Home → Information about diseases → Hydrocephalus (hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome of HHS)
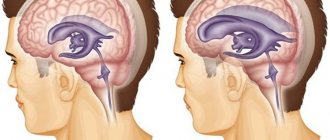
Absolutely all people have a small amount of fluid in the cranial cavity that washes the brain. This liquid is called “liquor”. Liquor is constantly produced and absorbed (renewed). If a person produces more cerebrospinal fluid than is absorbed, it begins to accumulate in the cranial cavity, and intracranial pressure increases. Excess fluid begins to put pressure on the brain, causing various disruptions to its functioning. This is called hydrocephalus (increased intracranial pressure, hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome or “dropsy of the brain”).
Causes
Congenital
- The course of pregnancy and childbirth with complications.
- Hypoxic (bradycardia, intrauterine hypoxia and intrauterine growth retardation) and ischemic (trauma during childbirth) brain damage.
- Premature birth (up to 36-34 weeks).
- Head injuries during childbirth (subarachnoid hemorrhage).
- Intrauterine infections (toxoplasmosis, influenza, cytomegalovirus infection and others).
- Congenital abnormalities of brain development.
- Delayed birth (at 42 weeks and later).
- Long water-free period (more than 12 hours).
- Chronic diseases of the mother (diabetes mellitus and others).
Purchased
- Tumors, abscesses, hematomas, parasitic cysts of the brain.
- Foreign bodies in the brain.
- Fractures of the skull bones.
- Causeless intracranial hypertension.
- Infectious diseases (malaria, tick-borne encephalitis).
- Metabolic disorders.
Treatment methods for hydrocephalus
The surgical method of treating hydrocephalus is used only in extreme cases (decompensated forms of internal hydrocephalus), excess fluid is drained from the cranial cavity into the abdominal cavity using a tube (shunt), this operation, like any other, is quite traumatic; in the future, several more surgical operations may be required interventions to replace and check the operation of the shunt.
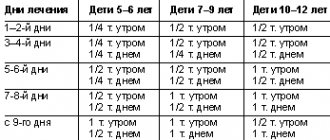
A medicinal method of treating hydrocephalus - the use of diuretics, such as Diacarb, is often used by neurologists in outpatient practice. Diakarb removes fluid not only from the cranial cavity, but also from the body as a whole, at the same time a loss of microelements occurs, the effect of this treatment method is temporary, after its cessation, the fluid begins to accumulate again and intracranial pressure increases.
Herbal medicine - the use of diuretic herbs (horsetail, fennel, lingonberry leaf), does not cause addiction and loss of microelements. It is used, as a rule, for preventive purposes: to avoid exacerbation of hydrocephalus during colds, when changing climatic zones, in the autumn-spring period with pronounced changes in weather conditions.
Massage is an effective method for children with motor impairments (increased muscle tone, delayed motor development), and is mainly aimed at relaxing tense muscles. It is advisable to use only in complex treatment, since massage does not affect the main cause of the disease - hydrocephalus and hypoxia of the cerebral cortex.
MICROCURRENT REFLEXOTHERAPY - the method is effective in children with various manifestations of hydrocephalus, it allows you to eliminate not only external manifestations (hysterics, developmental delays, etc.), but also treat hydrocephalus itself, that is, it has a complex therapeutic effect on the body. The effect of treatment is stable and does not stop after the end of treatment.
Symptoms
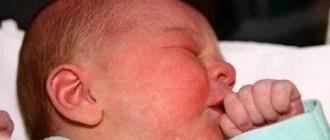
- Decreased muscle tone (“seal feet” and “heel feet”).
- Weak congenital reflexes (swallowing, grasping).
- The appearance of tremor (shaking) and convulsions.
- Vomiting like a fountain.
- Strabismus.
- Graefe's sign (a white stripe between the pupil and the upper eyelid).
- Rising sun sign (the iris is almost half hidden behind the lower eyelid).
- Opening of the sutures of the skull, bulging and tension of the fontanel.
- Increased head circumference growth (by 1cm every month).
- Swelling of the optic discs.
In order to establish the true cause of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive clinical examination of the child:
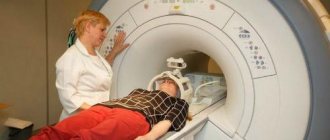
- Echoencephalography (EchoEG); rheoencephalogram (REG); radiography of the skull; computed tomography (CT); electroencephalography (EEG).
- Examinations by such specialists as an ophthalmologist, a neurologist, a psychiatrist (long-term hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome can lead to atrophy of the cerebral cortex and, subsequently, to delayed mental development), and a neurosurgeon are necessary.
Hydrocephalic syndrome in children
Hydrocephalus occurs in children and adults of any age. Most often, hydrocephalic syndrome occurs in children. If the cerebrospinal fluid begins to collect before the skull bones have fused, then the circumference of the child’s head increases and the skull becomes deformed, which can be seen with the naked eye.
At the same time, atrophy or arrest of tissue development of the cerebral hemispheres is recorded. Therefore, the pressure inside the skull with hydrocephalic syndrome in children does not increase too much. If the process continues for a long time, normal pressure hydrocephalus is formed, in which the ventricles are large and dilated, and atrophy of the medulla is pronounced.
Gradually developing hydrocephalus in children is characterized by progressive atrophy of brain tissue. The child is diagnosed with movement disorders due to conduction disturbances. When the paraventricular part of the pyramidal tract is affected, lower paraparesis is detected in children.
Typical symptoms are visual disturbances. There may be endocrine disorders. ICP increases, and long-term ischemia of brain tissue occurs. The child has intellectual-mnestic and mental disorders. A patient diagnosed with hydrocephalic syndrome has a typical appearance. His head is increased in size, especially in the sagittal direction, but his face remains small.
The skin on the surface of the head is stretched, therefore it is very thin, atrophic, you can see every wreath. There is thinning of the skull bones, with increased spaces between them. The anterior and posterior fontanelles are tense, dilated, sometimes protruded, there is no pulsation. Sutures that have not yet ossified may slowly diverge. If doctors tap the brain part of the head, there may be a sound of a cracked pot.
With the diagnosis under consideration, there is a violation of the motor innervation of the eyeball. The gaze is directed downward, convergent strabismus develops, visual acuity decreases, the final form of which can be absolute blindness. Hyperkinesis can develop in parallel with movement disorders.
With hydrocephalic syndrome in newborns, cerebellar symptoms appear a little later:
- impaired motor coordination
- violation of statics
- inability to sit
- inability to hold your head up
- the child cannot stand
Next, a gross deficit of mnestic functions arises; the child’s intelligence is greatly reduced. Also in some cases the following behavioral symptoms appear:
- irritability
- excitability
- indifference to the environment
- adynamia
Neurological symptoms:
- shrill scream
- headache
- drowsiness
- vomit
- decreased vision
- strabismus
- bulging fontanelle (only in infants)
Papilledema does not occur immediately as a manifestation of increased ICP levels. Due to increased pressure inside the skull, the following symptoms appear:
- disturbance in the acquisition and processing of information
- attention disorder
- Puberty is too early in girls
- dysfunction of the organization (difficulty with summarizing, presenting, justifying, etc.)
- memory problems
Consequences of hydrocephalic syndrome in children:
- Weakness in the muscles of the arms and legs
- Hearing and vision loss
- Dysregulation of body temperature
- Violation of fat and carbohydrate metabolism
- Risk of death
If the operation is performed in a timely manner, the patient recovers, there is a possibility of both stable remission and absolute recovery. With implanted shunts, the disease no longer bothers the person. The shunt is removed only after 3-4 years, if symptoms of hydrocephalic syndrome do not appear.
Treatment of hydrocephalus and hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome with osteopathy
The brain is a vital organ and needs protection and proper metabolism. These are the functions performed by cerebrospinal fluid, the fluid that washes the brain and spinal cord. This fluid is produced in the lateral ventricles of the brain for 24 hours, almost continuously.
Due to the fact that cerebrospinal fluid is produced continuously and is renewed 6 times during the day, drug therapy in the form of diuretics does not give the expected effect.
Osteopathic treatment in this situation is most effective. Imagine the cerebrospinal fluid system as a network of communicating vessels. On the one hand, a lot is produced, on the other hand, there are barriers along the way. With the help of osteopathic techniques, it becomes possible to eliminate barriers along the path of cerebrospinal fluid by freeing the membranes of the brain, improve the functioning of the nerve cell and stop the development of the pathological reflex of overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid, which ultimately eliminates the cause of hypotension-hydrocephalic syndrome and normalizes intracranial pressure.
Anatomy of the central nervous system of newborns
The central nervous system is the main part of the nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, located in the cranial cavity and the spinal canal. The central nervous system is responsible for controlling all vital processes in the body, thinking, speech, coordination, and the functioning of all senses.
The brain consists of the following sections:
- cerebral hemispheres (left and right)
- diencephalon
- midbrain
- bridge
- cerebellum
- medulla
Ultrasound examination of these sections allows us to assess the condition of the gray and white matter of the brain and exclude the presence of congenital pathology in the fetus (hemorrhages, tumors, malformations, cysts, hydrocephalus, dislocations, etc.), as well as possible changes associated with childbirth.
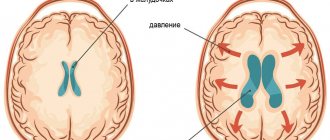
The liquor system consists of:
Internal liquor spaces
- Lateral ventricles of the brain (right and left)
- Third ventricle of the brain
- Fourth ventricle of the brain
External liquor spaces
- Subarachnoid space
- Interhemispheric fissure
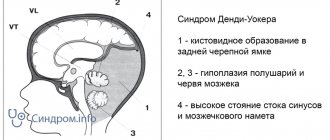
In accordance with this, hydrocephalus can be external - when the size of the interhemispheric fissure increases; internal - with expansion of the lateral ventricles (VLD, VLS), third and fourth ventricles (V3, V4); and mixed.
Each ventricle contains a choroid plexus (Plexus chorioidei). These plexuses play an important role in the production of cerebrospinal fluid - a fluid that circulates in the ventricles of the brain, the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord, and the cerebrospinal fluid ducts. Overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid leads to hydrocephalus and an increase in the size of the cerebrospinal fluid containing spaces.
Normal values for sizes V3, V4, MS, MD, VLS, VLD, m/p gap, bone/marrow diastasis, see below
Complications and prognosis
Complications of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome are possible at any age:
- delayed mental and physical development;
- blindness;
- deafness;
- coma;
- paralysis;
- epilepsy;
- urinary and fecal incontinence;
- death.
The prognosis is most favorable for hydrocephalic syndrome in infants. This is because they experience transient increases in blood pressure and cerebrospinal fluid, which stabilize with age.
In older children and adults, the prognosis is relatively favorable and depends on the cause of HGS, the timeliness and adequacy of treatment.
Sources:
- Bitterlich L.R. On the issue of differential diagnosis, classification and differentiated treatment of hydrocephalus and hirdocephalic syndromes in children. - International Neurological Journal, No. 1 (79), 2021.
- Order on approval of the standard of specialized medical care for children with hydrocephalus. — Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2013.
- Federal clinical guidelines for the provision of medical care to children with consequences of perinatal damage to the central nervous system with hydrocephalic and hypertension syndromes. — approved Union of Pediatricians of Russia February 14, 2015
Advantages of treatment at the Neonatus Sanus Osteopathy Clinic
Our clinic of osteopathy and neurology on Vasilyevsky Island “Neonatus Sanus” - health from birth, has extensive practical experience in the prevention and treatment of newborns, infants and infants.
We know how and love to work with young children!
Our clinic employs experienced osteopathic doctors and neurologists. A lot of attention is paid to each child in order to understand the child, accurately assess his condition, give recommendations to parents and, if necessary, carry out effective osteopathic treatment.
In our center you can get the best examination, treatment and recommendations from leading specialists in St. Petersburg.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hydrocephalic syndrome is difficult. Not all instrumental methods help establish a diagnosis in 100% of cases. In infants, regular measurement of head circumference, checking reflexes, dynamics of body weight gain, and neurological examinations are important.
Also in the definition of GGS is used:
- electroencephalography;
- lumbar puncture of the spinal cord to take cerebrospinal fluid to measure its pressure (the most reliable method);
- neurosonography (ultrasound examination of the anatomical structures of the brain, in particular the size of the ventricles);
- assessment of fundus vessels (swelling, congestion or vasospasm, hemorrhage);
- computed tomography () and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).