Dilatation is a persistent diffuse expansion of the lumen of a hollow organ. The reasons for this condition are different, for example, the heart can become enlarged due to heavy physical activity, then the reason will be natural. But if this happens due to any disease, then the nature of the cause will be pathological.
Do not self-medicate. At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications
- Prevention
As mentioned earlier, this can happen to any hollow internal organ of the body. But most often the concept of dilatation is applied to pathologies of the heart cavities.
Depending on where exactly the expansion occurred, cardiac dilatation can be divided into:
- dilatation of the left atrium;
- dilatation of the left ventricle;
- dilatation of the right atrium;
- dilatation of the right ventricle.
Typically, one chamber of the heart dilates; in rare cases, this can happen to the atria or ventricles. This condition can lead to arrhythmia, heart failure, thromboembolism or other diseases. Aortic dilatation is a direct symptom of connective tissue dysplasia.
Etiology
The resulting dilatation of the heart chambers will have its own causes of development.
For example, enlargement of the right atrium occurs due to high pressure in the pulmonary circulation, which, in turn, rises due to:
- infectious heart diseases;
- obstructive diseases of the lungs and bronchi;
- pulmonary hypertension;
- heart defects;
- tricuspid stenosis.
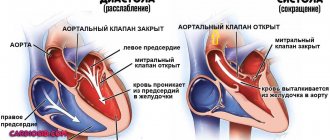
More often there is an expansion of the left sections, that is, the left atrium, because the valve through which blood flows from the left atrium into the left ventricle narrows. Disturbances also occur during the reverse movement of blood. Because of this, the pressure in the systemic circulation is also disturbed. It becomes difficult for the heart to work.
The main reasons in this case are:
- great physical activity;
- atrial fibrillation;
- atrial fibrillation;
- cardiomyopathy.
Blood enters the left ventricle from the left atrium, and then into the aorta, which nourishes the entire body. Dilatation of the left ventricle occurs due to narrowing of the aortic lumen.
The reasons for this are as follows:
- certain heart defects;
- aortic stenosis;
- cardiac ischemia;
- myocarditis;
- chronically high blood pressure.
The main reason for the expansion of the right ventricle is stenosis and insufficiency of the pulmonary valve, and they develop due to diseases such as:
- bacterial endocarditis;
- rheumatism;
- certain heart defects;
- pulmonary hypertension.
But there are also general reasons that can provoke expansion of the cavities of the heart, namely:
- complications that have arisen after certain infectious diseases, for example, due to tonsillitis or scarlet fever;
- viral and fungal pathologies;
- the presence of parasites in the body;
- poisoning of the body;
- neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature;
- thyroid diseases;
- certain autoimmune diseases;
- side effects after using medications.
It must be said that the expansion of organs can be both the cause of any cardiac pathology and its symptom.
Dilatation of the left ventricle of the heart
Definition
The human heart, like a hollow muscular organ, has its own margin of safety.
It consists of two atria and ventricles, through which blood is pumped throughout the body. Sometimes it happens that the amount of it entering the cavity exceeds the permissible volume. Thus, the walls are subjected to increased stress, which over time causes them to stretch (dilate). Dilatation of the left atrium is most common. A change in its size occurs against the background of impaired blood outflow. An increase in volume on the left side can lead to diseases of the right side of the heart if timely treatment is not resorted to. This condition is dangerous because it does not manifest itself in any way in the first stages of development.
To fully diagnose this pathology, the patient is prescribed a series of studies. During their implementation, concomitant diseases are often discovered, which are the cause of impaired heart function. This may be tachycardia, stenosis or measuring arrhythmia.
It is worth understanding that early diagnosis will allow you to avoid irreversible consequences, which is why it is important to consult a doctor at the slightest ailment.
Classification
In medicine, atrial dilatation is divided into two forms:
- Tonogenic dilatation, which occurs against the background of increased pressure, as well as due to a large amount of blood in the chambers of the heart. This form runs parallel to or precedes myocardial hypertrophy.
- Myogenic dilatation. Occurs due to various heart diseases. It affects the weakening of the contractility of the heart.
Any change that occurs in the myocardial cavities is irreversible.
As mentioned earlier, expansion can affect any internal organ, namely:
- Balloon dilatation of the auditory tube is a narrow lumen of the tube or its limited ability to open. This pathology develops in parallel with a chronic functional defect. A complication is chronic otitis media, which can lead to irreversible damage to the middle ear. Because of this, a person’s hearing decreases.
- Kidney dilatation. It is characterized by dilation of the pelvis and delayed urine outflow. It is a congenital pathology, however, in some cases it can occur when the ureter is blocked by a large stone. Treatment is carried out through surgery and the use of medications.
- Toxic developing dilatation of the colon is a complication of ulcerative colitis. It appears after the use of barium enemas, narcotic drugs and hormones. This causes abdominal pain, fever and bloating. This condition must be observed and controlled. But if the pathology begins to progress, then an urgent operation is necessary.
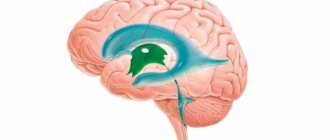
- Dilated lesion of the lateral ventricles of the brain. They produce cerebrospinal fluid, which drains through special channels. If dilatation of the cerebral ventricles occurs, this indicates a large amount of fluid or problems with outflow. Such expansion is a symptom of a disease. Doctors must identify it during diagnosis. It should be noted that quite often pathology of the ventricles of the brain appears in newborns.
- Balloon dilatation of the narrowed esophagus, or more precisely, its upper section. Dilatation of the esophagus is performed using an endoscope. Balloon dilatation is performed only if there are indications for it and there is no oncology.
- Dilatation of the ureter. Due to this expansion, the functioning of the urinary system is disrupted, and abdominal pain begins. Treatment of this pathology is carried out only with the help of surgery, during which the diameter of the ureter is narrowed and its length is shortened.
- Dilation of the milk ducts in most cases is not a pathology, since this condition is completely normal and occurs periodically, depending on the physiological processes in the body. But if a woman experiences discomfort, she needs to see a doctor.
In addition, there are other areas of damage. Thus, dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain, interhemispheric fissure and other organs is diagnosed.
Is dilatation always dangerous?
Clinical practice shows that dilation is not always a sign of the presence of some significant pathology. It most often occurs in premature babies, due to the fact that the size of these ventricles is much larger than in babies born at term, or it is a feature of the structure of the skull of a particular child.
But nevertheless, the presence of diagnosed dilatation of the lateral ventricles of the brain requires monitoring the dynamics of the baby’s growth and development. If no abnormalities are detected during the control period, then the baby is considered healthy.
Do not be ill!
Symptoms
Symptoms of cardiac enlargement, if slight, are practically unnoticeable because moderate dilatation shows no signs.
If the expansion of the left atrium is too large, the work of the heart deteriorates and the following symptoms occur:
- dyspnea;
- cardiopalmus;
- heart failure;
- fibrillation;
- thromboembolism.
They cannot be called specific, and they are practically invisible. A doctor can identify such a pathology during a preventive examination.
Clinical manifestations
Shortness of breath on exertion
The human heart is infinitely unable to cope with the increased load. Tonogenic dilatation is replaced by myogenic dilatation, and signs of circulatory failure appear. If the left chambers of the heart are overloaded, they speak of left ventricular failure; if the overload falls on the right chambers, right ventricular failure develops.
The main manifestations of left ventricular failure are shortness of breath during exercise, pain in the heart area, a feeling of interruptions and palpitations, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, swelling of the legs and feet.
With right ventricular failure, patients complain of rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, swelling of the neck veins, low blood pressure, heaviness in the right hypochondrium, and swelling of the extremities.
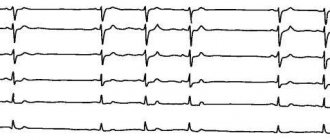
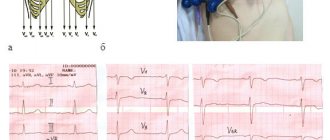
Diagnostics
To detect heart enlargement, the doctor prescribes the following diagnostic methods:
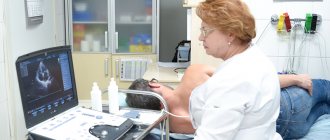
- Echocardiography. This ultrasound examination will help establish the correct diagnosis. In addition, it will be possible to identify the cause of this condition, for example, myocardial infarction, valve insufficiency and much more.
- Electrocardiography. Prescribed if necessary as an additional diagnosis.
- Scintigraphy. It is prescribed for differential diagnosis, in which it is possible to distinguish organ enlargement from ischemic disease.
- X-ray.
Cardiac scintigraphy
If the results show that the chambers have expanded by more than 5%, then the doctor will make an appropriate diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at getting rid of or correcting the primary pathology that caused the expansion. Therefore, the prescribed therapy will be aimed at eliminating the root cause.
The doctor may prescribe drugs with the following spectrum of action:
- antibiotics;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- drugs against coronary disease;
- drugs that reduce heart rate;
- beta blockers;
- blood pressure lowering agents;
- blood thinning medications;
- diuretics.
If the prescribed treatment does not help, it is necessary to undergo surgery, during which a pacemaker will be installed.
In general, if treatment is started correctly and in a timely manner, the risk of developing any complications can be significantly reduced, but in this case it is impossible to completely eliminate them.
There is not and cannot be an unambiguous prognosis, since everything will depend on the nature of the course of the clinical picture, the severity of the pathology, as well as the general health indicators of the patient.
Symptoms
The manifestation of clinical signs is heterogeneous. The nature of the clinic will depend on which areas are enlarged.
Typically this is:
- chest discomfort or pain;
- dyspnea;
- loss of strength, fatigue;
- cardiomyopathy;
- rhythm disturbance;
- peripheral edema.
Other symptoms will depend on the underlying cause that causes the dilatation.
The appearance of shortness of breath is one of the first signs of the disease
Possible complications
Dilatation affecting the aortic root or cardiac chamber can cause serious complications. For example, the walls of the heart will stretch and thicken.
Because of this, the following conditions will arise:
- chronic heart failure;
- infectious chronic heart diseases;
- expansion of ring valves;
- thrombosis and much more.
These pathologies worsen a person’s quality of life, and if nothing is done about them, death is possible. Therefore, when they appear, you need to seek help from a cardiologist.
Stomach
Considering the emergence of highly effective antiulcer therapy and a significant reduction in the frequency of ulcer recurrences after successful HP eradication, balloon dilatation can be successfully used for cicatricial narrowing of the pylorus and duodenum as an alternative to surgical intervention. Of course, there is no point in dilation with decompensated stenosis. Dilatation is also possible for malignant ones, as palliative treatment, and after burn strictures, anastomotic strictures. Solt J., et al., published long-term results of dilatation in patients with benign gastric outlet stenosis (after surgery, peptic, corrosive and post-vagotomy strictures) [15]. He performed 117 balloon dilations on 72 patients and had a mean follow-up of 98 months. The average diameter of the stenosis was 6 mm before treatment and 16 mm after it. Reduction and disappearance of symptoms was observed in 80% immediately after the procedure and in 70% after three months. In 16 patients, restenosis was observed within 1-18 months after the intervention. Complications included one case of arterial bleeding and two perforations. Boylan JJ, and Gradzka MI, emphasize that proper antiulcer treatment, especially HP eradication and cessation of NSAIDs, is necessary to maintain the result of successful dilatation for gastric outlet stricture of peptic nature [2]. Anastomotic strictures and strictures of a malignant nature are more prone to rapid recurrence [11].
Prevention
Preventive measures are part of the treatment of this condition: without them there will be no positive result.
In this regard, the following rules should be adhered to:
- balance your diet, which will contain only plant foods, lean meat and fish, seafood, dairy products, nuts and grains;
- spend more time outdoors;
- doing physical exercise;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol.
All this will help improve blood circulation, strengthen myocardial muscles, increase immunity, and then life expectancy will increase.
Small and large intestine
The main indications for dilatation are strictures due to Crohn's disease or UC and anastomotic strictures. Although there are reports of the use of this method for diverticular, tumor and ischemic strictures [8]. A retrospective analysis of balloon dilatation of strictures through a colonoscope in 59 patients with Crohn's disease (53 with anastomotic strictures and 6 with primary strictures) showed that a long-term positive result was achieved in 41% of patients, and in 17% after one dilation. However, in 59% of patients during the observation period, there was a need for surgical treatment as a result of stricture recurrence. Complications included two perforations [17]. Brooker JC, et al., reported the combination of balloon dilatation with the administration of long-acting steroids for strictures resulting from Crohn's disease [3]. In 50% of patients, remission was achieved after one dilatation with the introduction of steroids, in 28.5% several interventions were required, and, finally, in 21.4% of cases dilation was not effective.
When dilating colonic anastomotic strictures, balloon dilatation has proven to be more effective than bougienage [14]. Virgilio C., et al., using a balloon intended for the treatment of achalasia to dilate anastomotic strictures with a diameter of 2 mm or less, achieved results in 94% of cases [18].
Tumor strictures of the colon are dilated both for the purpose of emergency decompression [1] and for better preoperative preparation [16] or palliative treatment, in the latter case the installation of metal self-expanding stents is preferable.