Ultrasound at the 6th obstetric week of pregnancy
The 6th obstetric week of pregnancy is the time when the fetus can be seen quite clearly on an ultrasound. As prescribed by the attending physician, a woman can undergo this procedure at this time to determine a further pregnancy management strategy.
Why is an ultrasound scan necessary at 6 weeks of pregnancy?
The timing of mandatory ultrasound is established by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. For the 1st trimester it is 10-13 weeks, for the 2nd – 20-24, for the 3rd – 32-34 weeks. But there are cases when ultrasound diagnostics can be performed earlier:
- the woman has already had miscarriages or missed pregnancies;
- fertilization was performed in vitro (IVF);
- previous pregnancies ended in a cesarean section (that is, a scar was left on the uterus, and it is important to see how close the chorion is attached to it).
An ultrasound is performed to first confirm the fact of pregnancy, then assess where the fertilized egg is attached (in the uterus or outside it), then assess its size and identify existing threats to pregnancy.
What do they look for on an ultrasound?
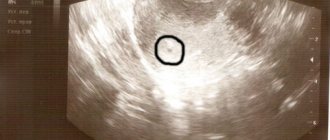
Performing an ultrasound in the sixth week of pregnancy
, the doctor will first look to see if the fertilized egg is visualized in the uterus. Next, you need to evaluate its size and see if there is a living embryo in the egg.
Also, with the help of ultrasound, you need to see how the fetal heart is formed and at what frequency it beats.
It is important to look at the condition of the organs of the reproductive system of the expectant mother. In particular, evaluate the length of the cervix, since a cervix that is too short can cause miscarriage or premature birth.
In the sixth week, the endometrium is also examined using ultrasound, identifying its pathologies.
Why does pregnancy stop?
Some women mistakenly believe that a non-developing pregnancy is a problem for those who do not properly prepare for conception: they do not take preliminary tests, do not take vitamins, and generally hope for chance. Actually this is not true. Of course, a reasonable approach to planning a baby and caring for the health of the expectant mother is extremely important, but even the most responsible and disciplined are not immune from the whims and cruelty of nature.
Irina Fedyunina, obstetrician-gynecologist, candidate of medical sciences at the Medsi clinic on Leningradsky Prospekt, says that frozen pregnancy can have many reasons, which are divided into two large groups:
- factors associated with abnormalities of the embryo itself;
- problems in the functioning of the mother's body that do not prevent conception, but have a detrimental effect on the fetus and prevent its further development.
pixabay.co/nasta_gepp
Those who are prone to excessive self-criticism and stubbornly blame themselves for what happened should remember that various types of genetic and chromosomal disorders are confidently leading among the causes of intrauterine fetal death. They account for up to 70% of all frozen pregnancies. It’s no one’s fault—that’s how the circumstances developed. In most cases, such an embryo dies in the early stages - up to seven to eight weeks.
Irina Fedyunina explains that genetic damage that occurred in the fetus and made it non-viable is in no way a mandatory sign that this kind of anomaly is present in the parents, and does not indicate the genetic incompatibility of a particular man and woman. The first pregnancy that froze in the first trimester is not a reason to despair. If no serious disturbances in the functioning of the body are detected, the doctor may allow planning after six months, or even earlier. If the misfortune recurs and the couple has to experience a second and subsequent frozen pregnancies, recurrent miscarriage may occur. Then you should seek the help of a reproductive specialist and conduct a more thorough examination.
If we talk about reasons related to the health of a pregnant woman, experts identify the following factors that threaten successful pregnancy:
- Various types of infections. Even a common flu or acute respiratory viral infection can interfere with the normal nutrition of the embryo, so it is so important for the expectant mother to take care of herself and, if possible, avoid places with large crowds of people, especially in the early stages, when the immune system is already weakened due to the new condition. Diseases of the TORCH group are especially dangerous. This concept includes infections that are dangerous for the unborn child, such as toxoplasmosis (T - toxoplasmosis), rubella (R - rubella), cytomegalovirus (C - cytomegalovirus), herpes (herpes simplex virus). The letter O in the English abbreviation means others, that is, “others,” which are usually understood as, for example, hepatitis B and C, syphilis, listeriosis, HIV. However, most often TORCH infections mean toxoplasmosis, rubella, herpes and cytomegalovirus. Each of them is extremely dangerous and can lead to vices that are incompatible with life. Sexually transmitted infections also pose a threat to pregnancy, so it is important to contact your family planning office or your gynecologist before pregnancy occurs, so that the doctor can prescribe the full range of necessary tests for your partners.
- Hormonal imbalances. An imbalance of female and male sex hormones is quite often the cause of miscarriage.
- Problems in the immune system lead to the mother's body rejecting the fetus. Own antibodies do not accept foreign cells and destroy them.
- If a child who was not destined to be born was conceived through IVF, some women unknowingly blame the in vitro fertilization procedure itself for their misfortune. This is not true. In this case, what matters is not the method of conception, but the factors that forced you to seek the help of reproductive specialists. Features of the body that prevented pregnancy from occurring naturally could most likely provoke its fading in the early stages.
- The age of the expectant mother also plays a significant role in successful pregnancy. Modern medicine has stepped far forward; I would like to hope that the offensive term “starparous” is a thing of the past, giving women the opportunity to independently decide when to give birth and whether to give birth at all. However, experts still agree that the older the patient, the greater the risk of various complications.
- Bad habits and unhealthy lifestyle. Even one smoked cigarette or glass of wine can lead to tragic consequences, not to mention the abuse of drugs or strong alcohol. Ideally, both spouses should give up addictions at least six months before planning begins. Proper nutrition, moderate exercise and walks in the fresh air will significantly increase the couple’s chances of soon becoming happy parents.
- Abortion , as well as a history of stillbirth and ectopic pregnancy.
- Constant nervous tension and stress.
- Diabetes and endocrine disorders.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome is a condition in which the blood clots too quickly, causing the fetus to be unable to receive adequate nutrition through the placenta.
- Disorders in the structure of the female reproductive organs.
Global Look Press / Ottfried Schreiter / imagebroker.com
What happens to the fetus in the sixth week?
By the sixth week of pregnancy, the fetus has grown to approximately 5 mm. Now his heart makes from 140 to 160 beats per minute, that is, it beats almost twice as fast as the heart of the expectant mother. The shape of the fetus’s body already resembles a human’s; you can distinguish where its head is and where its limbs will be.
The fetal head still remains disproportionately large, but the places where the eyes, ears and mouth will be located in the future are already marked on it.
An amniotic sac has already formed, in which the baby will remain throughout the entire pregnancy until birth.
At the sixth week, the fetus begins to actively form muscles, which means it will soon be able to make its first active movements. At first, the mother will not feel them, only by about 15-16 weeks she will feel the first pleasant kicks of the baby.
This week, all internal organs of the fetus, its nervous system, and brain also continue to develop and grow.
Is there a need for an examination after a miscarriage?
It is important to emphasize that expectant management is only suitable in a situation where a woman has no external symptoms of miscarriage. She has no bleeding, nagging pain in the lower abdomen or dizziness. If such signs still exist, you should not delay your visit to the clinic. Doctors will help you safely remove the dead embryo and, if necessary, send it for histological examination. Such research will help to understand what the root cause of miscarriage is.
A single case of frozen pregnancy, according to the clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health and the world's leading associations of reproductive medicine, is not an indication for diagnosis. It is assumed that the miscarriage occurred due to an error in the chromosomal structure of the embryo and is a random one-time occurrence.
If miscarriages and spontaneous pregnancy loss occur repeatedly, you need to understand the reasons. The exact examination plan is drawn up by the attending physician individually, based on the specific clinical picture. The only thing that is recommended under any circumstances is to conduct a study of the karyotype of the deceased embryo.
Histological analysis will determine the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the development of the embryo. If such disorders are identified, the woman is given a favorable diagnosis and the likelihood of a favorable resolution of the second pregnancy is assessed as quite high. If the structure of the embryo is normal, then the causes of the miscarriage should be looked for in the parents. The doctor can prescribe a comprehensive examination of the health of men and women, smears for infections, checking hormonal levels and the functioning of the immune system, hysteroscopy, biopsy and other diagnostic procedures. It is the identification and elimination of the real cause of miscarriage that increases the chance of having a child.
How is an ultrasound performed at 6 weeks of pregnancy?
There are two options for how doctors do an ultrasound in the 6th week of pregnancy:
- The transvaginal method
is the insertion of a vaginal ultrasound sensor protected by a special condom into the vaginal cavity of a pregnant woman. - Transabdominal method
- through the skin of the abdomen. Before the scan, women apply a special gel to their abdomen.
The first method may cause some discomfort to the woman, but its results will be more accurate and complete. Contraindications to transvaginal ultrasound for a pregnant woman may include bleeding or abdominal pain.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of a frozen pregnancy are the same in any trimester. The main signs that may indicate such a pathology are:
- vaginal discharge with blood;
- general weakness, chills, increased body temperature;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- cessation of swelling and soreness of the mammary glands;
- sudden disappearance of toxicosis manifestations;
- absence of fetal movements (with pathology in the second trimester).
Despite the existence of characteristic symptoms of the pathology, often the cessation of fetal development goes unnoticed, since the basal temperature can remain within 37 degrees, and the hCG level remains high for several more weeks. In this case, the woman learns about the problem only at her next doctor’s appointment or routine ultrasound.
What will an ultrasound show at 6 weeks of pregnancy?
What an ultrasound scan shows at the 6th week of pregnancy is very important, since it determines how the pregnancy will proceed in the future and whether its continuation is possible in principle.
Ultrasound at 6 weeks
shows:
- Is there a pregnancy?
- Location of the fertilized egg. The norm is the uterine location.
- Number of embryos. At the 6th week it will be possible to determine a multiple pregnancy.
- Dimensions of the fertilized egg. This indicator is necessary for doctors to clarify the gestational age.
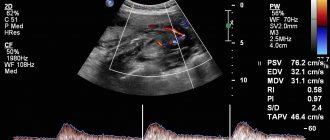
- Fetal heartbeat. Only modern equipment can allow you to listen to the heart of an unborn baby at the 6th week. If the ultrasound machine does not have this capability, you will have to wait another 1-2 weeks to accurately assess the beating frequency of the small heart.
At the 6th week, it is too early to talk about identifying any developmental defects, since not a single system or organ in the fetus has yet formed.
If the embryo in the cavity of the ovum is not visualized, this may signal the fading of pregnancy (that is, the death of the fetus). After the ultrasound, you can take a photo in which the outlines of the future baby will be visible.
Causes of heart rate disturbances
There are often cases when a baby’s heart beats faster or slower than the generally accepted norm.
There may be several reasons for this. For example, if at a period of 6–8 embryonic weeks the heart rate is 200, this may indicate the development of hypoxia in the child - oxygen starvation. In this case, various pathologies of the development of the cardiovascular system or physiological disorders may occur.
In the same case, when the beat is heard less frequently than the established norm (80 times per minute), this may signal the development of bradycardia in the fetus.
The reasons for the absence of a heartbeat may include factors such as the mother’s smoking or drinking alcoholic beverages, her development of anemia, severe toxicosis, etc.
There are often cases when in the initial stages of pregnancy the heartbeat is not heard at all or is heard very faintly. There are several main reasons:
- old equipment - in this case, the woman can be advised to go to another clinic, where the equipment is more sensitive, which will allow the fetal heartbeat to be heard;
- too much or insufficient amount of amniotic fluid - this situation simply does not make it possible to hear the baby’s heart beat. In this case, it is recommended to wait a while and repeat the examination;
- multiple births - during an ultrasound examination, the specialist cannot listen to the mixed sound of beating several hearts;
- the woman’s pregnancy period is incorrectly determined - since heartbeats can be heard for the first time only after six weeks, if the period is incorrectly determined (too short), this is simply impossible to do;
- fetal position - if the baby lies pressed against the opposite abdominal wall, during an ultrasound examination the contractions of his heart are simply not audible.
These indicators cannot be considered borderline. In each individual case there may be slight deviations from the above standards. But this is not a reason to panic.