- What pressure is normal?
- Why might your heart rate increase with low blood pressure?
- Symptoms
- How to help a person with hypotension due to diabetes, anaphylaxis and bleeding?
- Help with hypotension and tachycardia in other cases
- What should you not do if you have hypotension?
- Prevention measures
People prone to low blood pressure (hypotension, hypotension) often encounter a problem such as tachycardia.
It is characterized by an acceleration of the pulse: the heartbeat becomes too fast, reaching 90 beats per minute or higher at rest. What is the reason for this phenomenon, and how to deal with it? In a healthy person, the heartbeat increases during physical activity and strong emotions. This is a physiological norm and does not harm health.
An excessively fast resting pulse is a sign of poor health, which may indicate heart disease and other pathologies.
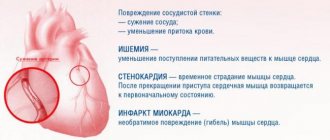
With hypotension, vascular tone decreases, which leads to slower blood flow and stagnation of blood in the arteries. Organs and tissues, including the heart and brain, suffer from a lack of oxygen. The acceleration of heart rate at low pressure is a physiologically determined compensation mechanism. The pulse quickens as the body seeks to compensate for the lack of oxygen and stagnation of blood in the arteries due to more intense work of the heart.
This negatively affects the state of the cardiovascular system. With chronic arterial hypotension, the heart is forced to work hard to maintain normal blood supply to organs and tissues. This increases the load on the heart muscle and leads to undesirable consequences.
What pathologies can cause increased heart rate with low blood pressure?
A rapid pulse with hypotension is a characteristic feature of a number of conditions and pathologies. Among them:
- adaptation to new climatic conditions when climbing mountains or changing time zones, which is caused by changes in atmospheric pressure;
- stress, emotional turmoil;
- lack of nutrients due to a strict diet or poor diet;
- visiting a sauna, bathhouse, staying in a stuffy room;
- severe blood loss due to injury or complications after surgery;
- anaphylaxis due to an allergic reaction;
- heatstroke;
- dehydration due to improper drinking regimen, with prolonged vomiting;
- pregnancy period;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- neurocirculatory dystonia and other neurological diseases;
- severe hypoglycemia;
- blood poisoning;
- taking medications that affect blood pressure and can lead to symptomatic hypotension;
- hypothyroidism - insufficient production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland;
- alcohol abuse, drug use;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Necessary examinations
Mandatory diagnostics for a decrease in heart rate combined with hypertension includes the following:
- Examination by a specialist - cardiologist, therapist or family doctor.
- Electrocardiography (ECG).
- Ultrasound of the heart (echocardiography).
- Holter monitoring (daily ECG recording and pressure recording).
Additionally, general, biochemical and blood tests for the level of hormones of the thyroid and other glands, extended ultrasound and x-ray examinations may be required.
Diagnostic methods for decreased heart rate, which is combined with hypertension
Symptoms
In addition to rapid heartbeat, patients with tachycardia at low blood pressure note the following signs of pathology:
- weakness and drowsiness, decreased performance;
- dizziness, headache;
- violation of movement coordination;
- darkening of the eyes;
- pale skin, sweating;
- feeling of lack of air;
- nausea that progresses to vomiting.
In severe cases, a drop in pressure leads to loss of consciousness.
List of necessary studies
If you have tachycardia, consult a cardiologist. He, at his own discretion, refers the patient to an endocrinologist or neurologist to clarify the etiology of the condition.
The list of studies is quite wide:
- Oral questioning of the patient to objectify complaints and symptoms of a probable disease.
- Anamnesis collection.
- Heart rate assessment. It is carried out in the old-fashioned way by eye or with a special sensor. The second is preferable.
- Measuring blood pressure levels. As a rule, we are talking about a consistently low indicator.
- Daily monitoring. Shows the process over time over 24 hours. Prescribed in all cases.
- Electrocardiography. Profile research. Provides comprehensive information about the nature of cardiac activity. But it requires great qualifications from the diagnostician, which not everyone has.
- Angiography. Vascular examination.
- Assessment of the level of specific hormones in the patient’s blood.
- Examination of neurological status.
The list may be expanded at the discretion of specialists. This is a minimum program.
Additionally, blood tests, urine tests, and tomographic techniques may be prescribed.
How to help a person with hypotension due to diabetes, anaphylaxis and bleeding?
First aid for hypotension depends on the cause of the drop in blood pressure. If this is due to severe bleeding or anaphylactic shock, the patient needs urgent medical attention. In the first case, doctors take measures to stop the bleeding and replace blood loss.
If a patient develops anaphylactic shock due to an allergic reaction to an injection or an insect bite, there is a sharp drop in blood pressure, heart rhythm is disturbed, swelling of the larynx occurs, which leads to breathing problems.
If you suspect anaphylactic shock, you should urgently call an ambulance. At home, it is necessary to limit the spread of the allergen. To do this, remove the insect sting or apply a tourniquet above the injection site. The victim must be laid on a horizontal surface with his legs raised. If a person is vomiting, the head must be turned to the side. The room should be well ventilated. If the victim loses his pulse, an indirect cardiac massage is performed with a frequency of 60-100 compressions before the ambulance arrives.
To relieve anaphylactic shock, doctors administer adrenaline and glucocorticosteroids and use antihistamine treatment.
Emergency measures are also required in situations in which patients with diabetes may find themselves. If the blood glucose level falls below 3.3 mmol/l, a state of hypoglycemia occurs, which is characterized by weakness, a drop in blood pressure, shallow breathing, a weak pulse, and in some cases, an increased heart rate, and sweating.
To increase blood pressure in diabetes, you must first normalize the level of glucose in the blood. If a person is conscious, he needs to eat or drink a drink with fast carbohydrates. Sugar or honey, glucose-based gel, and a sweet drink are suitable for these purposes.
It is not advisable to use chocolate, cookies or other confectionery products that contain carbohydrates and fat, as it slows down the absorption of glucose.
If a diabetic is unconscious, one should not try to pour a sweet drink or sugar through the mouth, as the person will not be able to swallow. Food can get stuck in the throat and cause asphyxia.
If a person is unconscious, it is permissible to rub honey or sugar syrup into the gums. To treat severe hypoglycemia, health care providers use intravenous glucose injections or the drug glucagon, which releases stored glucose from the liver.
Once a diabetic's blood sugar level is normalized, blood pressure and pulse return to normal.
Is this condition dangerous and why exactly?
Bradycardia (with a pulse less than 50 beats per minute) is somewhat less dangerous than tachycardia, even without a background of high blood pressure (within 140-160 mm Hg). There are four possible consequences.
Heart failure
Occurs relatively rarely with bradycardia. Usually associated with impaired myocardial conduction or changes in the sinus node. Without resuscitation measures, the little man dies. Help needs to be provided urgently.
Heart failure
Associated with a change in the nature of the body’s activities. There is insufficient tissue trophism and, as a result, the inability to adequately supply the body with nutrients and oxygen.
Hypoxia and atrophy of anatomical structures leads to a lot of symptoms. The myocardium also suffers. In the absence of treatment, the next step in the development of pathology is a heart attack.
Heart attack
Cardiac emergency. Associated with acute malnutrition in the heart muscle and tissue death.
During the recovery period, destroyed tissues are replaced by scar tissue (post-infarction cardiosclerosis), and the nature of cardiac activity changes. The consequences remain with a person for life.
Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome
A sharp disturbance in cardiac output as a result of a decrease in heart rate. Accompanied by acute ischemia of cerebral circulation. One of the most dangerous complications of bradycardia. Requires cardiac surgery. Read more about MAS syndrome here.
In addition, the condition is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, such as decreased performance, constant drowsiness, chest pain, dizziness, etc. So, if your blood pressure is high and your pulse is low, it is a risk. Treatment is needed.
Help with hypotension and tachycardia in other cases
If the drop in blood pressure is not related to diabetes, an allergic reaction, or injury, the following measures should be taken:
- The person is laid on a flat surface.
- Place a pillow, folded blanket or other handy object under the shins so that the victim’s legs are elevated.
- In the room you need to open a vent or window for fresh air and turn on the air conditioner.
- If a person is wearing tight clothing, it should be removed or unbuttoned.
- For many people, a drop in pressure is accompanied by a decrease in body temperature, so the victim should be covered with a warm blanket.
- Strong sweet tea helps to quickly raise blood pressure during hypotension.
When providing assistance, you need to regularly measure blood pressure. If, despite the measures taken, a person becomes worse, it is necessary to call an ambulance or take the patient to a medical facility for examination and treatment.
Is it possible to lower your heart rate at home?
Is it even possible to do anything on our own? If the patient has not been to a cardiologist and has not received clear instructions in this regard, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Tachycardia lasting more than 2 minutes is considered pathological. Before the doctors arrive, you can try to do something using non-drug methods.
- For example, take a horizontal position, breathe slowly and evenly, holding your breath for a few seconds as you exhale.
- You cannot take any medications without a doctor’s approval. It is not known how such amateur activity will turn out.
The issue of hospitalization of the patient for further examination is decided on the spot.
Whether to agree or not is up to the person to decide. But you shouldn't refuse. It is important to find out the reason. This is the only way to prescribe the correct treatment.
Prevention measures
To treat hypotension, it is important to identify and eliminate its cause. Normalizing blood pressure will relieve poor health and tachycardia. If the patient is prone to low blood pressure, it is important to consume sufficient amounts of fluid and salt and ensure regular moderate physical activity. Movement improves blood circulation in the vessels and helps maintain normal blood pressure.
If you have hypotension, you should avoid severe stress and activities that involve physical and emotional stress. To feel well, it is important for hypotensive patients to get a good night's sleep and rest properly.
Water procedures have a positive effect: contrast showers, hydromassage. It is important that temperature changes are not too sudden.
What does an increase in heart rate due to hypotension mean?
Doesn't mean anything at all.
Low blood pressure and high heart rate are not related to each other. These are two different processes. Tachycardia is based on irritation or stimulation of a special reflexogenic zone of the heart.
As a result, the organ begins to work more actively. Whether such an influence occurs from the outside or is endogenous in nature needs to be examined separately.
Hypotension is caused by a lot of reasons, often extracardiac. The main factor is a drop in hemodynamics (blood flow) at a general level.
To compensate for the lack of force of heart contractions, the organ is given a signal to speed up its activity.
Methods of therapy
Treatment methods depend on the nature of the pathological process. It is necessary to eliminate the root cause of bradycardia and high blood pressure.
- If heart rhythm deviations are caused by drugs, adjustment of therapeutic doses and treatment regimens is required.
- Hemodynamic disturbances are corrected with drugs to dilate blood vessels. Only a specialist selects specific names.
- If the cause of low pulse with high blood pressure is Morgagni-Adams-Stokes syndrome, it is necessary to decide on the surgical treatment of the pathology with the introduction of a pacemaker.
After the operation, both indicators, both pulse and blood pressure, return to the physiological norm.