The most common form of coronary artery disease is angina pectoris. An exacerbation of this disease occurs with increasing physical stress on the body and the inability of affected or narrowed vessels to fully satisfy the increased demands of the myocardium for blood flow. According to statistics, IHD diseases are the most common causes of death, both in Russia and throughout the world. They account for up to seventy percent of all deaths associated with human cardiovascular diseases.
Signs
The main signs of exertional angina in a patient are:
- dyspnea;
- the appearance of pain in the heart;
- tightness of breathing and discomfort in the chest area.
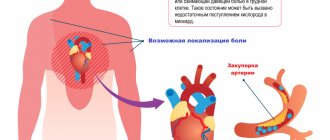
With this disease, pain can be felt in the sternum, but can radiate to the cheek, neck, left arm or under the left shoulder blade. When an attack of illness occurs, other phenomena are possible:
- sudden weakness;
- the appearance of cold sweat;
- Heart arythmy;
- pressure surges.
Sometimes such an attack causes stomach pain, vomiting, nausea, and flatulence. A typical attack of the disease lasts from two to five minutes. Depending on the form of the disease, such exacerbations can be repeated from several attacks a day to one over several weeks or even months.
Prevalence of the disease
Angina pectoris is most common among older people. For example, among men aged 45 to 55 years it occurs in 2-5%, and among men over 65 years old - in 10-20%. Among women, this disease is less common. Factors that increase the risk of contracting this disease are:
- smoking;
- physical inactivity;
- diabetes;
- obesity.
First aid for an attack
Since the origin of the negative sensation is not clear, you need to call an ambulance immediately after the pain begins. There is no need to be shy, life is much more valuable.
The following is the algorithm:
- Measure blood pressure and heart rate. If both indicators are above normal, this is typical for the clinical picture.
- Take a Nitroglycerin tablet to relieve pain. Intense tachycardia is eliminated with Anaprilin (1 tablet); it is also possible to use Captopril (1/4 tablet) if blood pressure reaches critical values (over 180 per 100 mm Hg). However, this is a last resort.
- Open a window or vent to ensure adequate ventilation of the room. On the street, try to go into the nearest building; you cannot be in the cold, as this aggravates the general condition of angina pectoris.
- Sit down and relax. It is not recommended to lie down; shortness of breath may increase. There is no need to panic.
- Unfasten the collar and remove body jewelry from the neck. This will prevent the progression of symptoms against the background of a reflex reaction.
Wait for the medical team to arrive and tell about your complaints. Further, the issue is resolved at the discretion of the paramedic.
Causes
Most heart diseases are associated with vascular ischemia. The occurrence of ischemia, that is, the appearance of an imbalance between the blood supply required by the heart muscle and the actual coronary blood flow, is associated with a decrease in the capacity of the blood vessels. The reason for this is atherosclerosis. This phenomenon appears when blood vessels narrow, plaques, tumors, and the like appear in blood vessels.
The heart and its muscle, the myocardium, play a major role in the human body. Normal functioning of the cardiovascular system occurs due to the contraction and relaxation of the myocardium. But such work requires a large amount of energy. The myocardium receives this energy thanks to chemical reactions that implement metabolic processes, that is, myocardial metabolism.
For normal functioning of the myocardium, it must be supplied with oxygen through the blood supply system. As the load on a person increases, the amount of oxygen entering the myocardium should increase. However, in people with atherosclerotic coronary arteries, blood flow is limited. With increasing load, this blood flow does not increase, and therefore ischemia occurs. As a result, the contractile action of the myocardium worsens and the metabolic processes occurring there are disrupted. In this case, there is a lack of oxygen, which leads to depletion of energy potential and to an attack of angina pectoris.
Classification
Angina pectoris is divided into the following forms:
- primary;
- stable;
- progressive.
The disease is considered primary if less than one month has passed since the first attack. Then the disease can behave differently - either go into the second (stable) form or disappear completely. The stable form continues for a longer time and is distinguished by the fact that under the same load the body behaves in the same way. The disease in this form can persist for several years.
The third (progressive) form is unstable. With this form, the same load causes more and more severe attacks, which become more and more prolonged.
Depending on the patient’s ability to tolerate stress, angina pectoris is divided into 4 functional classes (FC). At the same time, the lightest classes are 1FC and 2FC, and the more dangerous are 3FC and 4FC.
In the presence of a disease of the first functional class, a person easily overcomes standard loads, and exacerbations occur only with relatively large efforts. For example, during a long climb up the stairs or a short jog.
A person who has been diagnosed by a doctor with “effort angina of functional class 2” has some restrictions on exercise. Ordinary walking over a distance of 500 m or climbing stairs to the second floor of a house can cause seizures in such a patient. In this case, the occurrence of exacerbations can also be affected by wind, cold weather or human emotions.
Persons with such a diagnosis may qualify for group 3 disability. But this is only possible if they previously suffered an uncomplicated myocardial infarction.
For a person diagnosed with a disease of the third functional class, the loads have significant limitations. Exacerbations in him can be caused by walking a hundred to five hundred meters or climbing the stairs of a house just one flight. In a patient with a fourth functional class disease, physical activity is severely limited. He may have seizures with little effort or even in a calm state.
How does pathology develop?
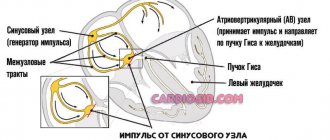
Normally, the heart, including muscle fibers, is supplied with blood, nutrients and oxygen through the coronary arteries.
During certain pathological processes, stenosis (narrowing) or occlusion (blockage) of these vessels occurs. Dystrophy of anatomical structures occurs, which ends with attacks of myocyte necrosis of varying frequency and intensity.
Then the contractility of the heart decreases, and both general and local hemodynamics are disrupted. Blood circulation in the heart suffers even more.
It turns out to be a vicious circle. The pathology worsens in a cyclical, independent manner. Starting from the second functional class, spontaneous regression should no longer be expected.
Angina pectoris differs from other forms by a provoking factor.
An episode of pain and symptoms develops due to intense physical activity or a strong emotion (negative most often, but possibly positive). Stress in general with an average manifestation of affect also has an effect.
The etiological aspects are somewhat different. In this regard, angina is a secondary process.
The primary ones are cardiac changes and vascular diseases. Often a person himself is the creator of his own condition. Patients who smoke and drink are especially at risk. Heredity plays a big role.
According to the classification, there are four functional classes (abbreviated FC). Each subsequent one imposes great restrictions on the patient’s physical activity (more details here).
At the last, fourth stage, attacks occur in a state of rest, and there are no prospects for cure.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of the disease can be made by a cardiologist after conducting a series of studies. They may be:
- ECG;
- EchoCG;
- load tests (bicycle ergonometry, treadmill test, walking tests);
- stress echocardiography;
- Holter monitoring;
- positron emission tomography.
In addition, a biochemical blood test is performed. According to this analysis, depending on the content of cholesterol and lipids in the blood, the possibility of vascular atherosclerosis is assessed. When diagnosing this disease, the cardiologist must distinguish this disease from other diseases that may have similar symptoms. Such diseases include:
- osteochondrosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- lung diseases (pneumonia).
Angina pectoris 3 FC
Patients suffering from this type of illness often limit themselves in exercise in order not to experience discomfort. Angina pectoris is provoked even by walking on a level road at the speed at which an ordinary person walks. Five hundred meters traveled is enough for patients to develop progressive angina. Also, for such patients, angina pectoris can also be triggered by external influences (adverse weather conditions, stress, emotional overload). Doctors working with patients in this category note that this condition occurs against the background of coronary artery disease, which the patients suffer from.
Treatment
To stop an attack of angina pectoris FC 2 you need to:
- remove the load;
- sit down or lie down;
- take a nitroglycerin tablet.
Treatment of the disease is usually aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of attacks. For this, the following recommendations are available:
- lifestyle changes (quitting smoking, alcohol and other bad excesses);
- reducing stress that provokes attacks;
- mandatory intake of medications prescribed by the doctor.
Medicines for the treatment of angina pectoris FC 2 usually include the following drugs:
- aspirin (reduces the possibility of blood clots);
- nitrates (isosorbitol dinitrate, isosorbitol mononitrate, nitroglycerin ointment);
- beta-blockers, which reduce myocardial oxygen demand;
- statins – to reduce cholesterol levels.
Folk remedies
When treating angina, in consultation with your doctor, you can use folk remedies along with medications. For example, these include:
- hawthorn;
- horseradish with honey;
- herbal infusion.
To obtain a hawthorn tincture, seven tablespoons of berries are brewed with boiling water and infused. Then strain and drink 1 glass during meals. Horseradish, grated, is mixed with honey (ratio 1:4). Take 1 teaspoon twice. This remedy is used for mild angina if it occurs without pain in the chest.
An infusion of herbs helps with palpitations and relieves pain in the heart area. The infusion consists of hawthorn, lemon balm, horsetail and valerian, poured with boiling water. To obtain an infusion, pour 1 tablespoon of the mixture into 1 glass of boiling water. Then infuse and drink one third of a glass before meals.
Why is angina pectoris FC 2 dangerous?
The main threat is to cardiac structures.
An approximate list of complications:
- Heart failure. As a result of acute malnutrition, or as a result of prolonged ischemia. With stable angina, FC 2 occurs in 15% of cases. For progressive (unstable) forms - up to 30%.
- Heart attack. Avalanche-like myocardial necrosis. This is the only difference between the phenomena under consideration. It is the final stage of coronary artery disease and coronary insufficiency in general.
- Stroke. Death of nerve tissue of cerebral structures. Leads to the development of a permanent defect. Which one depends on the location of the lesion.
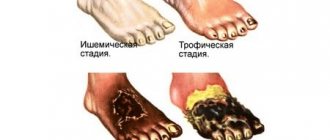
- Ischemia of the lower extremities, secondary atherosclerosis with the prospect of developing gangrene.
- Vascular dementia.
All conditions are potentially fatal and carry a risk of disability. Preventing dangerous consequences is one of the key goals of therapy.
Forecast
The prognosis for the disease depends on its severity. The most favorable prognosis is in the presence of a stable type of disease. A more dangerous prognosis is possible with primary angina. This is due to the uncertainty of the further course of the disease. The most severe prognosis is for the unstable form of the disease. The following additional factors negatively affect the prognosis of this disease:
- presence of a heart attack;
- advanced age;
- presence of coronary artery stenosis;
- presence of class 4 angina pectoris.
Diagnosis of the disease
Basically, this type of disease is diagnosed based on the following examinations:
- examination and questioning of the patient;
- research in the laboratory;
- research using special equipment.
In the first case, after listening to the patient’s complaints, he compares them with symptoms characteristic of IHD. The basis of the examination is auscultation, thanks to which the doctor identifies heart rhythm disturbances and cardiac murmurs.
Laboratory tests include a coagulogram and a lipid profile, since only these two examinations can provide the necessary information for selecting the correct therapeutic treatment.
The list of instrumental studies includes such procedures as:
- coronary angiography;
- echocardiography;
- electrocardiography.
Using the above methods for diagnosing IHD, it is possible to identify not only the exact form of the disease, but also to establish a disability group.
Prevention
To prevent angina pectoris 2 FC it is necessary:
- quit smoking, which negatively affects blood vessels;
- take measures to reduce weight;
- follow a diet (reduce caloric intake and eliminate fatty foods);
- treat high blood pressure (hypertension);
- Take preventive medications prescribed by your doctor.
conclusions
- Angina pectoris is one of the forms of coronary artery disease. It poses a danger to human health and life.
- To detect the disease, as prescribed by a cardiologist, studies of the condition of the heart and blood vessels, as well as a biochemical blood test, are performed.
- To stop an attack of the disease, a nitroglycerin tablet is used, and for the complex treatment of the disease, a set of drugs is usually used, including aspirin, nitrates, beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers, as well as cholesterol-lowering agents.
- To prevent exacerbation of angina pectoris FC 2, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and follow a diet. At the same time, you should not be overloaded physically and emotionally.
Symptoms
Manifestations of FC 2 of exertional angina occur as a result of moderate physical and emotional activity and are quite pronounced.
If we translate abstract words into something concrete: it is impossible to climb to the 2-3 floor, sports are also no longer available. Even intensive walking is difficult.
The following manifestations occur:
- Chest pain of moderate intensity, not too pronounced, is the main characteristic symptom. It radiates to the shoulder blade and left arm, moving as if through the veins and reaching the hand. It does not intensify with movement or breathing, which distinguishes it from the discomfort caused by intercostal neuralgia. Treated with Nitroglycerin. Duration: 10-12 minutes, but no more than half an hour. Deviations towards intensification indicate a possible heart attack.
- Dyspnea. Increase in the number of movements per minute. In the second class of angina, it is already difficult not to notice it. Characterized by discomfort and dissatisfaction with inhalation. Accompanies moderate physical activity.
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, blue discoloration of the area around the mouth.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Panic attack. The patient becomes anxious and is in an inadequate state. Help Wanted.
- Increase in blood pressure. Not always, but often. Within insignificant limits.
- Nausea, dizziness.
- Arrhythmias. By type of tachycardia, as a rule. The frequency of contractions remains normal, but the intensity of work is higher.
- Fainting is possible. Relatively rare. Indicate the involvement of cerebral structures in the pathological process.
At the end of the attack, the entire clinical picture disappears.
Attention:
If it lasts more than 30 minutes, there is a high risk of a heart attack. It is easy to confuse it with angina pectoris without experience. Mortality is many times higher. It is also possible to smoothly flow from one state to another.