Hypertension at a young age: questions and nuances
In modern society, there is a significant prevalence of arterial hypertension (AH), which affects 30-45% of the adult population. According to the World Health Organization, about 17 million people die each year due to cardiovascular diseases, of which complications of hypertension, such as heart attack and stroke, account for more than 9 million (55.3%).
Currently, arterial hypertension is becoming more common among young people. Early detection of hypertension through the use of the most modern diagnostic tests allows for timely treatment and prevention of complications.
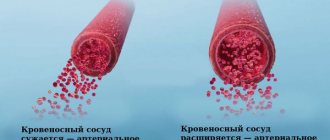
Arterial hypertension is a persistent increase in blood pressure (BP) from 140/90 and above. Only a small part of elevated blood pressure (5-10%) is associated with secondary (symptomatic) hypertension, which occurs as a complication of other diseases (renal, endocrine). Basically, high blood pressure (90-95%) is a primary vascular disease, or hypertension.
Arterial hypertension, acting as an independent chronic disease, often becomes a cause of disability and disability. Moreover, in recent years there has been a “rejuvenation” of this pathology, i.e. Hypertension goes beyond the “disease of the elderly” and is increasingly found in young and middle age. The share of young able-bodied hypertensive patients (25-35 years old) accounts for 11.9%.
The development of hypertension in adolescence and young adulthood contributes to early damage to the most important organs (heart, kidneys, brain) and, as a consequence, a decrease in both the quality of life and its duration. Currently, effective measures have been developed for the prevention and treatment of patients with high blood pressure. The success of these interventions depends on the timely detection of hypertension, especially in young people.
There are a number of problems associated with diagnosing arterial hypertension in the young population:
- Low turnover of young patients, because In most cases, the disease is asymptomatic until organs are affected.
- Lack of dispensary (regular) monitoring of young people who are at high risk for developing hypertension. First of all, this is a burdened heredity (presence of high blood pressure among close relatives).
- Young people are often exposed to several risk factors for hypertension (chronic stress, smoking, excess body weight, abuse of table salt and alcohol, low physical activity).
Every sixth man under 44 years of age (at the peak of working activity) has high blood pressure and is at risk of developing complications of hypertension, such as heart attack, coronary heart disease, stroke and other diseases.
To identify the hereditary predisposition of young people to high blood pressure, a unique genetic test “Arterial Hypertension” has been developed and introduced into practice at the Center for High Blood Pressure.
This analysis allows you to calculate the individual risk of arterial hypertension and select medications that optimally and effectively reduce high blood pressure for a particular patient. To undergo this test, you simply need to donate blood from a vein. The analysis is taken once, its results are valid throughout a person’s life.
In addition, a patient with suspected hypertension is recommended to undergo the following tests:
- General blood and urine analysis; blood plasma glucose test (fasting); study of total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides (TG); study of potassium, sodium in blood serum.
- Determination of creatinine and protein in blood plasma, ultrasound of the kidneys.
- Ultrasound of the heart and ultrasound of the arteries of the neck to detect damage to other organs.
- Ambulatory BP monitoring, which provides information about the patient's real-life BP level, provides information about the BP level during the night; more accurately assesses the effectiveness of medications used to normalize blood pressure.
The choice of treatment tactics in patients with arterial hypertension is based on the degree of increase in blood pressure and individual risks of cardiovascular complications. All patients with hypertension and moderately high blood pressure (130-140/80-90), first of all, are recommended to change their lifestyle! Stop smoking, normalize your diet by reducing salt intake, and increase physical activity. You need to walk for 30 minutes 5 times a week.
Drug treatment for hypertension will be selected by a general practitioner. In difficult cases, patients with hypertension are treated by a cardiologist.
Thanks to a huge amount of research, the benefits of lowering blood pressure below 140/90 have been absolutely proven. This really prolongs life and protects a person from heart attacks and strokes. If you notice high blood pressure, do not delay seeing a doctor. Only a doctor can develop an individual program of examination, treatment and observation for you!
Hypertension in men.
“Knowing the disease is already half the disease. M. Mudrov"
Blood pressure (blood pressure) reflects the degree and nature of a person’s activity, his attitude towards various events, positive and negative.
Arterial hypertension
in men it is most often a certain reaction to such events in life. Men develop arterial hypertension 10-15 years earlier than women. As a rule, they experience internal tension and resistance for a long time, generated by all kinds of fears, mistrust, and reluctance to accept this or that situation. They are under pressure from troubles that they cannot cope with at the moment.
Causes
The reasons for the development of arterial hypertension can also be heredity, increased body weight, sedentary lifestyle, alcohol, consumption of large amounts of salt in food, unbalanced diet, and smoking. As I.P. said Pavlov: “Don’t drink wine, don’t sadden your heart with tobacco - you will live as long as Titian lived.”
Why is it necessary to treat arterial hypertension?
This “silent killer” sometimes leads to severe complications such as strokes and heart attacks. Fortunately, today hypertension is not a death sentence; it can and should be treated, but the main thing is not to try to pretend that this problem does not exist.
In order to choose the right therapy and protect yourself from such dangerous complications, you need to consult a therapist or cardiologist in time, get qualified advice, and undergo the necessary laboratory and instrumental examinations to clarify the extent and stage of the disease. Currently, various modern methods of therapy and diagnosis are used to treat hypertension. This includes ABPM for blood pressure control, the use of sartans, calcium inhibitors, cardioselective B-blockers, and metabolic drugs.
As a preventative measure, don’t forget about a healthy lifestyle, walking, playing sports and fitness, and swimming. Sanatorium-resort treatment also helps perfectly to recover after therapy.
The main thing is not to miss the problem
, and contact a specialist (general practitioner or cardiologist) as early as possible and begin treatment for arterial hypertension in the initial stages. Then in the future you will not have to deal with more serious illnesses.
Prepared information for you:
Vitaly Vladimirovich Tsirkunov – general practitioner. Conducts receptions in the clinic building on Ozerkovskaya.
What studies and tests should you undergo if you have high blood pressure?
Arterial hypertension is a condition that is often accompanied by changes in metabolism and disorders of internal organs. Therefore, simply monitoring blood pressure levels using a tonometer is not enough.
It is advisable for all hypertensive patients and people with a tendency to high blood pressure to undergo periodic examinations consisting of the following studies and tests:
- To begin with, you must undergo general clinical tests : a general blood test and a general urine test. They will help assess your health, identify inflammatory processes in the body, anemia, and metabolic disorders.
- Biochemical blood test with a targeted study of cholesterol . This test is recommended once a year for all people over 30 years of age. It is atherosclerosis, caused by increased cholesterol levels in the blood, that is the main cause of arterial hypertension in older age. Metabolism is disrupted, a large amount of “bad” cholesterol enters the bloodstream, and cholesterol plaques begin to grow in the lumen of blood vessels.
- Blood glucose test . This analysis is most relevant for people over 40 years of age. With excess body weight, poor nutrition, and a predominance of fatty and sweet foods, there is a very high load on the pancreas. The result may be type 2 diabetes. This disease is accompanied by an increase in blood glucose levels, does not manifest itself for a long time and contributes to the development of symptomatic hypertension.
- Study of blood electrolytes . High blood pressure is often accompanied by increased sodium in the blood.
- Blood clotting study . Often, increased blood pressure is accompanied by impaired blood flow and the formation of blood clots.
- Electrocardiography is a study that helps assess the functional state of the heart, identify disturbances in its functioning, and enlargement of the atria and ventricles.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys . The kidneys are an organ that greatly influences blood pressure levels. After all, they are the ones who filter the blood and turn it into urine.
Among medical specialists, it is advisable to periodically visit a therapist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, neurologist.
Those taking potassium-sparing drugs (veroshpiron, ACE inhibitors, sartans) are recommended to periodically check the level of potassium in the blood.
Cardiologist Nartova N. A
HYPERTENSION IS A DISEASE OF YOUNG CAREERISTS
09.Sep.2019
Recently, doctors have been sounding the alarm: hypertension has become much younger. Moreover, this disease often affects men and women in the prime of life, successful in their careers, professionals in their field, in general, avid workaholics.
What is the reason?
Why do such, at first glance, young and healthy representatives of the strong and beautiful half of humanity often experience unexpected heart attacks and acute heart failure? Medical professionals name several reasons...
Reason 1.
Doctors have long noticed that hypertension is much more common among people of the so-called type A - responsible, ambitious, striving for excellence, experiencing any “inconsistency” as a personal tragedy. Such people occupy leadership positions and are always trying to make the world a better place (unlike Type B people, who take everything as it is and calmly float with the flow of life).
What to do?
Change your attitude a little towards everything that happens. Try to protect yourself from stress. For example, if you work, try to never combine two things of paramount importance, do not schedule an important meeting for you 2 hours before a meeting with your boss or a scheduled visit to the doctor.
Remember, there is nothing that cannot be fixed.
Reason 2.
Eating out. Restaurant food has several deficiencies that increase the risk of hypertension. Typically, such dishes contain more salt than when cooking at home. Sometimes not only sodium chloride is used, but also sodium gluconate, which makes the taste of food more intense. Excess sodium in the body retains water, and the blood vessels narrow. As a result, blood pressure immediately increases. In addition, such food contains a lot of fat, which contributes to the growth of excess weight. And the risk of developing hypertension is 6 times higher in those who suffer from excessive obesity.
What to do?
Limit the consumption of table salt. This can be easily achieved if you ask your family to add less salt to their food and take food from home with them. Following this rule can normalize blood pressure without the help of medications. Eat dried apricots, spinach, buckwheat, millet and oatmeal, beans, prunes, dates, peaches, watermelons, beets, zucchini, eggplants, herbs, and nuts more often. Move more. The most accessible and safe types of physical activity are swimming and walking for an hour a day. But an abrupt start in a sports club if you are prone to hypertension can provoke a heart attack.
Reason 3.
Smoking and alcohol. Each cigarette smoked causes a short-term but significant increase in blood pressure, which has a harmful effect on the elasticity of blood vessels. Alcohol consumption has the same effect. What to do? Try to quit smoking or at least reduce the number of cigarettes.
Replace strong drinks with dry wine, preferably red. Scientific research by Norwegian scientists in recent years has shown that a glass of dry red wine a day reduces the risk of developing atherosclerosis and hypertension by 23%.
Reason 4.
Carelessness. Do you not really think about what your blood pressure is, and attribute frequent headaches, tinnitus and heart tingling to fatigue? Meanwhile, high blood pressure paves the way not only for chronic hypertension, but also for heart attack, stroke and heart failure.
What to do?
Doctors have long noticed that for hypertensive patients there is a “law of halves.” Half of them do not know about their disease, and of those who know, only half are treated. Try to be among those who find out about their illness in time and begin to fight the disease in a timely manner. Dear workaholics, devoting yourself entirely to work, do not forget about your health, because your productivity, family well-being and your success in all endeavors will depend on it.
Yulia Maslova,
general practitioner, Nyagan City Clinic