A condition in which the rhythm, frequency and depth of breathing is disrupted, and a feeling of air deficiency occurs, is called shortness of breath. The causes and treatment of this disorder can be very diverse. Shortness of breath can occur under various conditions. So, for example, there is shortness of breath when talking, shortness of breath when lying down, after sleep, shortness of breath at rest, etc. The breathing of a person with shortness of breath is frequent and noisy; it is these manifestations that give others reason to assume the presence of shortness of breath. Shortness of breath can be a consequence of quite serious diseases, therefore, when it appears, it is necessary to contact a specialist as quickly as possible, who will competently explain what shortness of breath is and how it manifests itself, and also prescribe a comprehensive diagnostic examination to identify the causes of its occurrence.
The Therapy Center of the Yusupov Hospital offers high-quality diagnostics and effective treatment of diseases accompanied by shortness of breath. If necessary, a pulmonologist can be called to your home.
Types of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath can be of several types:
- inspiratory (shortness of breath while inhaling), expiratory (during exhalation) and mixed (with difficulty in inhaling and exhaling);
- tachypnea (increased shallow breathing) and bradypnea (decreased breathing);
- physiological - transient, reversible intensification of breathing (shortness of breath during physical exertion). The causes of shortness of breath in this case are that it is an adequate adaptive response to stress, injury, or an objectively low level of oxygen in the inhaled air;
- pathological (in case of airway obstructions due to bad habits, cardiovascular failure, obesity, lung diseases, hematopoietic system, etc.).
Why does shortness of breath occur?
If a person suddenly develops severe shortness of breath, the reasons can be very diverse. Most often it is caused by the following conditions:
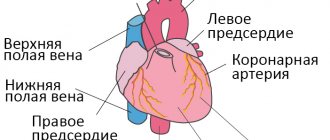
- cardiovascular diseases – due to these pathologies, blood circulation is impaired. Internal organs suffer from a lack of oxygen, and carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood. The body’s reaction to this condition is increased breathing: a larger volume of air is pumped through the lungs per unit of time. In the supine position and after physical activity, shortness of breath associated with heart pathology occurs or intensifies. Severe shortness of breath occurs with the patient sitting or half-sitting. This kind of shortness of breath is characterized by difficulty breathing;
- diseases of the respiratory system - the appearance of shortness of breath is associated with obstacles to the passage of air through the respiratory tract (for example, narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi). Therefore, shortness of breath is considered a typical symptom of bronchial asthma. With this disease, the patient experiences difficulty in exhaling. In addition, shortness of breath occurs in cases where the respiratory surface of the lung tissue is reduced. Such a decrease is accompanied by an increase in the intensity of lung function, i.e. frequent inhalation, which is necessary to maintain the required amount of oxygen entering the blood. The list of pathologies of the respiratory system accompanied by shortness of breath includes neoplasms, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, etc.;
- anemia - even with normal activity of the lungs and heart, a deficiency of hemoglobin and red blood cells leads to insufficient provision of the organs with the necessary amount of oxygen. To compensate for this disorder, the body increases its breathing rate;
- neuroses and panic attacks - in these cases, clinical examinations do not reveal the presence of cardiovascular and pulmonary pathologies, but subjectively the patient suffers from lack of air, and the appearance of psycho-emotional changes provokes increased breathing, which causes shortness of breath;
- various tumors – shortness of breath occurs with a tumor of the thalamus, intestinal tumors, etc.;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract. For example, hoarseness, cough, shortness of breath with esophagitis are characteristic symptoms;
- obesity and diabetes are common causes of shortness of breath.
Respiratory neurosis
There are many types of neuroses, each of which is distinguished by a specific group of symptoms. One of them is respiratory neurosis, which is characterized primarily by neurogenic breathing disorder.
The concept was introduced into use in 1871 by the American scientist Da Costa. It has several related names: “respiratory neurosis”, “neurorespiratory syndrome”, “respiratory dystonia”. But the term most often used is “hyperventilation syndrome” (HVS) . It accounts for approximately 10% of cases. Among the patients there are both children and adults. It is worth noting that women suffer from this disease several times more often than men.
The causes of the syndrome are divided into mental, organic, and mixed. Of course, the majority (about 60%) is due to psychogenic factors.
5% of cases include organic etiology. These include disorders of the structure of the central nervous system: encephalopathy, hydrocephalus, inflammation of the meninges, as well as diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, chronic bronchitis. Sometimes the reason is taking certain medications.
During the course of the disease, there are 3 groups of signs:
- respiratory;
- psycho-emotional;
- muscular.
Group I has several forms of manifestations:
- Empty breathing is a feeling of lack of air, its pace quickens.
- It seems that air is forced into the lungs, and there is a lump in the throat. Accessory muscles are involved in the respiratory act.
- A premonition of breathing stopping appears, and the person is forced to control its process by consciously inhaling.
- Yawning, moaning, sighing.
Group II symptoms include nervous tension and concern about one’s condition. The patient cannot relax. He develops phobias, in particular, a fear of open areas and places with large crowds of people.
Symptomatic group III includes muscle hypertonicity, various tactile sensations in the form of tingling, burning, and “goosebumps.”
This triad of symptoms is a typical, leading manifestation of the disease.
The disease is characterized by a chronic course, in which exacerbations occur.
An exacerbation of hyperventilation syndrome is called a hyperventilation crisis. This is a condition in which the manifestations of the disease intensify. Characterized by an increased sense of fear. The patient is suffocating, hysterical, and feels “near death.” At the same time, he is accompanied by chills, dizziness, nausea, and becomes covered in sticky cold sweat.
A crisis is caused by a negative psychological environment. A unique way to relieve an attack is to breathe into a bag. In this case, carbon dioxide is concentrated in it, which the neurotic inhales. Gas balance is restored, breathing is leveled out. This is the first aid in this situation.
As for children, they are also characterized by such a pathology as respiratory neurosis, which is also caused by stress, phobias and anxiety disorders. But it is worth noting that the main role in their occurrence is played by an unfavorable situation in the family, and this applies not only to rude and inadequate attitude towards the child, but also to the relationship between parents. Constant quarrels and conflicts in the family, aggression can provoke the development of psychogenic shortness of breath in children.
Such children are characterized by anxiety and lability (instability) of mood. They experience outbursts of anger over trifles, general nervousness, refusal to communicate with friends, and sleep disturbances.
Parents should be more vigilant and sensitive in raising their children.
Shortness of breath in people of different age categories
Shortness of breath can occur in people of all ages, from infants to the elderly.
In children, shortness of breath can be both physiological and pathological. The appearance of physiological shortness of breath is caused by physical exertion or high anxiety, which is considered normal. When the respiratory system is immature, pathological shortness of breath occurs in the infant. How to determine the type of shortness of breath and its causes is decided by the pediatrician, selecting the necessary diagnostic methods.
In old age, people's tolerance to physical activity decreases and the efficiency of the respiratory system decreases. Due to age-related changes, the physical strength of the respiratory muscles decreases, as a result of which gas exchange worsens and normal breathing becomes difficult. In addition, older people tend to have diseases of the cardiovascular system and lungs, which lead to shortness of breath. Most often, they do not pay attention to this symptom for a long time, so the diseases that accompany it are diagnosed at advanced stages. As a result, treatment becomes more difficult, the quality of life and its duration are significantly reduced. So it is better to immediately seek medical help if shortness of breath occurs in older people, without waiting for the condition to worsen.
The best pulmonologists in Moscow - Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Alexander Vyacheslavovich Averyanov, Candidate of Medical Sciences Alexander Evgenievich Shuganov are receiving appointments at the therapy center of the Yusupov Hospital. Klina is equipped with innovative high-tech equipment for conducting the most modern diagnostic studies. Thanks to an integrated approach involving specialized specialists in various fields, our doctors identify the exact cause of shortness of breath and select an effective treatment regimen, taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient.
What is shortness of breath in humans: symptoms
The occurrence of shortness of breath in the initial stages of damage to the cardiovascular and respiratory systems is associated with physical exertion (for example, when the patient climbs up the stairs). As the pathology progresses, shortness of breath and fatigue appear even with a slight load (walking on a flat surface, tying shoelaces, etc.), as well as at rest.
Patients perceive shortness of breath quite subjectively. It may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- difficulty breathing (inhalation/exhalation);
- compression in the chest;
- feeling of congestion in the chest area;
- tightness in the chest;
- feeling of lack of air;
- inability to take a deep breath or exhale completely;
- suffocation.
Which doctor should I contact if I have shortness of breath?
If this clinical manifestation is regular, you should first visit your doctor. He will conduct an examination, collect anamnesis - and, based on the information received, send the patient to an appointment with a specialist in pulmonology, cariology, hematology, neurology or endocrinology.
If a patient has a traumatic injury to the chest, he should consult a traumatologist. In cases where shortness of breath is part of an emergency condition - it appears suddenly and sharply - you should immediately call an ambulance.
Shortness of breath: diagnosis
Diagnosis of the underlying pathology that provoked shortness of breath is carried out using the following research methods:
- general examination (general medical examination, counting the frequency of respiratory movements of the chest, listening to the lungs with a phonendoscope);
- general blood test;
- chest radiography;
- computed tomography of the chest;
- spirometry (spirography) – to assess air flow through the respiratory tract and the ability of the lungs to expand;
- tests using a bronchodilator - spirometry is performed before and after inhalation with a bronchodilator drug. This study allows us to evaluate the reversibility of bronchial narrowing;
- bronchoprovocation test - spirometry is performed before and after inhalation of histamine and methacholine. It is carried out to detect increased sensitivity of the bronchi, which causes bronchospasms;
- studies of the gas composition of the blood (the level of tension in the blood of carbon dioxide, oxygen is determined, the saturation of the blood with oxygen is assessed);
- body plethysmography – allows you to evaluate the function of external respiration. It is used to assess all volumes and capacities of the lungs, incl. those that spirography cannot determine;
- electrocardiography (ECG), echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart, echocardiography) - allows you to assess the functional state of the heart and pressure in the pulmonary artery system;
- fiberoptic bronchoscopy is a study that is used to examine the mucous membrane of the bronchi from the inside and study its cellular composition with a special preparation. The use of this method is advisable for patients with an unclear diagnosis. Allows you to exclude other possible diseases with similar symptoms;
- angiopulmonography – during the procedure the blood vessels of the lungs are examined;
- lung biopsy;
- consultations with a pulmonologist, cardiologist.
How is it detected?
If you experience symptoms of shortness of breath, you should consult a doctor. First of all, he must check whether the symptom is a sign of physical pathology. To do this, the doctor conducts a survey of the patient, and then proceeds to an objective examination: examines and listens to the patient.
To exclude diseases of internal organs, a number of examinations are prescribed:
- radiography;
- allergy tests;
- CT or MRI;
- ECG, ultrasound of the heart;
- UAC.
Without identifying pathology, the doctor sends the patient to a neurologist or psychotherapist.
The psychotherapist collects a psychogenic history, which includes information about the presence of mental disorders, possible traumatic factors, as well as developmental features in childhood.
Psychological analysis involves the study of personality, including through testing. The Nymigen questionnaire is especially effective, being effective in 90% of cases. It was developed by Dutch pulmonologists. Includes 16 positions characterizing the signs of hot water supply. Their severity is assessed within 0-4 points.
During the neurological examination, neurological symptoms are checked and excessive sweating of the palms and feet is determined. Electromyography may be performed.
Additional examinations include hyperventilation test, acid-base blood test, and electrolyte balance. As a rule, with neurogenic shortness of breath, a deficiency of magnesium and calcium in the blood is detected.
Shortness of breath: treatment
Pulmonologists at the Yusupov Hospital Therapy Center select an individual drug therapy regimen for each patient, depending on the disease that provoked the onset of shortness of breath.
The clinic’s rehabilitators draw up a plan for physical training and pulmonary rehabilitation to increase the patient’s tolerance to physical activity, and prescribe breathing exercises using various methods (diaphragmatic breathing, inflating balloons, blowing air through a tube, etc.) that train the respiratory muscles.
In severe cases, artificial ventilation is used.
Shortness of breath accompanies pathologies of various organs and systems of the human body. Therefore, each individual case requires specific therapy, aimed primarily at eliminating the underlying disease causing shortness of breath.
How to treat shortness of breath caused by cardiovascular diseases?
Patients with shortness of breath associated with cardiovascular diseases are prescribed therapy, the goals of which are:
- improve oxygen supply to the heart;
- increase cardiac output;
- reduce blood stagnation in the lungs.
The use of nitrates, glycosides, and diuretics is effective. Patients with heart failure are recommended to always have nitroglycerin available, which helps to immediately dilate the blood vessels of the heart muscle.
Oxygen therapy is used to replenish the lack of oxygen in the blood.
How to get rid of shortness of breath: first aid
Providing first aid for shortness of breath to a person suffering from heart disease involves doing the following:
- call an ambulance;
- before the arrival of doctors, it is necessary to ensure the flow of fresh air into the room where the patient is located by opening the window;
- the patient must be seated on a chair;
- remove the tie and scarf from the patient’s neck, unbutton the top buttons on the shirt;
- Place a nitrosorbide tablet under the patient’s tongue and give any diuretic.
How to cure shortness of breath associated with pulmonary diseases?
For shortness of breath caused by pulmonary pathologies, patients are advised to drink plenty of alkaline fluids (except for patients with pulmonary edema).
To relieve bronchospasm, selective β2-adrenergic agonists (salbutamol, fenoterol, terbutaline, formoterol, clenbuterol, salmeterol) are prescribed. M-cholinergic receptor blockers are effective for relaxing the muscles of the bronchi.
Patients suffering from bronchial asthma are prescribed inhalations with NSAIDs and steroid therapy.
Treatment of shortness of breath due to bronchitis involves the use of medications to separate sputum. These include:
- acetylcysteine;
- carbocysteine;
- bromhexine;
- ambroxol.
How to get rid of shortness of breath associated with allergies?
Every person suffering from allergic diseases should know what to take for shortness of breath of this etiology:
- diazolin;
- diphenhydramine;
- suprastin;
- tavegil;
- fenistil;
- claritin;
- desloratodine, etc.
As an additional therapy for shortness of breath caused by allergies, you can use traditional medicine: decoctions of plants that have an expectorant effect (from plantain, pine buds, coltsfoot), as well as hot foot baths.
How to deal with shortness of breath of a psychogenic nature?
Shortness of breath quite often accompanies mental disorders - melancholy, panic attack, depression. Patients suffering from these conditions are prescribed sedatives, antidepressants and tranquilizers. The use of therapeutic hypnosis is also effective. Treatment is prescribed exclusively by a psychotherapist.
Shortness of breath, especially at rest, is an alarming symptom that often manifests quite serious pathologies that require immediate examination and urgent medical care. Therefore, if such a respiratory disorder occurs, it is necessary to urgently visit your doctor. You can make an appointment with a therapist or pulmonologist at the Yusupov Hospital by calling the phone number listed on the clinic’s website.
Stopping intermittent breathing
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital treat breathing disorders due to VSD with sedatives, physical exercise, and psychotraining. During training sessions, psychologists try to teach the patient how to properly cope with a stressful situation. If the patient is simply very worried, take sedative medications - valerian, novo-passit, motherwort. If the patient has ever suffered a panic attack or has previously been diagnosed with neurosis, neurologists use tranquilizers, antipsychotics, and nootropic drugs. In severe cases, cyclic antidepressants are prescribed.
To relieve an attack of suffocation during VSD, the patient should be seated and calmed down. The patient needs rest. It is necessary to unfasten the compressive elements of clothing and ventilate the room. If this does not help, the patient needs a motherwort or valerian tablet. If there is information about a panic attack or neurosis, you must immediately give the medicine previously prescribed by a psychiatrist.