Cardiologist
Sokolov
Denis Vladimirovich
16 years of experience
Cardiologist of the first category, candidate of medical sciences, member of the Asute Cardiovascular Care Association (ASSA)
Make an appointment
Angina pectoris is a pathology that manifests itself in representatives of different age groups in the form of attacks of myocardial ischemia. Symptoms arise against the background of increased physical or emotional stress that the patient faces. People suffering from angina pectoris experience pain in the heart area and shortness of breath. Autonomic reactions develop as a result of exposure to unfavorable external factors on the body.
Reasons for the development of pathology
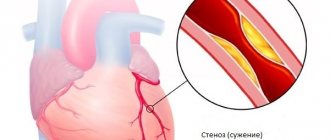
Often the symptoms of angina pectoris develop against the background of atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. The lumen of the blood vessels narrows by 50-70%, which leads to the delivery of less oxygen to the heart muscle with constant consumption. Common causes of angina remain arterial hypertension, coronary spasm, aortic stenosis, and congenital anomalies of the coronary arteries. Pathology can become a complication in acute coronary thrombosis.
Risk factors include:
- systematic smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- age over 55 years;
- obesity 3-4 degrees;
- early menopause;
- diabetes.
The risk group includes patients with pathologies of the cardiovascular system in a family history. Severe forms of anemia and hypoxia can complicate the course of the disease.
Why does angina pectoris FC 3 develop?
The main reason for the progression of cardiac diseases associated with a lack of oxygen in the myocardium is atherosclerotic plaques that appear due to elevated cholesterol levels in the blood. They clog blood vessels, preventing blood from circulating normally. Several factors can provoke atherosclerosis:
- Increased blood pressure - the walls of blood vessels become thinner and more susceptible to damage, which simplifies the formation of plaques;
- Male gender is another risk factor. If women have the hormone estrogen in their blood, which helps eliminate cholesterol, then in men this harmful substance accumulates in the body;
- Poor nutrition is the main reason. Patients whose heart condition requires diagnosis and treatment usually abuse fatty, smoked, and fried foods. They do not watch what they eat, may be overweight, and constantly overeat;
- Cardiovascular diseases are one of the provocateurs of attacks and are often hereditary;
- Insufficient level of physical activity;
- Increased heart rate – when the heart rate increases, the body requires more oxygen. An attack can be triggered by playing sports, emotional shock, and even a regular walk at a slow pace.
However, it is not enough for the patient to remove physical stress - the pain will continue despite the reduction in stress. In the most severe cases, when an attack occurs at rest, and functional class 3 changes to FC 4, surgical intervention is required.
Forms of pathology
Cardiologists distinguish three types of the disease: primary, stable and progressive. The first and second forms can transform into the third over time. A more extensive classification of angina pectoris is based on the patient's tolerance to physical activity. The intensity of the maximum permissible human activity allows us to distinguish four functional classes.
| Functional class (FC) | Description |
| I | Daily loads are tolerated without consequences. The attack develops against the background of unusual activity - running, climbing a large number of flights of stairs, lifting heavy objects. |
| II | Minor physical activity provokes the development of symptoms. Causes may include leisurely walking, climbing stairs to a height of more than one floor, emotional stress |
| III | The patient cannot tolerate minimal physical activity. An attack occurs when walking a distance of 50-100 meters. Climbing stairs is difficult |
| IV | Activity is significantly limited. Angina pectoris occurs when performing basic actions or while at rest |
First aid for a seizure
Angina pectoris is a chronic disease. Therefore, a complete cure is not always possible and only through surgical intervention.
But first of all, the patient and his immediate environment need to learn how to provide first aid during attacks.
Nitroglycerin and drugs based on it are the main means for stopping a crisis. At the first symptoms, the patient needs to put one tablet under the tongue and dissolve it. If the attack is severe, you can give it twice. It is better if the oral cavity is sufficiently moist. The maximum dose, 5 tablets, is taken in extremely severe cases when medical help is not expected.
You can also use a spray instead of tablets. The results of the action of nitroglycerin can be seen within a couple of minutes.
- IHD, exertional angina: diagnosis and treatment
Sometimes they try to stop the attack with validol. This is a grave mistake, since this medicine not only does not help, but can cause serious harm to health.
But those around you can use simple ways to ease the crisis. To do this, it is necessary to stabilize the patient’s condition as much as possible, both physically and morally:
- the person must be allowed to stand for a while and catch his breath if the attack was provoked by intense physical activity;
- if the cause is stress, the patient needs to be reassured;
- it is important to provide the person with a sitting or semi-sitting position, as well as an influx of fresh oxygen;
- the body should be freed from any oppressive objects, including belts, collars, and excess outerwear;
- You can place heating pads with warm water on your feet.
Symptoms of angina pectoris
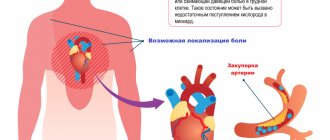
Patients experience pain of varying intensity: from mild discomfort behind the sternum to severe pain in the heart muscle. The duration of a typical attack is 3-5 minutes, there are pronounced onset and end phases. The intensity of symptoms decreases when the provoking factor is eliminated. The pain of angina pectoris is radiating and can affect the jaw, shoulder blade, arm or neck.
During an attack, the patient feels weak, shortness of breath appears, and tachycardia and arrhythmia develop. Representatives of the older age group may experience a sharp increase or decrease in blood pressure. In rare cases, an atypical attack develops, accompanied by abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
The frequency of manifestations of angina pectoris varies. Patients may experience up to five attacks per day or experience a sharp increase in symptoms every few months. If left untreated, angina at rest may develop against the background of exertional angina.
Are you experiencing symptoms of angina pectoris?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
How it manifests itself
Stable angina pectoris is divided into classes depending on the factors that provoke the appearance of pain. The mildest degree (FC 1) corresponds to the occurrence of an anginal attack when performing extremely strong work.
A pathology with a slight limitation of normal physical activity is placed one step higher, when the patient finds it difficult to walk more than two blocks or climb to the second floor.
Angina pectoris, in which an attack develops when climbing one flight of stairs or walking at a normal pace of 100-200 m, corresponds to FC 3.
Functional class 4 is considered the most severe, with the development of the syndrome at rest up to difficulty in self-care.
The nature of pain in ischemic heart disease:
- Localized behind the sternum;
- They have a pressing, squeezing character. Some patients describe burning pain.
- They radiate to the shoulder blade, left shoulder girdle, arm, lower jaw.
The clinical picture is complemented by increased heart rate, pallor, the appearance of sweat on the forehead, and other subjectively unpleasant sensations.
Among the common features inherent in cardiac ischemia, some individual differences can be identified for each form of coronary artery disease.
- Angina pectoris: general information
Pain syndrome with stable angina is characterized by attacks lasting up to 3–5 minutes, which subside on their own or after taking nitrates.
The equivalent of pain can be shortness of breath, which impedes activity and replaces cardiology.
Diagnosis of pathology
The patient is examined by a cardiologist. The most effective way to diagnose exertional angina is an ECG obtained during an attack. Ischemia is induced by stress testing. Conducting them in a clinical setting eliminates the possibility of complications developing in the patient. Holter monitoring can detect myocardial ischemia and heart rhythm disturbances.
EchoCG is aimed at assessing myocardial contractility. The use of this technique allows for differential diagnosis and exclusion of other pathologies of the cardiovascular system from the patient’s medical history. Laboratory tests - general and biochemical blood tests - provide an opportunity to detect signs of atherosclerotic damage to the patient’s blood vessels.
When should you see a doctor?
The severity, duration and form of angina may vary. It is important to determine whether your chest pain is changing or developing new sensations. A signal of a more dangerous form of unstable angina or a heart attack (myocardial infarction) may be the appearance of new symptoms or a change in existing ones.
If you notice that angina attacks have begun to recur more often, their nature and intensity have changed - this is a reason to think about a cardiac examination as soon as possible. You can make an appointment with a specialist at our clinic or get answers to your questions using a service such as online consultation with a cardiologist - it is available on our website at any time.
Treatment
Therapy begins with the elimination of all provoking factors that can affect the condition of a person suffering from the pathology. The attacks are controlled by taking nitroglycerin. After making a diagnosis, the cardiologist can prescribe the patient long-acting nitrates, antiplatelet agents, calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers.
The persistence of symptoms during conservative treatment becomes a reason to refer a child or adult for surgery. During the intervention, surgeons perform stenting of the coronary arteries and perform endovascular angioplasty. Clinical recommendations provide for the possibility of coronary artery bypass grafting against the background of exertional angina. The effectiveness of surgical treatment is 90-95%.
Questions and answers
Is there a set of preventive measures to prevent the development of angina pectoris?
Recommendations from cardiologists are addressed to people with a family history of coronary heart disease. Doctors insist that patients stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Fatty foods should be excluded from the diet. The dosage of medications prescribed for pathologies of the cardiovascular system should be observed.
Is surgery necessary for exertional angina?
The need for surgical intervention is determined by the clinical picture of the disease. For mild cases, patients are prescribed medication. The risk of complications or a severe form of pathology can become a decisive factor when a doctor makes a decision on surgical treatment.
Definition
Functional classes of angina pectoris are the division of the disease depending on the patient’s tolerance to physical activity.
Functional classes (FC) of angina are distinguished according to the classification proposed by the Canadian Heart Association. Angina pectoris occurs as a result of insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle during work. When performing physical exercises, stress and anxiety, the heart's need for oxygen increases, which is why attacks with angina pectoris are associated with any kind of stress. There are four functional classes of angina: I-III refer to stable angina, IV - to unstable form. The higher the class, the less the patient is able to freely perform physical activity.
Statistical data
Pathologies of the cardiovascular system remain the most common cause of death among Muscovites – 55% of cases in 2019. This figure is three times higher than the European average. The total number of Russian residents suffering from heart disease exceeds 16 million people. A quarter of them have congenital pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Prevention of attacks of myocardial ischemia remains one of the key tasks of cardiologists when monitoring patients at risk.