Symptoms and signs of decreased hemoglobin
Clinical signs of anemia do not have clearly defined boundaries. The most common symptoms of low hemoglobin are:
- hair loss;
- brittle nails;
- feeling of coldness in the feet and palms;
- headache;
- low pressure;
- drowsiness and loss of strength.
If a nursing woman experiences 3 or more signs from the above list, then she needs to see a doctor to make or exclude a diagnosis.
In severe cases, fainting, short-term loss of orientation in space, a decrease in heart rate to 40 beats per minute, and visual hallucinations may occur.
Important! Low hemoglobin can manifest itself in the form of specific taste and smell preferences - the desire to smell gasoline, acetone, eat earth, damp plaster, and the like.
Causes of low hemoglobin
A low level of hemoglobin is a dangerous condition, which is popularly called anemia, and in medicine - anemia. The causes of low hemoglobin are varied. Most often, anemia develops in the following cases:
- Blood loss . Bleeding can be associated with various injuries and operations. Sometimes blood loss is associated with diseases, for example, with fibroids, women experience heavy periods. With ulcers in the intestines or stomachs, internal bleeding develops, blood is lost little by little, but constantly.
- Poor absorption of iron . With some gastrointestinal diseases and metabolic disorders, the body begins to poorly absorb iron from food, which leads to the development of anemia.
- Stress . Prolonged nervous tension affects health. A person's appetite decreases; in addition, metabolic processes may be disrupted, which leads to the development of anemia.
- Passive lifestyle . If a person is not physically active, then the blood moves more slowly through the vessels. And this causes a decrease in the level of red blood cell production.
- Poor nutrition . Vegetarians are especially likely to suffer from iron deficiency.
Important! With a reduced level of hemoglobin, a person constantly feels weak and gets tired quickly. A decrease in hemoglobin in pregnant women is especially dangerous. Lack of oxygen leads to delayed development of the child and can provoke premature birth.
Laboratory indicators
In the last trimester of pregnancy, the hemoglobin level decreases by 10-15 units from the norm for a healthy, non-pregnant woman. When breastfeeding, reference standards are also reduced by no more than 20 units. If there was a large blood loss during childbirth, then hemoglobin may drop to 90 g/l, but these indicators should return to normal by 10 days after birth.
| Laboratory indicators of hemoglobin levels in the blood of women | |
| Healthy non-pregnant woman, 18-65 l | 120-150 g/l |
| 32-45 weeks of pregnancy | 110-115 g/l |
| Difficult birth | 90-100 g/l |
| The first three months under guards | 110-120 g/l |
| 4-12 months guards | 120-130 g/l |
For laboratory testing of hemoglobin levels in women after childbirth, a capillary (from a finger) or venous method of blood sampling is performed. In both cases, the test should be taken on an empty stomach, and medications containing iron and animal blood serum should be avoided.
Iron deficiency anemia of nursing mothers
It affects about 700 million people around the world. This is the most common form (80% of all) anemia. 20 - 50% of women of childbearing age, 90% of women become anemic by the end of pregnancy. Anemia means:
- The number of your red blood cells is below normal 3.8-3.6 x 106 g/l
- Your hemoglobin level is below normal -115-110 g/l, i.e. the amount of oxygen carried by the blood to the tissues is reduced.
Signs of anemia in your body (syndromes):
- General anemic: Shortness of breath, tachycardia, fainting, weakness, pallor of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Sideropenic (low iron levels): dry skin, premature appearance of wrinkles; brittle nails and hair, flat spoon-shaped nails, catches in the corners of the mouth, inflammation of the red border of the lips, decreased immunity, frequent infections, chronic infections, muscle weakness (frequent urge to urinate, urinary incontinence when laughing, coughing, straining), perversion of taste (desire eat chalk, lime, ice, paper), addiction to smells - substance abuse, morning swelling of the face above and below the eyes, pasty legs due to increased permeability of small vessels.
The possibility of physiological absorption of iron from food is limited. The diet of women is 2000-2500 kcal, i.e. 12-15 mg of iron, of which 1-1.3 mg is absorbed, but with increased body needs for iron, a maximum of 2 mg can be absorbed from food. The daily requirement for iron in women during pregnancy and lactation often increases to 3.5 mg.
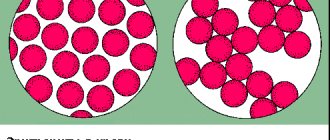
| Red blood cells in anemia: different sizes, “gutted”. How will they perform their functions? | Red blood cells of a healthy person. |
Preventive nutrition for anemia Nutrition should be complete. Meat products are especially useful: 6% of iron is absorbed from meat, 2 times less from eggs and fish, and only 0.2% from plant foods. The diet should contain 120-200g of meat or 125-250g of fish per day, 1 egg, up to 1 kg of dairy products (cheese, cottage cheese, kefir), 80-100g of fat; about 800g of vegetables and fruits, some of which are raw (carrots , turnips, cabbage, apples). Along with this, vitamins: C-100 mg, A-6600ME, B1-2.5 mg, B2-4 mg, PP-20 mg. Iron in foods of animal and plant origin (mg/100g)
| Liver-9 Beef tongue-5 Rabbit meat-4.4 Turkey meat-4 Beef-2.9 Chicken meat-2.2 Pork-1.5 Smoked sausage-2.6 Boiled sausage-1.8 Cutlets-1 Fish( hake, perch) -1 Egg -2.5 | Dried mushrooms - 35 Seaweed - 16 Rose hips - 11.5 Buckwheat - 7.8 Hercules - 7.8 Beans, peas - 7 Fresh mushrooms - 5.2 Peaches - 4.1 Rye bread - 3.9 Nuts - 3 .5 Pear-2.3 Apple-2.2 |
Causes of anemia in a nursing mother
Rarely does a woman in labor avoid the problem of iron deficiency in the blood. For 9 months, all vitamins, minerals, macro and microelements were spent on the formation and gestation of the fetus, which caused a deficiency of nutrients. Also, birth factors and injuries to the genital tract lead to heavy blood loss, which reduces the total amount of blood in the body, and as a consequence, the number of red blood cells. The number of red blood cells is directly related to the level of hemoglobin in the blood. If there is a lack of the former, the latter also decreases.
Healthy recipes
There are several recipes that will help restore iron levels in the blood:
- Pour a glass of boiling water over 4 clover flowers, an hour after steeping, strain. Take ½ glass three times a day on an empty stomach for 30 days.
- Take a glass of walnut kernels and green buckwheat, chop in any convenient way, add honey, stir. Take 1 tbsp daily. l.
- Mix aloe leaves ground in a meat grinder with honey in equal quantities. Close the lid tightly and keep in a dark place for 5 days. Take 1 tbsp. l. in the morning, at lunch and in the evening before meals every day until you use it up.
- Make a mixture of honey, prunes, dried apricots and raisins - 500 g of each component. Take 3 tbsp. l. per day for a month. Mix dry nettle leaves with pollen and natural honey in a ratio of 3:1:2. Take 1 tsp. on an empty stomach half an hour before meals, washed down with water.
- You can increase hemoglobin using chyawanprash.
- Take 1 tsp on an empty stomach. milk thistle with a small amount of water.
For better absorption, iron must be taken with vitamin C (ascorbic acid), as well as preparations or products containing copper, zinc and manganese. These include tomatoes, lettuce, raisins, spinach. Some vegetables and fruits contain a complex of essential substances - iron and components that promote its absorption.
To increase hemoglobin, it is useful to take a long walk in the fresh air and give the body moderate physical activity, for example, yoga, swimming under water.
In addition to proper nutrition, it is necessary to reconsider your views and beliefs: a positive and optimistic person is less susceptible to this disease.
How can you increase hemoglobin?
You can increase hemoglobin after childbirth using both medications and traditional methods. If iron deficiency is slight, doctors most often recommend enriching the diet with foods that increase hemoglobin levels. If anemia has developed into a chronic form, the deviation from the norm exceeds 20% or more, then medications that increase hemoglobin are prescribed.
Diet and healthy foods
To increase hemoglobin in a nursing mother after childbirth, you can use a protein diet, the main product of which will be red meat (lean beef, veal) and liver. The daily calorie intake of the diet should be adjusted upward by 10-20%, since the calorie intake of such a diet is not designed for a nursing woman.
You can also increase the hemoglobin level of a nursing mother with the help of beets, carrots, pomegranates, potatoes and grapes. It is also good to consume milk and fermented milk products daily. Freshly squeezed unpackaged juices are diluted with water in a 2:1 ratio, best apple, pear, grape and tomato. A nursing mother should always have fruits and vegetables in her diet.
Traditional methods
In ancient times, a nursing mother was able to increase hemoglobin after childbirth. Low hemoglobin is well cured by nettle tea. 1 tbsp. dry nettle leaves are poured with a glass of boiling water and left for 9-12 hours. Drink on an empty stomach in the morning for 14-21 days. Then a break in the course for a month, after which the use of the infusion is resumed again.
St. John's wort helps with low hemoglobin. This decoction can only be treated by women who are protected by barrier methods of contraception, since hormonal pills can fail with this herb. After childbirth, hemoglobin will return to normal within 1 month. To prepare the decoction you need 100 grams of dried St. John's wort, 20 grams of dried dandelion and 0.5 liters of boiling water. The herbs are mixed and poured with boiling water. After cooling, the steamed herb is squeezed out, and the decoction is infused in a cool, dark place for 12 hours. Take 5 tablespoons in the morning and evening, diluted in half a glass of warm water.
How to deal with anemia
The first thing you need to do is adjust your diet. If you have no contraindications, drink freshly squeezed juices from beets, carrots, pomegranates and apples. They can be mixed or diluted with boiled water.
The most valuable sources of iron:
- pomegranate;
- amaranth and alfalfa sprouts;
- Jerusalem artichoke;
- green buckwheat;
- rye;
- legumes;
- chlorophyll from nettle leaves, leafy greens, beet and carrot leaves;
- Milk thistle meal.
Among vegetables, tomatoes, herbs, pumpkin, beets and green vegetables will help increase hemoglobin. Fruits that contain large amounts of iron are quinces, peaches, apples, plums, apricots, persimmons and pears. Berries in the diet should include currants, cranberries, strawberries, strawberries and blueberries.
Diagnostics
Hemoglobin levels are checked repeatedly during breastfeeding. While a woman is in the maternity hospital, this test is taken at least three times (on the day of birth, the next day and upon discharge). In the future, the schedule for taking tests is prescribed by the local doctor or visiting nurse. A nursing mother should undergo examinations and donate blood on time to prevent the development of chronic anemia.
The hemoglobin level is determined during a general blood test. In front of it, you cannot eat, smoke, or drink iron-containing medications 12 hours before donating blood.
What is hemoglobin and what does it affect?
When we inhale air, oxygen enters our lungs, which must be distributed to all organs and tissues. Hemoglobin acts as a “transport” that delivers oxygen. This is a protein of complex composition found in red blood cells. Having “delivered” oxygen to its destination, hemoglobin “carries back” carbon dioxide, which is expelled out through exhalation.
Thus, the existence of an organism without hemoglobin is simply impossible. And a change in its quantity, both up and down, affects well-being. When hemoglobin levels decrease, “oxygen starvation” occurs, which affects general well-being.
Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of acute anemia, you need to follow simple rules:
- If there is prolonged bleeding, consult a doctor. Minor but long-term blood loss can lead to iron deficiency.
- Avoid blood donation in the first year after childbirth and for 6 months from the date of the end of the guard.
- Eat right - your diet should be rich in foods that contain a lot of iron.
- Avoid stressful situations, try not to get nervous.
- Boost your immunity and avoid getting sick.
Important! Low levels of ascorbic acid in the body can lead to problems with iron absorption, so it is recommended to take preventive courses of vitamin C during breastfeeding.
A nursing woman should take care not only of the child, but also of her body, because the condition of the baby will depend on her health. When the first symptoms of anemia appear, you need to take a blood test and consult a doctor. The diet of a nursing mother should be rich in red meat, beef and rabbit liver, eggs, grapes, cabbage, tomatoes and red peppers.
Iron-rich foods that are not recommended for breastfeeding mothers
Although some ingredients in our kitchen are rightfully considered very useful for increasing blood hemoglobin, it is better to avoid them during lactation - at least in the first couple of months after birth.
This recommendation from doctors can be explained simply - these products contain many allergens, and therefore, when feeding a newborn with breast milk, the mother should eat them with great caution. It is better to replace potentially dangerous ingredients from the list with approved ones in order to prevent the baby from developing an allergic reaction.
But if the baby is already six months old and is gradually starting to switch to complementary feeding, then the woman is allowed to try foods from the list below, but only while maintaining moderation.
If a child reacts normally to strawberries or cocoa, does not have a tummy ache after drinking mother’s milk and does not have red spots or stomach upset, then you can safely use this component as a preventive measure for iron deficiency anemia.
Dangerous and allergenic products to increase hemoglobin during breastfeeding
Grape
One hundred grams of grapes contain 0.6 mg of iron. However, such a product is often poorly tolerated by the baby’s tummy - after grapes eaten by a nursing mother, the newborn may experience intestinal colic or bloating.
Strawberry
This berry is considered one of the most allergenic and not very desirable in the diet of a young mother, despite the fact that it contains slightly more iron than grapes - 0.7 mg.
Chocolate
Real dark chocolate, prepared according to all the rules, is a real record holder for the amount of useful minerals - it contains as much as 11.7 mg of iron per 100 grams. But, like strawberries, in the first months after childbirth, such a dessert will be very undesirable during breastfeeding due to its allergenicity.
Cocoa
Cocoa powder is almost the same as chocolate, because your favorite dessert is made from cocoa beans. Therefore, along with its high iron content, cocoa is also an ingredient with a high risk of developing an allergic reaction.
Citrus
During lactation, lemons, oranges and tangerines eaten by a mother can cause serious complications in the body of her newborn. Since these fruits are traditionally classified as highly allergenic, they should not be consumed during the first months after the baby is born.
Honey
100 grams of bee honey contains 1.1 mg of iron. This value is classified as a product that is moderately beneficial for blood hemoglobin, and honey is rightfully considered an activator of the immune system. However, during lactation, this ingredient can be replaced with any other that will not cause an allergic rash in the infant.