chest x-ray, laboratory blood diagnostics, etc. are additionally performed.
How is cardiac ultrasound performed?
Like preparation for the study, the results shown by ultrasound of the heart depend on the type of technique. There are also technical parameters of ultrasound that expand diagnostic capabilities.
One-dimensional ultrasound in M-mode
One-dimensional echocardiography shows the heart in one plane in real time. Interpretation of the results of a one-dimensional ultrasound of the heart will show the size of the chambers and the lumen of the heart valves.
2D ultrasound
This research method allows you to examine the heart in two planes to see the areas of the valve openings and the lumens of the great vessels.
Three-dimensional ultrasonic scanning
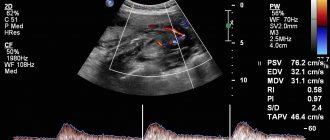
This type of study is also called Doppler. Three-dimensional ultrasound of the heart, which simultaneously shows the movement of blood flow and the anatomy of the organ, is the most advanced method of ultrasound diagnostics.
What abbreviations are used in the protocol?
Having received the EchoCG protocol completed by a specialist, the patient is faced with abbreviations that are incomprehensible to him. For example, MPAP is the average pressure in the pulmonary artery, CO and DO are the short and long axis. The most commonly used abbreviations can be seen in the figure.
Basic abbreviations that are indicated in the ultrasound protocol
In most cases, it is impossible to make a diagnosis based only on the results of the protocol. The specialist takes into account such features as ultrasound indicators, the patient’s medical history, the chronology and intensity of the development of symptoms, and other nuances. Taken together, these data help to accurately determine a particular pathology.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the heart
A full interpretation of the results of a cardiac ultrasound is carried out by the attending cardiologist, however, a sonologist can also provide preliminary information about the condition of the organ during or after the study.
What does an ultrasound of the heart show?
Interpretation of ultrasound of the heart
takes into account normal indicators obtained by world medicine: the sizes of the ventricles and atria, the diameter of the aorta and signs of valve dysfunction. Many patients are interested in whether cardiac ultrasound shows arrhythmia. Arrhythmia, like coronary heart disease, is detected during a stress test. It should be taken into account that the norm for cardiac ultrasound in women differs from that in men.
Norms of cardiac echocardiography in children
In pediatrics, standard indicators are directly related to the patient’s body area. It can be determined using a formula using the child’s height and weight data. During diagnostics, review and note information on:
- cavities of the right/left ventricle, as well as the left atrium;
- wall density;
- aorta, especially its ascending section;
- hemodynamics;
- the septum between the heart ventricles.
Competent interpretation of cardiac echocardiography in children requires care and responsibility in all situations.
| Parameters for diagnosing myocardium in newborns | Male | Female |
| Left ventricular EDR | From 19 to 25 mm | From 18 to 24 mm |
| Left atrium diameter | From 13 to 18 mm | From 12 to 17 mm |
| Left ventricle diameter | From 6 to 14 mm | From 5 to 13 mm |
| Left ventricular ESR | From 12 to 17 mm | |
| MZhP (thickness) | From 3 to 6 mm | |
| Right ventricular wall thickness | From 2 to 3 mm | |
| Blood flow speed | About 1.3 m per second | |
| Ejection fraction varies in infants | From 65 to 75% | |
Please note that sometimes after cardiac echocardiography has been performed, interpretation is carried out directly in the diagnostician’s office. The fact is that often the hardware examination is carried out by the attending physician himself, which significantly saves time for the patient and helps the doctor quickly make the correct diagnosis.
Sometimes the list of parameters in the response is different. This happens if the research was carried out with devices of different manufacture and power, that is, devices with different technical characteristics and capabilities.
How can a doctor identify signs of IHD if there are no symptoms?
- It is possible that there are symptoms, but it is difficult for a lay person to assess them. For example, decreased exercise tolerance and shortness of breath in patients are often “equivalents of angina.” A professional cardiologist can correctly assess your well-being and symptoms.
- Perform a load test. During physical activity, the heart beats faster and stronger and its need for blood increases greatly. If the vessels of the heart are “clogged” with plaques, we will see signs of ischemia (lack of blood) of the myocardium - changes on the cardiogram and ultrasound of the heart. The stress test is the internationally recommended standard test for the detection of CAD. The most informative is stress echocardiography, in which you can evaluate not only the cardiogram, but also the function of the heart using ultrasound.
- Perform coronary angiography. Coronary angiography is the “gold standard for diagnosing coronary heart disease.” With coronary angiography, the arteries are visible extremely clearly and you can definitely say whether there are plaques or not, how many there are, and how much they limit the blood flow through the artery. However, coronary angiography requires introduction into the human arterial system and is performed strictly according to indications. For example, with a heart attack, new-onset angina, worsening angina, or based on the results of a stress test.
How does an ECG differ from an EchoCG?
Patients often wonder what is the difference between an electrocardiogram and an echocardiogram? Both methods help diagnose cardiovascular pathologies, but are carried out according to different principles.
An ECG is a method during which special sensors are attached to a person’s chest to record the electrical impulses of the heart. The sensors convert the signals into a complex curve, from which the specialist evaluates the main indicators of the functioning of the organ.
EchoCG differs in that the examination uses high-frequency ultrasound waves, which penetrate into the tissues of the organ and are reflected by it. This makes it possible to see the picture on the monitor in real time. An electrocardiogram provides information about the electrical conductivity of the heart, calculates the heart rhythm and its electrical axis.
An echocardiogram determines the direction and speed of blood flow, helps to see the condition of the arteries and valves, the thickness of the myocardium and the size of the ventricles.
Important! ECG and EchoCG are widely applicable diagnostic techniques that are often used in combination with each other.
How to recognize myocardial infarction?
Heaviness, burning, pressure, tearing pain behind the sternum are the most common symptoms of myocardial infarction. The pain often radiates to the neck, lower jaw, and left arm. Many patients report a feeling of lack of air and fear of death. It is very important to call an ambulance at the first symptoms. In large cities of Russia, a special network of hospitals has been created, on duty around the clock to treat patients with myocardial infarction. Unfortunately, the main reason for the poor results of this treatment is the late presentation of the patient.
Use among pregnant women
During pregnancy, women are susceptible to many diseases. Due to changes occurring in the body, the load on the heart also increases.
Echocardiography is often performed on pregnant women
Indications for echocardiography:
- diabetes;
- hereditary predisposition to heart disease;
- if the patient fell ill with rubella while carrying a baby, or a high concentration of bodies for this disease was detected in the plasma;
- if in the first trimester the woman took any strong medications;
- in the presence of miscarriages in the medical history.
Ultrasounds are often performed on an unborn baby in the womb. The procedure is performed to detect heart defects in the fetus at an early stage and is performed at 18–22 weeks.